Introduction
Lower Cambrian rocks are widely distributed in the Great Basin of western United States. Besides the extensive research on trilobite assemblages from this region (e.g., Palmer, Reference Palmer1964; Sundberg and McCollum, Reference Sundberg and McCollum2003), brachiopods—one of the most abundant faunal components of benthic communities in this area—have been the subject of several studies for more than a century. It was the extensive, pioneering fieldwork mainly by Walcott (Reference Walcott1902, Reference Walcott1905, Reference Walcott1908) and Rowell (Reference Rowell1966, Reference Rowell1977, Reference Rowell1980; Rowell and Henderson, Reference Rowell and Henderson1978) that made the Great Basin one of the best-studied regions of Laurentia concerning brachiopods. The lower Cambrian biostratigraphy in White-Inyo Mountains/Esmeralda County has been well studied (Fig. 1); abundant archaeocyathids and trilobites, together with brachiopods and hyoliths, are known from the Campito and the Poleta Formation (e.g., Nelson, Reference Nelson1978; Rowland et al., Reference Rowland, Oliver, Hicks, Duebendorfer and Smith2008; Hollingsworth, Reference Hollingsworth2011; Cordie et al., Reference Cordie, Dornbos and Marenco2019); small skeletal brachiopods and associated fossils were reported from the Harkless Formation (Skovsted and Holmer, Reference Skovsted and Holmer2006). In contrast, less is known from the comparable Marble Mountains area.
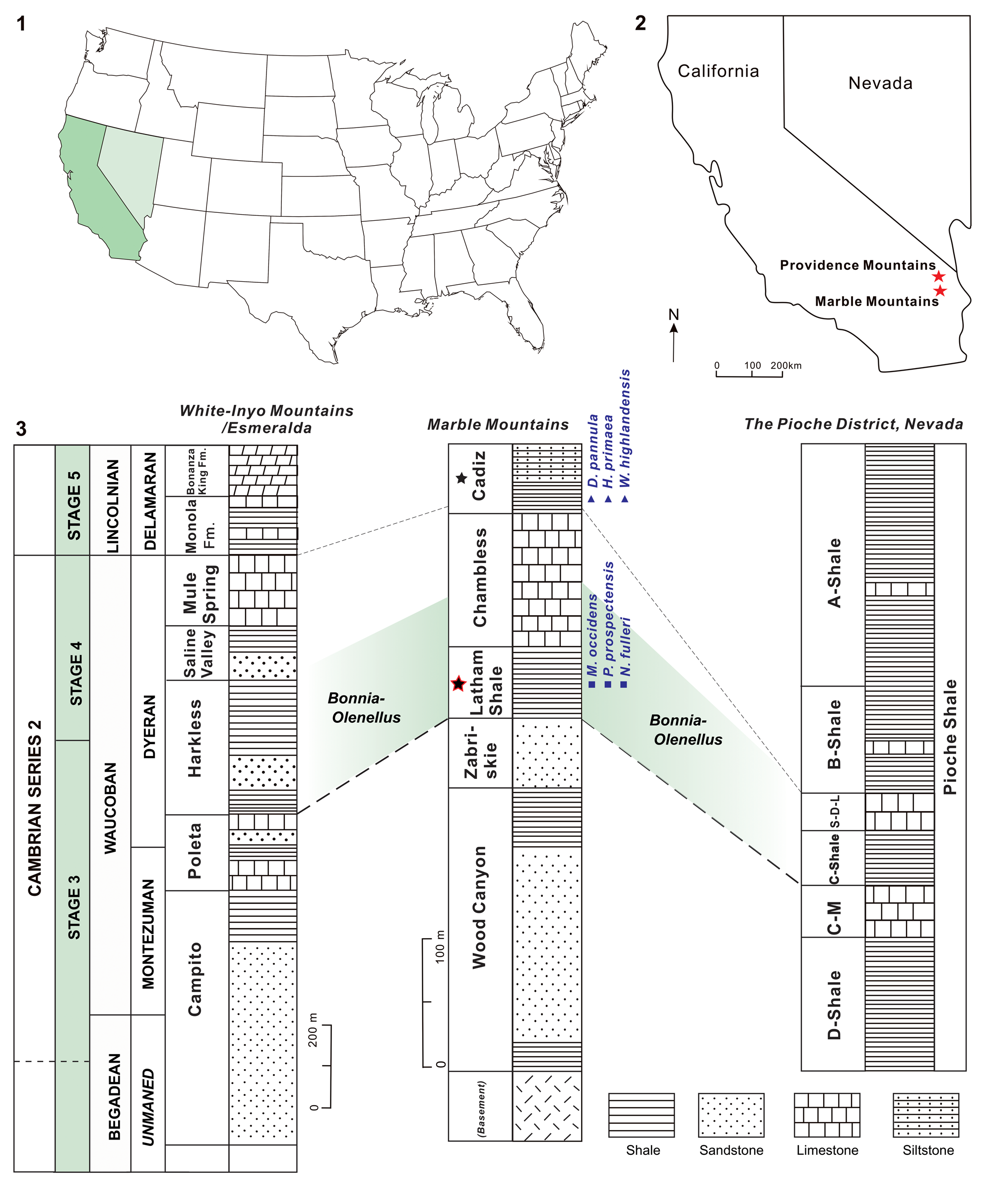
Figure 1. The study area and stratigraphical columns of the Latham Shale and the Cadiz Formation: (1, 2) location maps of the study area; (3) lower Cambrian stratigraphy of the study area and tentative correlation based on trilobite zonation, showing strata containing Dictyonina pannula (White, Reference White1874); Hadrotreta primaea (Walcott, Reference Walcott1902); Mickwitzia occidens Walcott, Reference Walcott1908; Nisusia fulleri Mount, Reference Mount1981; Paterina prospectensis (Walcott, Reference Walcott1884); and Wimanella highlandensis (Walcott, Reference Walcott1886) (modified from Stewart and Poole, Reference Stewart and Poole1975; Palmer and Halley, Reference Palmer and Halley1979; Rowell, Reference Rowell1980; Palmer, Reference Palmer1998; Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Ahlberg, Babcock, Choi, Geyer, Gozalo, Hollingsworth, Li, Naimark, Tatyana, Steiner, Wotte and Zhang2017; stars = location of the Latham Shale and the Cadiz Formation in California; light green shadow = Bonnia-Olenellus Biozone. C-M, Combined Metals; S-D-L, Susan Duster Limestone.
The lower Cambrian Latham Shale crops out prominently in two ranges, the Providence Mountains and the Marble Mountains, in the Eastern Mojave of Southern California (Fig. 1.1, 1.2). Although the formation is highly fossiliferous, descriptions of this fauna are quite rare. The only available brief report of the entire fauna was published by Mount (Reference Mount1980), who unfortunately provided only sketchy line drawings of the taxa. The Latham Shale is well known for its abundant and well-preserved olenellid trilobites, but most importantly, also yields exceptionally preserved fossils (Liang et al., Reference Liang, Holmer, Hu and Zhang2020a). The fauna includes 12 trilobites and three brachiopods, as well as mollusks, annelids, anthozoans, echinoderms, algae, and one ichnofossil (Mount, Reference Mount1980). Some of them have been well reported, e.g., the stem group arthropod Anomalocaris Whiteaves, Reference Whiteaves1892 (Briggs and Mount, Reference Briggs and Mount1982), the alga Margaretia Walcott, Reference Walcott1931 (Waggoner and Hagadorn, Reference Waggoner and Hagadorn2004), some unnamed early Cambrian palaeoscolecidans (Conway Morris and Peel, Reference Conway Morris and Peel2010), eocrinoids (Durham, Reference Durham1978), and enigmatic conical fossils (Waggoner and Hagadorn, Reference Waggoner and Hagadorn2005). However, a detailed description of the brachiopod assemblage has never been published.
The highest lower Cambrian unit is the Cadiz Formation of Hazzard and Mason (Reference Hazzard and Mason1936). The Cadiz Formation contains both early and middle Cambrian fossils, but the stage level boundary has not been determined (Mason, Reference Mason1935). The fauna is less fossiliferous and less studied when compared to the underlying Latham Shale with 13 trilobites, three brachiopods, two mollusks, and one siliceous sponge (Mason, Reference Mason1935). Among them, three brachiopods and five trilobites have been described with sketched illustrations by Mount (Reference Mount1980).
The main objective of this paper is to provide the first comprehensive description of the brachiopods from the Latham Shale Lagerstätte (unnamed Series 2, upper Stage 4) and the upper Cadiz Formation (Miaolingian, Wuliuan) in the Providence Mountains and the Marble Mountains area, California. The fauna treated here includes four linguliform and two rhynchonelliform species and could represent the earliest onset of the transition from the Cambrian Evolutionary Fauna (CEF) to the Paleozoic Evolutionary Fauna (PEF).
Geological setting
The Latham Shale is best known from exposures in the southern Providence Mountains and the Marble Mountains (Fig. 1.1, 1.2), where fossils have been collected for over a century (e.g., Darton, Reference Darton1907; Clark, Reference Clark1921; Mount, Reference Mount1980). According to Hazzard (Reference Hazzard1954), the Latham Shale is ~15–45 m thick, with gray-green shale, platy micaceous siltstone, sandstone, and a minor amount of limestone. The shale weathers to red, paper-thin fragments and contains abundant olenellid trilobites, indicating that the formation lies within the Bonnia-Olenellus Biozone (Mount, Reference Mount1980).
The Cadiz Formation (Hazzard and Mason, Reference Hazzard and Mason1936) was redefined by Hazzard (Reference Hazzard1954) by lowering the lower boundary to include a 33+ m interval of the lower Cambrian strata. The formation consists of a heterogeneous assemblage of lithologies including sandstone, shale, siltstone, and limestone. The early Cambrian part of the Cadiz Formation lies in the Olenellus multinodus Subzone of the Bonnia-Olenellus Zone; the middle Cambrian portion of the Cadiz Formation contains faunas from the middle Cambrian Plagiura-Poliella, Albertella, and Glossopleura biozones, however, they have not received critical biostratigraphical study (Mount, Reference Mount1980; Waggoner and Collins, Reference Waggoner and Collins1995).
The specimens from the Latham Shale Lagerstätte and the Cadiz Formation originate from the collections of the University of California, Riverside (UCR). Unfortunately, historic museum collections from this area often lack precise locality and stratigraphic information. Some of the fossils have localities recorded only as ‘Marble Mountains’ or ‘southern end of the Marble Mountains.’ This probably indicates the best-known trilobite collecting areas in the Marble Mountains, which are near a limestone quarry at the southern tip of the mountain range, ~4 km (2.5 mi) north and east of the settlement of Cadiz, south of the National Trails Highway (formerly U.S. Route 66) (Waggoner and Hagadorn, Reference Waggoner and Hagadorn2005).
Material and methods
Fossils were examined under a Zeiss Stemi 305 microscope and photographed with a Zeiss Smart Zoom 5 Stereo-micrographic system and Cannon camera 5D Mark IV mounted on a photographic system. Uncoated specimens were examined with a FEI Quanta 400-FEG scanning electron microscope (SEM), equipped with backscattered and secondary electron detectors in addition to an energy-dispersive X-ray analyser (EDX) operating at accelerating voltages ranging from 5–15 kV, at the Department of Geology, Northwest University (NWU), Xi'an, China. Some specimens were tested by Bruker M4 Tornado table-top energy-dispersive micro-X-ray fluorescence (μ-XRF) to characterize the elemental abundances in samples from the fluorescence spectrum. Specimens were covered by wax for better preservation of the shell surface, so they were photographed and coated with ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) to reduce reflecting light during photography. Some of the shells have been subjected to deep weathering, and they were usually preserved as internal molds. To better display the ornamentation and shell structures in detail, a number of latex casts or molds were prepared using polyvinyl butyral (PVB) ethanol solution and latex.
Other materials examined
In addition to the fossils from the Latham Shale Lagerstätte and the Cadiz Formation, six specimens of Hadrotreta primaea (Walcott, Reference Walcott1902) from the basal Emigrant Formation of Split Mountain, Nevada, and one specimen of Heliomedusa orienta Sun and Hou, Reference Sun and Hou1987 from the Chengjiang Lagerstätte, South China were collected for comparison.
Repositories and institutional abbreviations
Most of the fossil specimens examined in this study were loaned from University of California, Riverside (UCR), USA. Other cited repositories are ELI = Early Life Institute, Northwest University Xi'an, China; and USNM = National Museum of Natural History (United States National Museum), Smithsonian Institution, Washington, DC, USA.
Systematic paleontology
Phylum Brachiopoda Duméril, Reference Duméril1806
Subphylum Linguliformea Williams et al., Reference Williams, Carlson, Brunton, Holmer and Popov1996
Class Lingulata Gorjansky and Popov, Reference Gorjansky and Popov1985
Order Acrotretida Kuhn, Reference Kuhn1949
Superfamily Acrotretoidea Schuchert, Reference Schuchert1893
Family Acrotretidae Schuchert, Reference Schuchert1893
Genus Hadrotreta Rowell, Reference Rowell1966
Type species
Acrotreta primaea Walcott, Reference Walcott1902, from the lower to middle Cambrian Pioche Shale, Nevada, USA.
Hadrotreta primaea (Walcott, Reference Walcott1902)
Figure 2
- Reference Walcott1902
Acrotreta primaea Walcott, p. 593.
- Reference Walcott1912
Acrotreta primaea; Walcott, p. 700, pl. 69, figs. la–f.
- Reference Rowell1966
Hadrotreta primaea; Rowell, p. 13, pl. 1, figs. 1–12.
- Reference Rowell1980
Hadrotreta primaea; Rowell, p. 7, pl. 4, figs. 8–12, pl. 5, figs. 1–10, pl. 6, figs. 1–9.
- Reference Roberts and Jell1990
Hadrotreta primaea; Roberts and Jell, figs. 22–24, table 3.
- Reference Holmer, Popov, Williams, Brunton and Carlson2007
Hadrotreta primaea; Holmer and Popov, p. 113, fig. 57.1a–f.
Description
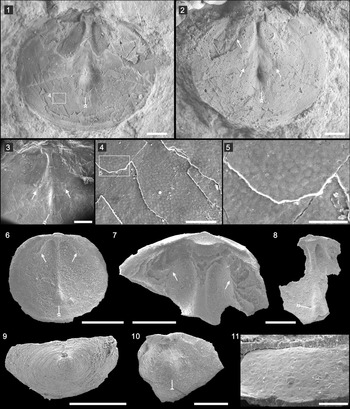
Dorsal valve subcircular in outline, of 6.89 mm width, 5.82 mm length (Fig. 2.1, 2.2). Shell gently convex, most strongly convex posteromedially, becoming gradually flattened anteriorly, with maximum width at midlength (Fig. 2.1, 2.2). Dorsal pseudointerarea small, occupying ~27% of total valve width, with faint median groove and propareas (Fig. 2.3). Dorsal median buttress strongly developed, extending 33% of valve length; strongly developed ridge-like median septum originating at approximate distal end of median buttress, extending ~67% of total valve length; terminal portion of median septum forming subtriangular platform-like swelling (Fig. 2.1–2.3, double-tailed arrows). Elongate impressions of anterocentral muscle scars on lateral edge of median septum (Fig. 2.2, 2.3, arrows). Cardinal muscle scars weakly impressed, extending anterolaterally from lateral edge of median groove, occupying 20% of total length, 46% of valve width (Fig. 2.2, doubled-headed arrow). Epithelial cell molds on different shell layers, ~7.22–12.57 μm in diameter (Fig. 2.4, 2.5).
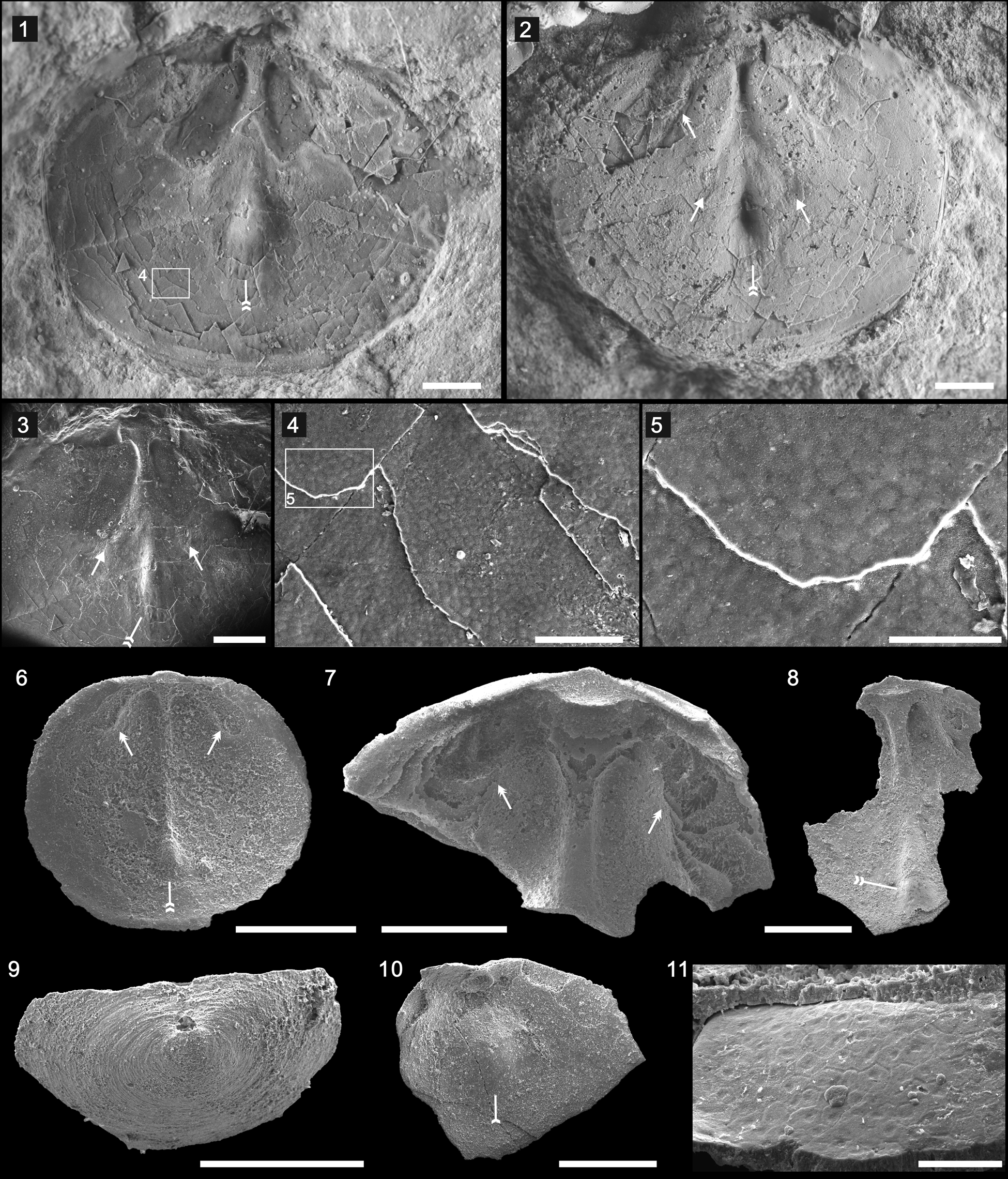
Figure 2. Hadrotreta primaea (Walcott, Reference Walcott1902): (1–5) from the Cadiz Formation (UCR 7312/1); dorsal valve (1, with boxed area of [4]) and latex cast (2) showing the median buttress, swelling median septum terminal (double-tailed arrows), cardinal muscle scars (double-headed arrow), and elongate impressions of anterocentral muscle scars on the lateral edge of the median septum (arrows); (3–5) SEM images showing swelling median septum terminal (double-tailed arrow), elongate impressions of anterocentral muscle scars (arrows), and the epithelial molds; (6–11) from the basal Emigrant Formation, Split Mountain, Nevada: (6) dorsal interior (ELI SMS 5) showing the median buttress, swelling median septum terminal (double-tailed arrow), and cardinal muscle scars (double-headed arrows); (7) enlarged dorsal interior (ELI SMS 3) showing well-defined cardinal muscle scars (double-headed arrows) and median buttress; (8) internal surface of a dorsal valve (ELI SMS 1) showing median septum and swelling median septum terminal (double-tailed arrow); (9) posterior view of the ventral valve (ELI SMS 8); (10) internal view of a ventral valve (ELI SMS 9) showing the apical process (single-tailed arrow); (11) the epithelial cell molds preserved in the interior surface of a ventral valve (ELI SMS 10). Scale bars = 1 mm (1–3); 500 μm (6–10); 100 μm (4); 50 μm (5, 11).
Materials
One dorsal valve (UCR 7312/1) recovered from the Cadiz Formation. Three dorsal valves (ELI SMS 1, 3, 5) and three ventral valves (ELI SMS 8, 9, 10) collected from the basal Emigrant Formation, Split Mountain, Nevada.
Remarks
After the genus Acrotreta was erected by Kutorga in 1848, the type material of the type species Acrotreta subconica Kutorga, Reference Kutorga1848 was lost and there was a lack of detailed information concerning interior characters, type locality, and type horizon. As a result, the genus was subsequently used worldwide as a ‘waste basket’ for almost any conical acrotretides from the Cambrian-Ordovician. Holmer and Popov (Reference Holmer and Popov1994) revised the type species and related lingulate brachiopods and suggested that Acrotreta is restricted to the Ordovician, because none of the numerous Cambrian records of the genus (see, e.g., Walcott, Reference Walcott1912) can be retained within the taxon. Rowell (Reference Rowell1966) erected the genus Hadrotreta as monotypic; its diagnosis and description were based on the etched topotype material of Acrotreta primaea.
Hadrotreta primaea has been described from the Pioche Shale of Nevada (Rowell, Reference Rowell1980) and the Coonigan Formation of western New South Wales, Australia (Roberts and Jell, Reference Roberts and Jell1990). The etched material of Hadrotreta primaea from the basal Emigrant Formation (Fig. 2.6–2.11) highly resembles the shale-hosted material, whereas the former has better-developed anterocentral muscle scars (Fig. 2.6, 2.7, arrows), a platform-like swelling at the termination of the dorsal median septum (Fig. 2.6, 2.8, double-tailed arrows), a ventral intertrough (Fig. 2.9) and most importantly a moderately high cape-like ventral apical process (Fig. 2.10, tailed arrow). Specimens from the lower Cambrian of South Australia referred to Hadrotreta primaea by Brock & Cooper (Reference Brock and Cooper1993) were later assigned to Vandalotreta djagoran (Kruse, Reference Kruse1990) by Holmer et al. (Reference Holmer, Popov and Wrona1996). In 2014, Percival and Kruse reassigned the material to Kostjubella Popov, Holmer, and Gorjansky, Reference Popov, Holmer and Gorjansky1996. ?Hadrotreta primaea has been described from the Harkless Formation, southern Nevada (Skovsted and Holmer, Reference Skovsted and Holmer2006), although the lack of internal information for the ventral valve hampered its accurate affinity.
Hadrotreta primaea differs from Hadrotreta taconica (Walcott, Reference Walcott1887) from the Forteau Formation of southern Labrador and western Newfoundland by having a more-pronounced, boss-like anterior termination of dorsal median ridge, and shorter dorsal pseudointerarea (Skovsted et al., Reference Skovsted, Knight, Balthasar and Boyce2017). Hadrotreta primaea is similar to Hadrotreta timchristiorum Popov et al., Reference Popov, Holmer, Hughes, Ghobadi Pour and Myrow2015 from the Himalaya (Popov et al., Reference Popov, Holmer, Hughes, Ghobadi Pour and Myrow2015), although the latter has a narrower and shallower ventral intertrough. The epithelial cell molds are reminiscent of those in etched material in their overall impression and average diameter, but those from acid-etched carbonate material better preserve the hexagonal network (Fig. 2.11).
Class Paterinata Williams et al., Reference Williams, Carlson, Brunton, Holmer and Popov1996
Order Paterinida Rowell, Reference Rowell and Moore1965
Superfamily Paterinoidea Schuchert, Reference Schuchert1893
Family Paterinidae Schuchert, Reference Schuchert1893
Genus Paterina Beecher, Reference Beecher1891
Type species
Obolus labradoricus Billings, Reference Billings1861 from the lower Cambrian of Labrador, Canada.
Paterina prospectensis (Walcott, Reference Walcott1884)
Figures 3, 8.1
- Reference Walcott1884
Kutorgina prospectensis Walcott, p. 19, pl. 9, fig. 1, 1a, b.
- Reference Walcott1886
Kutorgina prospectensis; Walcott, p. 106, pl. 9, fig. 3, 3a.
- Reference Walcott1897
Iphidea prospectensis; Walcott, p. 234.
- Reference Walcott1905
Iphidella prospectensis; Walcott, p. 307.
- Reference Walcott1912
Micromitra (Paterina) prospectensis; Walcott, p. 352, pl. 2, fig. 4, 4a.
- Reference Mount1980
Paterina prospectensis; Mount, fig. 2.
- Reference Liang, Holmer, Hu and Zhang2020a
Paterina prospectensis; Liang et al., fig. 1a, b, e, f.
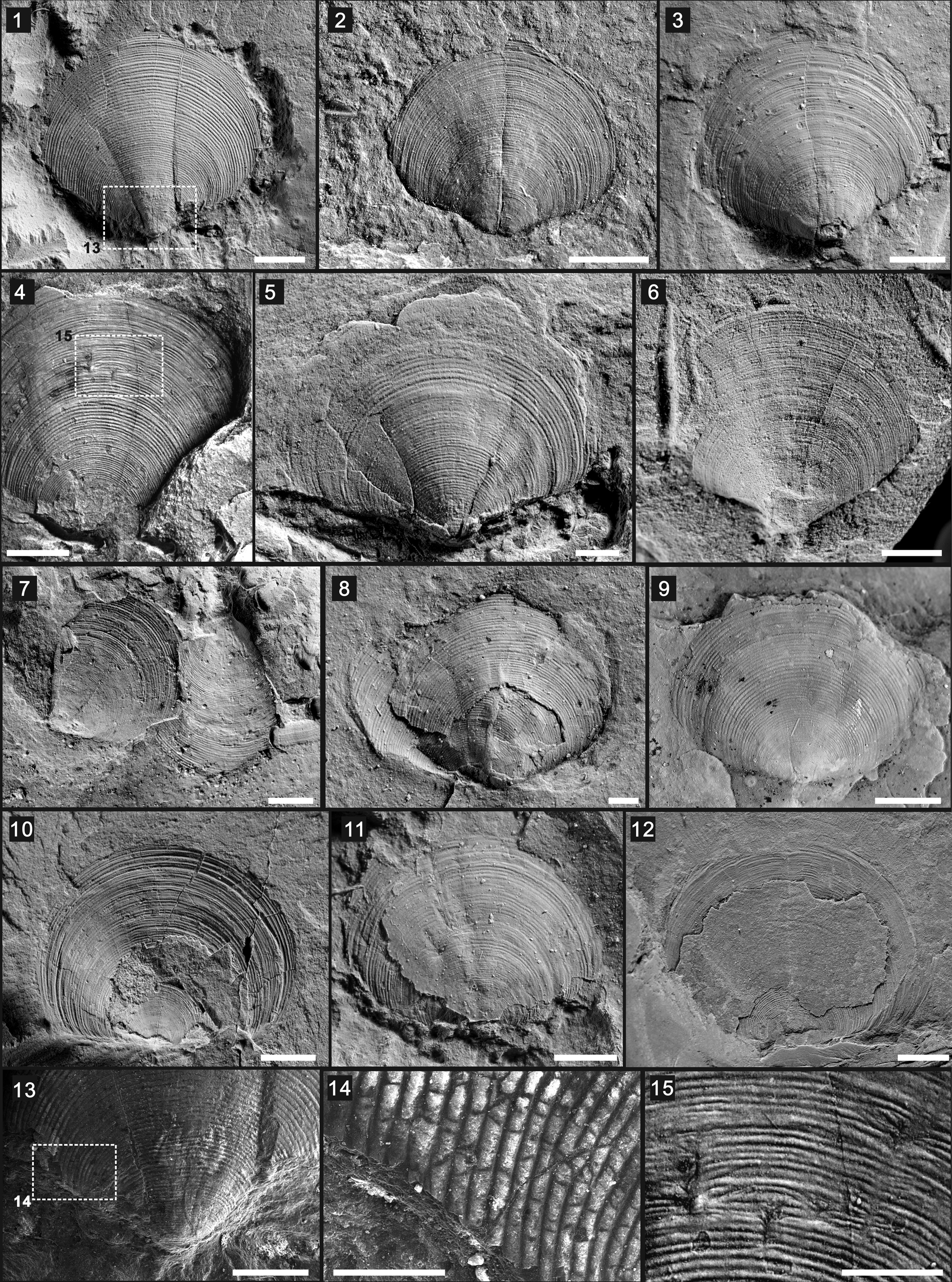
Figure 3. Paterina prospectensis (Walcott, Reference Walcott1884): (1) ventral valve exterior (UCR 10/3381), with boxed area of (13); (2) ventral valve exterior (UCR 10/3354); (3) ventral valve exterior (UCR 10/2006); (4) ventral valve exterior (UCR 7002/298) with boxed area of (15); (5) ventral valve exterior (UCR 10/3362); (6) ventral valve exterior (UCR 10/3351); (7) ventral valve exterior (UCR 10/8/34); (8) ventral valve exterior and dorsal valve interior (UCR 10/3369); (9) dorsal valve exterior (UCR 4079/10/1); (10) dorsal valve exterior (UCR 7271/6); (11) dorsal valve exterior (UCR 10/3366); (12) dorsal valve exterior (UCR 7002/300); (13, 14) SEM images showing the prominent growth lines (UCR 10/3381) and boxed area of (14); (15) enlarged view of boxed area in (4), showing drapes and nick points on the surface. Scale bars = 2 mm (1–12); 1 mm (13, 15); 500 μm (14).
Hypotype
A dorsal valve (UCR 10/2006), lower Cambrian Latham Shale, California, USA (Fig. 3.3).
Description
Shell ventribiconvex, subcircular in outline (Fig. 3.1–3.12). Shells relatively large, of 4.89–8.87 mm length, 5.99–11.2 mm width, with maximum width at midlength. Ventral valve convex, with apex at posterior part (Fig. 3.1–3.8). Ventral posterior margins oblique, well-illustrated in examined specimens (Fig. 3.1–3.8). Pseudointerarea and homeodeltidium poorly preserved. Dorsal valve less convex, with well-defined, nearly straight hinge line (Fig. 3.9–3.12). Dorsal valve larger than ventral valves in current collection. Shell interior not observed. External ornamentation on both valves consisting of regular, fine, concentric fila. Concentric growth lines spaced regularly (10–12 per mm; Fig. 3.13, 3.14), sometimes interrupted by nick points, forming sets of drapes (Fig. 3.4, 3.15).
Materials
Four dorsal (UCR 7002/300, 10/3366, 7271/6, and 4079/10/1) and eight ventral valves (UCR 10/3381, 10/3354, 10/2006, 7002/298, 10/3362, 10/3351, 10/8/34, and 10/3369), including one complete conjoined shell (UCR 10/3369) and one dorsal valve with soft-part preservation (UCR 7002/300; Liang et al., Reference Liang, Holmer, Hu and Zhang2020a), recovered from the lower Cambrian Latham Shale.
Remarks
Paterina prospectensis was originally assigned to Kutorgina Billings, Reference Billings1861 and Iphidea Billings, Reference Billings1872 by Walcott, but he later transferred it to Micromitra Meek, Reference Meek1873, based on its concentrically striated ornamentation. Later, it was known as Paterina prospectensis (see Mount, Reference Mount1976, Reference Mount1980; Gaines and Droser, Reference Gaines, Droser and Corsetti2002). The specimens studied here show distinct ornamentation of concentric growth fila and are markedly different from the surface ornamentation of Micromitra (Williams et al., Reference Williams, Popov, Holmer and Cusack1998). Another prominent difference between Paterina and Micromitra is that the former has an open delthyrium whereas the latter has a homeodeltidium (Laurie, Reference Laurie and Kaesler2000). Both genera belong within the class Paterinata, in which Paterina has a slightly earlier first appearance datum (FAD) and became extinct in the late Ordovician (Williams et al., Reference Williams, Popov, Holmer and Cusack1998).
The most comparable well-known species is Paterina zenobia Walcott, Reference Walcott1924, which is only known from the Burgess Shale (e.g., Topper et al., Reference Topper, Strotz, Holmer, Zhang, Tait and Caron2015). Both P. prospectensis and P. zenobia share a similar subcircular outline with a straight hinge line, although P. zenobia generally attains a larger size, reaching a maximum of 15 mm width and 14 mm length (Topper et al., Reference Topper, Strotz, Holmer, Zhang, Tait and Caron2015). The two species are also similar in the way they preserve the long marginal setae fringing the shell valve. Topper et al. (Reference Topper, Strotz, Holmer, Zhang, Tait and Caron2015) suggested that the sessile life strategy of P. zenobia might have included mimicry; the occurrence of P. prospectensis might suggest that this had already developed by Stage 4 (Liang et al., Reference Liang, Holmer, Hu and Zhang2020a). The poorly preserved open delthyrium and internal structures of the flattened material of P. prospectensis preclude further comparison. Other occurrences in the early Cambrian of Laurentia are difficult to compare in detail to P. prospectensis. Paterina sp. indet. from the Forteau Formation of southern Labrador and western Newfoundland, Canada has been kept under open nomenclature without formal description (Skovsted et al., Reference Skovsted, Knight, Balthasar and Boyce2017). The ventral valves of P. mediocris Poulsen, Reference Poulsen1932 from the Ella Island Formation, northeastern Greenland, share a similar overall morphology and general concentric fila with P. prospectensis, but the ventral valve of the latter is more convex and has a more oblique posterior margin (Skovsted and Holmer, Reference Skovsted and Holmer2005).
Paterina? suspiciosa Aksarina, Reference Aksarina1975 from the Parahio Formation, Tethyan Himalaya, shows concentric ornament typical for Paterina, but also retains a homeodeltidium, which is otherwise absent in other species of the genus characterized by an open delthyrium. Paterina sp. indet. from the same formation is more subrectangular in outline, but the lack of a ventral valve impedes further comparison (Popov et al., Reference Popov, Holmer, Hughes, Ghobadi Pour and Myrow2015). Paterina has also been reported from England, USA, France, and Spain (Termier and Termier, Reference Termier and Termier1974; Laurie, Reference Laurie1987, Reference Laurie and Kaesler2000; Liñán and Mergl, Reference Liñán and Mergl1982), however, the lack of internal musculature and vascular systems for the material of P. prospectensis prohibits further detailed comparison.
Genus Dictyonina Cooper, Reference Cooper1942
Type species
Trematis pannulus White, Reference White1874 from the lower to middle Cambrian Pioche Shale, Nevada, USA.
Dictyonina pannula (White, Reference White1874)
Figure 4.1–4.7
- Reference White1874
Trematis pannulus White, p. 6.
- Reference Walcott1912
Micromitra (Iphidella) pannula; Walcott, p. 361.
- Reference Cooper1942
Dictyonina pannula; Cooper, p. 228.
- Reference Mount1976
Dictyonina pannula; Mount, fig. 28.
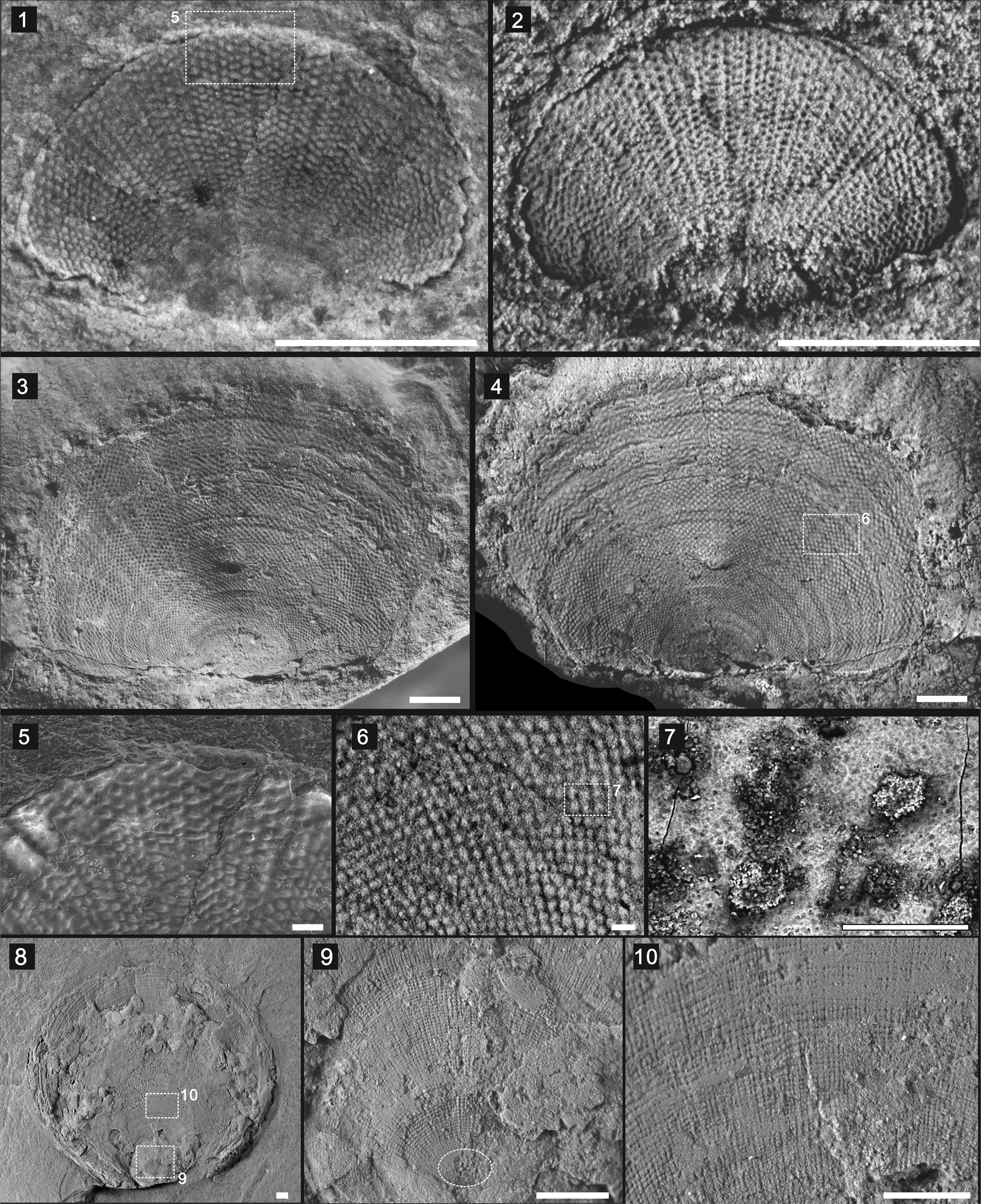
Figure 4. Dictyonina pannula (White, Reference White1874) and Mickwitzia occidens Walcott, Reference Walcott1908: (1–7) D. pannula: (1, 2) ventral valve (1) with boxed area of (5), and its latex cast (2) (UCR 7073/1); (3, 4) dorsal valve (3) and its latex cast (4) with boxed area of (6) (UCR 9925/9); (5) enlarged view of boxed area in (1) showing the pitted ornament; (6) enlarged view of boxed area in (4) showing the pitted ornament and concentric growth lines, with boxed area of (7); (7) SEM image of boxed area in (6) showing the pitted ornament; (8–10) Mickwitzia occidens (UCR 10/8/1): (8) dorsal valve with boxed areas of (9 and 10); (9) enlarged view of boxed area in (8) showing reticulate-pustulose ornamentation and smooth metamorphic shell indicated by dashed oval; (10) enlarged view of boxed area in (8) showing the reticulate-pustulose ornamentation. Scale bars = 1 mm (1–4, 8–10); 100 μm (5–7).
Holotype
A dorsal valve (USNM 15331a), lower to middle Cambrian Pioche Shale, Nevada, USA (Rowell, Reference Rowell1980).
Description
Shell semicircular to rounded rectangular, unequally biconvex, slightly flattened or compressed, but somewhat profiled laterally (Fig. 4.1–4.4). Ventral valve ovate to subquadrate, small, of 1.2 mm length, 1.9 mm width (Fig. 4.1, 4.2). Umbo bearing a prominent metamorphic shell, ~600 μm in diameter (Fig. 4.1, 4.2). Dorsal valve gently convex at umbo, flattened laterally and anteriorly, with nearly straight posterior margin (Fig. 4.3, 4.4). Dorsal valve relatively large, of 5.56 mm length, 7.75 mm width (Fig. 4.3, 4.4). Ornament of fine radiating rows of subhexagonal pits arising near umbo, increasing in size moderately by intercalation anteriorly; 8–10 concentric growth bands recognizable, alternatingly widening toward marginal edge (Fig. 4.3, 4.4). Diameter of pits 20–50 μm (Fig. 4.5–4.7). Ventral and dorsal interior not observed.
Materials
One ventral (UCR 7073/1) and one dorsal valve (UCR 9925/9) recovered from the Cadiz Formation.
Remarks
Dictyonina pannula is the type species of the genus. The holotype is a poorly preserved dorsal valve (USNM 15331a) that retains a small part of the original shell typified by the characteristic pitted ornament. The precise stratigraphic level from which the holotype came is unknown. It was collected in the Pioche District and previous studies show that only one species of Dictyonina occurs in the lower and middle Cambrian rocks of that area (Rowell, Reference Rowell1980).
Species of the Cambrian paterinate brachiopod Dictyonina from the lower to upper Cambrian are characterized by fine radiating rows of subhexagonal pits increasing in size distally (Laurie, Reference Laurie and Kaesler2000). This pitted ornament also represents a significant character in the younger, related genus Dictyonites from the Lower–Upper Ordovician, but Dictyonites has a more deeply pitted and perforated shell and pits increasing significantly in size distally (Laurie, Reference Laurie and Kaesler2000). The oldest known mickwitziid brachiopod Kerberellus marcouensis Devaere, Holmer, and Clausen in Devaere et al., Reference Devaere, Holmer, Clausen and Vachard2015 was previously described as Dictyonina? sp. indet. due to its ornamentation with radiating rows of subhexagonal pits. However, the latest revision of the problematic Kerberellus marcouensis suggested that the two species only share superficial similarities; Kerberellus marcouensis is characterized by large, radially ovoid, hourglass-shaped extensions that are interpreted as tubes (canals) running through a thick shell, the most significant character of the mickwitziid brachiopods, whereas the fine radiating rows in Dictyonina correspond to subhexagonal pits in the organophosphatic shell (Devaere et al., Reference Devaere, Holmer, Clausen and Vachard2015).
Dictyonina hexagona (Bell, Reference Bell1941) from the middle Cambrian of Montana, has hexagonal external pits, but these are much finer and the ventral valve has a more prominent umbo extending well behind the hinge line of the valves. Specimens of D. hexagona illustrated by Koneva (Reference Koneva1986) from the middle Cambrian of southern Kazakhstan have a less-prominent ventral umbo and coarser pitted ornament than the American material and are morphologically closer to D. pannula. Dictyonina australis Roberts and Jell, Reference Roberts and Jell1990 from the Coonigan Formation, western New South Wales resembles D. pannula but has a less-defined umbo, coarser diamond-shaped pits, and prominent radial ribs (Roberts and Jell, Reference Roberts and Jell1990).
The pitted ornament of Dictyonina pannula is shallow and consequently is readily affected by abrasion or diagenetic effects. Wright (Reference Wright1981) discussed the development of pits in Dictyonina, noting an increase in breadth and a reduction of definition with age. The formation and function of the coarsely pitted ornamentation in Ordovician linguliform brachiopods has been extensively discussed by Holmer et al. (Reference Holmer, Popov, Ghobadi Pour, Zhang and Zhang2017), however, those for Cambrian paterinides still remains poorly understood.
Stem group Brachiopoda
‘Mickwitziids’ sensu Holmer and Popov, Reference Holmer, Popov, Williams, Brunton and Carlson2007
(including Mickwitziidae Gorjansky, Reference Gorjansky1969)
Genus Mickwitzia Schmidt, Reference Schmidt1888
Type species
Lingula? monilifera Linnarsson, Reference Linnarsson1869 from the lower Cambrian (Series 2, Stage 4) Mickwitzia Sandstone Member of the File Haidar Formation near Lugnås, Västergötland (Sweden).
Mickwitzia occidens Walcott, Reference Walcott1908
Figures 4.8–4.10, 7.1
- Reference Walcott1908
Mickwitzia occidens Walcott, p. 54, pl. 7, fig. 1.
- Reference Walcott1912
Mickwitzia occidens; Walcott, p. 331, pl. 6, fig. 4.
- Reference Mount1976
Mickwitzia occidens; Mount, fig. 3.
- Reference Rowell1977
Mickwitzia occidens; Rowell, p. 79, pl. 1, fig. 12.
- Reference Mount1980
Mickwitzia occidens; Mount, fig. 3.
- ?Reference McMenamin1992
Mickwitzia muralensis Walcott, Reference Walcott1913; McMenamin, p. 181, figs. 4.1, 5.4, 5.6.
- non Reference Holmer, Skovsted and Williams2002
Mickwitzia cf. Mickwitzia occidens; Holmer et al., text-figs. 2, 3.
- Reference Skovsted and Holmer2003
Mickwitzia occidens; Skovsted and Holmer, fig. 2.
- non Reference Skovsted and Holmer2003
Mickwitzia cf. Mickwitzia occidens; Skovsted and Holmer, p. 3, figs. 3–5, 7–12.
- non Reference Skovsted and Holmer2005
Mickwitzia cf. Mickwitzia occidens; Skovsted and Holmer, p. 327, pl. 1, figs. 9–13.
- Reference Holmer, Popov, Williams, Brunton and Carlson2007
Mickwitzia occidens; Holmer and Popov, fig. 1711d–i.
- non Reference Holmer, Popov, Williams, Brunton and Carlson2007
Mickwitzia sp. cf. Mickwitzia occidens; Holmer and Popov, figs. 1712, 1713.
- Reference English and Babcock2010
Mickwitzia occidens; English and Babcock, fig. 4a, b.
- Reference Hollingsworth and Babcock2011
Mickwitzia occidens; Hollingsworth and Babcock, fig. 5.6, 5.7.
- Reference Butler, Streng, Holmer and Babcock2015
Mickwitzia occidens; Butler et al., figs. 3–13.
- Reference Liang, Holmer, Hu and Zhang2020a
Mickwitzia occidens; Liang et al., fig. 1c, d, g.
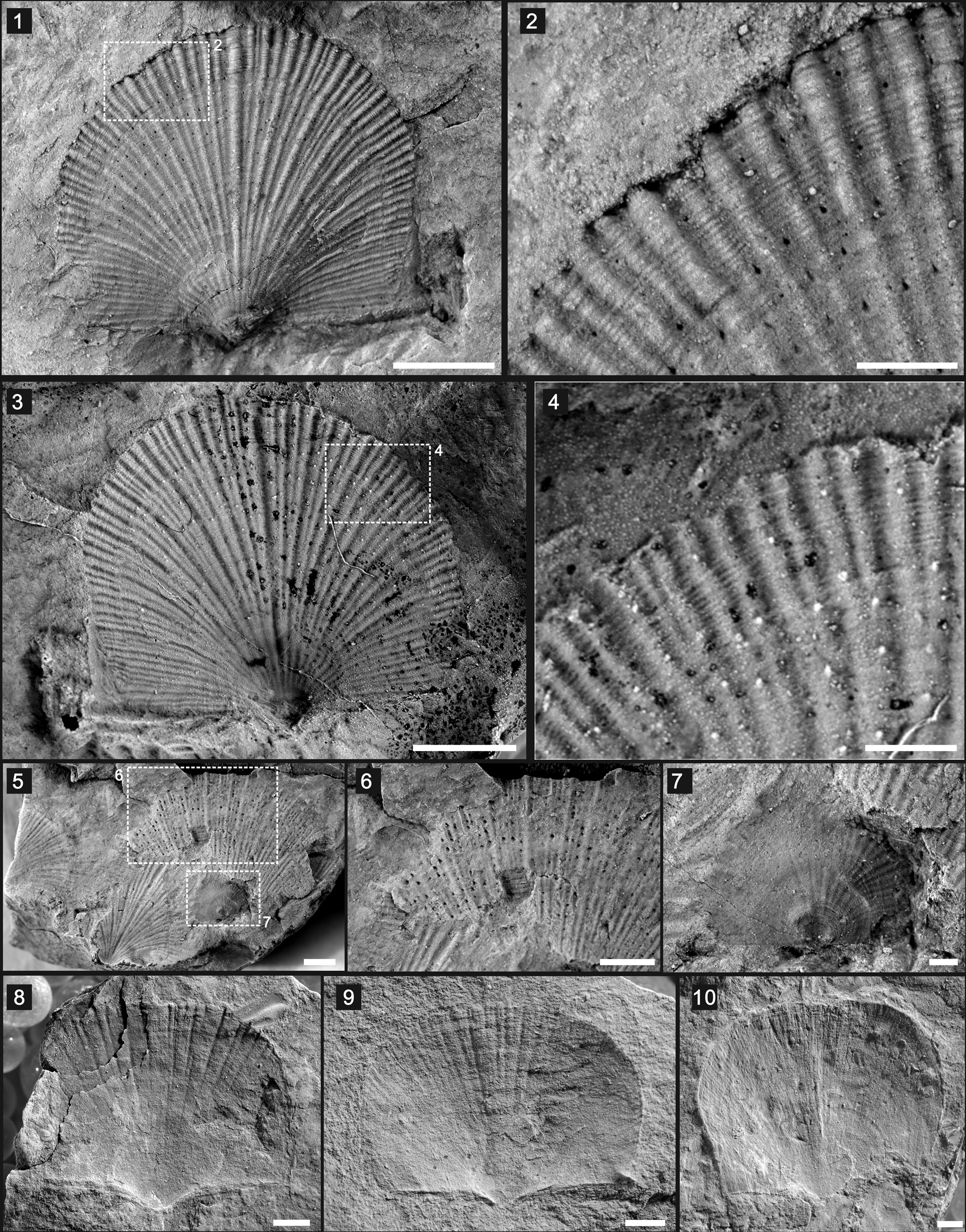

Figure 5. Nisusia fulleri Mount, Reference Mount1981 and Wimanella highlandensis (Walcott, Reference Walcott1886): (1–4) N. fulleri (UCR 10/2031): (1) dorsal valve exterior, with boxed area of (2); (2) enlarged view of boxed area in (1) showing thick constellate ornament and hollow spines on the anterior of the shell; (3) latex cast of the specimen in (1), with boxed area of (4); (4) enlarged view of boxed area in (3) showing the thick constellate ornament; (5–7) N. fulleri (UCR 10/2023): (5) an aggregation of individuals, with boxed areas of (6 and 7); (6) enlarged view of boxed area in (5) showing thick constellate ornament and hollow spines; (7) enlarged view of boxed area in (5), showing larval individual of N. fulleri; (8–10) Wimanella highlandensis, ventral valves (UCR 10/2019B, 7307-13, 7307/5, respectively). Scale bars = 2 mm (1, 3, 5, 6, 8–10); 500 μm (2, 4, 7).
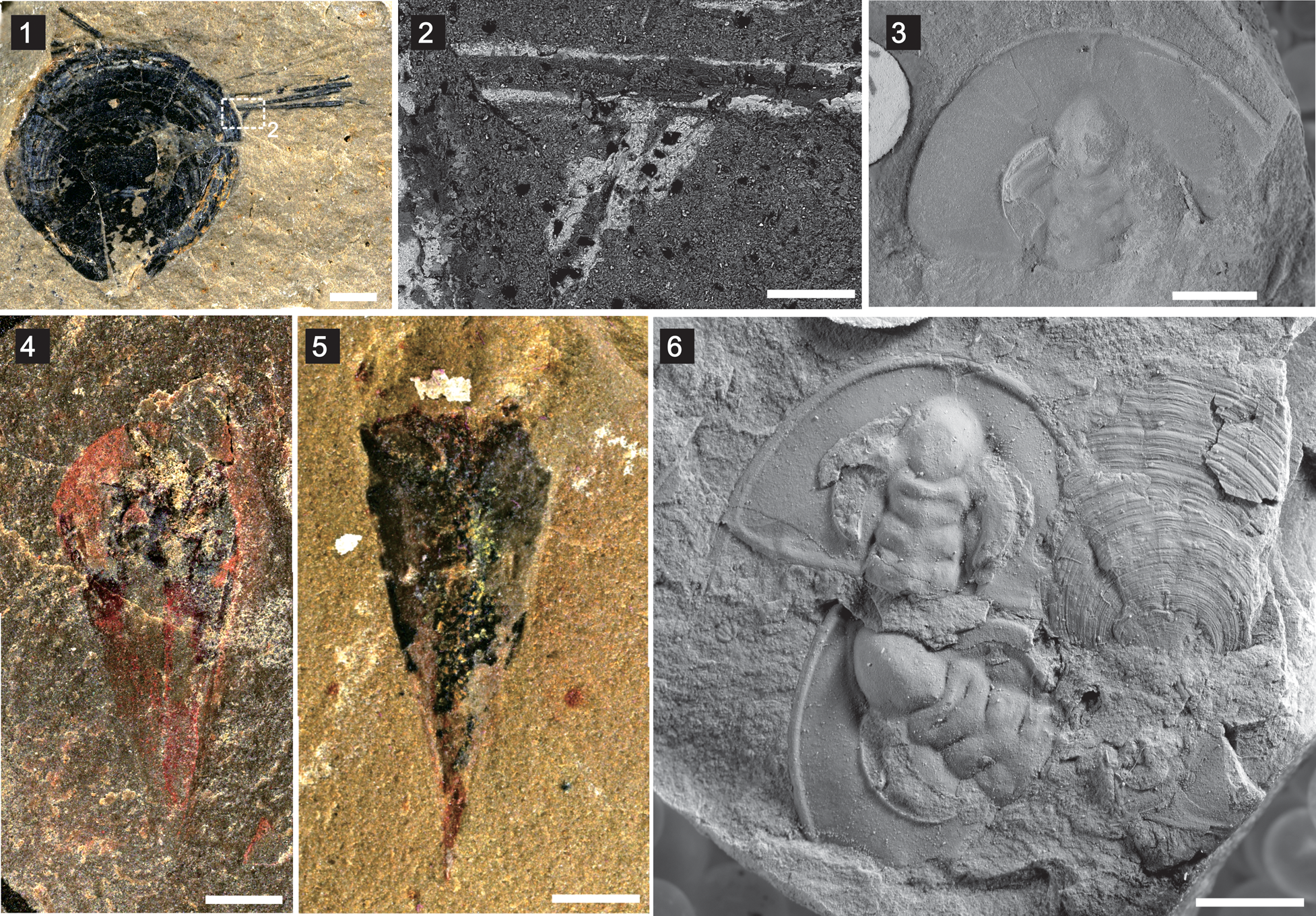
Figure 6. Other taxa from the Latham Shale: (1) brachiopod individual with possible Sphenothallus attached on the anterolateral part of the shell (UCR 7002/301), with boxed area of (2); (2) enlarged backscattered SEM image of boxed area in (1); (3) Olenellus nevadensis (Walcott, Reference Walcott1910) (UCR 10/3239); (4, 5) Hyolithes whitei Resser, Reference Resser1938 (UCR 10/2340, 10125/12, respectively); (6) Olenellus nevadensis (Walcott, Reference Walcott1910) and Paterina prospectensis (Walcott, Reference Walcott1884) (UCR 10). Scale bars = 2 mm (1, 3–6); 200 μm (2).
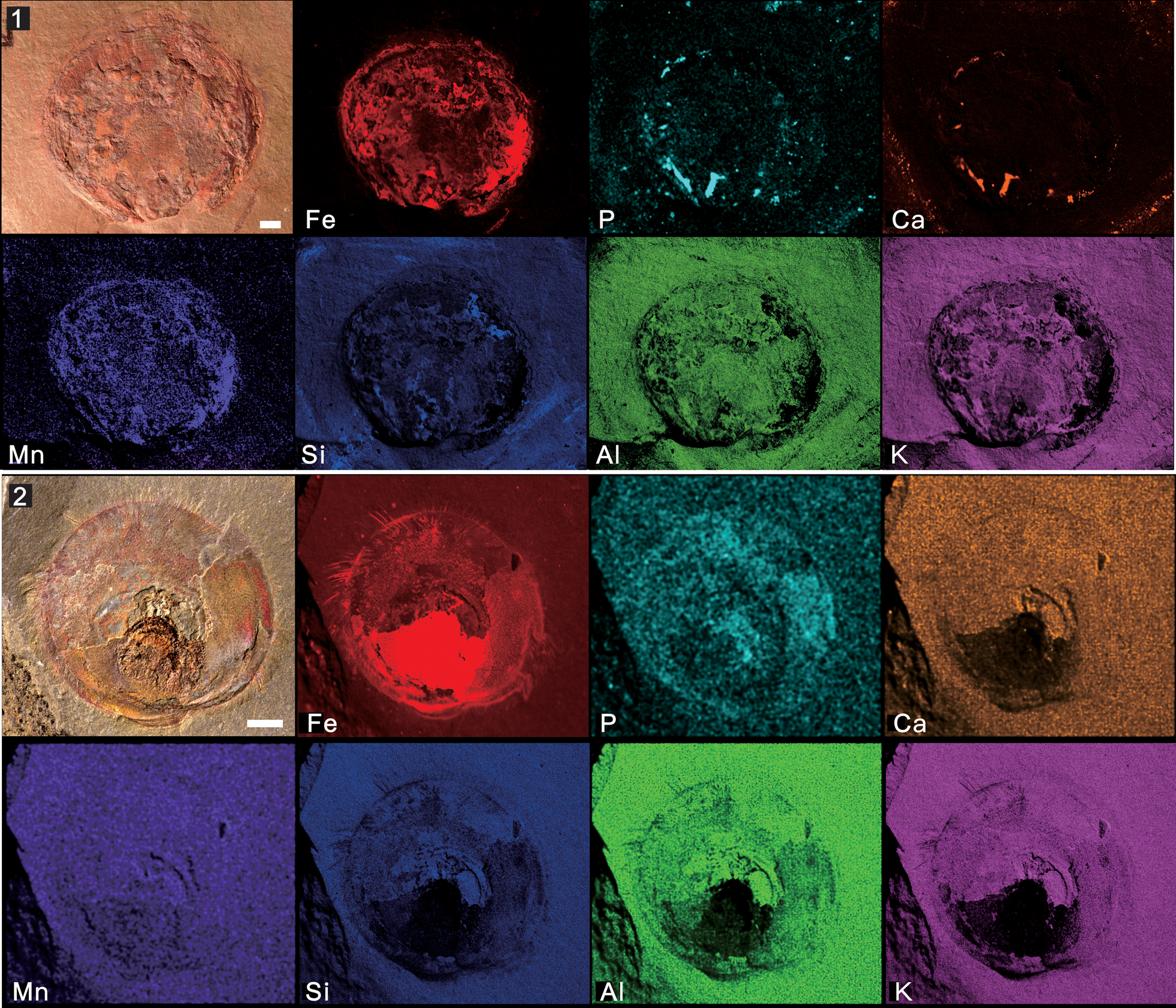
Figure 7. Micro X-ray florescence maps, showing elemental abundances of iron, phosphorus, calcium, manganese, silicon, aluminum, and potassium: (1) Mickwitzia occidens Walcott, Reference Walcott1908 from the Latham Shale (UCR 10/8/1, the same specimen displayed in Fig. 4.8); (2) Heliomedusa orienta Sun and Hou, Reference Sun and Hou1987 from the Chengjiang Lagerstätte (ELI SJZ 2322). Scale bars = 2 mm.
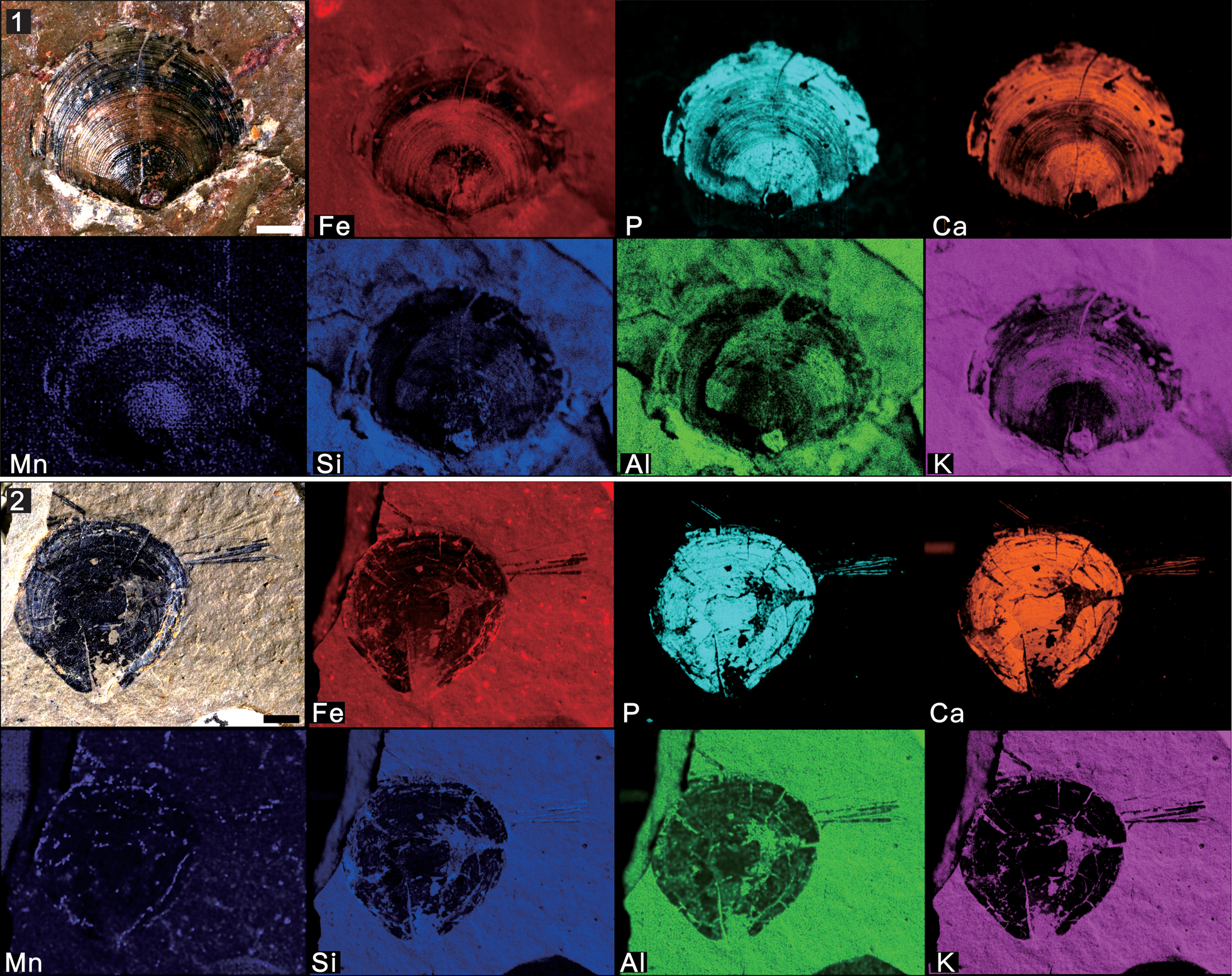
Figure 8. Micro X-ray florescence maps, showing elemental abundances as in (7): (1) Paterina prospectensis (Walcott, Reference Walcott1884) (UCR 10/2006, the same specimen displayed in Fig. 3.3); (2) brachiopod individual with possible Sphenothallus attached (UCR 7002/301, the same specimen displayed in Fig. 6.1). Scale bars = 2 mm.
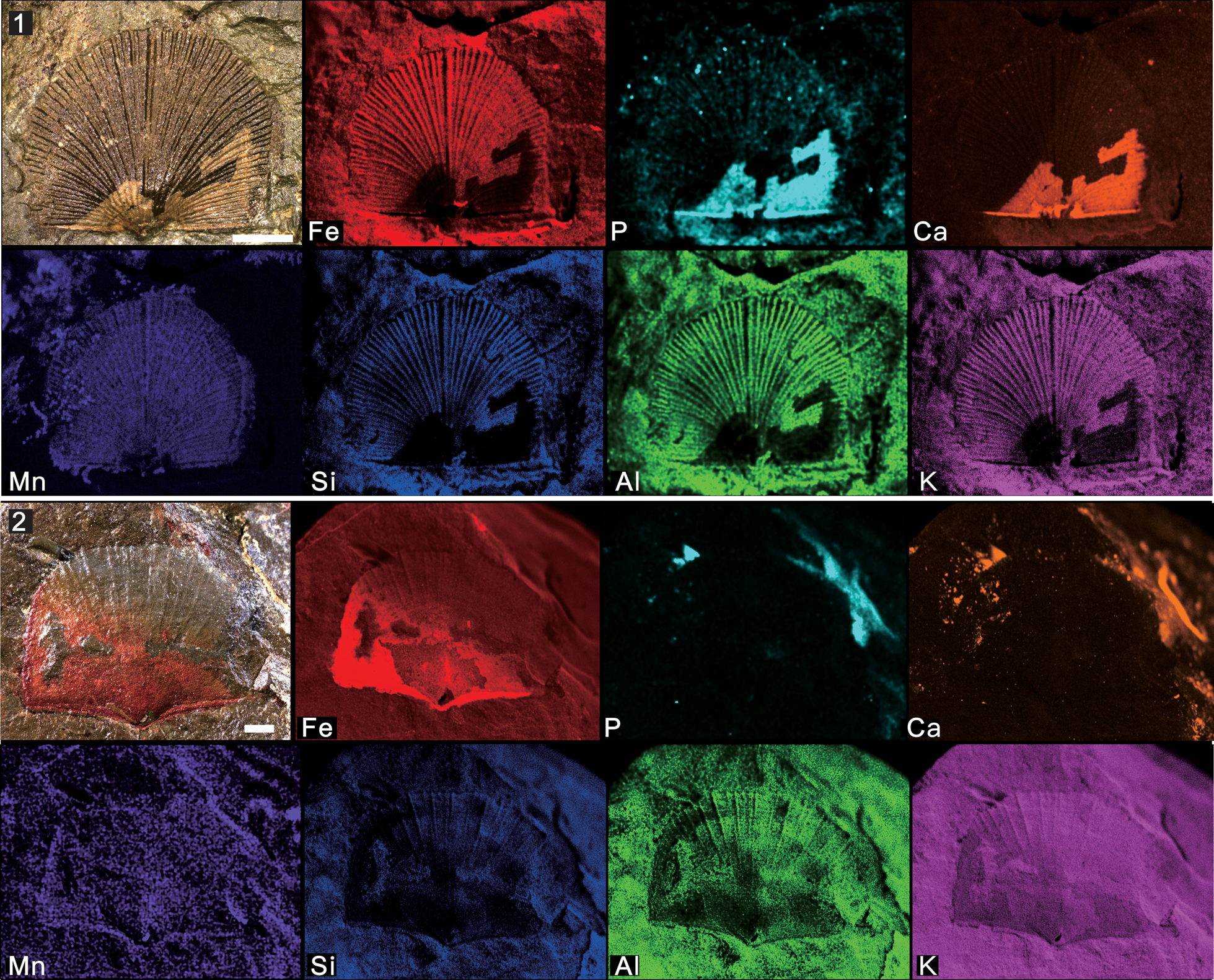
Figure 9. Micro X-ray florescence maps, showing elemental abundances as in (7): (1) Nisusia fulleri Mount, Reference Mount1981 from the Latham Shale (UCR 10/2031, the same specimen displayed in Fig. 5.1); (2) Wimanella highlandensis (Walcott, Reference Walcott1886) from the Cadiz Formation (UCR 10/2019A). Scale bars = 2 mm.
Holotype
An exfoliated valve (USNM 51518a), lower Cambrian (= Series 2), Silver Peak quadrangle, Esmeralda County, Nevada, U. S. Geological Survey locality 174c (Walcott, Reference Walcott1908, pl. 7, fig. 1; reillustrated by Rowell, Reference Rowell1977, pl. 1, fig. 12). According to Rowell (Reference Rowell1977) and Mount (Reference Mount1980), the holotype was collected from the Harkless Formation in the lower part of the Bonnia-Olenellus Zone.
Description
Outline of dorsal valve ovoid with apex at posterior margin (Fig. 4.8), more or less flat in lateral profile as other shale-hosted specimens. Size large, of 23 mm length, 26 mm width. Reticulate-pustulose ornament, typical of all known species of Mickwitzia, well defined (Fig. 4.9, 4.10). Concentric growth lines and radial costellae radiating from apex at posterior margin, with ~16 fila and 20 costellae per mm (Fig. 4.9, 4.10). Smooth metamorphic shell, ~500 μm in diameter, in posterior part of dorsal valve (Fig. 4.9).
Material
One dorsal valve (UCR 10/8/1) recovered from the Latham Shale.
Remarks
Mickwitzia remains an enigmatic taxon. Although it has an overall brachiopod-like appearance with two bilaterally symmetrical valves, it exhibits no character diagnostic for any know group of brachiopods, making it a hotly debated topic for nearly a century. Although Mickwitzia is neither new to paleontology nor rare in the lower Cambrian strata (e.g., Schmidt, Reference Schmidt1888; Walcott, Reference Walcott1912; Rowell, Reference Rowell1977; McMenamin, Reference McMenamin1986; Nemliher, Reference Nemliher2001; Balthasar, Reference Balthasar2004; Skovsted et al., Reference Skovsted, Brock, Holmer and Paterson2009; Butler et al., Reference Butler, Streng, Holmer and Babcock2015; Liang et al., Reference Liang, Holmer, Hu and Zhang2020a, Reference Liang, Holmer, Skovsted, Duan and Zhangb), its phylogenetic position has never been satisfactorily resolved. Holmer and Popov (Reference Holmer, Popov, Williams, Brunton and Carlson2007) included Mickwitzia and Heliomedusa Sun and Hou, Reference Sun and Hou1987 within the informal grouping of mickwitziid-like stem-group brachiopods. The taxonomic composition and phylogenetic position of this informal grouping need to be further investigated.
Detailed research in last two decades has greatly enhanced our understanding of mickwitziids. Balthasar (Reference Balthasar2004) suggested a close relationship between Mickwitzia muralensis (Mural Formation, Canada) and paterinids due to similarities in their stratiform shell microstructure, parvicostellate ornament, and posterior margin of juvenile and early-mature shells. Skovsted et al. (Reference Skovsted, Brock, Holmer and Paterson2009) reported an unnamed new species of Mickwitzia from Australia; the morphology of the dorsal valve apex and the extended cones on the internal surface indicate a close affinity with Mickwitzia muralensis from the lower Cambrian of British Columbia, and extend the known range of the pivotal stem group brachiopod Mickwitzia to East Gondwana. Butler et al. (Reference Butler, Streng, Holmer and Babcock2015) described Mickwitzia occidens from the Indian Springs Lagerstätte (Cambrian Stage 3), Nevada and suggested that the inwardly pointing cones are not consistent with the setal-bearing structure as previously thought. Furthermore, the presence of acrotretid-like shell structures and shell-penetrating setae in Mickwitzia occidens strengthen the previously proposed close relationship between stem-group brachiopods and tommotiids. Liang et al., (Reference Liang, Holmer, Skovsted, Duan and Zhang2020b) restudied Heliomedusa orienta from the Chengjiang Konservat-Lagerstätte and indicated its reticulate-pustulose ornament, tubular structure, and its marginal mantle setae and shell penetrative setae closely related to the type species Mickwitzia monilifera.
The specimen of Mickwitzia occidens collected from the Latham Shale is remarkably similar to specimens of Heliomedusa orienta from the Chengjiang Lagerstätte in size, morphology, preservation of setae, and the reticulate-pustulose ornament. Besides, the preservation mode also bears some overall similarities to the Chengjiang-type preservation in weathering and replication of the shell and soft parts as iron oxides. The occurrence of Heliomedusa-like Mickwitzia in the Latham Shale represents an important stratigraphic extension of this taxon in North America, making it reasonable to suggest that the FAD of mickwitziids in Laurentia and Gondwana could be diachronous (Liang et al., Reference Liang, Holmer, Hu and Zhang2020a). Although it is possible that Mickwitzia is a senior synonym of Heliomedusa, there remain difficulties in making detailed taxonomic comparisons between shale-hosted and three-dimensional material, and more material preserved in the Latham Shale is needed to test this hypothesis.
Subphylum Rhynchonelliformea Williams et al., Reference Williams, Carlson, Brunton, Holmer and Popov1996
Class Kutorginata Williams et al., Reference Williams, Carlson, Brunton, Holmer and Popov1996
Order Kutorginida Kuhn, Reference Kuhn1949
Superfamily Nisusioidea Walcott and Schuchert in Walcott, Reference Walcott1908
Family Nisusiidae Walcott and Schuchert in Walcott, Reference Walcott1908
Genus Nisusia Walcott, Reference Walcott1905
Type species
Orthisina festinata Billings, Reference Billings1861, from unnamed Cambrian Stage 4 (Bonnia–Olenellus Zone) of USA and Canada.
Nisusia fulleri Mount, Reference Mount1981
Figures 5.1–5.7, 9.1
- Reference Mount1980
Nisusia fulleri; Mount, fig. 4.
- Reference Mount1981
Nisusia fulleri Mount, figs. 1, 2.
Holotype
A dorsal valve (UCR 10/2031), Latham Shale of California, USA (Mount, Reference Mount1981).
Description
Shell transversely semioval in outline (Fig. 5.1–5.7), of 2.68–7.04 mm length, 3.82–7.59 mm width. Hinge line shorter than maximum width at midlength. Cardinal extremities slightly acute to almost rectangular; anterior commissure rectimarginate (Fig. 5.1, 5.3). Dorsal valve moderately and evenly convex, slightly carinate, with maximum convexity at posterior part; lateral slopes planar to gently concave. Umbo small, gently incurved (Fig. 5.1, 5.3). Thick costellae ornamenting shell surface, with median costellae most thickened; number of costellae increasing by intercalation and separated by narrow interspaces; hollow spines distributed in interspaces, ~60 μm in diameter, separated by 300 μm (Fig. 5.1–5.4), presenting on some broken shells (Fig. 5.5, 5.6). Cross striation on radial costellae, more prominent at distal 14% shell length where costellae become thicker. In total, ~12 ribs per 3 mm along anterior margin of mature individual. Dorsal interior not observed.
Materials
Two slabs (UCR 10/2031 and 10/2023) of specimens, including at least five valves, recovered from the Latham Shale.
Remarks
Nisusia has most commonly been regarded as a poorly defined ‘waste basket’ taxon, due to the fact that the morphology of many species described in the first half of the previous century are inadequately known. However, Holmer et al., (Reference Holmer, Kebria-ee Zadeh, Popov, Ghobadi Pour, Álvaro, Hairapetian and Zhang2019) recently reviewed the phylogeny and distribution of nisusioid brachiopods and restricted Nisusia to species provided with radiating costellae bearing hollow spines. Holmer et al. (Reference Holmer, Kebria-ee Zadeh, Popov, Ghobadi Pour, Álvaro, Hairapetian and Zhang2019) also suggested that most of the taxa (mainly from Laurentia) from the lower Cambrian (unnamed stages 3–4) that have been assigned to Nisusia, belong neither to Nisusia nor to Nisusioidea, and presently only 19 taxa, plus one described under open nomenclature, can be assigned to Nisusia with some degree of confidence, whereas the generic affinities of five more species require further study.
Nisusia fulleri from the Latham Shale was excluded from the genus due to insufficient description and illustrations, and was considered to be a nomen dubium (Holmer et al., Reference Holmer, Kebria-ee Zadeh, Popov, Ghobadi Pour, Álvaro, Hairapetian and Zhang2019). The new information on N. fulleri provided here substantiates the presence of thick costellae and hollow spines (Fig. 5.1–5.6), thus making it reasonable to bring the species back to the Nisusia group.
To date, four of the five nisusiid species documented from the unnamed Cambrian Series 2, including Eoconcha austini Cooper, Reference Cooper1951, Nisusia festinata (Billings, Reference Billings1861), Nisusia ancauchensis Benedetto and Foglia, Reference Benedetto and Foglia2012, and Nisusia fulleri described herein, are from Laurentia, suggesting that this continent was probably the major center of early Cambrian nisusiid dispersal (Holmer et al., Reference Holmer, Kebria-ee Zadeh, Popov, Ghobadi Pour, Álvaro, Hairapetian and Zhang2019). Nisusia fulleri is closely similar to the type species N. festinata, with the latter being spinocostellate and appears to have costellae of more even size and a narrower, deeper sulcus. Shell valves of N. ancauchensis, from olistolith (unnamed Cambrian Stage 4, Bonnia–Olenellus Zone), Quebrada Ancaucha, Argentina, is more convex and is ornamented with wider costellae (Benedetto and Foglia, Reference Benedetto and Foglia2012).
Class Rhynchonellata Williams et al., Reference Williams, Carlson, Brunton, Holmer and Popov1996
Order Orthida Schuchert and Cooper, Reference Schuchert and Cooper1932
Suborder Orthidina Schuchert and Cooper, Reference Schuchert and Cooper1932
Superfamily Orthoidea Woodward, Reference Woodward1852
Family Bohemiellidae Havlíček, Reference Havlíček1977
Genus Wimanella Walcott, Reference Walcott1908
Type species
Wimanella simplex Walcott, Reference Walcott1908 from the lower Cambrian of eastern British Columbia, Canada.
Wimanella highlandensis (Walcott, Reference Walcott1886)
Figures 5.8–5.10, 9.2
- Reference Walcott1886
Orthis? highlandensis Walcott, p. 119, pl. 8, fig. 3, 3a, 3b.
- Reference Walcott1905
Billingsella highlandensis; Walcott, p. 237.
- Reference Schuchert and Cooper1932
Wimanella highlandensis; Schuchert and Cooper, p. 50.
- Reference Mount1981
Nisusia fulleri; Mount, fig. 2.
Holotype
One valve (USNM 15355c), eastern side of anticline near Pioche, Nevada (Mount, Reference Mount1974a, who did not characterize it as dorsal or ventral).
Description
Shell subrectangular to trapezoidal in outline, ~16.37 ± 2.10 mm in width, with length/width ratio of 0.77 (N = 3) (Fig. 5.8–5.10). Rectangular to gently obtuse cardinal extremities; maximum width at midlength or slightly anterior to hinge line. Ventral valve moderately and evenly convex with broad shallow sulcus. Shell surface marked by prominent radial ribs and weak concentric growth lines. Radial ribs originating at 1/5–1/7 valve length from posterior margin, widening gradually to margin with increment; total number of ribs 40–140; new ribs appearing by intercalation and separated by interspaces. Ribbing impressed on internal molds. Cardinal area of ventral valve unknown except that its plane extends backward at angle of ~10° or 15° to plane of shell margin.
Materials
Three ventral valves (UCR 10/2019B, 7307-13, and 7307/5) recovered from the Cadiz Formation.
Remarks
Species of Wimanella are characterized by their smooth nonplicate shells (that Walcott previously referred to Billingsella Hall and Clarke, Reference Hall and Clarke1892). Wimanella is known from several lower to middle Cambrian areas, including North America, Australia, Siberia, and eastern China (e.g., Mount, Reference Mount1974b; Roberts and Jell, Reference Roberts and Jell1990; Benedetto and Foglia, Reference Benedetto and Foglia2012). The species from the Cadiz Formation was previously regarded as Nisusia fulleri by Mount (Reference Mount1981), however, they differ significantly in that W. highlandensis is more trapezoidal in outline, and N. fulleri has thicker striae and a more elevated umbo. Wimanella tricavata Roberts and Jell, Reference Roberts and Jell1990 from the middle Cambrian Coonigan Formation of New South Wales can be differentiated by its subequally biconvex shell profile, slightly auriculate outline, shallow dorsal sulcus, and indistinct cardinal process (Roberts and Jell, Reference Roberts and Jell1990). Wimanella mollensis Benedetto and Foglia, Reference Benedetto and Foglia2012 from the middle Cambrian La Laja Formation of the Precordilleran Terrane can be differentiated by its deeper dorsal sulcus and less-developed radial striae (Benedetto and Foglia, Reference Benedetto and Foglia2012).
Discussion and implication
Biostratigraphic correlation
Hazzard (Reference Hazzard1954) and Stewart (Reference Stewart1970) have described the lower Cambrian sections in the studied area, and divided the lower Cambrian into five formations (Fig. 1.3). Trilobites from the Latham Shale indicate that it lies within the Bonnia-Olenellus Zone (Vaccari, Reference Vaccari1988), which is approximately equivalent to the unnamed Stage 4 of the Cambrian Series 2. Only approximately the lower tenth of the Cadiz Formation is early Cambrian in age, whereas the major part belongs to the middle Cambrian and biozonation still needs further biostratigraphical study (Mount, Reference Mount1980; Waggoner and Collins, Reference Waggoner and Collins1995).
Other parts of Laurentia
The Pioche Shale in Nevada spans the early-middle Cambrian boundary (e.g., Merriam, Reference Merriam1964; Rowell, Reference Rowell1980; Lieberman, Reference Lieberman2003) (Fig. 1.3). This boundary is defined by the extinction of olenelloid trilobites (Palmer, Reference Palmer1998). Besides, the shift of δ13C and δ34S isotope values also indicates the significant climatic and paleoceanographic changes around the early-middle Cambrian boundary (Montañez et al., Reference Montañez, Osleger, Banner, Mack and Musgrove2000; Hough et al., Reference Hough, Shields, Evins, Strauss, Henderson and Mackenzie2006). Moore and Lieberman (Reference Moore and Lieberman2009) made a comprehensive study of the arthropod faunal composition and preservation of the Pioche Shale, suggesting that the fauna in the C-Shale Member of the Pioche Shale is similar to the Latham Shale of the Marble Mountains of southern California. Moreover, among the abundant brachiopod taxa from the Pioche Shale, both Hadrotreta primaea and Dictyonina pannula, which are also found in the Cadiz Formation, range from the Bonnia-Olenellus Zone into the pre-Albertella beds of the middle Cambrian (Rowell, Reference Rowell1980). Thus, it could be suggested that the Latham Shale and Cadiz Formation witnessed the transition from the early to middle Cambrian, which are quite comparable to the successive Pioche Shale (the Latham Shale correlates with the early Cambrian part, whereas the Cadiz Formation correlates with the middle Cambrian part).
The fauna of the Latham Shale and Cadiz Formation also correlate with the Forteau Formation of southern Labrador and western Newfoundland, Canada (Skovsted et al., Reference Skovsted, Knight, Balthasar and Boyce2017). Both the Latham Shale and the Forteau Formation contain paterinids, kutorginids, and problematic mickwitziids (represented by Mickwitzia occidens from the Latham Shale and Setatella significans Skovsted et al., Reference Skovsted, Streng, Knight and Holmer2010 from the Forteau Formation). At the generic level, the Forteau Formation yields Hadrotreta, which is also represented in the Cadiz Formation, and this extends the range of Hadrotreta from the early Cambrian to the middle Cambrian. Olenellid trilobites recovered from the Forteau Formation indicate that it lies entirely within the Bonnia-Olenellus Zone (Knight, Reference Knight1991, Reference Knight2013; Knight et al., Reference Knight, Boyce, Skovsted and Balthasar2017).
South Australia
The fauna of the Latham Shale and Cadiz Formation is most comparable to that of the Coonigan Formation, western New South Wales (Roberts and Jell, Reference Roberts and Jell1990). Both faunas contain four brachiopod genera: Hadrotreta, Dictyonina, Nisusia, and Wimanella. Roberts and Jell (Reference Roberts and Jell1990) noted that the brachiopod fauna (at least at the generic level) from the Coonigan Formation can be correlated with the brachiopod fauna described by Rowell (Reference Rowell1980) from the early-middle Cambrian boundary beds of the Pioche Shale in central Nevada. The precise stratigraphic ranges of brachiopods from the Coonigan Formation are poorly constrained, and it is thus possible that they might have a long stratigraphic range not appropriate for detailed biostratigraphic correlation (Brock and Percival, Reference Brock and Percival2006). Percival and Kruse (Reference Percival and Kruse2016) suggested that the brachiopod fauna in the Coonigan Formation is of stage 4 to possible early stage 5 age, which could be correlated with the Latham Shale and Cadiz Formation.
Broad correlation between South Australia and Laurentia is also made possible by the occurrence of Mickwitzia in both regions. In the Arrowie Basin and on the Stuart Shelf, occurrences of Mickwitzia are restricted to the Dailyatia odyssei Biozone (Betts et al., Reference Betts, Paterson, Jago, Jacquet, Skovsted, Topper and Brock2017). Mickwitzia occidens occurs both in the Indian Springs Lagerstätte (the Poleta Formation) in Nevada, and in the Latham Shale in California, which is of Nevadella Biozone to Bonnia-Olenellus Zone in age (English and Babcock, Reference English and Babcock2010; Butler et al., Reference Butler, Streng, Holmer and Babcock2015). Mickwitzia muralensis occurs in the Mural Formation belonging to the Nevadella Zone with the boundary to the overlying Bonnia-Olenellus Zone (Balthasar, Reference Balthasar2004; Skovsted et al., Reference Skovsted, Balthasar, Vinther and Sperling2021). Thus, these occurrences support tentative correlation of the Nevadella to Bonnia-Olenellus zones in Laurentia with the Dailyatia odyssei Zone in South Australia. Recovery of better-preserved Mickwitzia specimens from South Australia and Laurentia would allow for accurate species identification and could permit more robust correlations in the future.
International correlation of the lower-middle Cambrian boundary interval (Series 2–3, Stage 4–5) is still under discussion, and more detailed biostratigraphic work and application of multiproxy methods will be required before confident international correlation can be attempted. The extent that brachiopods can contribute to international biostratigraphic correlation in the Cambrian boundary interval (Series 2–3, Stage 4–5) still needs to be tested.
Preservation
Although the brachiopod fauna is not as diverse as that from other Lagerstätten (e.g., the Chengjiang and Guanshan biota), the fauna of the Latham Shale and Cadiz Formation is unique in its different preservational bias (Figs. 7–10). Three modes of preservation can be documented.
The first type is the replication of iron oxide films presented in Mickwitzia occidens, which is remarkably similar to the overall preservation of its close relative Heliomedusa orienta from the Chengjiang Lagerstätte (Figs. 7, 10.1) (Liang et al., Reference Liang, Holmer, Hu and Zhang2020a, Reference Liang, Holmer, Skovsted, Duan and Zhangb). The shells from both South China and Laurentia are preserved by pyrite (with a reddish-brown color), which was later pseudomorphed by iron oxides (Gabbott et al., Reference Gabbott, Hou, Norry and Siveter2004). The lack of sulphur has been interpreted as resulting from subsequent alteration of pyrite from iron oxides (Gabbott et al., Reference Gabbott, Hou, Norry and Siveter2004). It is significant that calcium was not detected in these fossils (with presumed organophosphatic hard parts); a likely interpretation of this fact is that the alteration of pyrite to iron oxide released small quantities of sulfuric acid, which would have leached the calcium from carbonates and phosphates (Gabbott et al., Reference Gabbott, Hou, Norry and Siveter2004).
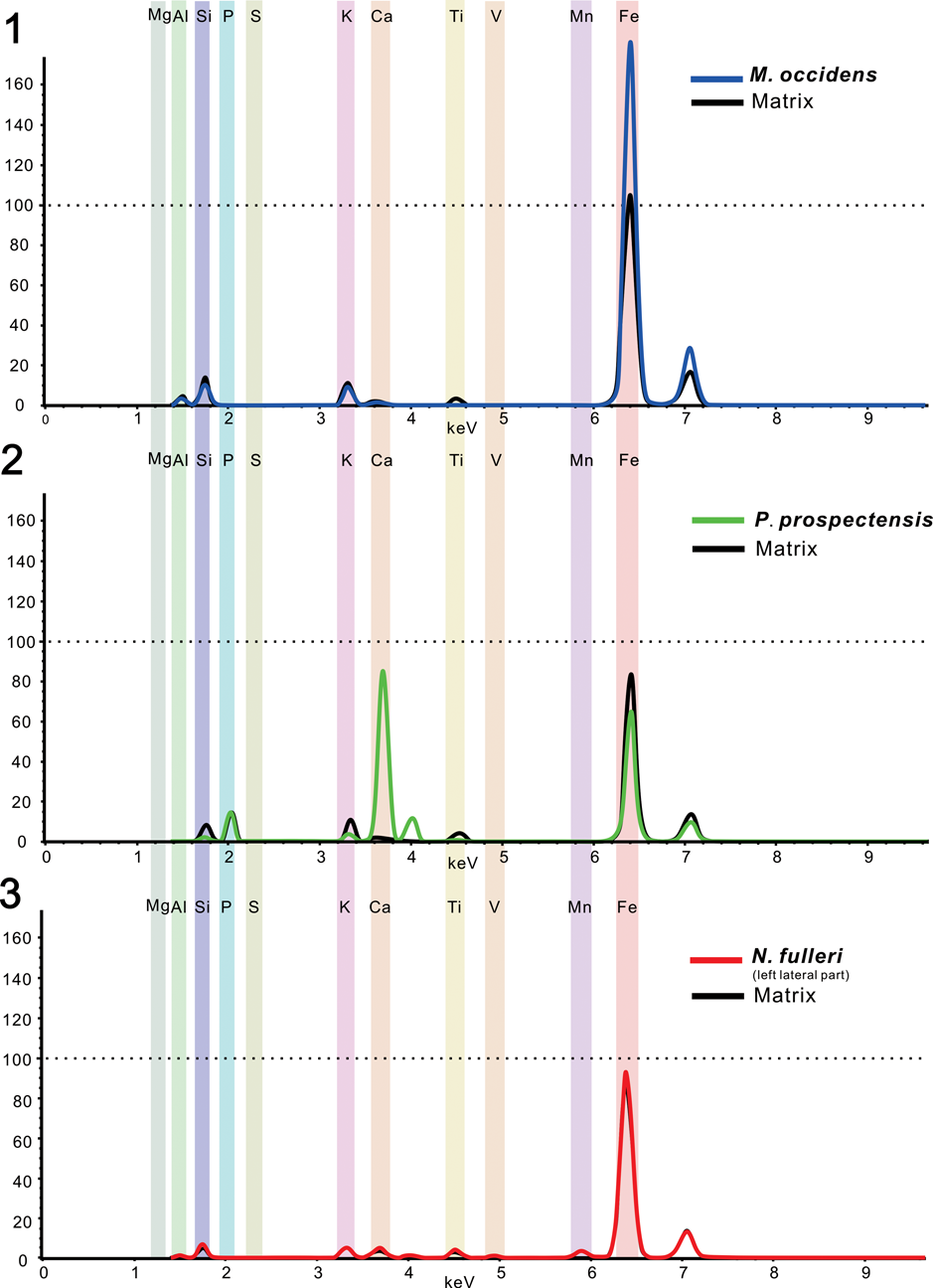
Figure 10. Mean μ-XRF spectra and main elemental contributions from specimens of: (1) Mickwitzia occidens Walcott, Reference Walcott1908 (UCR 10/8/1); (2) Paterina prospectensis (Walcott, Reference Walcott1884) (UCR 10/2006); (3) left lateral part of Nisusia fulleri Mount, Reference Mount1981 (UCR 10/2031).
The shells of linguliforms, including Paterina, Hadrotreta, and Dictyonina, not only exhibit well-defined shell ornament and nicely profiled valves, but also preserve their calcium phosphatic hard shells, distinguished by their dark color with high contrast to the gray-green, somewhat weathered, reddish shale (Figs. 8, 10.2). They were notably enriched in chemical components by calcium and phosphorus, with high elemental contrast to the matrix in both mapping results and elemental counting data. This is highly different from the preservation of the Chengjiang and Guanshan Lagerstätten, in which most phosphatic fossils are preserved by pyrite, and later replaced by iron oxides as mentioned above (Zhang et al., Reference Zhang, Strotz, Topper, Chen, Chen, Liang, Zhang, Skovsted and Brock2020a, Reference Zhang, Holmer, Liang, Chen and Duanb).
The carbonate-shelled rhynchonelliforms reveal an unusual preservation mode. Unlike the specimen of Mickwitzia occidens, iron is not concentrated on the shell, but has a relatively even distribution on both the fossil and the host rock (Figs. 9, 10.3). Furthermore, Nisusia fulleri displays a distinctive preservation in that the post-lateral part of the shell include calcium and phosphorus (Fig. 9.1), which remains problematic. One possible explanation is that this phosphorus could derive from the sedimentary environment during late diagenesis and result in secondary phosphatization. Nevertheless, another speculative interpretation is more challenging: both Cambrian rhynchonelliform and linguliform lineages included mineralization of calcium phosphate, followed by morphology differentiation and disparity. As the reconstruction of brachiopod phylogeny based on the study of their molecular/genetic rRNA characteristics demonstrates that the divergence between brachiopods with carbonate and phosphate shells occurred ~570 million years ago, in the Late Ediacaran (Cohen and Weydman, Reference Cohen and Weydmann2005), hence the two parallel lineages of brachiopod ancestors already existed by the beginning of the Cambrian. They lacked mineral skeletons, and one of the lineages quickly constructed external coverings from calcium phosphate and another from calcium carbonate (Ushatinskaya, Reference Ushatinskaya2008). The case of Nisusia fulleri is perhaps comparable to composition of the linguliform brachiopod Eoobolus Matthew, Reference Matthew1902 from the lower Cambrian Mural Formation—the original shell of Eoobolus contained microstructural small calcareous grains that were incorporated into organic-rich layers alongside apatite (Balthasar, Reference Balthasar2007)—and might also be reminiscent of Salanygolina obliqua Ushatinskaya, Reference Ushatinskaya1987 from the lower Cambrian of Mongolia, in which the laminar phosphatic secondary shell layer is composed of hexagonal prisms with organic sheaths representing calcite fibers (Holmer et al., Reference Holmer, Stolk, Skovsted, Balthasar and Popov2009). This seems to suggest that the mixed organophosphatic-calcareous shells were relatively common at that time. Although the shell composition of earliest brachiopods still remains uncertain, the information from both shale- and limestone-hosted material could give us clues for what to look for and how to look for it.
The systematic taphonomic bias for the Latham Shale and Cadiz Formation has significant implications for understanding the original faunal community assemblage, specifically in regard to shell composition of the early Cambrian articulate brachiopods. Accordingly, further stratigraphic sampling and mineralogical studies of the lower Cambrian section from the Latham Shale to the Cadiz Formation could yield additional useful information on the diagenetic relationship. This would also help determine the role of weathering on the preservation of these faunas and further clarify the degree of similarity to the preservation of the Chengjiang Biota, and hence the significance of global environmental changes on fossil preservation.
The transition from the Cambrian Evolutionary Fauna (CEF) to the Paleozoic Evolutionary Fauna (PEF)
The ‘Cambrian Explosion’ and the ‘Great Ordovician Biodiversification Event’ (GOBE) were the two most significant evolutionary events in the history of Paleozoic marine life. Based on multivariate statistical analyses, Sepkoski (e.g., Reference Sepkoski1981, Reference Sepkoski1991) defined three evolutionary faunas: a trilobite-dominated Cambrian Evolutionary Fauna (CEF), a brachiopod-dominated Paleozoic Evolutionary Fauna (PEF), and a mollusk-dominated Mesozoic-Cenozoic (or ‘Modern’) Evolutionary Fauna (MEF) (Fig. 11). The CEF is associated with (or is responsible for) the radiations of the early Cambrian Period and the diversity plateau of the middle–late Cambrian; the PEF is associated with the Ordovician radiations and the long Paleozoic equilibrium (Sepkoski, Reference Sepkoski1981). Although the PEF, represented mainly by the Ordovician biodiversification of families, grows in importance, it already presented a revolution of body plans during the Cambrian (Servais and Harper, Reference Servais and Harper2018; Harper et al., Reference Harper, Cascales-Miñana and Servais2019).
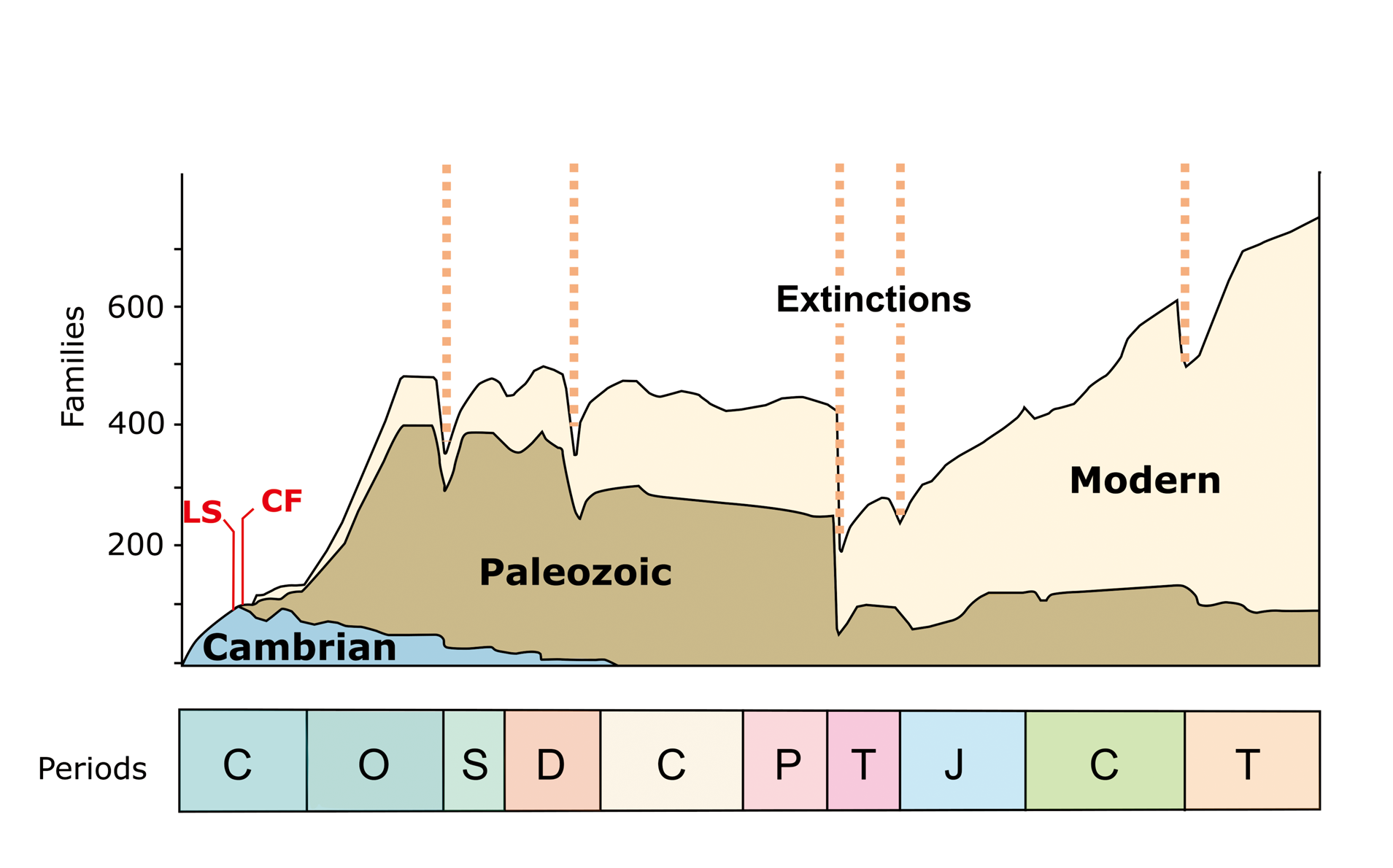
Figure 11. The classic Sepkoski diversity curve of marine invertebrate families through Phanerozoic time, documenting the Cambrian, Paleozoic, and Modern Evolutionary Faunas, and the ‘Big Five’ mass extinctions (dashed vertical lines) of marine invertebrates (modified from Sepkoski, Reference Sepkoski1981; Harper, Reference Harper2006). Solid red vertical lines represent the fauna of the Latham Shale (LS) and Cadiz Formation (CF). Geological periods (left to right): C = Cambrian; O = Ordovician; S = Silurian; D = Devonian; C = Carboniferous; P = Permian; T = Triassic; J = Jurassic; C = Cretaceous; T = Tertiary.
The brachiopod association in the Latham Shale is represented by Paterina prospectensis, Mickwitzia occidens, and Nisusia fulleri. Mickwitzia only occurred in the strata of the early Cambrian, and probably represents a stem-group brachiopod (Holmer and Popov, Reference Holmer, Popov, Williams, Brunton and Carlson2007; Butler et al., Reference Butler, Streng, Holmer and Babcock2015; Liang et al., Reference Liang, Holmer, Hu and Zhang2020a, Reference Liang, Holmer, Skovsted, Duan and Zhangb). Paterina has been of abiding interest since it was first separated taxonomically from the kutorginids (Beecher, Reference Beecher1891), and the group has already been recognized as among the oldest metazoans represented by biomineralized remains in the geological record (Williams et al., Reference Williams, Popov, Holmer and Cusack1998). Nisusia is one of the most common early–middle Cambrian rhynchonelliform brachiopods, with a stratigraphic range from the unnamed Cambrian Stage 3 to the Miaolingian (Drumian) (Holmer et al., Reference Holmer, Kebria-ee Zadeh, Popov, Ghobadi Pour, Álvaro, Hairapetian and Zhang2019). The abundant olenellid trilobites and hyolithids in this fauna (Fig. 6) (Mount, Reference Mount1980), together with brachiopod species commonly seen in early Cambrian time, comprise important components of the CEF, like the Chengjiang and Guanshan Lagerstätten, which were dominated by trilobites and nonarticulated brachiopods (Zhao et al., Reference Zhao, Zhu and Hu2010; Chen et al., Reference Chen, Zhang, Betts, Zhang and Liu2018, Reference Chen, Brock, Zhang, Laing, Ren and Zhang2021).
Three other species—Hadrotreta primaea, Dictyonina pannula, and Wimanella highlandensis—have been collected from the upper Cadiz Formation. Hadrotreta is a widespread taxon that achieved an almost cosmopolitan distribution at low latitudes during Miaolingian time (Popov et al., Reference Popov, Holmer, Hughes, Ghobadi Pour and Myrow2015). Dictyonina is a relatively common, cosmopolitan component in Drumian-Guzhangian linguliform faunas. The Orthida are one of the main components of the PEF (Zhan and Harper, Reference Zhan and Harper2006), and previous reports of Wimanella from the USA, Greenland, Australia, and Argentina are of middle Cambrian age (Bell, Reference Bell1941; Howell, Reference Howell1943; Roberts and Jell, Reference Roberts and Jell1990; Benedetto and Foglia, Reference Benedetto and Foglia2012). These three brachiopod species of middle Cambrian age indicate that this fauna likely presents the earliest onset of the PEF.
The organophosphatic linguliformeans had already radiated during the middle and late Cambrian and represented an integral part of the CEF. The acrotretides and the linguloids were significant components of the fauna and diversified during the middle and late Cambrian (Harper and Rong, Reference Harper and Rong2001). The Cambrian articulated rhynchonelliformean fauna since Epoch 2 and the Miaolingian boundary is generally of low diversity. The Kutorginida, including the families Kutorginidae and Nisusiidae, are the most abundant early Cambrian nonarticulated rhynchonelliformean brachiopods and became extinct at the end of the middle Cambrian. Generally, the typical Ordovician brachiopod fauna is taxonomically dominated by the articulated Orthida and Strophomenida (Harper et al., Reference Harper, Rong and Sheehan1999) that usually account for two-thirds of the total fauna. The occurrence of the transition from nonarticulated Kutorginida to articulated Orthida within these two brachiopod faunas possibly indicates the establishment of the more typical brachiopod components of the early PEF.
There remains some turnover in taxonomic composition within each of the evolutionary faunas during their periods of dominance, and transition from the CEF toward the PEF in one section could be somewhat difficult to correlate worldwide. The material from the Latham Shale and Cadiz Formation possibly provides evidence that the change of evolutionary faunas could be detected among brachiopods collected from one section. More material from the studied area would enable a comprehensive quantitative analysis of the transition between evolutionary faunas and related paleographic and paleoenvironmental implications.
Acknowledgments
The present research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 41720104002, 41890844, 41425008, and 41621003), by the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB26000000), and by 111 Project (D17013). The research of LEH is supported by the Swedish Research Council (VR project no. 2018-03390) and by a Zhongjian Yang Scholarship from the Department of Geology, Northwest University, Xi'an. YL sincerely acknowledges the China Scholarship Council (no. 202006970023) for one year of research as a visiting PhD student with LEH at Uppsala University. We thank N. Hughes and L. English (University of California, Riverside) for their kind permission and assistance with the loan of brachiopod specimens. Associate Editor C. Sproat and reviewers R. Freeman and C.B. Skovsted are greatly appreciated for their positive comments and insightful reviews.