1. Introduction
Gravitational-wave astronomy is reshaping our understanding of the Universe. Recent breakthroughs include the detection of many gravitational-wave signals from binary black hole collisions (Abbott et al. Reference Abbott2019a) leading to an enhanced understanding of their population properties (Abbott et al. Reference Abbott2019d), measurement of the Hubble parameter (Abbott et al. Reference Abbott2017d; Hotokezaka et al. Reference Hotokezaka, Nakar, Gottlieb, Nissanke, Masuda, Hallinan, Mooley and Deller2019), unprecedented tests of Einstein’s theory of General Relativity, including constraints on the speed of gravity (Abbott et al. Reference Abbott2017e) and hence the mass of the graviton (Abbott et al. Reference Abbott2017b; Reference Abbott2019b), to name a few. Plans for building the next generation of observatories are afoot. The United States National Science Foundation, Australian Research Council, and British government have financed an upgrade to Advanced LIGO (aLIGO) known as A+, which will increase the sensitivity of the current detectors by a factor of 2–3 dependent on the specific frequency of interest (Miller et al. Reference Miller, Barsotti, Vitale and Fritschel2015). Research and development is ongoing for third-generation observatories, the Einstein Telescope (Punturo et al. Reference Punturo2010a) and Cosmic Explorer (Abbott et al. Reference Abbott2017a): broadband instruments with capabilities of hearing black hole mergers out to the dawn of the Universe.
Third-generation observatories require substantial, global financial investments and significant technological development over many years. To bridge the gap between A+ and full-scale, third-generation instruments, it is necessary to explore smaller-scale facilities that will not only produce significant astrophysical and fundamental physics outcomes but will simultaneously drive technology development. In this spirit, we introduce a Neutron Star Extreme Matter Observatory (NEMO): a dedicated high-frequency gravitational-wave interferometer designed to measure the fundamental properties of nuclear matter at extreme densities with gravitational waves. We envision NEMO as a specialised detector with optimum sensitivity in the kilohertz band operating as part of a heterogeneous network with two or more A+ sensitivity observatories. The A+ observatories provide source localisation, while a NEMO measures the imprint of extreme matter in gravitational-wave signals from binary neutron star mergers. To maximise scientific impact, a NEMO must exist simultaneously with 2.5-generation observatories, but before full-scale third-generation instruments are realised.
Neutron stars are an end state of stellar evolution. They consist of the densest observable matter in the Universe and are believed to consist of a superfluid, superconducting core of matter at supranuclear densities. Such conditions are impossible to produce in the laboratory, and theoretical modelling of the matter requires extrapolation by many orders of magnitude beyond the point where nuclear physics is well understood. As two neutron stars coalesce, their composition leaves an imprint on the gravitational waveform, which becomes increasingly important at higher frequencies
![]() ${\sim}0.5{-}4\,{\rm kHz}$
.
${\sim}0.5{-}4\,{\rm kHz}$
.
Mergers produce remnants, some of which collapse to black holes and some of which survive as long-lived, massive neutron stars. Up to
![]() $\approx79\%$
of all binary neutron star mergers may produce massive neutron star remnants that emit strong gravitational-wave signatures (Margalit & Metzger Reference Margalit and Metzger2019). The precise nature of the remnant is strongly dependent on the details of nuclear physics, which is encoded in the neutron star equation of state (e.g., see Bernuzzi Reference Bernuzzi2020, and references therein). Measuring gravitational waves at these high frequencies therefore offers a window into the composition of neutron stars, not accessible with other astronomical observations or terrestrial experiments. We show that detection rates of gravitational waves from post-merger remnants with a network of only two A+ observatories is between one per decade and one per century, while adding a NEMO to the network increases this to more than one per year.
$\approx79\%$
of all binary neutron star mergers may produce massive neutron star remnants that emit strong gravitational-wave signatures (Margalit & Metzger Reference Margalit and Metzger2019). The precise nature of the remnant is strongly dependent on the details of nuclear physics, which is encoded in the neutron star equation of state (e.g., see Bernuzzi Reference Bernuzzi2020, and references therein). Measuring gravitational waves at these high frequencies therefore offers a window into the composition of neutron stars, not accessible with other astronomical observations or terrestrial experiments. We show that detection rates of gravitational waves from post-merger remnants with a network of only two A+ observatories is between one per decade and one per century, while adding a NEMO to the network increases this to more than one per year.
The technologies that will enable a NEMO are key components for third-generation observatories. In order to reduce quantum shot noise, future detectors aim to employ aggressive squeezing (e.g., up to
![]() $+ 10\,\textrm{dB}$
). To enable increased circulating power, reduce scattering losses, and thermal noise, future detectors may include cryogenic silicon test masses with high-power 2-
$+ 10\,\textrm{dB}$
). To enable increased circulating power, reduce scattering losses, and thermal noise, future detectors may include cryogenic silicon test masses with high-power 2-
![]() $\mu\textrm{m}$
lasers as proposed in the Voyager design (Adhikari et al. Reference Adhikari2020). A NEMO observatory also provides technological development for Cosmic Explorer-like detectors while producing impactful science results on a shorter timescale.
$\mu\textrm{m}$
lasers as proposed in the Voyager design (Adhikari et al. Reference Adhikari2020). A NEMO observatory also provides technological development for Cosmic Explorer-like detectors while producing impactful science results on a shorter timescale.
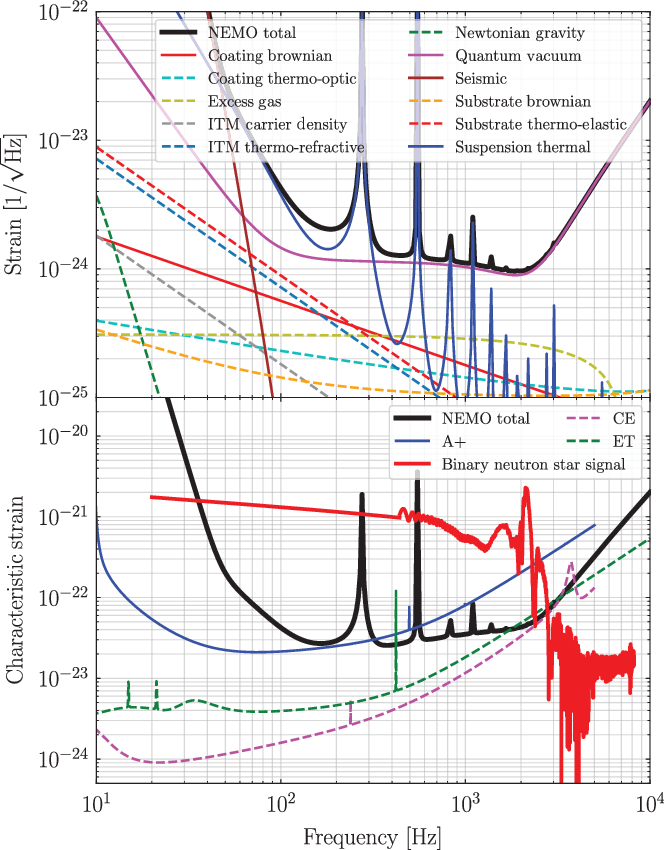
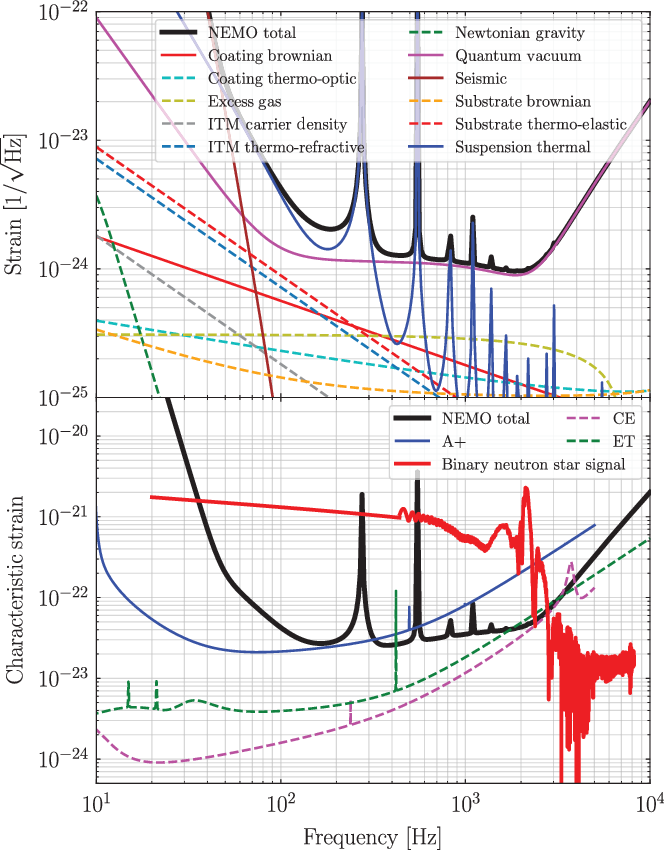
Figure 1. Noise budget and indicative gravitational-wave signal from a binary neutron star collision. Top panel: we show the amplitude spectral density of the various noise components that make up the total noise budget shown as the black curve. Bottom panel: The black curve is the same total noise budget as the top panel, now shown as the noise amplitude
![]() $h_n=\sqrt{f\,S_n(\,f)}$
, where
$h_n=\sqrt{f\,S_n(\,f)}$
, where
![]() $S_n(\,f)$
is the power-spectral density. This curve is shown in comparison to design sensitivity of A+ (blue), the Einstein Telescope (ET; green), and Cosmic Explorer (CE; pink). Also shown in red is the predicted characteristic gravitational-wave strain
$S_n(\,f)$
is the power-spectral density. This curve is shown in comparison to design sensitivity of A+ (blue), the Einstein Telescope (ET; green), and Cosmic Explorer (CE; pink). Also shown in red is the predicted characteristic gravitational-wave strain
![]() $h_c$
for a typical binary neutron star inspiral, merger, and post-merger at 40 Mpc, where the latter are derived from numerical-relativity simulations.
$h_c$
for a typical binary neutron star inspiral, merger, and post-merger at 40 Mpc, where the latter are derived from numerical-relativity simulations.
Figure 1 highlights both the key science case and the design principles for a NEMO that are elucidated throughout the paper. The top panel shows the strain sensitivity (amplitude spectral density
![]() $\sqrt{S_n(\,f)}$
) and all underlying noise sources of the proposed detector. This noise budget and the basic design principles of a NEMO, including a detector schematic, are laid out in Section 2. The bottom panel shows again the NEMO noise budget in black, this time in terms of the noise amplitude
$\sqrt{S_n(\,f)}$
) and all underlying noise sources of the proposed detector. This noise budget and the basic design principles of a NEMO, including a detector schematic, are laid out in Section 2. The bottom panel shows again the NEMO noise budget in black, this time in terms of the noise amplitude
![]() $h_n=\sqrt{fS_n(\,f)}$
, and a comparison with the design sensitivity curves of A+ (blue), Cosmic Explorer (pink), and the Einstein Telescope (green). The sensitivity of a NEMO is comparable to those third-generation instruments in the kilohertz regime. Also shown in the bottom panel is an example signal one might expect from a binary neutron star merger at 40 Mpc, the same distance as the first binary neutron star merger detection GW170817. Tidal effects during the inspiral become prominent around 500 Hz and above, while the post-merger signal is above 1 kHz. We detail these key science deliverables and more in Section 3. In Section 4, we provide concluding remarks and sketch a path forward to a high-frequency detector within the international gravitational wave network. Finding NEMO: a potential location for a NEMO includes Australia, where a design concept called OzHF is eventually extended to a full-scale broadband Cosmic Explorer South. For details, see Bailes et al. (Reference Bailes2019).
$h_n=\sqrt{fS_n(\,f)}$
, and a comparison with the design sensitivity curves of A+ (blue), Cosmic Explorer (pink), and the Einstein Telescope (green). The sensitivity of a NEMO is comparable to those third-generation instruments in the kilohertz regime. Also shown in the bottom panel is an example signal one might expect from a binary neutron star merger at 40 Mpc, the same distance as the first binary neutron star merger detection GW170817. Tidal effects during the inspiral become prominent around 500 Hz and above, while the post-merger signal is above 1 kHz. We detail these key science deliverables and more in Section 3. In Section 4, we provide concluding remarks and sketch a path forward to a high-frequency detector within the international gravitational wave network. Finding NEMO: a potential location for a NEMO includes Australia, where a design concept called OzHF is eventually extended to a full-scale broadband Cosmic Explorer South. For details, see Bailes et al. (Reference Bailes2019).
2. Building NEMO
Simultaneously achieving high sensitivity at low (
![]() $\lesssim 50$
Hz) and high (
$\lesssim 50$
Hz) and high (
![]() $\gtrsim$
1 kHz) frequencies in a single detector is extremely challenging. There are two main reasons for this. First, the optical bandwidth of high-sensitivity kilometre-scale detectors is limited. Thus, to achieve sensitivity peaked at
$\gtrsim$
1 kHz) frequencies in a single detector is extremely challenging. There are two main reasons for this. First, the optical bandwidth of high-sensitivity kilometre-scale detectors is limited. Thus, to achieve sensitivity peaked at
![]() $\approx2\,$
kHz requires a loss of optical sensitivity below
$\approx2\,$
kHz requires a loss of optical sensitivity below
![]() $\approx$
500 Hz. Second, the high-circulating power required to improve high-frequency sensitivity introduces opto-mechanical instabilities whose control strategies can easily increase the noise in the low-frequency band. Detectors like the Einstein Telescope (Punturo et al. Reference Punturo2010b) plan to limit low- and mid-band frequency noise sources such as thermal noise by operating at 20 K, which is not compatible with high-circulating power. Broadband operation will then be achieved by building multiple detectors in a common subterranean vacuum envelope. In NEMO, we only concentrate on the frequency regime above
$\approx$
500 Hz. Second, the high-circulating power required to improve high-frequency sensitivity introduces opto-mechanical instabilities whose control strategies can easily increase the noise in the low-frequency band. Detectors like the Einstein Telescope (Punturo et al. Reference Punturo2010b) plan to limit low- and mid-band frequency noise sources such as thermal noise by operating at 20 K, which is not compatible with high-circulating power. Broadband operation will then be achieved by building multiple detectors in a common subterranean vacuum envelope. In NEMO, we only concentrate on the frequency regime above
![]() $\approx1\,$
kHz, sacrificing low-frequency sensitivity and thereby decreasing engineering challenges and cost. The low-frequency sensitivity required for sky localisation will be achieved by the other detectors in the network.
$\approx1\,$
kHz, sacrificing low-frequency sensitivity and thereby decreasing engineering challenges and cost. The low-frequency sensitivity required for sky localisation will be achieved by the other detectors in the network.
Martynov et al. (Reference Martynov2019) have shown that the optimal length of a detector with optimum sensitivity at 2 kHz is 16 km. At this time, it is unlikely that the funds needed to build a dedicated high-frequency detector of this scale could be obtained; hence, we have compromised to an arm length of 4 km which is also compatible with existing facilities. This arm length is sufficient to prevent displacement noise sources causing concern without being prohibitively expensive to build (Miao, Yang, & Martynov Reference Miao, Yang and Martynov2018). This reduction in arm length reduces the maximum sensitivity that can be obtained by about a factor of 2, which may in principal be recovered in a future upgrade using a folded interferometer as outlined in Ballmer & Ottaway (Reference Ballmer and Ottaway2013).
Our approach for achieving kilohertz sensitivity with a NEMO that is comparable to third-generation gravitational-wave observatories is outlined below. A simplified schematic of the inteferometer is illustrated in Figure 2 and the design parameters are included in Table 1.
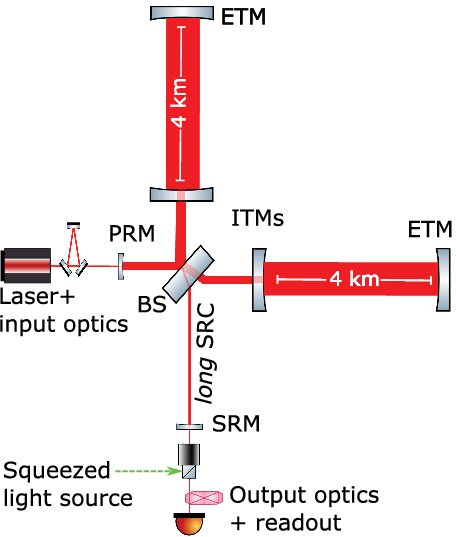
Figure 2. Simplified optical topology of NEMO. Folding of the recycling cavities, input and output optics, for example, various mode cleaners, not shown for clarity. A summary of the design parameters is included in Table 1. Acronyms in the figure are power recycling mirror (PRM), beam splitter (BS), input and end test mass (ITM and ETM, respectively) and Signal Recycling Cavity and Mirror (SRC and SRM, respectively).
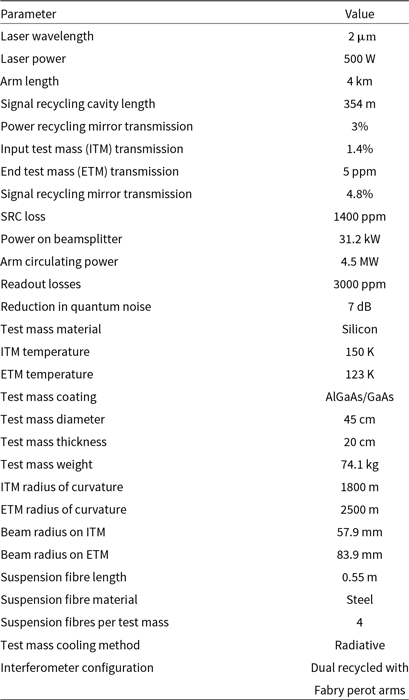
Table 1. Neutron Star Extreme Matter Observatory design parameters. All recycling cavities are stable cavities
The high-frequency sensitivity of interferometric gravitational-wave detectors is predominantly limited by quantum phase noise, which is due to the quantum nature of light, and not displacement noise sources such as seismic and thermal. Increasing the circulating power within the detector reduces the impact of this quantum phase noise proportional to the inverse of the square root of the power (Martynov et al. Reference Martynov2019). Therefore, to maximise sensitivity, the circulating power in the arms must be as large as possible. This quantum phase noise source can also be reduced by injecting squeezed vacuum into the dark port (Aasi et al. Reference Aasi2013). As a baseline design, we choose 4.5 MW of circulating power in the arms and inject 10 dB of squeezing which results in a 7-dB reduction in quantum noise. The circulating power and squeezing levels are chosen due to their feasibility given current technology constraints. If technology improves, both will be increased to further enhance the performance of the NEMO detector.
The quantum phase noise limited nature of high-frequency interferometers means that there are unlikely to be significant advantages in using exotic interferometer types such as speed metres (Chen Reference Chen2003) or other Sagnac style interferometers (Mizuno et al. Reference Mizuno, Rüdiger, Schilling, Winkler and Danzmann1997). For this reason, we choose a dual-recycled Michelson interferometer design with Fabry–Perot arm cavities, similar to current interferometric gravitational-wave detectors (Aasi et al. Reference Aasi2015; Acernese et al. Reference Acernese2015; Aso et al. Reference Aso, Michimura, Somiya, Ando, Miyakawa, Sekiguchi, Tatsumi and Yamamoto2013). However, there are some key differences targeted to maximise the sensitivity in the 1–4 kHz signal band of interest.
The signal-recycling cavity and the arm cavity of the interferometer form a coupled cavity system which determines the overall bandwidth of the interferometer. In order to maximise the sensitivity of a NEMO in the 1–4 kHz frequency band of interest, the length of the signal-recycling cavity and the transmission of the input test masses (ITMs) was optimised using numerical simulation tools PyKat and Finesse (Freise et al. Reference Freise, Heinzel, Lück, Schilling, Willke and Danzmann2004; Brown & Freise Reference Brown and Freise2014; Brown et al. Reference Brown, Jones, Rowlinson, Freise, Leavey, Green and Toyra2020). This resulted in the transmission of the ITM being set to 1.4% which resulted in 4.5 MW in the arm cavity and a signal-recycling cavity length of 354-m long. This ‘long’ signal-recycling cavity displays the characteristic splitting of a coupled cavity system (McClelland Reference McClelland1995; Martynov et al. Reference Martynov2019) around the interferometer carrier frequency where the gravitational-wave signal sidebands are resonantly enhanced. This splitting frequency is given by:
where TITM is the power transmissivity of the ITM, c is the speed of light, and Larm and Lsrc are the lengths of the arm cavities and the signal-recycling cavity, respectively. The bandwidth
![]() $\gamma$
of this coupled cavity system depends on the transmission of the signal recycling mirror as well as the length of the signal-recycling cavity.
$\gamma$
of this coupled cavity system depends on the transmission of the signal recycling mirror as well as the length of the signal-recycling cavity.
The same effect of enhanced sensitivity at certain frequencies can be obtained by detuning the signal-recycling cavity (Buonanno & Chen Reference Buonanno and Chen2002). However, this configuration comes with technical challenges pertaining to the control of the interferometer (Ward Reference Ward2010; Cahillane et al. Reference Cahillane2017).
Cryogenically cooled silicon test masses will be used to maximise the potential circulating-arm powers prior to adverse thermal distortions while also providing reduced coating thermal noise (Adhikari et al. Reference Adhikari2020). At cryogenic temperatures, silicon exhibits high thermal conductivity and low thermal expansion (Kim et al. Reference Kim2018). These test masses necessitate a departure from the 1.06-
![]() $\mu\textrm{m}$
lasers used in current generation gravitational-wave detectors. A NEMO operating with a 500-W,
$\mu\textrm{m}$
lasers used in current generation gravitational-wave detectors. A NEMO operating with a 500-W,
![]() $2\hbox{-}\mu\textrm{m}$
single-frequency diffraction limited laser is specified based on the silicon transmission window, the potential for reduced test mass coating absorption (Steinlechner et al. Reference Steinlechner2018), and the relative technological maturity of prospective sources. Thulium-doped fibre lasers are selected due to their intrinsic beam quality, demonstrated narrow linewidths at high power (Goodno, Book, & Rothenberg Reference Goodno, Book and Rothenberg2009), and potential for robust all-fibre architecture. While fibre laser technology has been demonstrated at 200 W at
$2\hbox{-}\mu\textrm{m}$
single-frequency diffraction limited laser is specified based on the silicon transmission window, the potential for reduced test mass coating absorption (Steinlechner et al. Reference Steinlechner2018), and the relative technological maturity of prospective sources. Thulium-doped fibre lasers are selected due to their intrinsic beam quality, demonstrated narrow linewidths at high power (Goodno, Book, & Rothenberg Reference Goodno, Book and Rothenberg2009), and potential for robust all-fibre architecture. While fibre laser technology has been demonstrated at 200 W at
![]() $ 1\,\mu\textrm{m}$
with the required intensity and frequency noise (Buikema et al. Reference Buikema, Jose, Augst, Fritschel and Mavalvala2019; Wellmann et al. Reference Wellmann, Steinke, Meylahn, Bode, Willke, Overmeyer, Neumann and Kracht2019), this has not yet been demonstrated at
$ 1\,\mu\textrm{m}$
with the required intensity and frequency noise (Buikema et al. Reference Buikema, Jose, Augst, Fritschel and Mavalvala2019; Wellmann et al. Reference Wellmann, Steinke, Meylahn, Bode, Willke, Overmeyer, Neumann and Kracht2019), this has not yet been demonstrated at
![]() $ 2\,\mu\textrm{m}$
. Recently, encouraging frequency and intensity noise levels have been demonstrated at low power using external cavity diode lasers (Kapasi et al. Reference Kapasi2020), which constitutes an important stepping stone. Fortunately, the thresholds of non-linear processes that limit the maximum power level of single-frequency fibre lasers increase faster than the wavelength squared (Dawson et al. Reference Dawson2008), implying it is likely that the 500 W of power required for a NEMO will be demonstrated in the near future.
$ 2\,\mu\textrm{m}$
. Recently, encouraging frequency and intensity noise levels have been demonstrated at low power using external cavity diode lasers (Kapasi et al. Reference Kapasi2020), which constitutes an important stepping stone. Fortunately, the thresholds of non-linear processes that limit the maximum power level of single-frequency fibre lasers increase faster than the wavelength squared (Dawson et al. Reference Dawson2008), implying it is likely that the 500 W of power required for a NEMO will be demonstrated in the near future.
In order to obtain the sensitivity target of a NEMO without further increasing the arm cavity power, introducing squeezed light is essential. For this purpose, we will inject 10 dB of frequency-independent squeezing into the interferometer, which will result in a quantum noise suppression of 7 dB. In the frequency range of 1–5 kHz, only quantum phase noise suppression is required, so systems to rotate the suppression quadrature to quantum radiation pressure noise reduction such as filter cavities are not required. The 7-dB reduction in quantum noise from injected squeezing assumed here is realistic as a 6-dB reduction in quantum shot noise in a kilometre-scale detector (GEO600 2018) has already been demonstrated. Squeezing at
![]() $2\,\mu$
m has already been demonstrated (Mansell et al. Reference Mansell, McRae, Altin, Yap, Ward, Slagmolen, Shaddock and McClelland2018; Yap et al. Reference Yap2019) and almost 12 dB of squeezing has been demonstrated at
$2\,\mu$
m has already been demonstrated (Mansell et al. Reference Mansell, McRae, Altin, Yap, Ward, Slagmolen, Shaddock and McClelland2018; Yap et al. Reference Yap2019) and almost 12 dB of squeezing has been demonstrated at
![]() $1.06\,\mu$
m in the frequency band of interest here (Stefszky et al. Reference Stefszky2012). Custom photodetectors at
$1.06\,\mu$
m in the frequency band of interest here (Stefszky et al. Reference Stefszky2012). Custom photodetectors at
![]() $1.06\,\mu$
m have a quantum efficiency of 99.5% (Vahlbruch et al. Reference Vahlbruch, Mehmet, Danzmann and Schnabel2016; Barsotti, Harms, & Schnabel Reference Barsotti, Harms and Schnabel2018), while at
$1.06\,\mu$
m have a quantum efficiency of 99.5% (Vahlbruch et al. Reference Vahlbruch, Mehmet, Danzmann and Schnabel2016; Barsotti, Harms, & Schnabel Reference Barsotti, Harms and Schnabel2018), while at
![]() $2\,\mu$
m the best known efficiency for extended InGaAs to date is 74% (Mansell et al. Reference Mansell, McRae, Altin, Yap, Ward, Slagmolen, Shaddock and McClelland2018). This has the implication that for 10-dB injected squeezing, the detected squeezing level stands lower than 4.5 dB (Barsotti et al. Reference Barsotti, Harms and Schnabel2018). In order to improve the detected reduction in quantum noise, this quantum efficiency needs to be improved and is currently work in progress. There is however no fundamental reason as to why >90% quantum efficiency photodiodes cannot be manufactured.
$2\,\mu$
m the best known efficiency for extended InGaAs to date is 74% (Mansell et al. Reference Mansell, McRae, Altin, Yap, Ward, Slagmolen, Shaddock and McClelland2018). This has the implication that for 10-dB injected squeezing, the detected squeezing level stands lower than 4.5 dB (Barsotti et al. Reference Barsotti, Harms and Schnabel2018). In order to improve the detected reduction in quantum noise, this quantum efficiency needs to be improved and is currently work in progress. There is however no fundamental reason as to why >90% quantum efficiency photodiodes cannot be manufactured.
The in-band noise performance can likely be achieved using a triple-stage suspension system similar to that of the Advanced LIGO (aLIGO) beam splitters and other auxiliary optics (Robertson Reference Robertson2010). Additional seismic isolation requirements in the control band (
![]() $\lesssim$
[50]Hz) should not be onerous and could be met by a simple active stage because of the increased actuation allowed on the test masses. The focus on the kilohertz band means that it is possible to use a steel suspension wires that are a reliable and proven suspension technology. Details of this are contained in a companion paper (Eichholz et al. Reference Eichholz, Holland, Adya, van Heijningen, Slagmolen, McClelland and Ottaway2020). The NEMO concept assumes only the last suspension stage to be cryogenic, both upper stages remain at room temperature. Further, to reduce the peak velocity of the optics in the pre-locked state, all the main optics are suspended by multi-stage suspension and isolation systems.
$\lesssim$
[50]Hz) should not be onerous and could be met by a simple active stage because of the increased actuation allowed on the test masses. The focus on the kilohertz band means that it is possible to use a steel suspension wires that are a reliable and proven suspension technology. Details of this are contained in a companion paper (Eichholz et al. Reference Eichholz, Holland, Adya, van Heijningen, Slagmolen, McClelland and Ottaway2020). The NEMO concept assumes only the last suspension stage to be cryogenic, both upper stages remain at room temperature. Further, to reduce the peak velocity of the optics in the pre-locked state, all the main optics are suspended by multi-stage suspension and isolation systems.
The performance of the second-generation detectors will be limited by coating thermal noise in the mid-band around 100 Hz once design sensitivity is reached. The order of magnitude improvement in quantum noise promised by high-frequency detectors promotes the coating thermal noise levels seen in current detectors to become a limitation at kHz frequencies, where it used to be of little concern. The constraints on coatings are further increased due to the requirement that coating absorption is very low.
Several potential coating choices are being actively researched for use in cryogenic third-generation detectors, such as ion-beam sputtered amorphous oxides, non-oxides, and crystalline thin films of III–V semiconductor materials. Two promising crystalline coating options are epitaxially grown multilayers of the AlGaAs/GaAs system (Cole et al. Reference Cole2008; Reference Cole, Zhang, Martin, Ye and Aspelmeyer2013) or the AlGaP/GaP system (Lin et al. Reference Lin2013; Cumming et al. Reference Cumming2015; Murray et al. Reference Murray2017). AlGaAs/GaAs coatings exhibit exceptionally low mechanical loss, optical absorption, and scatter. Of the possible amorphous coating materials, amorphous silicon (
![]() $\alpha$
-Si) is particularly attractive due to its low mechanical loss and high refractive index. The pairing of
$\alpha$
-Si) is particularly attractive due to its low mechanical loss and high refractive index. The pairing of
![]() $\alpha$
-Si with silicon dioxide (SiO
$\alpha$
-Si with silicon dioxide (SiO
![]() $_2$
) as a low-index material produces very thin coatings (Steinlechner et al. Reference Steinlechner2016; Birney et al. Reference Birney2018), which further benefits coating thermal noise due to its scaling with the square root of the coating thickness.
$_2$
) as a low-index material produces very thin coatings (Steinlechner et al. Reference Steinlechner2016; Birney et al. Reference Birney2018), which further benefits coating thermal noise due to its scaling with the square root of the coating thickness.
Currently, the choice of coatings is not clear-cut as
![]() $\alpha$
-Si/SiO
$\alpha$
-Si/SiO
![]() $_2$
coatings have a thermal noise advantage but unacceptably high projected absorption losses of 20 ppm (Steinlechner et al. Reference Steinlechner2018). On the other hand, AlGaAs/GaAs coatings suffer from elevated levels of thermo-optic noise principally due to high thermo-refractive and thermal expansion coefficients. With careful coating design, the partially coherent thermo-refractive and thermo-elastic noise terms can cancel each other for an overall reduction in thermo-optic noise (Evans et al. Reference Evans, Ballmer, Fejer, Fritschel, Harry and Ogin2008; Chalermsongsak et al. Reference Chalermsongsak2016). Another drawback of AlGaAs/GaAs coatings is that due to their lattice mismatch with silicon, they have to be grown on separate GaAs wafers and transferred onto the test masses. Steady progress is being made to upscale this technology with encouraging results (Penn et al. Reference Penn, Kinley-Hanlon, MacMillan, Heu, Follman, Deutsch, Cole and Harry2019).
$_2$
coatings have a thermal noise advantage but unacceptably high projected absorption losses of 20 ppm (Steinlechner et al. Reference Steinlechner2018). On the other hand, AlGaAs/GaAs coatings suffer from elevated levels of thermo-optic noise principally due to high thermo-refractive and thermal expansion coefficients. With careful coating design, the partially coherent thermo-refractive and thermo-elastic noise terms can cancel each other for an overall reduction in thermo-optic noise (Evans et al. Reference Evans, Ballmer, Fejer, Fritschel, Harry and Ogin2008; Chalermsongsak et al. Reference Chalermsongsak2016). Another drawback of AlGaAs/GaAs coatings is that due to their lattice mismatch with silicon, they have to be grown on separate GaAs wafers and transferred onto the test masses. Steady progress is being made to upscale this technology with encouraging results (Penn et al. Reference Penn, Kinley-Hanlon, MacMillan, Heu, Follman, Deutsch, Cole and Harry2019).
Both issues require time to be addressed, but the high absorption of
![]() $\alpha$
-Si presents a more fundamental issue for a NEMO detector. While
$\alpha$
-Si presents a more fundamental issue for a NEMO detector. While
![]() $\alpha$
-Si is a broadly studied material for its use in photovoltaics, the cryogenic material properties of AlGaAs/GaAs are better documented in the literature, which makes it easier to reliably predict thermal noise levels. The temperature dependence of thermal noise in AlGaAs/GaAs coatings is more fully explored in Eichholz et al. (Reference Eichholz, Holland, Adya, van Heijningen, Slagmolen, McClelland and Ottaway2020). For the noise budget in Figure 1, simple quarter-wave multi-layer AlGaAs/GaAs coatings that accomplish the ITM and end test mass (ETM) transmissions listed in Table 1 were assumed.
$\alpha$
-Si is a broadly studied material for its use in photovoltaics, the cryogenic material properties of AlGaAs/GaAs are better documented in the literature, which makes it easier to reliably predict thermal noise levels. The temperature dependence of thermal noise in AlGaAs/GaAs coatings is more fully explored in Eichholz et al. (Reference Eichholz, Holland, Adya, van Heijningen, Slagmolen, McClelland and Ottaway2020). For the noise budget in Figure 1, simple quarter-wave multi-layer AlGaAs/GaAs coatings that accomplish the ITM and end test mass (ETM) transmissions listed in Table 1 were assumed.
AlGaAs/GaAs coatings are a new coating technology, and their optimisation and limitations have not been fully explored. It is worth pointing out that the titania-doped tantala/silica (TiO
![]() $_2$
:Ta
$_2$
:Ta
![]() $_2\textit{O}_5$
/SiO
$_2\textit{O}_5$
/SiO
![]() $_2$
) coatings of aLIGO and Advanced Virgo (AdVirgo) may be a suitable lower risk alternative coating for the NEMO detector despite their increase in mechanical loss towards cryogenic temperatures. Compared to AlGaAs/GaAs coatings, Brownian noise rises by roughly a factor of 3.8, but at the same time thermo-optic noise is reduced by 35% in the case of conservative quarter-wave coatings. However, using aLIGO coatings would only result in a 15% overall increase in detector noise of a NEMO because the thermal noise of AlGaAs/GaAs coatings is significantly below the quantum noise in the kilohertz band (Eichholz et al. Reference Eichholz, Holland, Adya, van Heijningen, Slagmolen, McClelland and Ottaway2020).
$_2$
) coatings of aLIGO and Advanced Virgo (AdVirgo) may be a suitable lower risk alternative coating for the NEMO detector despite their increase in mechanical loss towards cryogenic temperatures. Compared to AlGaAs/GaAs coatings, Brownian noise rises by roughly a factor of 3.8, but at the same time thermo-optic noise is reduced by 35% in the case of conservative quarter-wave coatings. However, using aLIGO coatings would only result in a 15% overall increase in detector noise of a NEMO because the thermal noise of AlGaAs/GaAs coatings is significantly below the quantum noise in the kilohertz band (Eichholz et al. Reference Eichholz, Holland, Adya, van Heijningen, Slagmolen, McClelland and Ottaway2020).
We choose to operate the ITMs of the interferometer at 150 K rather than the 123 K specified for other third-generation silicon designs. This will allow the high power absorbed in the test masses to be radiatively dissipated to the 77 K cooled shields that will surround the test masses. We therefore do not require conductive cooling (Eichholz et al. Reference Eichholz, Holland, Adya, van Heijningen, Slagmolen, McClelland and Ottaway2020), which can compromise the suspension thermal noise of the detector. The details of this design are outlined in a companion paper (Eichholz et al. Reference Eichholz, Holland, Adya, van Heijningen, Slagmolen, McClelland and Ottaway2020) and are summarised below.
Silicon at a temperature in the range of 120–150 K has a low thermal expansion coefficient and a very high thermal conductivity, resulting in low thermal distortion of mirror surfaces. The thermo-optic coefficient of silicon is higher than that of room temperature silica that is used in the current detectors. However, the dramatically increased thermal conductivity of silicon means that the thermal lensing in the substrates will be reduced despite the greater absorption in silicon substrates compared with a similar room temperature silica detector. The 10
![]() ${\rm ppm}\,{\rm cm}^{-1}$
assumed for the absorption of silicon substrates does not represent a fundamental limit on silicon absorption and we expect this to improve with time. If this does not improve, then the thermal compensation system will need to work very well. Calculations have suggested that two orders of magnitude of suppression of substrate thermal lensing caused by uniform substrate and coating absorption is possible (Lawrence Reference Lawrence2003) which should be sufficient to prevent thermal lensing from limiting the sensitivity of NEMO. It should also be noted that we calculate our choice of a 2
${\rm ppm}\,{\rm cm}^{-1}$
assumed for the absorption of silicon substrates does not represent a fundamental limit on silicon absorption and we expect this to improve with time. If this does not improve, then the thermal compensation system will need to work very well. Calculations have suggested that two orders of magnitude of suppression of substrate thermal lensing caused by uniform substrate and coating absorption is possible (Lawrence Reference Lawrence2003) which should be sufficient to prevent thermal lensing from limiting the sensitivity of NEMO. It should also be noted that we calculate our choice of a 2
![]() $\,\mu$
m cryogenic silicon-based detector reduces this effect by a factor 6 c.f a room temperature 1
$\,\mu$
m cryogenic silicon-based detector reduces this effect by a factor 6 c.f a room temperature 1
![]() $\,\mu$
m silica-based detector.
$\,\mu$
m silica-based detector.
Point absorbers on the high-reflectivity surfaces of the test masses have caused significant local distortions of these surfaces in the aLIGO detector (Buikema et al. Reference Buikema2020). The impact of point absorbers will be reduced by a factor of over 300 for a silicon interferometer operating at 150 K compared with a silica interferometer operating at room temperature (Eichholz et al. Reference Eichholz, Holland, Adya, van Heijningen, Slagmolen, McClelland and Ottaway2020).
To maximise the surface area for radiative heat transfer, we assume a mirror diameter of 45 cm, which is projected to become available in the form of single-crystal cylindrical silicon boules grown by a magnetically assisted Czochralski method (m-Cz) for semiconductor applications (Lin & Huff Reference Lin, Huff, Doering and Nishi2008). Absorption levels of 10
![]() ${\rm ppm}\,{\rm cm}^{-1}$
have been demonstrated in m-Cz silicon (Adhikari et al. Reference Adhikari2020). A thickness of 20 cm results in a total mass of 74.1 kg. A black body of equivalent dimensions, held at 123 K, thermally radiates a total power of 7.8 W into its environment. At 150 K, this increases to 17.2 W. We assume that a cooling rate of about 70% of these values can be achieved, as shown by detailed finite element simulations for Voyager (Adhikari et al. Reference Adhikari2020), resulting in 5.5 and 12.1 W, respectively.
${\rm ppm}\,{\rm cm}^{-1}$
have been demonstrated in m-Cz silicon (Adhikari et al. Reference Adhikari2020). A thickness of 20 cm results in a total mass of 74.1 kg. A black body of equivalent dimensions, held at 123 K, thermally radiates a total power of 7.8 W into its environment. At 150 K, this increases to 17.2 W. We assume that a cooling rate of about 70% of these values can be achieved, as shown by detailed finite element simulations for Voyager (Adhikari et al. Reference Adhikari2020), resulting in 5.5 and 12.1 W, respectively.
A heat load of 4.5 W on the test masses is expected from a residual 1 ppm absorption of the high-reflectively coatings. Heating due to the transmitted light in the ETMs is negligible, however, with about 31-kW incident on the beam splitter, and each beam performing a double-pass through its respective ITM, the bulk heating power becomes 0.31
![]() ${\rm W}\,{\rm cm}^{-1}$
, for a total of 6.2 W. We therefore select an elevated temperature of 150 K for the ITMs, while the ETMs remain at 123 K. At these temperatures, the radiative cooling rate provides a margin of more than 1 W to the budgeted beam heating. For more details on this elevated temperature operation, see Eichholz et al. (Reference Eichholz, Holland, Adya, van Heijningen, Slagmolen, McClelland and Ottaway2020). Summarising, we can state that radiatively cooling the ITM, considering the heat load by absorption, needs an elevated temperature to increase the thermal gradient between test mass and cold shield. We model a trade-off between this and increased thermal lensing and low-frequency thermal noise to give an optimum temperature of 150 K.
${\rm W}\,{\rm cm}^{-1}$
, for a total of 6.2 W. We therefore select an elevated temperature of 150 K for the ITMs, while the ETMs remain at 123 K. At these temperatures, the radiative cooling rate provides a margin of more than 1 W to the budgeted beam heating. For more details on this elevated temperature operation, see Eichholz et al. (Reference Eichholz, Holland, Adya, van Heijningen, Slagmolen, McClelland and Ottaway2020). Summarising, we can state that radiatively cooling the ITM, considering the heat load by absorption, needs an elevated temperature to increase the thermal gradient between test mass and cold shield. We model a trade-off between this and increased thermal lensing and low-frequency thermal noise to give an optimum temperature of 150 K.
The beam splitter material choice is still an open question. The 31-kW incident on the beam splitter will result in significant astigmatic thermal lensing, even when the absorption in the substrate is low. In this situation, as with the GEO600 detector (Wittel et al. Reference Wittel2018), the beam splitter will need to be compensated. Different schemes to provide this compensation are actively being investigated.
Experience with current gravitational-wave detectors has shown that opto-mechanical instabilities arise when operating with high-circulating powers, such as parametric instabilities (Evans et al. Reference Evans2015b) and angular misalignment (Sidles & Sigg Reference Sidles and Sigg2006; Hirose et al. Reference Hirose, Kawabe, Sigg, Adhikari and Saulson2010). The high-circulating power inside the arm cavities could make a NEMO quite sensitive to opto-mechanical instabilities. However, this is where the dedicated high-frequency nature of the detector really comes into its own. In the case of angular instabilities, the bandwidth of the angular control loops can be significantly increased beyond what can be used for broadband detectors. Modelling has shown even at 5 MW of circulating power, the coupled opto-mechanical tilt modes of the NEMO arm cavities will not exceed 15 Hz. We estimate that these tilt modes can be controlled with angular control bandwidth of
![]() $\sim$
3 times the modified mode frequency, with sufficient noise suppression (
$\sim$
3 times the modified mode frequency, with sufficient noise suppression (
![]() $>$
60 dB) at
$>$
60 dB) at
![]() $\sim$
10 times the modified mode frequency (Barsotti, Evans, & Fritschel Reference Barsotti, Evans and Fritschel2010; Adhikari et al. Reference Adhikari2020). Hence, the noise injected by the required angular control loops should be insignificant for frequencies above
$\sim$
10 times the modified mode frequency (Barsotti, Evans, & Fritschel Reference Barsotti, Evans and Fritschel2010; Adhikari et al. Reference Adhikari2020). Hence, the noise injected by the required angular control loops should be insignificant for frequencies above
![]() $\approx$
1 kHz.
$\approx$
1 kHz.
Parametric instability was first observed at aLIGO with about 40 kW (Evans et al. Reference Evans, Gras, Fritschel, Miller, Barsotti and Martynov2015a) of circulating power in the arms, while AdVirgo (Acernese et al. Reference Acernese2015) did not observe parametric instabilities with circulating power of around 100 kW in 2019. This is indicative of the sensitivity of parametric instability to cavity and test mass parameters, detailed models are required for an accurate prediction of parametric instability. This detailed analysis is currently being performed (Pan et al. Reference Pan2020). However, rough estimation can be performed by assuming a scaling of aLIGO parameters and related scaling of the severity of parametric instabilities described in Braginsky et al. (Reference Braginsky, Strigin and Vyatchanin2001).
Parametric instability severity scales proportional to circulating power and optical quality factors and inversely proportional to mirror mass and mechanical eigen frequencies. The power will be 112.5 times higher than where aLIGO first observed parametric instability, the optical quality factors will be 1.35 times higher, the mirror mass will be 1.8 times heavier, and the lowest mechanical frequency is 1.08 times higher. If other parameters are considered unchanged, parametric instability is expected to be 98 times worse than aLIGO with 40-kW circulating power from this scaling argument. However, thermal tuning (Zhao et al. Reference Zhao2006; Hardwick et al. Reference Hardwick, Hamedan, Blair, Green and Vander-Hyde2020) allowed optical power to be increased by a factor of 4.3 at aLIGO. Resonant mass dampers attached to the test masses have been demonstrated to reduce mechanical mode quality factors by 10–100 (Biscans et al. Reference Biscans, Gras, Blair, Driggers, Evans, Fritschel, Hardwick and Mansell2019), introducing negligible thermal noise and electrostatic actuation has been demonstrated to reduce parametric gain by a factor of 13 and is inferred to be strong enough to reduce mode quality factors by 1 000 s (Blair et al. Reference Blair2017). This leads us to believe that with proper consideration of parametric instability and its mitigation, it may be controlled in a NEMO.
The noise budget for NEMO is illustrated in Figure 1. Assuming that the vacuum envelope will have similar or better performance than current detectors, the sensitivity of NEMO will be limited by quantum noise above 500 Hz. All other noise sources are a factor of 5 below this. The performance of a NEMO is compared to A+, Cosmic Explorer, and Einstein Telescope in the bottom panel of Figure 1 (bottom) which clearly illustrates that NEMO has comparable performance to the third-generation detectors around 2 kHz.
3. Scientific deliverables
To motivate the science case for a NEMO, we discuss physics encoded in the kilohertz gravitational-wave emission during both the inspiral and post-merger phases of a binary neutron star merger. These two phases probe different temperature regimes of the neutron star equation of state. During inspiral, neutron stars are relatively cold, with temperature
![]() $T\ll 10^{9} \textrm{K}$
, having had sufficient time to cool since birth. Under such conditions, the temperature does not significantly affect internal physical structure that determines bulk stellar quantities such as the stellar radius. Temperatures during merger can reach as high as
$T\ll 10^{9} \textrm{K}$
, having had sufficient time to cool since birth. Under such conditions, the temperature does not significantly affect internal physical structure that determines bulk stellar quantities such as the stellar radius. Temperatures during merger can reach as high as
![]() $T\sim 10^{11} \textrm{K}$
(e.g., Baiotti, Giacomazzo, & Rezzolla Reference Baiotti, Giacomazzo and Rezzolla2008; Foucart et al. Reference Foucart, O’Connor, Roberts, Kidder, Pfeiffer and Scheel2016) and can therefore affect the equation of state.
$T\sim 10^{11} \textrm{K}$
(e.g., Baiotti, Giacomazzo, & Rezzolla Reference Baiotti, Giacomazzo and Rezzolla2008; Foucart et al. Reference Foucart, O’Connor, Roberts, Kidder, Pfeiffer and Scheel2016) and can therefore affect the equation of state.
3.1. The physics of cold neutron stars
For cold neutron stars in the pre-merger phase, the tidal deformation of the individual components is imprinted in the gravitational-wave emission. The tidal deformation is dependent on the equation of state and is parameterised by the ‘combined dimensionless tidal deformability’
![]() $\tilde\Lambda$
, given by:
$\tilde\Lambda$
, given by:
Here
![]() $m_1$
and
$m_1$
and
![]() $m_2$
are the masses of the component neutron stars, and
$m_2$
are the masses of the component neutron stars, and
![]() $\Lambda_1$
and
$\Lambda_1$
and
![]() $\Lambda_2$
are the tidal deformabilities of each neutron star, defined as:
$\Lambda_2$
are the tidal deformabilities of each neutron star, defined as:
where R is the radius and
![]() $k_{2}$
is the second Love number, which measures the rigidity of the neutron star. Gravitational-wave astronomers measure
$k_{2}$
is the second Love number, which measures the rigidity of the neutron star. Gravitational-wave astronomers measure
![]() $\tilde\Lambda$
because it is the leading-order correction to gravitational waveforms due to tides. For a fixed mass, both R and
$\tilde\Lambda$
because it is the leading-order correction to gravitational waveforms due to tides. For a fixed mass, both R and
![]() $k_2$
are determined by the neutron star equation of state. Small values of
$k_2$
are determined by the neutron star equation of state. Small values of
![]() $\Lambda$
imply soft equations of state, corresponding to small, compact neutron stars. Large values of
$\Lambda$
imply soft equations of state, corresponding to small, compact neutron stars. Large values of
![]() $\Lambda$
imply stiff equations of state, where neutron stars are large and comparatively fluffy. Black holes have
$\Lambda$
imply stiff equations of state, where neutron stars are large and comparatively fluffy. Black holes have
![]() $k_2=0$
, implying the tidal deformability also vanishes.
$k_2=0$
, implying the tidal deformability also vanishes.
A key goal in nuclear astrophysics is to measure the tidal deformability as a function of neutron star mass. These tidal effects become increasingly important when the two neutrons stars are close to one another, which occurs late in coalescence and therefore at kilohertz gravitational-wave frequencies. In the bottom panel of Figure 1, we plot the NEMO (black) and A+ (blue) noise amplitude curves
![]() $h_n(\,f)=\sqrt{f\,S_n(\,f)}$
, where
$h_n(\,f)=\sqrt{f\,S_n(\,f)}$
, where
![]() $S_n(\,f)$
is the detector power spectral density, alongside the gravitational-wave characteristic strain
$S_n(\,f)$
is the detector power spectral density, alongside the gravitational-wave characteristic strain
![]() $h_c=2\,f\tilde{h}(\,f)$
from the inspiral and post-merger phase of an equal-mass binary neutron star coalescence at 40 Mpc (red). With these quantities, the expected signal-to-noise ratio
$h_c=2\,f\tilde{h}(\,f)$
from the inspiral and post-merger phase of an equal-mass binary neutron star coalescence at 40 Mpc (red). With these quantities, the expected signal-to-noise ratio
![]() $\rho$
is simply as (e.g., Moore, Cole, & Berry Reference Moore, Cole and Berry2015):
$\rho$
is simply as (e.g., Moore, Cole, & Berry Reference Moore, Cole and Berry2015):
Tidal effects become important at frequencies
![]() $\gtrsim$
400 Hz (Harry & Hinderer Reference Harry and Hinderer2018); at that point, the gravitational waveforms describing a binary black hole system and a binary neutron star system begin to dephase. A NEMO is designed to be sensitive to the physics of this late inspiral phase.
$\gtrsim$
400 Hz (Harry & Hinderer Reference Harry and Hinderer2018); at that point, the gravitational waveforms describing a binary black hole system and a binary neutron star system begin to dephase. A NEMO is designed to be sensitive to the physics of this late inspiral phase.
To study the sensitivity with which a NEMO can measure tidal deformability, we perform a Monte Carlo study in which we inject binary neutron star inspiral signals into simulated noise from two different detector networks. Network I consists of two A+ detectors located at Hanford and Livingston, and Network II is a three-detector network that adds a NEMO observatory. We locate the third detector in Gingin, near Perth in Australia.
We assume the population of mergers is distributed uniformly in co-moving volume, with a binary neutron star merger rate given by the mean merger rate inferred in Abbott et al. (Reference Abbott2020). In just over 6 months of observation, this corresponds to 44 detected binary neutron star merger signals with matched-filter signal-to-noise ratio
![]() $\rho_{\rm mf}>20$
with Network I and 61 such detected signals with Network II. We choose
$\rho_{\rm mf}>20$
with Network I and 61 such detected signals with Network II. We choose
![]() $\rho_{\rm mf}>20$
as signals weaker than this do not contribute appreciably to the cumulative inference of the equation of state (Hernandez Vivanco et al. Reference Hernandez Vivanco, Smith, Thrane, Lasky, Talbot and Raymond2019).
$\rho_{\rm mf}>20$
as signals weaker than this do not contribute appreciably to the cumulative inference of the equation of state (Hernandez Vivanco et al. Reference Hernandez Vivanco, Smith, Thrane, Lasky, Talbot and Raymond2019).
For simplicity, we further assume the chirp mass of these systems is uniformly distributed between 1 and
![]() $ 1.74 {M_\odot}$
, and that all systems are equal-mass, non-spinning binary mergers. We do not expect these assumptions to change our inference of the equation of state. Our injections are performed using an SLy equation of state (Douchin & Haensel Reference Douchin and Haensel2001), and we calculate the uncertainty on the masses, tidal deformability, time of coalescence, and phase using a Fisher matrix approximation (Martynov et al. Reference Martynov2019); we ignore uncertainties on other parameters as they do not correlate with the equation of state (e.g., see Abbott et al. Reference Abbott2017c, and references therein). We reconstruct the equation of state following the procedure outlined in Lackey & Wade (Reference Lackey and Wade2015) and Hernandez Vivanco et al. (Reference Hernandez Vivanco, Smith, Thrane, Lasky, Talbot and Raymond2019).
$ 1.74 {M_\odot}$
, and that all systems are equal-mass, non-spinning binary mergers. We do not expect these assumptions to change our inference of the equation of state. Our injections are performed using an SLy equation of state (Douchin & Haensel Reference Douchin and Haensel2001), and we calculate the uncertainty on the masses, tidal deformability, time of coalescence, and phase using a Fisher matrix approximation (Martynov et al. Reference Martynov2019); we ignore uncertainties on other parameters as they do not correlate with the equation of state (e.g., see Abbott et al. Reference Abbott2017c, and references therein). We reconstruct the equation of state following the procedure outlined in Lackey & Wade (Reference Lackey and Wade2015) and Hernandez Vivanco et al. (Reference Hernandez Vivanco, Smith, Thrane, Lasky, Talbot and Raymond2019).
In Figure 3, we show a reconstruction of the mass–radius relation using the above prescription. The grey and green contours show, respectively, the 90% credible interval obtained using Network I and Network II (i.e., adding a NEMO), and the SLy equation of state that we use for the injection is shown as the solid black curve. We also show other a set of other indicative equations of states commonly used in gravitational-wave analyses (e.g., Abbott et al. Reference Abbott2017c; Reference Abbott2020). The inclusion of a NEMO provides a significant improvement in the accuracy with which the equation of state can be measured,due to the improved high-frequency sensitivity of the network attributed to the addition of NEMO. For example, we see that the constraints on the equation of state are significantly less than 1 km at a fixed mass. Figure 3 also shows the posterior distributions are well enough constrained to rule out a large number of equations of state. In this figure, one would confidently rule out all equations of state, including APR4 with Network II, but not necessarily with Network I.
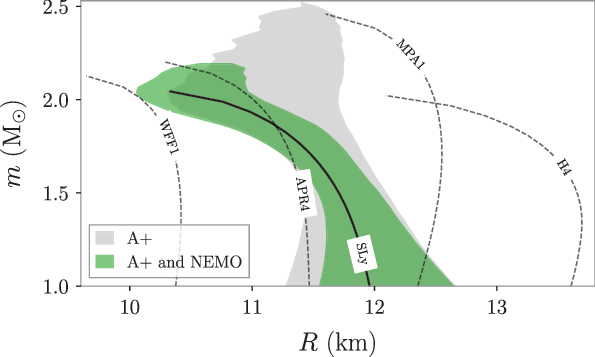
Figure 3. Reconstruction of the neutron star mass–radius relation using simulated data from 40 binary neutron star mergers. The true relation is shown with the solid black line, labelled SLy, while alternative equations of state are shown with dashed black curves. The grey contour shows the 90% credible interval obtained using a network of two A+ interferometers, while the green shows the same interval obtained when a NEMO is added to the network, assuming approximately six months of operation. In this example, from all of the equations of state shown, all but SLy equation are ruled out.
Our equation-of-state posterior distributions also imply we can infer the maximum neutron star mass allowed by that equation of state. In the example presented here, we are able to constrain the maximum mass with an accuracy of
![]() $\approx 0.3\,{\textrm{M}_\odot}$
at 90% confidence with Network I, which improves to
$\approx 0.3\,{\textrm{M}_\odot}$
at 90% confidence with Network I, which improves to
![]() $\approx 0.15\,{\textrm{M}_\odot}$
with the inclusion of a NEMO. This method for constraining the important maximum neutron star mass is complementary to the myriad of other direct and indirect methods in the literature (e.g., Margalit & Metzger Reference Margalit and Metzger2017; Ruiz, Shapiro, & Tsokaros Reference Ruiz, Shapiro and Tsokaros2018; Alsing, Silva, & Berti Reference Alsing, Silva and Berti2018; Sarin, Lasky, & Ashton Reference Sarin, Lasky and Ashton2020; Chatziioannou & Farr Reference Chatziioannou and Farr2020; Landry, Essick, & Chatziioannou Reference Landry, Essick and Chatziioannou2020).
$\approx 0.15\,{\textrm{M}_\odot}$
with the inclusion of a NEMO. This method for constraining the important maximum neutron star mass is complementary to the myriad of other direct and indirect methods in the literature (e.g., Margalit & Metzger Reference Margalit and Metzger2017; Ruiz, Shapiro, & Tsokaros Reference Ruiz, Shapiro and Tsokaros2018; Alsing, Silva, & Berti Reference Alsing, Silva and Berti2018; Sarin, Lasky, & Ashton Reference Sarin, Lasky and Ashton2020; Chatziioannou & Farr Reference Chatziioannou and Farr2020; Landry, Essick, & Chatziioannou Reference Landry, Essick and Chatziioannou2020).
In general, equation-of-state constraints such as those presented in this section and highlighted with Figure 3 are complementary to those using other methods such as X-ray and radio observations of isolated and accreting neutron stars (see Lattimer & Prakash Reference Lattimer and Prakash2007, for a review) and observations of post-merger remnants (see below). Each of these methods relies on different modelling assumptions and/or probes different regions of the equation-of-state parameter space.
3.2. The physics of hot neutron stars
Following the merger of two neutron stars, a new compact object is created. Depending on the remnant mass, this compact object can be a black hole or a massive neutron star. In the former case, gravitational-wave emission is difficult to observe because of the relatively short damping time and high frequency
![]() $\gtrsim$
6 kHz (Echeverria Reference Echeverria1989). However, if a neutron star survives the merger, gravitational waves can be emitted at frequencies of
$\gtrsim$
6 kHz (Echeverria Reference Echeverria1989). However, if a neutron star survives the merger, gravitational waves can be emitted at frequencies of
![]() ${\sim}1-4\,\textrm{kHz}$
for up to hundreds of milliseconds (Baiotti et al. Reference Baiotti, Giacomazzo and Rezzolla2008; Shibata & Taniguchi Reference Shibata and Taniguchi2006). The spectral content of the post-merger gravitational waves contains information about the neutron star equation of state (Takami, Rezzolla, & Baiotti Reference Takami, Rezzolla and Baiotti2015). Following merger, the temperature becomes an important equation-of-state parameter. For example, temperature-dependent phase transitions may occur in the core of post-merger neutron stars. Measuring gravitational waves from the inspiral and post-merger phase could provide a unique opportunity to identify phase transitions from hadronic matter to deconfined quark matter (Bauswein et al. Reference Bauswein2019). Furthermore, as the remnant is supported by differential rotation, the resulting neutron star in the post-merger phase has a higher density than the component neutron stars from the pre-merger phase. Thus gravitational-wave emission from the post-merger phase affords the opportunity to probe the equation of state in a different density regime.
${\sim}1-4\,\textrm{kHz}$
for up to hundreds of milliseconds (Baiotti et al. Reference Baiotti, Giacomazzo and Rezzolla2008; Shibata & Taniguchi Reference Shibata and Taniguchi2006). The spectral content of the post-merger gravitational waves contains information about the neutron star equation of state (Takami, Rezzolla, & Baiotti Reference Takami, Rezzolla and Baiotti2015). Following merger, the temperature becomes an important equation-of-state parameter. For example, temperature-dependent phase transitions may occur in the core of post-merger neutron stars. Measuring gravitational waves from the inspiral and post-merger phase could provide a unique opportunity to identify phase transitions from hadronic matter to deconfined quark matter (Bauswein et al. Reference Bauswein2019). Furthermore, as the remnant is supported by differential rotation, the resulting neutron star in the post-merger phase has a higher density than the component neutron stars from the pre-merger phase. Thus gravitational-wave emission from the post-merger phase affords the opportunity to probe the equation of state in a different density regime.
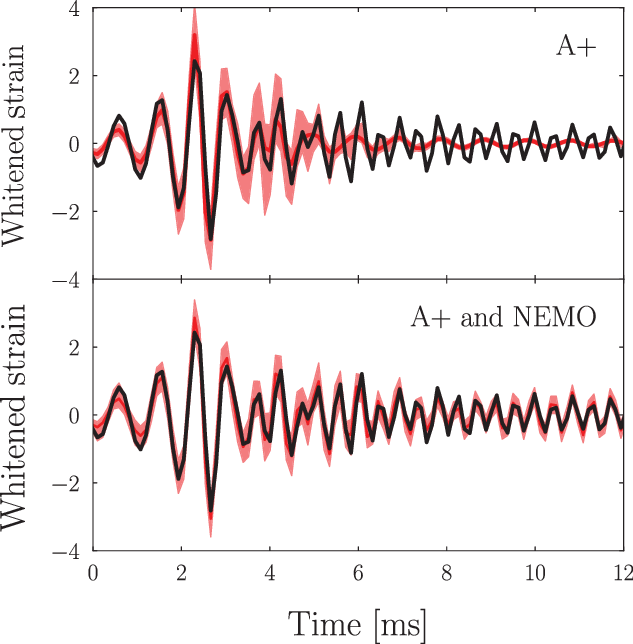
Figure 4. Gravitational-wave reconstruction of a post-merger signal with and without a NEMO. We inject the same numerical-relativity post-merger waveform as Figure 1 into a detector network consisting of two A+ detectors (top panel), and two A+ detectors and a NEMO detector (bottom panel). The black curve shows the injected signal, while the shaded regions show the 90% confidence interval reconstruction. Without a NEMO, the signal reconstruction fails to track the phase of the signal, whereas with a NEMO, the gravitational-wave phase is correctly tracked throughout the signal duration.
The precise signal morphology of neutron star post-merger gravitational waves remains unknown. However, numerical simulations have shown that the spectra of the emission from the nascent neutron star contain a characteristic peak frequency, approximately related to the fundamental quadrupolar mode of that neutron star and lower-frequency peaks (e.g., Bauswein & Stergioulas Reference Bauswein and Stergioulas2015, and references therein).
Using an algorithm that reconstructs gravitational-wave signals as a sum of sine-Gaussian wavelets called BayesWave (Cornish & Littenberg Reference Cornish and Littenberg2015), the post-merger waveform can be reconstructed with minimal assumptions on the exact morphology of the signal. From this reconstruction, it is possible to produce posterior distributions of the characteristic peak frequency. For signals where the post-merger matched-filter signal-to-noise ratio
![]() $\rho_{\text{mf}}\gtrsim 5 $
, the peak frequency can be constrained to within tens of Hertz (Chatziioannou et al. Reference Chatziioannou, Clark, Bauswein, Millhouse, Littenberg and Cornish2017; Torres-Rivas et al. Reference Torres-Rivas, Chatziioannou, Bauswein and Clark2019).
$\rho_{\text{mf}}\gtrsim 5 $
, the peak frequency can be constrained to within tens of Hertz (Chatziioannou et al. Reference Chatziioannou, Clark, Bauswein, Millhouse, Littenberg and Cornish2017; Torres-Rivas et al. Reference Torres-Rivas, Chatziioannou, Bauswein and Clark2019).
In Figure 4, we show an example of a reconstructed post-merger signal for an event like GW170817 obtained using the BayesWave algorithm following Chatziioannou et al. (Reference Chatziioannou, Clark, Bauswein, Millhouse, Littenberg and Cornish2017). The top panel shows the 90% credible interval obtained with Network I (two A+ observatories) and the bottom panel shows the 90% credible interval obtained with Network II (adding a NEMO). Qualitatively, without a NEMO only the first couple of milliseconds of the post-merger signal are reconstructed, while the reconstruction with a NEMO correctly tracks the signal for
![]() $\gtrsim10$
ms. In the top panel of Figure 4, the reconstruction is consistent with zero signal—the immediate post-merger signal (from approximately
$\gtrsim10$
ms. In the top panel of Figure 4, the reconstruction is consistent with zero signal—the immediate post-merger signal (from approximately
![]() $t=0$
to 4 ms) is reconstructed with short-lived wavelets, while the wavelets that fit the inspiral are relatively long-lived and well constrained. The small extent of the 90% credible interval after
$t=0$
to 4 ms) is reconstructed with short-lived wavelets, while the wavelets that fit the inspiral are relatively long-lived and well constrained. The small extent of the 90% credible interval after
![]() $\approx5$
ms is therefore an artefact of these basis functions, where tight constraint on the pre-merger signal leaks into post-merger region. The estimation of the peak frequency only uses wavelets with central times after the merger, implying these small post-merger artefacts do not affect the peak-frequency posterior nor the inferred physics of the post-merger remnant; for details, see Chatziioannou et al. (Reference Chatziioannou, Clark, Bauswein, Millhouse, Littenberg and Cornish2017). Using Network I, the characteristic peak frequency is mostly unconstrained with the 90% credible intervals covering most of the prior range. However, when adding a NEMO as in Network II, the characteristic peak frequency is constrained to a few tens of Hertz. In other words, the addition of a NEMO allows for a stringent measurement of the hot equation of state, whereas no information is gained about the post-merger remnant in the case of the two A+ detectors.
$\approx5$
ms is therefore an artefact of these basis functions, where tight constraint on the pre-merger signal leaks into post-merger region. The estimation of the peak frequency only uses wavelets with central times after the merger, implying these small post-merger artefacts do not affect the peak-frequency posterior nor the inferred physics of the post-merger remnant; for details, see Chatziioannou et al. (Reference Chatziioannou, Clark, Bauswein, Millhouse, Littenberg and Cornish2017). Using Network I, the characteristic peak frequency is mostly unconstrained with the 90% credible intervals covering most of the prior range. However, when adding a NEMO as in Network II, the characteristic peak frequency is constrained to a few tens of Hertz. In other words, the addition of a NEMO allows for a stringent measurement of the hot equation of state, whereas no information is gained about the post-merger remnant in the case of the two A+ detectors.
In order to showcase the advantage gained by a NEMO, we plot in Figure 5 the number of expected post-merger events per year for Network I with two A+ observatories (dashed blue) and Network II, which adds a NEMO (solid black). We inject post-merger gravitational waveforms from numerical relativity simulations for a variety of equations of state. We calculate the matched-filter signal-to-noise ratio for each signal injection for a realistic distribution of source distances, orientations, etc, and then calculate the average number of detections (defined as having
![]() $\rho_{\rm mf}>5$
) per year in either network. The results are plotted as a function of peak frequency, which depends on the equation of state. The length of each line indicates the 90% credible interval due to uncertainty in the binary neutron star merger rate (Abbott et al. Reference Abbott2020).
$\rho_{\rm mf}>5$
) per year in either network. The results are plotted as a function of peak frequency, which depends on the equation of state. The length of each line indicates the 90% credible interval due to uncertainty in the binary neutron star merger rate (Abbott et al. Reference Abbott2020).

Figure 5. The expected number of post-merger signals per year with matched-filter signal-to-noise ratio
![]() $\rho_{\text{mf}} > 5$
as a function of peak gravitational-wave frequency. In dashed blue, we show the number of detections for Network I with two A+ observatories while black indicates the number of detections for Network II when we add a NEMO to make a three-detector network. The length of the vertical lines shows the 90% credible interval owing to uncertainty from the binary neutron star merger rate (Abbott et al. Reference Abbott2020).
$\rho_{\text{mf}} > 5$
as a function of peak gravitational-wave frequency. In dashed blue, we show the number of detections for Network I with two A+ observatories while black indicates the number of detections for Network II when we add a NEMO to make a three-detector network. The length of the vertical lines shows the 90% credible interval owing to uncertainty from the binary neutron star merger rate (Abbott et al. Reference Abbott2020).
Figure 5 clearly shows that the average number of detections per year for a network of A+ interferometers not including a NEMO is significantly below one. Put another way, one would have to wait potentially many tens of years for the first post-merger detection without a NEMO. That number increases to an average of about one detection per year with a NEMO, ranging anywhere from one every few years to a few per year. We emphasise that the uncertainty here encodes our uncertainty in the binary neutron star merger rate.
3.3. Other science
Neutron star science is the key science driver for a NEMO. Since the natural timescale for neutron star physics is
![]() ${\mathcal{O}}( 1 {ms})$
, the frequency of gravitational waves from binary neutron star mergers is well matched to a NEMO. Recent observations of binary neutron star mergers (Abbott et al. Reference Abbott2017c; Reference Abbott2020) make neutron star science low risk because there is no doubt that binary neutron stars merge frequently enough for NEMO science. The direct measurement of the effects of matter in binary neutron stars will facilitate additional science, for example, breaking degeneracies in measurements of the Hubble flow (Messenger & Read Reference Messenger and Read2012; Calderón Bustillo, Dietrich, & Lasky Reference Calderón Bustillo, Dietrich and Lasky2020), helping to distinguish between neutron stars and black holes (e.g., Fasano et al. Reference Fasano, Wong, Maselli, Berti, Ferrari and Sathyaprakash2020) and any potential cosmological effects on the equation of state (e.g., Haster et al. Reference Haster, Chatziioannou, Bauswein and Clark2020).
${\mathcal{O}}( 1 {ms})$
, the frequency of gravitational waves from binary neutron star mergers is well matched to a NEMO. Recent observations of binary neutron star mergers (Abbott et al. Reference Abbott2017c; Reference Abbott2020) make neutron star science low risk because there is no doubt that binary neutron stars merge frequently enough for NEMO science. The direct measurement of the effects of matter in binary neutron stars will facilitate additional science, for example, breaking degeneracies in measurements of the Hubble flow (Messenger & Read Reference Messenger and Read2012; Calderón Bustillo, Dietrich, & Lasky Reference Calderón Bustillo, Dietrich and Lasky2020), helping to distinguish between neutron stars and black holes (e.g., Fasano et al. Reference Fasano, Wong, Maselli, Berti, Ferrari and Sathyaprakash2020) and any potential cosmological effects on the equation of state (e.g., Haster et al. Reference Haster, Chatziioannou, Bauswein and Clark2020).
The operation of a NEMO in a heterogeneous gravitational-wave network with two A+ interferometers will allow an unprecedented view into the hearts of short gamma-ray bursts. Low-frequency A+ sensitivity will see negative-latency triggers for electromagnetic telescopes—that is, telescopes will receive alerts before the two neutron stars merge—allowing early-time, multi-wavelength observations of the prompt emission, afterglow, and kilonovae (e.g., Metzger, Thompson, & Quataert Reference Metzger, Thompson and Quataert2018; James et al. Reference James, Anderson, Wen, Bosveld, Chu, Kovalam, Slaven-Blair and Williams2019). That information, together with gravitational-wave observations elucidating the nature of the remnant (e.g., Shibata et al. Reference Shibata, Zhou, Kiuchi and Fujibayashi2019) and time it takes for the remnant to collapse to a black hole (Lucca & Sagunski Reference Lucca and Sagunski2020; Easter, Lasky, & Casey Reference Easter, Lasky and Casey2020), will be as important to our understanding of gamma-ray burst physics as the first multimessenger gravitational-wave observation GW170817/GRB170817A. The precise nature of the remnant of GW170817 is not known (e.g., Ai, Gao, & Zhang Reference Ai, Gao and Zhang2020), in large part due to the non-detection of post-merger gravitational waves (Abbott et al. Reference Abbott2017f; Reference Abbott2019c). The joint electromagnetic and gravitational-wave detection of GW170817-like events with the addition of a NEMO will enable significant further insight into gamma-ray burst physics. For example, the delay time between the collapse and the prompt emission will drive studies into the jet-launching mechanism (e.g., Zhang Reference Zhang2019; Beniamini et al. Reference Beniamini, Barniol Duran, Petropoulou and Giannios2020) that is currently ill-understood (Zhang Reference Zhang2018), and the existence and lifetime of the remnant will reveal the impact of neutrino radiation on heavy-element formation through the rapid neutron-capture process in kilonovae (Metzger & Fernández Reference Metzger and Fernández2014; Martin et al. Reference Martin, Perego, Arcones, Thielemann, Korobkin and Rosswog2015; Fernández et al. Reference Fernández, Tchekhovskoy, Quataert, Foucart and Kasen2019; Kawaguchi, Shibata, & Tanaka Reference Kawaguchi, Shibata and Tanaka2020).
Neutron star–black hole mergers are also a target for a NEMO, where the primary science case is again to measure the tidal effects of a neutron star through the inspiral and merger phase. In general, neutron star–black hole binaries are a less sensitive probe of the equation of state than binary neutron star mergers (e.g., see Kumar, Pürrer, & Pfeiffer Reference Kumar, Pürrer and Pfeiffer2017, cf. Lackey & Wade Reference Lackey and Wade2015; Hernandez Vivanco et al. Reference Hernandez Vivanco, Smith, Thrane, Lasky, Talbot and Raymond2019 for binary neutron stars). The unknown rate estimates for neutron star–black hole binaries imply it is difficult to estimate the frequency of detections and therefore the potential science output. However, this situation may rapidly change with numerous neutron star–black hole candidates identified made during the third observing run of aLIGO and AdVirgo.Footnote a
Additional sources may be within the reach of a NEMO, for example, supernovae (e.g., Powell & Müller Reference Powell and Müller2019), quasi-monochromatic signals from rotating neutron stars (e.g., Lasky Reference Lasky2015; Riles Reference Riles2017), or more speculatively, superradiance from axion clouds (Yoshino & Kodama Reference Yoshino and Kodama2014). However, the detectability (and/or existence) of these sources is more speculative, and hence the great scientific impact of these targets must be tempered with theoretical uncertainty. Other sources such as binary black holes and the stochastic background are more easily studied at lower frequencies; a NEMO can detect them, but no better than broadband observatories such as A+.
By expanding the observing band of gravitational-wave networks, a NEMO will explore a new region of parameter space. History suggests that opening a new window on the Universe often yields unexpected discoveries; gamma-ray bursts are the great example. While a NEMO may detect something unexpected, we can be confident that it will measure the properties of matter effects in neutron stars.
4. Conclusion
We present the technology requirements and key science drivers for an Extreme Matter Observatory: a kilohertz gravitational-wave observatory optimised to study nuclear physics with merging neutron stars. A NEMO utilises high-circulating laser power and quantum squeezing to achieve necessary high-frequency noise, while sacrificing difficult and costly low-frequency sensitivity. Reaching a strain sensitivity of
![]() $\approx$
$\approx$
![]() $10^{-24} {1/\sqrt{\textrm{Hz}}}$
in the
$10^{-24} {1/\sqrt{\textrm{Hz}}}$
in the
![]() $\sim$
1–
$\sim$
1–
![]() $ 3\,\textrm{kHz}$
regime allows gravitational waves from the post-merger remnant of a binary neutron star collision to be detected with sufficient regularity. Such a NEMO should operate simultaneously with the A+ network which drives the sky localisation of sources and enables rapid electromagnetic identification of neutron star merger counterparts. The combination of electromagnetic observations, such as those achieved for GW170817, together with precision gravitational-wave observations of the inspiral, merger, and post-merger remnant will provide unprecedented insight into both the hot and cold equations of state of nuclear matter at supranuclear densities.
$ 3\,\textrm{kHz}$
regime allows gravitational waves from the post-merger remnant of a binary neutron star collision to be detected with sufficient regularity. Such a NEMO should operate simultaneously with the A+ network which drives the sky localisation of sources and enables rapid electromagnetic identification of neutron star merger counterparts. The combination of electromagnetic observations, such as those achieved for GW170817, together with precision gravitational-wave observations of the inspiral, merger, and post-merger remnant will provide unprecedented insight into both the hot and cold equations of state of nuclear matter at supranuclear densities.
The timescale for the development and construction of a NEMO is driven on two fronts. First, the science is maximised in a heterogeneous network of interferometers, such that the broadband A+ instruments realise the sky localisation of sources. Second, that NEMO is a key technology driver for full-scale third-generation instruments implies it must operate prior to the Cosmic Explorer and Einstein Telescope. Realistically, such a NEMO could be operational in the late 2020s and early 2030s, giving sufficient time for cooperations with the A+ network while impacting technology development for third-generation detectors. Such a proposal relies on engineering and detector design studies to be funded and implemented soon. Preliminary investigations show that a NEMO costs on the order of $50 to $100 M, a fraction of the
![]() $\sim$
billion-dollar budget required for third-generation broadband instruments.
$\sim$
billion-dollar budget required for third-generation broadband instruments.
The location of a NEMO is less critical than that of broadband detectors, where the network relies on long baselines to increase sky localisation accuracy. One suitable location includes Australia, where the OzHF concept (Bailes et al. Reference Bailes2019) sees the 4-km NEMO eventually extended into a 10 s of kilometre scale, broadband Cosmic Explorer South; the need for which has been identified by the Gravitational Wave International Committee to, for example, enable precision localisation of all merging stellar-mass binary black holes throughout the Universe.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Matt Evans and the anonymous referee for valuable comments on the manuscript. This work was supported through Australian Research Council (ARC) Centre of Excellence CE170100004, ARC Future Fellowships FT150100281, FT160100112, and FT190100574, ARC Discovery Project DP180103155, and the Direct Grant, Project 4053406, from the Research Committee of the Chinese University of Hong Kong.