Myasthenia gravis (MG) is an antibody-mediated disorder of the neuromuscular junction characterized by fatigable weakness. The majority of patients with MG are found to have autoantibodies against the muscle acetylcholine receptor (AChR), and 10–15% of patients with MG have an associated thymoma – nearly all of whom are found to be AChR positive. Reference Evoli, Alboini and Damato1 A subset of AChR-antibody seronegative MG patients have antibodies against the muscle-specific receptor tyrosine kinase (MuSK). Reference Evoli, Alboini and Damato1 MuSK-associated MG (MuSK-MG) classically presents with predominant bulbar symptoms without pathologic changes in the thymus. Reference Narayanaswami, Sanders and Wolfe2 We present a rare case of rituximab refractory MuSK-MG with an associated microscopic thymoma.
A 64-year-old woman with a history of reflux esophagitis, hypertension, and dyslipidemia was admitted to the hospital with a 6-month history of binocular horizontal diplopia and a 4-month history of bilateral ptosis, dyspnea, dysphagia, dysarthria, and leg weakness. Examination revealed bilateral ptosis with fatigability, ophthalmoparesis with near complete limitation of upgaze and downgaze, and weak orbicularis oculi bilaterally. Neck flexors and extensors were weak (4/5 MRC scale). There was fatigable weakness in deltoids, finger extensors, and hip flexors, bilaterally. Bedside pulmonary function testing revealed negative inspiratory flow of -28 cm H2O and forced vital capacity of 1.4 L.
Repetitive nerve conduction studies were carried out and the right trapezius muscle revealed a significant electrodecremental response which was exacerbated following exercise (Figure 1). Serum AChR-antibody testing was negative but anti-MuSK testing was subsequently positive. Chest computed tomography (CT) revealed a 17 × 10 mm anterior mediastinal nodule consistent with thymoma (Figure 2a). She was treated with a 5-day course of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg), prednisone 30 mg daily, and pyridostigmine 60 mg four times per day, which led to limited improvement of dyspnea and limb weakness. Her ptosis and ophthalmoparesis did not improve. She was treated with plasma exchange (PLEX), which led to the resolution of ptosis and ophthalmoparesis, and further improvement of dyspnea. She then underwent video-assisted thorascopic thymectomy, and her thymus showed a multifocal microscopic thymoma with a mixture of bland spindle and polygonal epithelial cells forming microscopic nodules embedded within thymic tissue (Figure 2b). She returned to the hospital 3 weeks later with an MG exacerbation and was initiated on PLEX with clinical improvement.
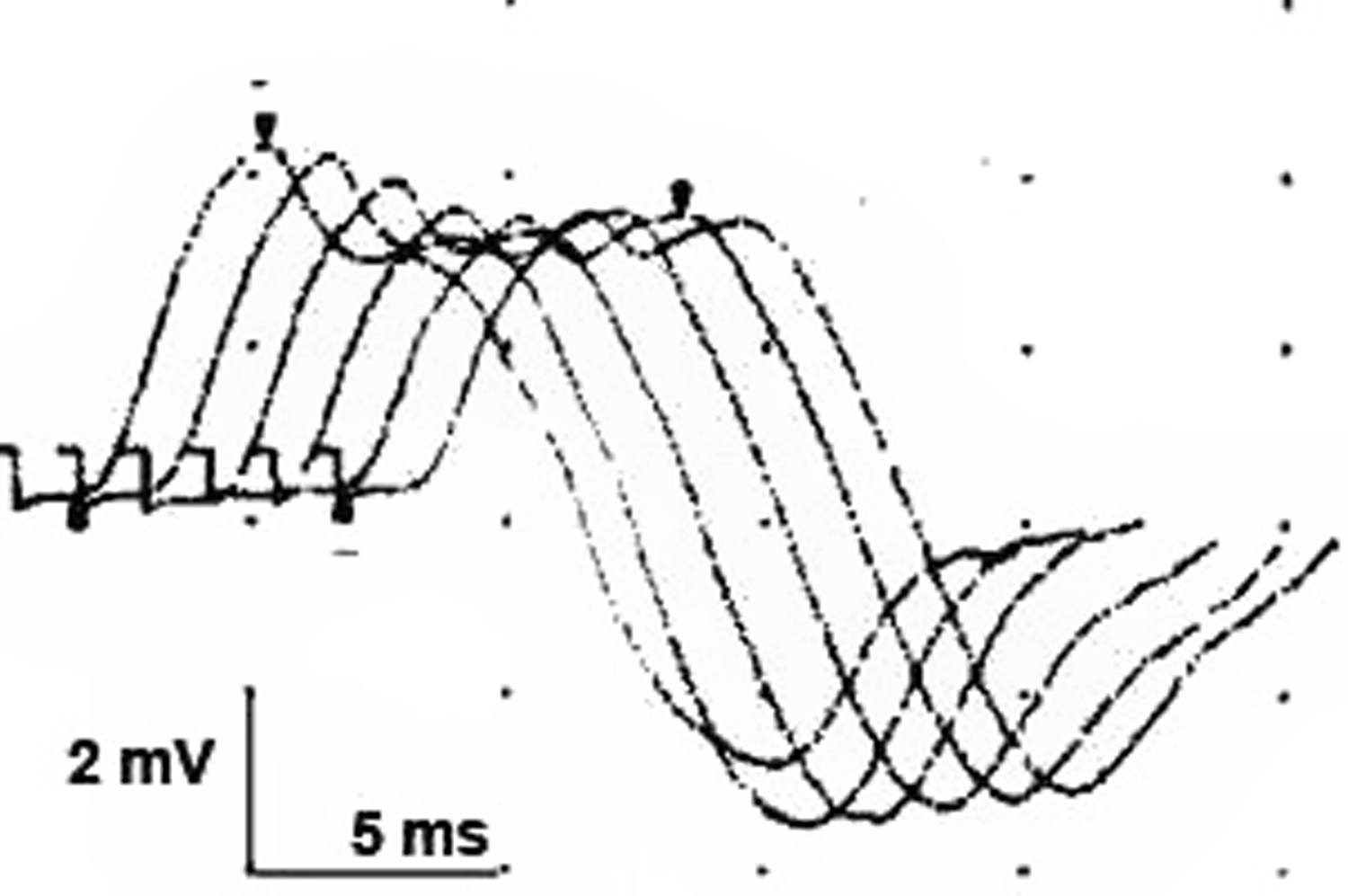
Figure 1: Repetitive conduction studies (2 Hz) of the accessory nerve recording over the right trapezius at 2 minutes post exercise. There was a 21% decline in amplitude (N < 5%) indicating a neuromuscular transmission deficit.
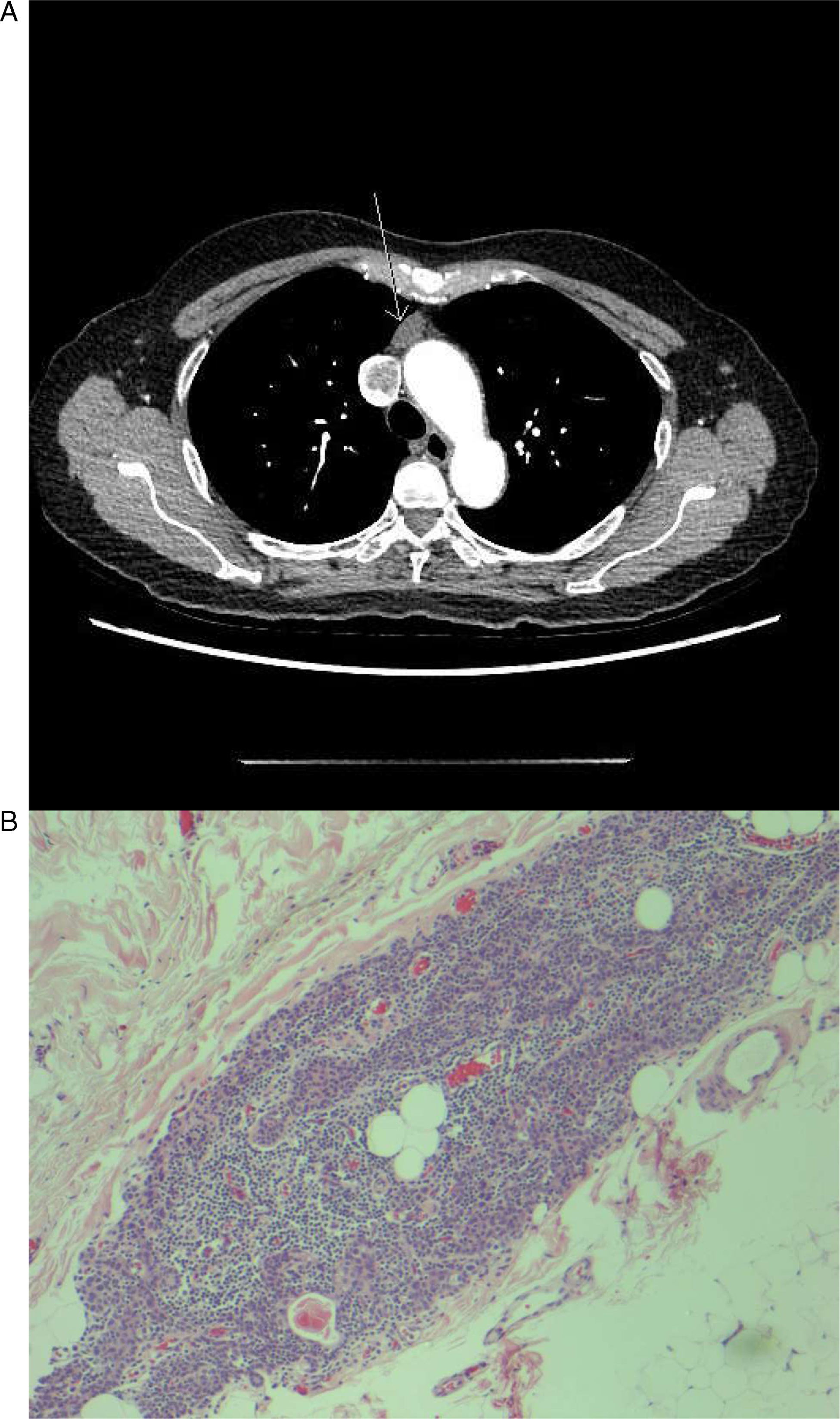
Figure 2: (a) Anterior mediastinal nodule compatible with a small thymoma (arrow) demonstrated on CT chest enhanced. (b) Pathology with hematoxylin-eosin stain demonstrating one focus of multifocal microscopic thymoma (magnification × 100).
The patient was subsequently treated with two doses of 1000mg IV rituximab. Although the combination of the above treatments was associated with largely stable symptoms for 15 months, she then had another exacerbation of MG and respiratory crisis, with no clear trigger identified. Despite the relapse, her B-cell CD-19 level remained undetectable, indicating persistent activity of the rituximab. She was again treated with five rounds of PLEX with clinical improvement. Given the refractory MG, she was started on azathioprine. Unfortunately, she developed disseminated varicella zoster virus infection approximately 3 weeks after starting azathioprine, at which point the medication was stopped. Her current treatment is as follows: monthly PLEX, prednisone 25 mg daily, and pyridostigmine 30 mg four times per day. Throughout her course, she has not displayed exaggerated nicotinic side effects or any worsening of her MG symptoms from the pyridostigmine. On her current regimen, her condition has remained stable with no diplopia, ptosis, or dysphagia – some shortness of breath on exertion remains, though this is not functionally limiting for the patient, as well as some mild finger weakness which tends to be most prominent just prior to her next scheduled appointment for PLEX. She has had no further hospitalizations from additional MG exacerbations to date.
While retaining the central feature of fatigable weakness, MuSK-MG can present quite distinctively from the more common AChR-associated MG. Reference Evoli, Alboini and Damato1 MuSK-MG is more common in young women and often presents acutely, with prominent bulbar symptoms including dysarthria, dysphagia, and dysphonia alongside weakness in axial and respiratory muscles, putting patients at risk of a potentially life-threatening respiratory crisis. Reference Evoli, Alboini and Damato1 Classically, an underlying thymic pathology is not thought to be part of MuSK-MG. Reference Evoli, Alboini and Damato1,Reference Narayanaswami, Sanders and Wolfe2 The 2020 update for the international consensus guidelines for the management of MG suggests no indication for thymectomy in patients with MuSK-MG. Reference Narayanaswami, Sanders and Wolfe2 Furthermore, a study comparing MuSK-MG patients treated with thymectomy with those not undergoing thymectomy did not find any differences with respect to clinical outcomes; however, this study did not have any cases of thymoma in their group, only thymic hyperplasia in 23% and 19% reported as unknown, with the rest being normal. Reference Clifford, Hobson-Webb and Benatar3 To our knowledge, there are four reported cases of MuSK-MG-associated thymoma to date. Reference Saka, Topcuoglu, Akkaya, Galati, Onal and Vincent4–Reference Narasimhaiah, Sreedharan, Anoop, Radhakrishnan and Poyuran7 We report the fifth patient with MuSK-MG and an associated thymoma.
Treatment for MuSK-MG generally relies on PLEX and immunosuppression, particularly with steroid therapy. Reference Evoli, Alboini and Damato1 Unfortunately, 10%–15% of patients overall with MG suffer from refractory disease, which is especially common in MuSK-MG. Reference Evoli, Alboini and Damato1 Rituximab has become an important therapeutic option in MG, with some recent data suggesting that MuSK-MG patients in particular may experience greater benefits with earlier time to remission and fewer exacerbations. Reference Litchman, Roy and Kumar8 Our patient had brittle disease requiring repeated hospitalizations, thymectomy for microscopic multifocal thymoma, and multiple therapeutic agents to achieve satisfactory control of her condition. We initiated rituximab early which did provide 15 months of clinical stability. It is unclear why she developed an MG exacerbation after sustained stability on the rituximab, given that the thymoma had been resected by this point and as such is unlikely to have contributed to further relapses. While no unequivocally established infusion protocol for rituximab in MG exists to our knowledge, and because her CD-19 level remained undetectable at that time, we felt that this could suggest persistent activity of the rituximab. We then decided to try alternative immunosuppressive agents to achieve control of her disease. Given her tolerance of and initial efficacy of rituximab treatment and the development of zoster infection on azathioprine, should she experience further relapse we would likely consider re-trial of rituximab regardless of CD-19 levels at that time. At this point our experience suggests that in cases of refractory disease, there may be a role to exclude and resect a thymoma in MuSK-MG with an expectation that it may have a potential impact on the course of MG.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr Nenad Lilic for his assistance with the pathology images.
Statement of Authorship
AB, NN, KP, KP, ZS, and DZ contributed to the conception and design of the study, acquisition of data, and analysis/interpretation of data. AB, NN, and DZ contributed to drafting the manuscript. AB, NN, KP, KP, ZS, and DZ contributed to revising the manuscript critically for important intellectual content. All authors provided approval of the version of the manuscript to be published.
Conflicts of Interest
None of the authors have any conflicts of interest to disclose.
Patient Consent
Full and informed consent was obtained from the patient for the publication of this case.




