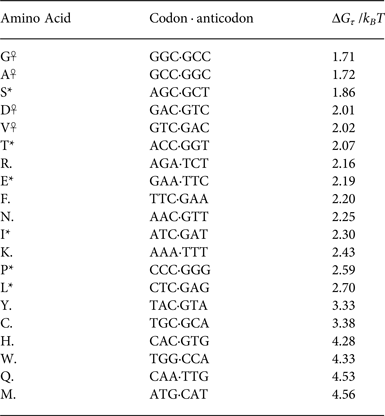
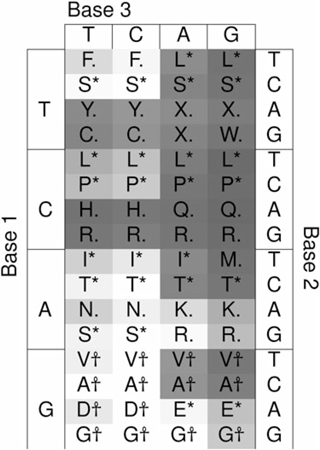
In the original version of the article the codon TGG was incorrectly entered as giving Tyrosine (Y) rather than the correct amino acid Tryptophan (W). This does not alter the argument of the paper, however the triplet propensity of W was therefore not calculated. Corrected versions of Table 1 and Table 2 (below) show triplet propensities recalculated with the correct encoding for TGG.
In figure 2(b) the arrows 5′->3′ indicating strand direction were placed next to the wrong strands.
The authors apologise for these errors.




