Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Suatmadi, Anissa Yuniashaesa
Creutzig, Felix
and
Otto, Ilona M.
2019.
On-demand motorcycle taxis improve mobility, not sustainability.
Case Studies on Transport Policy,
Vol. 7,
Issue. 2,
p.
218.
Li, Qirui
2020.
Resilience Thinking as a System Approach to Promote China’s Sustainability Transitions.
Sustainability,
Vol. 12,
Issue. 12,
p.
5008.
Soomauroo, Zakia
Blechinger, Philipp
and
Creutzig, Felix
2020.
Unique Opportunities of Island States to Transition to a Low-Carbon Mobility System.
Sustainability,
Vol. 12,
Issue. 4,
p.
1435.
Butler, Luke
Yigitcanlar, Tan
and
Paz, Alexander
2020.
How Can Smart Mobility Innovations Alleviate Transportation Disadvantage? Assembling a Conceptual Framework through a Systematic Review.
Applied Sciences,
Vol. 10,
Issue. 18,
p.
6306.
Lobo, Jose
Alberti, Marina
Allen-Dumas, Melissa
Arcaute, Elsa
Barthelemy, Marc
Bojorquez Tapia, Luis A.
Brail, Shauna
Bettencourt, Luis
Beukes, Anni
Chen, Wei‐Qiang
Florida, Richard
Gonzalez, Marta
Grimm, Nancy
Hamilton, Marcus
Kempes, Chris
Kontokosta, Constantine E.
Mellander, Charlotta
Neal, Zachary P.
Ortman, Scott
Pfeiffer, Deirdre
Price, Michael
Revi, Aromar
Rozenblat, Céline
Rybski, Diego
Siemiatycki, Matthew
Shutters, Shade T.
Smith, Michael E.
Stokes, Eleanor C.
Strumsky, Deborah
West, Geoffrey
White, Devin
Wu, Jingle
Yang, Vicky Chuqiao
York, Abigail
and
Youn, Hyejin
2020.
Urban Science: Integrated Theory from the First Cities to Sustainable Metropolises.
SSRN Electronic Journal,
Braun, Maximilian
Kunkler, Jan
and
Kellner, Florian
2020.
Towards Sustainable Cities: Utilizing Floating Car Data to Support Location-Based Road Network Performance Measurements.
Sustainability,
Vol. 12,
Issue. 19,
p.
8145.
Wilson, Charlie
Kerr, Laurie
Sprei, Frances
Vrain, Emilie
and
Wilson, Mark
2020.
Potential Climate Benefits of Digital Consumer Innovations.
Annual Review of Environment and Resources,
Vol. 45,
Issue. 1,
p.
113.
Creutzig, Felix
Javaid, Aneeque
Soomauroo, Zakia
Lohrey, Steffen
Milojevic-Dupont, Nikola
Ramakrishnan, Anjali
Sethi, Mahendra
Liu, Lijing
Niamir, Leila
Bren d’Amour, Christopher
Weddige, Ulf
Lenzi, Dominic
Kowarsch, Martin
Arndt, Luisa
Baumann, Lulzim
Betzien, Jody
Fonkwa, Lesly
Huber, Bettina
Mendez, Ernesto
Misiou, Alexandra
Pearce, Cameron
Radman, Paula
Skaloud, Paul
and
Zausch, J. Marco
2020.
Fair street space allocation: ethical principles and empirical insights.
Transport Reviews,
Vol. 40,
Issue. 6,
p.
711.
Hu, Jia-Wei
Javaid, Aneeque
and
Creutzig, Felix
2021.
Leverage points for accelerating adoption of shared electric cars: Perceived benefits and environmental impact of NEVs.
Energy Policy,
Vol. 155,
Issue. ,
p.
112349.
Truong, Thi My Thanh
2021.
Impacts of digitalisation on travel behaviour in Hanoi city centre.
Vol. 2429,
Issue. ,
p.
040004.
Duggal, Angel Swastik
Singh, Rajesh
Gehlot, Anita
Gupta, Lovi Raj
Akram, Sheik Vaseem
Prakash, Chander
Singh, Sunpreet
and
Kumar, Raman
2021.
Infrastructure, mobility and safety 4.0: Modernization in road transportation.
Technology in Society,
Vol. 67,
Issue. ,
p.
101791.
Nemoto, Eliane Horschutz
Issaoui, Roukaya
Korbee, Dorien
Jaroudi, Ines
and
Fournier, Guy
2021.
How to measure the impacts of shared automated electric vehicles on urban mobility.
Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment,
Vol. 93,
Issue. ,
p.
102766.
Leite de Almeida, Constança Martins
Silveira, Semida
Jeneulis, Erik
and
Fuso-Nerini, Francesco
2021.
Using the Sustainable Development Goals to Evaluate Possible Transport Policies for the City of Curitiba.
Sustainability,
Vol. 13,
Issue. 21,
p.
12222.
Creutzig, Felix
2021.
From smart city to digital urban commons: Institutional considerations for governing shared mobility data.
Environmental Research: Infrastructure and Sustainability,
Vol. 1,
Issue. 2,
p.
025004.
Anastasiadou, Konstantina
Gavanas, Nikolaos
Pyrgidis, Christos
and
Pitsiava-Latinopoulou, Magda
2021.
Identifying and Prioritizing Sustainable Urban Mobility Barriers through a Modified Delphi-AHP Approach.
Sustainability,
Vol. 13,
Issue. 18,
p.
10386.
Wang, Ke
Zhao, Yafei
Gangadhari, Rajan Kumar
and
Li, Zhixing
2021.
Analyzing the Adoption Challenges of the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Smart Cities in China.
Sustainability,
Vol. 13,
Issue. 19,
p.
10983.
CABİROĞLU, Seda
and
ÖZDEN, Abdulkadir
2022.
Türkiye'de Uzun Bisiklet Parkurlarının Bisiklet Kullanımına Etkisinin İncelenmesi.
European Journal of Science and Technology,
Schwinger, Felix
Forster, Lucas
and
Jarke, Matthias
2022.
Population Synthesis by Disaggregating OD Matrices with Time-Progressive Graphs for Agent-based Simulations.
Procedia Computer Science,
Vol. 201,
Issue. ,
p.
560.
Hu, Jia-Wei
and
Creutzig, Felix
2022.
A systematic review on shared mobility in China.
International Journal of Sustainable Transportation,
Vol. 16,
Issue. 4,
p.
374.
Zioło, Magdalena
Niedzielski, Piotr
Kuzionko-Ochrymiuk, Ewa
Marcinkiewicz, Jacek
Łobacz, Katarzyna
Dyl, Krzysztof
and
Szanter, Renata
2022.
E-Government Development in European Countries: Socio-Economic and Environmental Aspects.
Energies,
Vol. 15,
Issue. 23,
p.
8870.
Social media summary
Public policies are central to rendering low-carbon smart mobility and avoiding problematic rebound effects.
1. Introduction
With urbanization and big data, two megatrends of the twenty-first century merge in the concept of the so-called smart city. Before we reach 2050, more than two-thirds of humanity will live in cities – and they will increasingly encounter the digitalization of cities, including the use of big data technologies, artificial intelligence and automatization (WBGU, 2019). The design of cities, including their digitalization, will be decisive in shaping greenhouse gas emission trajectories and climate change mitigation (Bai et al., Reference Bai, Dawson, Ürge-Vorsatz, Delgado, Barau, Dhakal and Schultz2018; Creutzig et al., Reference Creutzig, Agoston, Minx, Canadell, Andrew, Le Quéré and Dhakal2016), will risk the spectre of social control and surveillance, questioning the right to the city (Harvey, Reference Harvey2003; Sadowski & Pasquale, Reference Sadowski and Pasquale2015), and will provide both chances for and risks to social inclusion (Fossati, Reference Fossati and Bruglieri2018; Reckien et al., Reference Reckien, Creutzig, Fernandez, Lwasa, Tovar-Restrepo, McEvoy and Satterthwaite2017). With the rapid rise of digital technologies, including artificial intelligence methods targeted for climate change (Rolnick et al., Reference Rolnick, Donti, Kaack, Kochanski, Lacoste, Sankaran and Waldman-Brown2019) and meeting unprepared regulatory environments, it becomes increasingly urgent to provide urban governance of digitalization that ensures that digitalization can help to provision public goods and environmentally beneficial outcomes. With this framing, this article agrees with the German Advisory Council on Global Change that digitalization is not an external upheaval to which we must adapt, but rather a dynamic process that must be shaped to deliver a transformation towards sustainable and low-carbon societies (WBGU, 2019).
Some policy-makers and businesses herald the smart city as the solution to high resource consumption and consumption footprints. High-tech smart devices ‘everyware’ enable instant digital self-awareness and the uptake of hyper-efficient solutions (Kitchin, Reference Kitchin2014). Already today, smartphone applications provide access to free-floating shared vehicle fleets in cities from Berlin to Vancouver. Hundreds of thousands of bikes available instantly on demand fill Chinese cities, from Beijing to Kunming, and they have changed mobility choices for the better (Wu & Xue, Reference Wu and Xue2017). Transportation network companies, such as Uber and Lyft, provide added mobility for car-free households and potentially reduce the need to own a car (Henao & Marshall, Reference Henao and Marshall2018). The high utilization of vehicle stocks in sharing services fosters electrification and automatization, two technological innovations associated with high capital but low usage costs (Fulton, Mason & Meroux, Reference Fulton, Mason and Meroux2017). Automatization itself will heavily rely on big data for optimal dispatch and routing of vehicle fleets.
The smart city is not limited to urban transport. In the building sector, for example, combining spatially explicit data with neural network models enables the prediction of building energy demand (Silva, Leal, Oliveira & Horta, Reference Silva, Leal, Oliveira and Horta2018). We argue here, however, that big data applications in urban transport are of particular relevance, as they have the capacity to transform urban mobility and lifestyles, with the potential to make them better or worse. Personalized geo-located user data pose particular risks for loss of privacy and autonomy on the one hand through the internalization of a ‘big brother’ mind-set, and on the other hand via substantial biometric surveillance and automated policing (Sadowski & Pasquale, Reference Sadowski and Pasquale2015). Here, we build on recent ground-breaking academic work on the governance of smart mobility (Docherty, Marsden & Anable, Reference Docherty, Marsden and Anable2018; Marsden & Reardon, Reference Marsden and Reardon2018) and focus on the crossroad that digitalization encounters both for social sustainability and climate change. We call for urban regulatory action to steer digitalization towards sustainable outcomes.
2. Opportunities and risks of digitalization in urban transport
There is no doubt that big data and specific digitalization technologies provide opportunities for transport operators, planners and users (Davidsson, Hajinasab, Holmgren, Jevinger & Persson, Reference Davidsson, Hajinasab, Holmgren, Jevinger and Persson2016). Specific examples also demonstrate economic benefits. The consumer surplus of ride-sharing services is estimated at $1.60 for each $1.00 spent, providing notable benefits to consumers (Cohen, Hahn, Hall, Levitt & Metcalfe, Reference Cohen, Hahn, Hall, Levitt and Metcalfe2016).
At the same time, however, several social and environmental risks emerge from the massive and mostly unregulated use of big data and artificial intelligence (Kitchin, Reference Kitchin2014; Linkov, Trump, Poinsatte-Jones & Florin, Reference Linkov, Trump, Poinsatte-Jones and Florin2018), and efficiency gains in mobility could be rendered meaningless by induced demand for additional mobility, the shift from transit and non-motorized travel to automotive travel, deteriorating urban quality of life and further increasing environmental footprints (Cohen & Cavoli, Reference Cohen and Cavoli2019; Wadud, MacKenzie & Leiby, Reference Wadud, MacKenzie and Leiby2016). The loss of privacy and individual autonomy leads to an increasing and digitalization-specific power concentration, where those who create digital footprints become reduced to data sources and objects to be controlled by those with the means to collect or analyse data (Manovich, Reference Manovich2011). Transportation network companies, for example, collect vast amounts of data that help improve their profitability, but these data commonly are not shared with transport planners or researchers (Castiglione et al., Reference Castiglione, Roy, Cooper, Sana, Chen and Erhardt2019). Ever fewer people can exert greater control over ever more people with both soft habitual nudges and hard surveillance. The ambition of the Chinese government to control their populace with social scoring cards makes this risk evident. Jaywalking, among many items, is surveilled and leads to negative scores. The nudging of Uber drivers to drive for longer times than intended is another example (Scheiber, Reference Scheiber2017). Hacking of autonomous vehicles and smart appliances at home poses another obvious risk. While automatization creates new jobs in computer science, it can also generate loss of employment and status in other industries. Conservative estimates suggest that approximately 6–12% of all jobs are at risk of automatization, increasing pressure primarily on lower-paying jobs (Arntz, Gregory & Zierahn, Reference Arntz, Gregory and Zierahn2016). Automation might also compromise the working ethos and social identity of certain occupations, such as taxi drivers, leading to social dissatisfaction.
The application of big data and artificial intelligence also impacts environmental sustainability. Big data methods revolutionize the research on cities worldwide, providing the quantitative foundations of an emerging global urban sustainability science, with direct applications for urban planning (Creutzig et al., Reference Creutzig, Lohrey, Bai, Baklanov, Dawson, Dhakal and Munoz2019). Preliminary examples and state-of-the-art research demonstrate that big data, at least in principle, can generate environmental benefits in urban transport. Flexible bike and car sharing has the potential to make urban transport more efficient and less dependent on owning a car. Studies of Lisbon and Berlin show that if travel demand should remain unchanged, sharing strategies could reduce the number of cars by more than 90%, also saving valuable urban space for human-scale activity (Bischoff & Maciejewski, Reference Bischoff and Maciejewski2016; Martinez & Viegas, Reference Martinez and Viegas2017). Car-sharing studies demonstrate that public (autonomous) ride-sharing systems could substitute for private cars, with beneficial effects on reducing congestion, air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
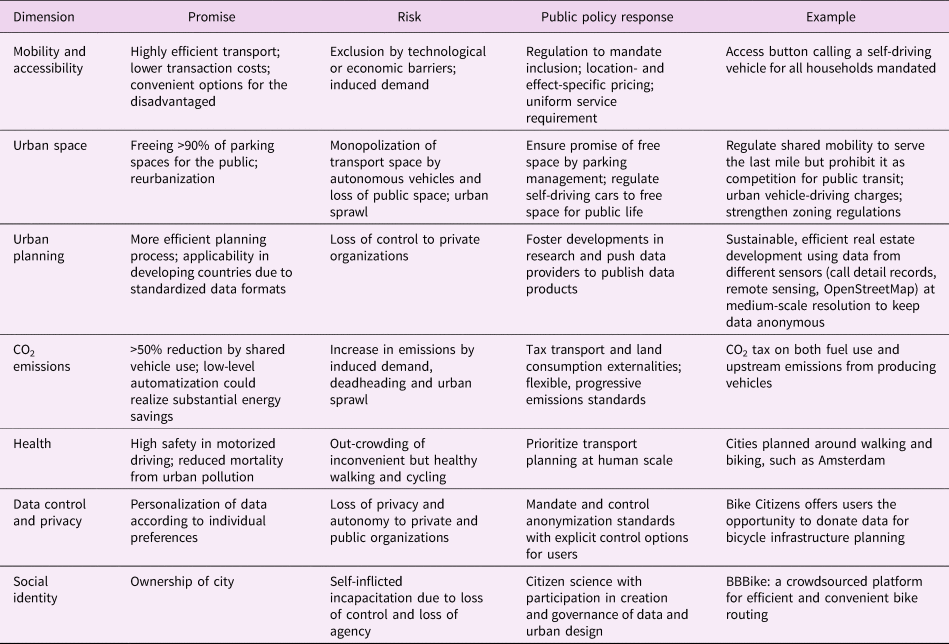
However, even environmental benefits are not obvious, and big data, machine learning and automatization strategies could backfire. Surveys demonstrate that users often take free-floating car-sharing services as a substitute for public transit, and much less as a means to replace their private cars (Herrmann, Schulte & Voß, Reference Herrmann, Schulte and Voß2014). A case study of Djakarta shows that flexible moto-cycle sharing at best is neutral to overall greenhouse gas emissions if substitution effects and deadheading are accounted for (Suatmadi, Creutzig & Otto, Reference Suatmadi, Creutzig and Otto2019). Car sharing with automated vehicles could even worsen congestion and emissions by generating additional travel demand (Rubin, Reference Rubin, Meyer and Beiker2016). Some 22% of all trips travelled with Uber and Lyft would have been travelled by transit, 12% would have walked or biked and another 12% would not have travelled at all (induced demand) (Henao & Marshall, Reference Henao and Marshall2018). Travel time in autonomous vehicles can be used for other activities, but driving and travel costs are expected to decrease, which most likely will lead to additional demand for auto travel (Moeckel, Reference Moeckel2017) and could even create incentives for further urban sprawl. Such developments would likely increase residential energy demand, commuting distances and the conversion rate of bio-productive land into low-density residential areas. More generally, the increased efficiency generated by big data and smart algorithms may generate rebound effects in demand and potentially compromise the public benefits of their efficiency promise (Gossart, Reference Gossart2015). Research on smart cities concerning both conceptual frameworks and empirical findings is still at a relative early stage, and it offers potential both for improvements and deteriorations (Kitchin, Reference Kitchin2015). Similarly, automated driving offers the potential for substantial energy savings in a low-level setting, but also the risk of significantly increased demand for automotive travel and for resulting fuel consumption if automation sharply reduces the costs of drivers’ time (Wadud et al., Reference Wadud, MacKenzie and Leiby2016). We can only tentatively anticipate the overall effects of big data and artificial intelligence, and some unexpected dynamics will certainly surprise researchers and technology futurists. Nonetheless, the current understanding of this large-scale technological paradigm shift towards digitalization demonstrates two things: (1) the risks of socially and environmentally unsustainable outcomes is large; and (2) if properly managed, decision-makers can leverage big data, artificial intelligence and automatization for urban sustainability goals (Table 1).
Table 1. Risks, promises and policy options of digitalization (including big data technologies, artificial intelligence and automatization) for sustainability in cities.
3. The emerging governance of digitalization
Achieving these goals requires dealing with important trade-offs. For example, if big data remain unregulated, social risks could be realized and the potential environmental benefits or harms would become subject to hard-to-predict technological innovation rates and system dynamics, but unregulated digitalization could also bring first-mover advantages in developing new markets and models of living. This model is best encapsulated by the US state of Arizona, which attracts the car fleets of companies invested into automated driving by providing unregulated access to Phoenix's roads, a pattern that is also likely to further lock in the structure of the automobile city. Tight social control managed by big data technology in turn might enable environmental benefits, but reduce the autonomy of individuals. The rule of the Communist Party in China closely resembles this model, where punishing polluters is enabled by a dense matrix of surveillance and big data technologies. But regulating both the social and environmental risks of big data is also possible. The EU, with its concern for both privacy and environmental issues, might be a candidate to implement comprehensive sustainable data regulation, but it shows only reluctant signs of moving in this direction.
The emerging transition research suggests that big data can not only support standard policies, but also facilitate the transition process itself. With digital citizen science, non-professional individuals are invited to join the production of knowledge and big data (e.g., by collecting, classifying and sharing acoustic or visual signals of urban spaces recorded with their smart phones), or groups of activist individuals generate new knowledge uninvited (Dickel & Franzen, Reference Dickel and Franzen2016). The intended production of user-generated data is a performative act and can produce a self-association with the goals underlying research, a process related to social identification (Deaux, Reference Deaux, Higgins and Kruglanski1996). Different forms of citizen science and the sharing of results and visualizations with the public can produce relevant niche cultures, and hence also become the starting points of a transition towards sustainability. Through understanding environmental problems as social problems that affect everyone, the search for solutions must include broad environmental citizenship, with citizens actively defining research and the policy agenda in local settings (Irwin, Reference Irwin1995). Citizen science projects are particularly widespread in the environmental sector, where volunteers are involved with their mobile devices (e.g., to monitor air, light or water pollution at different locations). OpenStreetMap might serve as a best-practice example in the field of volunteered geographic information usage (Haklay, Reference Haklay2010; Haklay & Weber, Reference Haklay and Weber2008). It is an open-access database of street networks, buildings and public facilities around the world (www.openstreetmap.org) that is community driven. BBBike is a crowdsourcing project based on OpenStreetMap that provides free optimal bike routing for Berlin and 200 other cities worldwide (Lenz & Heinrichs, Reference Lenz and Heinrichs2017). In the reality of the emerging field of citizen science, however, volunteers are much more likely to act as human sensors for data collection rather than as self-determined researchers, and it is important to learn from both failed citizen science projects and successful examples, such as BBBike, to make citizen science useful for the public governance of big data by empowering people. This includes fostering a public understanding of big data (Michael & Lupton, Reference Michael and Lupton2016).
Societal inclusion means having access to all provisioning systems (Luhmann, Reference Luhmann and Luhmann1995). A growing body of sociological literature analyses the mechanisms of inclusion and exclusion in contemporary societies (Stichweh, Reference Stichweh2016), but the crucial role that access to mobility has for inclusion in all other provision systems is often ignored. The issue was put firmly on the political agenda by the Social Exclusion Unit of the UK government that existed between 1997 and 2010. A 2003 study for the UK found that young people with driving licenses are twice as likely to get jobs as those without; that nearly half of 16–18-year-olds experience difficulty in paying for transport to get to their place of study; that almost a third of carless households have difficulties in accessing their local hospital; and that children from the lowest social class are five times as likely to die in car accidents as children from the highest social class (SEU, 2003). The report's proposal of an accessibility planning framework that would include a range of public services and organizations is equally relevant for managing digitalization for sustainability in cities. Such accessibility planning must also consider that cheap, on-demand, door-to-door transport via autonomous vehicles is not desirable, because it would discourage active modes of transport – walking and cycling – that have proven co-benefits in terms of health and climate (Shaw, Hales, Howden-Chapman & Edwards, Reference Shaw, Hales, Howden-Chapman and Edwards2014). The important leverage that local governments have to shift modal shares towards active modes is demonstrated in cities such as Copenhagen, where, in 2017, 62% of citizens chose to bike to work and study, while the relative risk of having a serious bicycle accident has decreased by 23% since 2006 (City of Copenhagen, 2017; Pucher & Buehler, Reference Pucher and Buehler2017).
In times when governments around the globe are trying to reduce expenditure by seeking to increase efficiency and shrink administrative costs, the risk of not being able to set the right framework conditions for sustainable transport systems and being overtaken by technological developments and innovation in the private sector are considerable (Docherty et al., Reference Docherty, Marsden and Anable2018). Therefore, transnational institutions, like the EU, are crucial to regulating data ownership, preserve autonomy and privacy. But also governance of cities and human settlements play crucial and underestimated roles in implementing solutions for environmental sustainability. Most relevant big data are geocoded and develop their full potential in the specific spatial setting. In the context of big data, governance levels of localities (cities, towns, villages) can best implement concrete political action that can push urban communities to sustainability.
4. Three directions of action
We suggest three directions of actions for cities to make best use of big data and digitalization for sustainable urban transport that could be spearheaded by cities like Berlin (Box 1). First, municipal administrations should establish an officer for digitalization and sustainability, who is responsible for coordinating digitalization efforts across departments and who coordinates with external non-profit and for-profit partners (e.g., non-governmental organizations and app developers). For example, in Tel Aviv, a new position of Central Information Officer was established, promoting digitalization to achieve the following (Press, Reference Press2018): (1) better data integration and cross-department collaboration; (2) targeting communication to citizens; (3) bidirectional participative formats with citizens; (4) improved tracking of service use enabling targeting improvements; (5) providing a digital geographic information system for planning for all stakeholders; and (6) remain supportive of providing high-quality public spaces. Such a digitalization officer would immediately raise attention and bring policy-oriented focus to the topic. Public agencies should also consider making the license to operate a certain transport service, such as Uber or Lyft, contingent on the willingness to share (anonymized) user data (cf. Chase, Reference Chase2015; Docherty et al., Reference Docherty, Marsden and Anable2018).
Box 1. Berlin as a testbed for big data and sustainability.
In Berlin, business, science and municipal policy are all developing rapid expertise and interest in the governance of digitalization of the urban transport. Berlin is an established centre for new sharing services for cars (car2go, DriveNow, Flinkster), bikes (nextbike, Mobike, LIDL-Bikes, Byke) and scooters (emmy, COUP). The Berlin-based Innovation Center for Mobility and Societal Change (InnoZ) not only analyses big data from sharing services, but also offers an app, called modalyzer, which transport users can use to record their travel patterns and donate their data explicitly and voluntarily for research and optimization of mobility services (Lugano, Reference Lugano2017). Similarly, Berlin-based Bike Citizens developed an app that allows users to map their own travel patterns and to provide them for urban planning and research purposes (Gössling, Reference Gössling2018). Academic institutions, and especially the Technical University Berlin, perform a multitude of studies on Berlin mobility transitions, inter alia with the agent-based transport model, MATSim, whose Berlin specification is open access (https://github.com/matsim-vsp/matsim-berlin) (Ziemke, Kaddoura & Nagel, Reference Ziemke, Kaddoura and Nagel2019). Since 2011, the state of Berlin follows an open data strategy that gives practitioners and scientists extensive access to information about demography, infrastructure and transport. A popular petition effort successfully pushed for a new mobility law that provides new opportunities for low-carbon modes of transport, such as cycling, which has been ratified by the Berlin Senate. Importantly, the Berlin Senate aims to expand this mobility law with a new focus on digitalization. This will offer an opportunity to implement regulation and provide new digital platforms that facilitate sustainability in urban transport.
Second, municipalities and foundations should push for digital platforms that provide seamless integration of all mobility services, including bike sharing, taxis and public transport, to foster multi-modal and sustainable transport. A seamless integration of services could result into a cooperative transport system based on human engagement and shared decision-making (Miller, Reference Miller2013). These platforms should facilitate and reward the sharing of information to contribute to societal benefits generated with open data. Importantly, such services should be delivered as open-source code and as not-for-profit infrastructure. In addition, collaboration in identifying, collecting, generating and using data across stakeholder groups is key to delivering sustainable urban development (Paskaleva et al., Reference Paskaleva, Evans, Martin, Linjordet, Yang, Karvonen and Karvonen2017). Blockchain technologies could enable decentralized payment services, keeping users in control of their data, as is currently being explored by the TravelSpirit Foundation (Lopez & Farooq, Reference Lopez and Farooq2018) (it would be crucial, however, to control the immense energy demand of blockchain technologies and decarbonize its supply chain; Truby, Reference Truby2018). Users could nonetheless choose to donate their data for purposes of public interest. Municipalities can use such geo-located data generated by mobility users and other sources to cost-effectively advance urban planning and transport infrastructure decisions (Toole et al., Reference Toole, Colak, Sturt, Alexander, Evsukoff and González2015). Municipalities can also leverage their control over public spaces to obtain some control over the urban digital space. Our own modelling results suggest that relatively coarse resolution is sufficient for planning, thus allowing anonymized data encodings that abstract from individual users.
Third, digitalization strategies will develop their full sustainability potential in the interplay with traditional urban planning, especially for walking, cycling and efficient public transit. These modes enable face-to-face contact in public settings, which are, if well designed, a key ingredient to urban quality of life (Gehl, Reference Gehl2013) and enable a transition away from the fossil city (Bongardt, Breithaupt & Creutzig, Reference Bongardt, Breithaupt and Creutzig2010; Bongardt et al., Reference Bongardt, Creutzig, Hüging, Sakamoto, Bakker, Gota and Böhler-Baedeker2013). The sharpened focus on urban planning is particularly warranted in the case of autonomous vehicles, which, if left unregulated, might induce more traffic and compete with transit, biking and walking. To avoid this competition for passengers, autonomous vehicles could be limited to serve as last-mile connections for transit, acting as a complement to rather than a substitute for efficient mobility structures. If artificial intelligence and smart and low-carbon public vehicles can serve cities, space currently used for parking can be put to better use. To avoid rebound effects, pricing signals should limit harmful effects, such as congestion and greenhouse gas emissions (e.g., with inner city tolls and CO2 or energy pricing) (Kaddoura, Bischoff & Nagel, Reference Kaddoura, Bischoff and Nagel2018). Such pricing schemes may be more acceptable to users of shared mobility platforms (mobility as a service) than for privately owned vehicles, and they would provide a revenue stream for city governments. Infrastructure policies are equally relevant. To advance this agenda, however, key challenges in information integration (already done in products like Google Maps), fare and ticketing integration (technically feasible), operational integration (difficult), business model integration (very difficult) and regulation integration (extremely challenging) need to be overcome (Kamargianni, Li, Matyas & Schafer, Reference Kamargianni, Li, Matyas and Schafer2016).
Successful governance of big data will bridge the gap between user control (e.g., decentralized payment with blockchain technologies) and data availability for public policies (e.g., data donations by users to municipalities to improve transport planning). There is no reason to either demonize or deify big data and artificial intelligence. There is, however, a need to encounter these technologies actively with measured policies and applications, leveraging their potential for urban sustainability and beyond. In the USA or Canada, we see the first urban labs led by tech companies like Alphabet or Microsoft emerging in which the concept of the smart city is being tested. However, politics is needed to strengthen the common good instead of entering into far-reaching public–private partnerships (Sadowski, Reference Sadowski2017). Municipalities and other public agencies need to take responsibility and to start governing the data and technologies generated in their cities in order to reap their benefits and minimize their risks.
Author contributions
FC conceived and designed the study. All authors contributed to writing the text.
Financial support
None.
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical standards
None.