Introduction
Worldwide, freshwater turtle populations are undergoing severe declines from habitat loss, collection, and additive mortality of adults (Gibbons et al., Reference Gibbons, Scott, Ryan, Buhlmann, Tuberville and Metts2000). In temperate North America extensive road networks cause excessive mortality of adult turtles and pose barriers for movement between wetlands and nesting areas (Steen et al., Reference Steen, Aresco, Beilke, Compton, Condon and Dodd2006). Large terrestrial forays by female turtles (Steen et al., Reference Steen, Gibbs, Buhlmann, Carr, Compton and Congdon2012) are important to locate appropriate nesting sites but expose them to an increased risk of mortality on roads (Haxton, Reference Haxton2000; Gibbs & Shriver, Reference Gibbs and Shriver2002; Steen et al., Reference Steen, Aresco, Beilke, Compton, Condon and Dodd2006). This mortality has demographic consequences including decreased population sizes and recruitment rates, and skewed sex ratios (Marchand & Litvaitis, Reference Marchand and Litvaitis2004a; Aresco, Reference Aresco2005). Unpaved roads and roadside shoulders may attract nesting female turtles (Steen et al., Reference Steen, Aresco, Beilke, Compton, Condon and Dodd2006) and these sites not only present a mortality risk, they may also reduce nesting success through compaction of soil (inhibiting emerging hatchlings or crushing eggs), pollution, and road mortality of emerging hatchlings (Aresco, Reference Aresco2005).
Artificial nesting mounds have been suggested as a conservation tool to reduce adult turtle mortality on roads and increase recruitment (Kiviat et al., Reference Kiviat, Stevens, Brauman, Hoeger, Petokas and Hollands2000; Marchand & Litvaitis, Reference Marchand and Litvaitis2004b; Beaudry et al., Reference Beaudry, de Maynadier and Hunter2010). By placing mounds that can successfully incubate eggs in close proximity to aquatic habitats used by turtles, migrations to nesting sites will be shorter and will reduce the risk of adult females being killed on roads. In addition, increasing the number and/or quality of nesting sites may increase recruitment in degraded or fragmented habitat if hatching success is equal to or greater than at natural nesting sites. Nest-site characteristics and location have important implications for recruitment and affect hatching success (Wilson, Reference Wilson1998; Kolbe & Janzen, Reference Kolbe and Janzen2002a), predation risk to the female and nest (Temple, Reference Temple1987; Spencer, Reference Spencer2002; Spencer & Thompson, Reference Spencer and Thompson2003), and the fitness of hatchlings (O'Steen, Reference O'Steen1998; Kolbe & Janzen, Reference Kolbe and Janzen2001, Reference Kolbe and Janzen2002b). Although the successful use of artificial nesting sites has been noted previously (Dowling et al., Reference Dowling, Hartwig, Kiviat and Keesing2010; Buhlmann & Osborn, Reference Buhlmann and Osborn2011), ours is the first study to evaluate their efficiency by comparing mound use and nest success to natural nest sites. The objective of our study was to evaluate quantitatively the use of artificial nesting mounds as a conservation tool for freshwater turtles. We based our evaluation on five criteria, and deemed the artificial mounds to be successful if (1) turtles encountered and used the artificial mounds, (2) hatching success was equal to or higher at artificial sites vs natural sites, (3) the fitness of hatchlings from artificial mounds was equal to or higher than that of hatchlings from natural nests, (4) incubation conditions were similar in artificial and natural sites, and (5) emergence dates and incubation durations were similar at artificial and natural sites.
Study area
The study site is in Algonquin Provincial Park, Ontario, Canada. We withhold the specific locations, to prevent illegal collection. The area is relatively undisturbed and consists of a mosaic of wetlands, rivers, and lakes in an upland pine forest accessible by logging roads. The study area was c. 2,000 ha and is home to four species of freshwater turtles: Blanding's turtles Emydoidea blandingii, painted turtles Chrysemys picta, snapping turtles Chelydra serpentina, and wood turtles Glyptemys insculpta. C. picta and C. serpentina are relatively abundant at the study site but E. blandingii and G. insculpta use only specialized habitats (Compton et al., Reference Compton, Rhymer and McCollough2002; Edge et al., Reference Edge, Steinberg, Brooks and Litzgus2010), occur at low densities, and are categorized as Endangered on the IUCN Red List (IUCN, 2011).
Methods
Artificial nesting mounds
Four artificial nesting mounds were installed on 30 April 2009. The substrate was a mixture of granular A gravel (60%) and sand (40%), to imitate the consistency of nesting sites favoured by turtles. A layer of geotextile cloth was placed underneath mounds to prevent growth of vegetation. Each mound was approximately circular with a 3 m radius and standing 0.5 m high with a south-west facing slope. Locations were selected based on previous observations of turtles nesting and the perceived risk of road mortality. Each mound was placed within 100 m of an aquatic habitat and within 50 m of known nesting sites. Mounds were at least 1.5 km apart, and no females switched nesting sites during the study (four independent groups of nesting turtles).
Nest monitoring
Artificial mounds, known natural nesting sites, and potential nesting sites within 1 km of artificial mounds were monitored each night (17.00–24.00), on foot, during the nesting seasons of 2009 (27 May–26 June) and 2010 (19 May–16 June) by teams of 2–4 researchers. This time was chosen because the majority of nesting behaviour for the study species occurs in the late afternoon or evening (Christens & Bider, Reference Christens and Bider1987; Congdon et al., Reference Congdon, Breitenbach, van Loben Sels and Tinkle1987; Standing et al., Reference Standing, Herman and Morisson1999; Walde et al., Reference Walde, Bider, Masse, Saumure and Titman2007). Sites were also monitored opportunistically at dawn for nesting C. serpentina. Nests were excavated within the first 24 hours after oviposition (Samson et al., Reference Samson, Hughes and Brooks2007) to determine clutch size, maximum nest width, and maximum nest depth (cm). Eggs were returned to the nest chamber in the same orientation as found.
Encounter rate and use of artificial nesting sites (criterion 1)
All known natural nesting sites and the artificial nesting mounds were monitored, as described above, to determine their extent of use. The locations of nests were recorded with a global positioning system (GPS).
Based on their availability as potential nesting habitat, we estimated how many nests were expected to be in artificial nesting mounds. Using ArcGIS v. 9.2 (ESRI, Redlands, USA) potential nesting habitat, which was restricted to areas with open canopy and low ground cover, was mapped within 500 m of a wetland at each site. We then calculated the proportion of nesting habitat at each site covered by artificial nesting mounds. Mounds were assumed to be perfect circles with a radius of 3 m (i.e. an area of 28.26 m2). If the artificial mounds were preferred equally to natural sites then the proportion of nests in artificial mounds would be proportional to the amount of available nesting habitat they comprised.
To test the likelihood of females encountering artificial mounds while searching for nest sites, we modelled their paths from the nearest aquatic habitat to actual nest locations using correlated random walks in Hawth's Tools (Beyer, Reference Beyer2004) for ArcGIS. This was done at two sites (Sites 1 and 2; Fig. 1) that each had > 20 natural nests (any turtle species) combined over the two field seasons. The other sites had low densities of nests and were excluded from these analyses. Although nest-site selection is not random, correlated random walk models may appropriately represent likely paths used by nest-searching females because they are biased in one direction but allow random deviations in angles and path length to occur from aquatic habitat to nest sites. The parameters used in the model were based on Bowne & White's (Reference Bowne and White2004) observations of terrestrial movements by homing C. picta. We assumed that turtles moved overland at a mean speed of 1 m per minute. Every path used a maximum of 40 steps that each represented a 10 minute period (maximum 400 minutes nesting foray) and had a mean length of 10 ± SD 4.8 m. Because turtles moving through terrestrial habitats to nesting sites tend to travel in a relatively straight line (Graham et al., Reference Graham, Georges and McElhinney1996; Caldwell & Nams, Reference Caldwell and Nams2006) we used a mean turning angle of 0 ± SD 12°. For each nest 100 paths were simulated from water to that nest. The encounter rate with artificial nesting mounds was estimated using the mean number of paths per nest that crossed the mound. A kernel density estimate of paths was generated using ArcGIS, to determine where path densities were highest; locations with higher path densities would intercept more nesting females.

Fig. 1 The path density of modelled paths of turtles from wetlands to nests at (a) Site 1 (n = 31 nests), and (b) Site 2 (n = 21 nests) in relation to artificial nesting mounds (n = 1 at each site). Each nest had 100 paths constructed using correlated random walk paths (see text for details).
Transplant experiment (criteria 2–5)
Differences in recruitment success and incubation environments between nests on artificial mounds and natural nests were measured using a transplant experiment during 2010. Clutches of C. serpentina (n = 12) and C. picta (n = 9) were divided equally to control for maternal effects: half the eggs were incubated in the natural nest cavity, and half were transferred to the closest artificial mound. The clutch sizes, nest depths and incubation requirements of these two species are varied and encompass the requirements of the other two species at the site (E. blandingii and G. insculpta). All eggs (natural and transplants) were removed from the original cavity and transported in the same container to remove the effect of transport on hatching success. All eggs were placed in nest cavities (natural or transplant) in the same orientation in which they were found. Eggs transferred to artificial mounds were placed in a cavity the same width and depth as the natural nest. A predator exclusion cage was buried over the top and down the sides of all nests to prevent predation of the eggs. The predator exclusion cage was made of 2.5 cm grid hardware cloth and the design was uniform across both treatments so that any minor effects on microclimate were equal for both groups. Although differences in nest predation between natural and artificial nesting sites should be addressed, the goal of our study was to determine if hatching success and incubation conditions were similar between treatment groups. Natural nest predation rates are often high, and predators were excluded to avoid the loss of replicates. C. picta clutches with 10 or more eggs were used to ensure a sufficient number of eggs in each treatment.
Beginning in early August nests were checked daily for emerging hatchlings. Carapace length was measured to the nearest 0.01 cm using callipers and mass (± 0.1 g) was measured using Pesola spring scales. In October, nests with hatchlings that did not emerge were excavated to determine the fate of the remaining embryos. Hatching success (arcsine-square-root transformed to normalize) of C. picta and C. serpentina nests transplanted to artificial mounds were compared to nests at natural sites using a paired t-test to control for maternity, with both species pooled together because they were being used to test the same hypothesis regarding hatching success. The hatching success of a nest was the proportion of fertilized eggs that pipped successfully.
The fitness of emerging hatchlings was estimated through proxies: body condition and deformities. Body condition refers to the relative amount of fat and water stored in an organism (Jakob et al., Reference Jakob, Marshall and Uetz1996; Litzgus et al., Reference Litzgus, Bolton and Schulte-Hostedde2008). Mixed-effects linear models were used to test the effect of nest treatment (natural or transplanted to artificial mound) on hatchling mass using carapace length as a covariate and clutch as a random effect. This test compared body condition between treatments using a size corrected mass (Garcia-Berthou, Reference Garcia-Berthou2001). We compared the rates of deformities in clutches of both species between natural nests and those transplanted to artificial mounds, using a two-way ANOVA. A hatchling was considered to have a deformity if the pattern of scutes on the carapace or plastron deviated from the normal complement (Ernst & Lovich, Reference Ernst and Lovich2009). Colour variations were not considered deformities.
Physical characteristics were measured at natural nesting sites and on artificial mounds to compare incubation conditions between treatments. A temperature datalogger (iButton, Maxim, Sunnydale, USA) in the centre of each nest recorded hourly temperature (± 0.5 °C). Heat unit accumulation is used to predict the outcome of a biological process (Arnold, Reference Arnold1960; i.e. embryological development in our case) and is expressed in degree days (Bakersville & Emin, Reference Bakersville and Emin1969). The total heat units above a threshold temperature of 20 °C accumulated hourly were calculated for each nest. Below this temperature, embryos survive but do not develop (Schwarzkopf & Brooks, Reference Schwarzkopf and Brooks1987). Total heat units for a nest were calculated from the day after eggs were laid until the day hatchlings emerged from that nest. If no hatchlings emerged, heat units were calculated until the last day a hatchling naturally emerged at any site (13 September for C. picta, 30 September for C. serpentina). The hydric environment of a nest affects nest success and hatchling body size (Packard et al., Reference Packard, Packard, Miller and Boardman1987; Janzen et al., Reference Janzen, Ast and Paukstis1995, Reference Janzen, Tucker and Paukstis2000), therefore percentage soil moisture was measured in all nests on 15 July 2010 (after the nesting season) using a HydroSense soil moisture probe (Campbell Scientific, Edmonton, Canada). Overstorey canopy cover (%) was measured at all nests using a densiometer, on 15 July 2010. Soil moisture (%, log transformed), overstorey canopy cover (%), and total heat units (degree days), were compared between natural nests and nests transplanted to artificial mounds using two-way ANOVAs with species and treatment as predictor variables. Relationships between heat units and soil moisture were tested using linear regressions for each species.
To determine whether clutches in one treatment group emerged earlier, the time (days, log transformed) from oviposition to the first emergence was compared between treatments using a two-way ANOVA with species and treatment as predictor variables.
Results
Encounter rate and use of artificial nesting sites (criterion 1)
Over the two nesting seasons four turtles nested on the artificial mounds. In 2009 one C. picta and one C. serpentina nested on the same mound. In 2010 two E. blandingii nested on artificial mounds. All of these nests had 100% hatching success. In addition, five other turtles were observed test-pitting (a nest-searching behaviour) on three out of four mounds in 2010. G. insculpta was the only species that was not observed on artificial nesting mounds in either year. The mean proportion of nests that were in artificial mounds (3.8% ± SE 2.8) was higher than expected (1.7% ± SE 1.7) based on the mean proportion of available nesting habitat in artificial mounds.
The probability that females would encounter artificial nesting mounds was low. The mean probability of a turtle's path intercepting the artificial mound at Site 1 was 2.6% ± SE 0.8. The kernel density estimator showed that although the mound would probably intercept some females (4–6 paths m−2), encounter rate could have been increased to 7–11 paths m−2 by placing it on the north side of the site (Fig. 1a). The mean probability of a turtle's path intercepting the artificial mound at Site 2 was 5.8% ± SE 2.7. The kernel density estimator showed that the artificial nesting mound was in a location that would probably intercept close to the maximum possible number of nesting turtles (7–11 paths m−2; Fig. 1b).
Transplant experiment (criteria 2–5)
Hatching success was high overall among nests of both C. picta and C. serpentina (Table 1). Hatching success, in the absence of predation, was higher in nests on artificial nesting mounds (mean = 93%) than in natural nests (mean = 56%; t = 2.74, df = 20, P < 0.02).
Table 1 Mean ± SE measurements of variables in Chrysemys picta (n = 9) and Chelydra serpentina (n = 12) nests that incubated in sites chosen by females (Natural) and in those transplanted to artificial nesting mounds (Transplant). Probabilities from two-way ANOVAs are given for each variable, except hatching success for which the probability is from a paired t-test with species pooled (see text for details). Statistically significant probabilities are in bold.

A total of 74 C. picta hatchlings (33 from natural nests, 41 from artificial mounds) and 193 C. serpentina hatchlings (83 from natural nests, 110 from artificial mounds) were used for analyses of body condition. Size-adjusted masses of C. picta hatchlings from nests on artificial mounds were not different from those of hatchlings from natural nests (F = 1.34, df = 1,62, P = 0.19; Fig. 2a). Size-corrected hatchling mass of C. serpentina did not differ between treatment groups (F = 1.05, df = 1,180, P = 0.29; Fig. 2b). There was a higher rate of scute deformities in C. picta than in C. serpentina (F = 8.30, df = 1,28, P < 0.01) but deformity rates did not differ between treatments (F = 1.98, df = 1,28, P = 0.17). The interaction between deformity rate and species was not significant (F = 0.08, df = 1,28, P = 0.78).
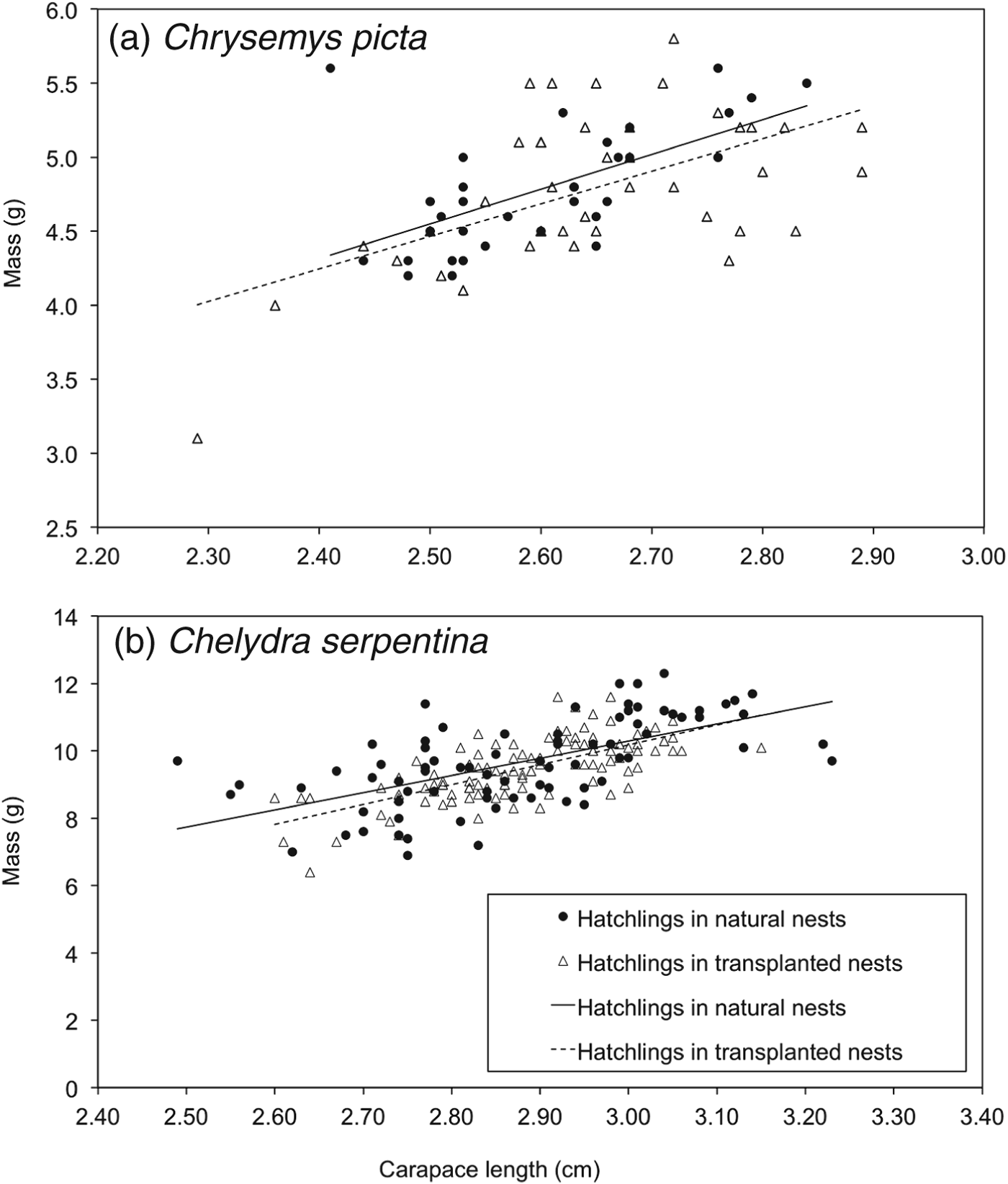
Fig. 2 Body condition of (a) Chrysemys picta (n = 74), and (b) Chelydra serpentina (n = 193) hatchlings emerging from natural nests and artificial nesting mounds in the transplant experiment, in 2010. There was no difference in body condition between the two treatments for either species (see text for details).
Physical conditions of natural nests vs those transplanted to artificial mounds are summarized in Table 1. Heat units accumulated during incubation did not differ between natural and artificial sites (F = 0.24, df = 1,36, P = 0.63), or between species (F = 2.84, df = 1,36, P = 0.10). Moisture in nests differed between artificial mounds and natural nests (F = 5.48, df = 1,36, P = 0.04) but not between species (F = 3.63, df = 1,36, P = 0.06). Overstorey canopy cover of nests did not differ between treatments (F = 2.30, df = 1,36, P = 0.14) or between species (F = 2.86, df = 1,36, P = 0.10). Hatching success was not related to heat units in C. picta nests (F = 0.69, df = 1,16, P = 0.42; Fig. 3a) but increased linearly with heat units in C. serpentina nests (F = 13.72, df = 1,22, P < 0.01; Fig. 3b). Soil moisture was not related to hatching success in C. picta (F = 0.90, df = 1,16, P = 0.77) or C. serpentina (F = 0.60, df = 1,22, P = 0.45).

Fig. 3 Relationship between hatching success and accumulated heat units for nests of (a) C. picta, and (b) C. serpentina in the transplant experiment, in 2010.
Hatchlings began emerging earlier from natural nests (12 August and 28 August for C. picta and C. serpentina, respectively) than from nests on artificial mounds (29 August and 2 September for C. picta and C. serpentina, respectively). However, time from oviposition to first emergence (days, log transformed) did not differ between natural and artificial sites (F = 0.11, df = 1,19, P = 0.74) or between species (F = 0.02, df = 1,19, P = 0.89).
Discussion
Although we observed few nests in artificial sites, more turtles used mounds than expected based on their availability. Nesting habitat was readily available at the site but artificial mounds may have higher use and effectiveness in degraded systems with low availability of nesting sites. In addition to the fact that artificial mounds constituted only a small fraction of available nesting habitat, low rates of mound use may have also occurred because (1) the mounds were not attractive habitat for nesting turtles, (2) only small numbers of females have so far encountered them, or (3) nest-site fidelity reduced the likelihood that turtles would switch nest locations.
Mounds appear to have provided attractive habitat for nesting turtles. The transplant experiment revealed similar environmental conditions (e.g. temperature, canopy cover) in artificial mounds vs natural nests for variables that turtles may use to select nesting sites (Morjan & Valenzuela, Reference Morjan and Valenzuela2001; Spencer, Reference Spencer2002). In contrast, the simulations of turtle paths to nests suggest that there was a low probability that turtles would encounter sites, probably because they constituted a small fraction of the available habitat. If few turtles have so far encountered mounds but they are suitable nesting habitat, then mound use should increase over time and this should be monitored.
Another factor that may reduce use of artificial nesting mounds is nest-site fidelity, which is common in freshwater turtles (Freedberg et al., Reference Freedberg, Ewert, Ridenhour, Neiman and Nelson2005; Rowe et al., Reference Rowe, Coval and Dugan2005). Females may be unlikely to switch nesting sites even if alternate habitat is suitable and readily available. However, many species demonstrate flexibility in nest-site selection (Schwarzkopf & Brooks, Reference Schwarzkopf and Brooks1987; Spencer & Thompson, Reference Spencer and Thompson2003) and some species, such as spotted turtles Clemmys guttata, show fidelity to substrate type rather than geographical location (Rasmussen & Litzgus, Reference Rasmussen and Litzgus2010). Therefore, artificial nesting sites may still attract females if they previously nested on similar substrate types (e.g. road-side shoulders, open fields, gravel pits, beaches). In addition, turtles often use nesting sites that are of recent anthropogenic origin (Beaudry et al., Reference Beaudry, de Maynadier and Hunter2010); this indicates that females can switch nesting sites when suitable habitat is created.
An important consideration for the use of nesting mounds as a conservation tool is the predation rate on nests. Predation rates on freshwater turtle nests are typically high (Congdon et al., Reference Congdon, Breitenbach, van Loben Sels and Tinkle1987; Spencer, Reference Spencer2002; Marchand & Litvaitis, Reference Marchand and Litvaitis2004b) and a limitation of our study is that we did not address whether nest predation rates differed on artificial mounds vs natural nesting sites because all nests had predator exclusion cages. Artificial mounds, which could have high densities of nests in degraded habitats, may attract predators and act as population sinks for turtles (Burke et al., Reference Burke, Rathbun, Bodie and Gibbons1998; Doody et al., Reference Doody, Sims and Georges2003; Marchand & Litvaitis, Reference Marchand and Litvaitis2004b). Predation rates may also vary by mound location and thus placement of mounds should incorporate other landscape features that may reduce predation, such as being placed away from habitat edges (Temple, Reference Temple1987; Kolbe & Janzen, Reference Kolbe and Janzen2002c; Marchand & Litvaitis, Reference Marchand and Litvaitis2004b). Future work should compare predation rates on artificial nesting mounds vs natural nests at the same site.
Hatching success of eggs transplanted to artificial nesting mounds was significantly higher than that of eggs in natural nests, indicating that artificial mounds have the potential to improve recruitment. Although there were no differences in heat units, moisture levels were significantly lower in artificial mounds. However, the difference in moisture between treatments (mean = 1.4%) probably does not represent a biologically relevant difference for females selecting nest sites. It is possible the difference in moisture arose because the artificial mounds had looser soil than natural sites, although they retained their shape and profile throughout the two seasons. Artificial nesting mounds successfully incubated turtle eggs at biologically relevant depths and conditions that were similar to natural nests.
There was no difference in body condition between hatchlings from natural nests and those from eggs transplanted to artificial mounds. Because nest moisture and maternal effects are probably the most important factors determining hatchling size (Packard et al., Reference Packard, Packard, Miller and Boardman1987; Janzen et al., Reference Janzen, Ast and Paukstis1995), the lack of difference in hatchling body condition observed in our study also suggests that the small difference in hydric conditions between treatments may not be biologically relevant. In addition, there was no difference in deformity rate between treatments. Environmental and genetic factors were similar between treatments, and these factors are the largest sources of deformities in hatchlings (Gutzke et al., Reference Gutzke, Packard, Packard and Boardman1987; Steyermark & Spotila, Reference Steyermark and Spotila2001; de Solla et al., Reference de Solla, Fernie and Ashpole2008).
Thermal conditions in nests transplanted to artificial mounds were similar to those in nest sites chosen by turtles, suggesting that cues used by turtles to select nesting sites could promote the use of artificial mounds and that these nests will experience similar success to natural nests, if not higher. The thermal regime in a nest has strong conservation implications for turtle species with temperature-dependent sex determination (Ewert & Nelson, Reference Ewert and Nelson1991). The lack of a relationship in C. picta nests between hatching success and heat units suggests that all nests of both treatments received sufficient heat units to complete development. In contrast, the heat units accumulated by C. serpentina nests limited hatching success. C. picta nested earlier in the season (first nest 19 May 2010) and had shallower nests than those of C. serpentina (first nest 28 May 2010). Heat unit accumulation at nesting sites may be limiting for C. serpentina, which in most years do not successfully develop and emerge in Algonquin Park because of the short summer season (Obbard & Brooks, Reference Obbard and Brooks1981; R.J. Brooks pers. comm.).
Hatchlings emerged from natural nests and nests transplanted to artificial mounds after a similar number of days. Hatchlings emerging from nests in artificial mounds would therefore experience similar environmental stresses and predation levels as those emerging from natural nests. Differences in emergence timing could affect mortality rates of hatchlings from predators and from environmental factors such as sub-freezing autumn temperatures (Obbard & Brooks, Reference Obbard and Brooks1981; Draud et al., Reference Draud, Bossert and Zimavoda2004). The success of artificial nesting mounds relies not only on the successful incubation of embryos but also on the success of emerging juveniles in being recruited into the population. The lack of difference in incubation duration further supports the appropriateness of artificial nesting mounds as a conservation tool.
We observed low but nonetheless higher than expected use of artificial nesting mounds based on their availability, and the incubation conditions at artificial mounds were similar to those observed at natural nests. Sufficient heat units were accumulated to allow development of turtle embryos at biologically relevant depths and hatchlings emerged naturally on similar dates to natural nests. In addition, higher hatching success at artificial sites vs natural nests indicates that the creation of additional nesting habitat for turtles may increase recruitment. The placement of mounds will probably intercept female turtles moving to nesting sites but several nesting seasons may be required to reach maximum encounter rate. Spatial analyses of nest location and nest searching paths should therefore be used to place future nesting mounds strategically, to reduce the risk of road mortality of females, and larger or more numerous mounds should be created to increase the probability that turtles searching for nesting sites will encounter them. Based on the analyses of our five criteria, artificial nesting mounds present a promising conservation tool for freshwater turtles.
Acknowledgements
Financial support was provided by Environment Canada's Habitat Stewardship Program, Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources (OMNR) Species at Risk Stewardship Fund, Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (PGS-M Scholarship to JEP and Discovery Grant to JDL), and Laurentian University. Extensive in-kind contributions and financial support were provided by Algonquin Park (OMNR). Algonquin Forestry Authority constructed the artificial nesting mounds. E. Newton, E. Upham-Mills, M. McDermott, M. Keevil, A. Bennett, M. Rasmussen, E. Huner, T. Cameron, J. Riley and A. Leifso assisted in the field. All work was carried out under an approved Laurentian University Animal Care protocol and was authorized by permits from OMNR.
Biographical sketches
James E. Paterson is interested in answering questions related to spatial ecology to improve conservation methods and in testing hypotheses about how animal populations use resources at different spatial and temporal scales. Brad D. Steinberg's research interests focus on the practical application of field data to the conservation and management of species at risk. Jacqueline D. Litzgus is interested in the life history, natural history, and physiological ecology of reptiles, and the application of these data to the recovery of species at risk.






