Introduction
Eczema and psoriasis are chronic inflammatory skin conditions that present as raised, red patches on the skin that can be itchy and painful. Eczema affects up to 24.6% of children worldwide (Odhiambo et al., Reference Odhiambo, Williams, Clayton, Robertson, Asher and Group2009); psoriasis affects up to 2.1% of children worldwide (Parisi et al., Reference Parisi, Symmons, Griffiths and Ashcroft2013). Children with these skin conditions report experiencing stigmatisation, fatigue due to night-time itching, and frustration due to lengthy treatment regimens (Ablett and Thompson, Reference Ablett and Thompson2016; Bronkhorst et al., Reference Bronkhorst, Shellack and Motswaledi2016; Jager et al., Reference Jager, Kerkhof, Jong and Seyger2010; Randa et al., Reference Randa, Lomholt, Skov and Zachariae2018). Compared with children without skin disease, those with eczema and psoriasis have poorer quality of life and increased risk of developing depression and anxiety (Bronkhorst et al., Reference Bronkhorst, Shellack and Motswaledi2016; Hammer-Helmich et al., Reference Hammer-Helmich, Linneberg, Obel, Thomsen, Møllehave and Glümer2016; Kimball et al., Reference Kimball, Wu, Guérin, Yu, Tsaneva, Gupta and Mulani2012; Varni et al., Reference Varni, Globe, Gandra, Harrison, Hooper and Baumgartner2011). Furthermore, childhood eczema and psoriasis have been found to have a greater impact on quality of life than other childhood skin conditions (Beattie and Lewis-Jones, Reference Beattie and Lewis-Jones2006).
Childhood eczema or psoriasis also have a negative impact on parents and the wider family (Ablett and Thompson, Reference Ablett and Thompson2016). Parents typically need to assist with time-consuming treatments that reduce their leisure and work opportunities; they also sleep poorly due to their child’s night-time scratching, and witness their child suffering (Amaro, Reference Amaro2020; Rasmussen et al., Reference Rasmussen, Kragballe, Maindal and Lomborg2019; Tollefson et al., Reference Tollefson, Finnie, Schoch and Eton2017). Childhood skin conditions may therefore compromise parents’ mental health (i.e. increase levels of depression and anxiety) and quality of life, and increase parenting stress – defined as stress related to general parenting and specific to parenting a child with a health condition (Cousino and Hazen, Reference Cousino and Hazen2013; Faught et al., Reference Faught, Bierl, Barton and Kemp2007; Na et al., Reference Na, Chung and Simpson2019; Tollefson et al., Reference Tollefson, Finnie, Schoch and Eton2017).
Parenting stress may exacerbate child mental health and quality of life by altering parenting behaviours (Cousino and Hazen, Reference Cousino and Hazen2013; Emerson and Bögels, Reference Emerson and Bögels2017; Wan et al., Reference Wan, Song, Feng, Xiong and Zhang2015). Parenting stress has been associated with less positive parent–child interactions; for example, less warmth, and more commands and criticisms (Crnic et al., Reference Crnic, Gaze and Hoffman2005; Webster-Stratton, Reference Webster-Stratton1988). Parenting stress may also worsen a child’s skin condition. For example, parenting stress may contribute to reduced vigilance to the child’s condition and compromise adherence to treatment regimens (Wood et al., Reference Wood, Miller and Lehman2015). In this way, parenting stress can negatively impact the parent’s capacity to effectively manage their child’s condition and support their child to do so (Emerson and Bögels, Reference Emerson and Bögels2017; Bögels and Emerson, Reference Bögels and Emerson2019; Mitchell et al., Reference Mitchell, Fraser, Morawska, Ramsbotham and Yates2016; Vrijhof et al., Reference Vrijhof, Voort, IJzendoorn and Euser2018).
High levels of parenting stress have been related to adverse outcomes, such as depression and anxiety in children and their parents (Deater-Deckard, Reference Deater-Deckard1998; Fonseca et al., Reference Fonseca, Moreira and Canavarro2020), child maladaptive behaviours (Semke et al., Reference Semke, Garbacz, Kwon, Sheridan and Woods2010), and impaired cognitive development (Grunau et al., Reference Grunau, Whitfield, Petrie-Thomas, Synnes, Cepeda, Keidar, Rogers, Mackay, Hubber-Richard and Johannesen2009; Molfese et al., Reference Molfese, Rudasill, Beswick, Jacobi-Vessels, Ferguson and White2010). Increased parenting stress may also drive parents to use maladaptive parenting practices (Farmer and Lee, Reference Farmer and Lee2011). In the case of chronic conditions, parenting stress may interfere with the management of a child’s illness (Cousino and Hazen, Reference Cousino and Hazen2013; Streisand et al., Reference Streisand, Braniecki, Tercyak and Kazak2001).
Mindfulness-based interventions could potentially reduce parenting stress in parents of children with skin conditions such as eczema and psoriasis. Available evidence indicates that mindfulness interventions reduce parenting stress in parents of children with a range of mental health and developmental difficulties (Burgdorf et al., Reference Burgdorf, Szabó and Abbott2019). Furthermore, children also show reductions in a range of psychological, social and cognitive difficulties (Burgdorf et al., Reference Burgdorf, Szabó and Abbott2019), via a pathway of changed parenting practices (i.e. less reactive, more aware parenting practices; Emerson et al., Reference Emerson, Aktar, de Bruin, Potharst and Bögels2019). Thus, mindfulness-based interventions for parents have the potential to have cascading effects within the family system (Bögels and Emerson, Reference Bögels and Emerson2019). Of particular relevance are mindfulness-based interventions that aim to decrease parenting stress and increase ‘mindful parenting’: an approach to parenting that involves intentional and non-judgemental attention to the child, and regulation of the parent’s own emotion in challenging parenting situations (Kabat-Zinn and Kabat-Zinn, Reference Kabat-Zinn and Kabat-Zinn1997). As a disposition, mindful parenting is related to reduced mental health challenges in children and adolescents (Geurtzen et al., Reference Geurtzen, Scholte, Engels, Tak and van Zundert2015; Parent et al., Reference Parent, McKee, Rough and Forehand2016) and improved management of childhood chronic health conditions (Serkel-Schrama et al., Reference Serkel-Schrama, de Vries, Nieuwesteeg, Pouwer, Nyklíček, Speight and Hartman2016). Mindful parenting training has been shown to reduce parenting stress and distress, increase adaptive parenting practices, including mindful parenting, and improve child outcomes in community and mental health settings (Bögels et al., Reference Bögels, Hellemans, van Deursen, Romer and van der Meulen2014; Potharst et al., Reference Potharst, Baartmans and Bögels2021; Singh et al., Reference Singh, Lancioni, Medvedev, Hwang and Myers2021). Given these known benefits for parents and their children, mindful parenting training could be a viable approach to supporting parents of children with skin conditions (Emerson and Bögels, Reference Bögels and Emerson2019).
In this study, we aimed to investigate the effectiveness, feasibility and acceptability of a mindful parenting intervention for parents of children with eczema or psoriasis. Whilst the focus of the study was on parents, child outcomes were also collected. The Mindful Parenting training intervention (Bögels and Restifo, Reference Bögels and Restifo2013) is a parent-based adaptation of mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) for depression (Segal et al., Reference Segal, Williams and Teasdale2012) and the Mindful-Based Stress Reduction program (MBSR; Kabat-Zinn, Reference Kabat-Zinn1990). It provides experiential training to groups of parents in the application of mindfulness skills to the task of parenting; for example, responding rather than reacting to their child. We were particularly interested in the impact of this intervention on parenting stress in relation to their child’s condition as the primary outcome. To achieve our aims, we adopted a single-case experimental design, whereby parent and child wellbeing variables were assessed before, during and after the Mindful Parenting intervention. This approach enables rigorous investigation of psychological interventions – particularly those in the preliminary stage of investigation – with less resource requirements than randomised controlled trials (Smith, Reference Smith2012). Single-case design studies also enable measurement of idiosyncratic targets that are important to individual participants that, unlike randomised controlled trials, ensures that the impact of the intervention on key problems is assessed (Morley, Reference Morley2017). These idiosyncratic targets are measured daily, allowing the effects of the intervention to be examined in detail over time. We predicted that the Mindful Parenting intervention would benefit the mental health and quality of life of both the child with eczema or psoriasis, and the parent.
Method
Design
This study adopted an A-B-A1 single-group case-series design. Phase A was a 2-week baseline period. Phase B was an eight-session group intervention run over 10 weeksFootnote 1 . Phase A1 was a 6-week follow-up period that involved a single follow-up intervention session in the sixth week. The main outcome variable was idiographic parenting stress associated with the child’s skin condition. Secondary outcome variables were standardised measures of mindful parenting, parenting stress, parent anxiety, parent depression, parent quality of life, and child quality of life. Feasibility was assessed by participant retention, adherence to home practice, and treatment fidelity. Acceptability was assessed by participant evaluations of the intervention.
Participants
Seven parent–child dyads were recruited to the study; six via social media and one via a university volunteer email list. Inclusion criteria were: (i) parent aged 16 or over, (ii) child aged 4–16 years old, (iii) parent self-identified as experiencing parenting stress, and (iv) child’s primary health concern was eczema or psoriasis. Exclusion criteria were: (i) parent had active thoughts of suicide or self-harm, (ii) parent engaged in psychological therapy, (iii) parent previously attended a mindful parenting group, (iv) parent experienced psychotic episode or deliberate self-harm in last 12 months, and (v) parent experiencing physical problems that would be worsened by yoga. No participants were excluded based on these criteria. No participants dropped out from the study. Participants’ demographic information is presented in Table 1. The Mindful Parenting intervention was free for participants and travel costs were reimbursed.
Table 1. Characteristics of parents who attended the mindful parenting course, and their children

Measures
Demographic
Demographic information was collected at the start of the study. Parents reported their age, ethnicity, gender and education level; as well as their child’s age, gender and skin condition (see Table 1). Characteristics of the child’s skin condition was also collected at the start of the study (‘baseline’) and end of the study (‘follow-up’) (see Table in Supplementary material). More specifically, parents were asked to rate the child’s perceived skin severity from 0 (‘extremely mild’) to 10 (‘extremely severe’), and children were asked to report how itchy their skin was from 0 (‘not itchy at all’) to 10 (‘the worst itch imagineable’). Parents were also asked to indicate which parts of the child’s body were currently affected by their skin condition and were given the following options to choose from: ‘face/neck’, ‘scalp’, ‘hands/arms’, ‘torso’, ‘legs/feet’, ‘genital area’ and ‘other’.
Idiographic measures of parenting stress
Parenting stress was assessed by two idiographic questions that were chosen by the participants and completed each day across a baseline, intervention and follow-up period. These questions represented areas of parenting stress, associated with the child’s skin condition, that parents wanted to address. Question 1 was decrease-framed (i.e. something the parent wanted to decrease; e.g. ‘how stressed did you feel when you last applied treatment to [child]?’) and Question 2 was increase-framed (i.e. something the parent wanted to increase; e.g. ‘how calm did you feel with [child] during your last daily cream routine?’). Questions were rated on a scale from 0 (‘not at all’) to 100 (‘extremely’). Idiographic questions were completed by parents each day from baseline until the follow-up session.
Standardised measures of quality of life and distress
Parents completed measures of the following constructs at four time points (baseline, pre-intervention, post-intervention, follow-up): mindful parenting, parenting stress, depression, anxiety, and quality of life. Children also completed a measure of quality of life at the same four time points.
Parent measures
Parent’s levels of mindful parenting were assessed using the Interpersonal Mindfulness in Parenting scale (IEM-P; Duncan, Reference Duncan2007). This 10-item self-report questionnaire assesses one higher order mindful parenting factor and four first-order factors: (1) present-centered attention in parenting; (2) present-centered emotional awareness in parenting; (3) non-reactivity/low-reactivity in parenting; and (4) non-judgemental acceptance in parenting. Items are rated on 5-point Likert scales and responses to each factor are summed. Total scores range from 10 to 50, with higher scores indicating higher levels of mindful parenting. The IEM-P has demonstrated adequate reliability and validity in parents (Duncan, Reference Duncan2007).
Parenting stress was assessed using the Parenting Stress Index Short Form-4 (PSI-SF-4; Abidin, Reference Abidin1995; Abidin, Reference Abidin2012). This 36-item self-report questionnaire assesses parenting stress across three factors (parental distress, dysfunctional parent–child interactions, and difficult child) and one total stress factor (Abidin, Reference Abidin2012). Items are rated on a 5-point Likert scale and scores for each factor are summed. Total scores range from 36 to 180, with higher scores indicating higher levels of parenting stress. Scores of 115 or above suggest clinically significant levels of stress (Abidin, Reference Abidin2012). The PSI-SF-4 has demonstrated good reliability and validity (Abidin, Reference Abidin2012; Haskett et al., Reference Haskett, Ahern, Ward and Allaire2006).
Parent depression was assessed using the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9; Spitzer et al., Reference Spitzer, Kroenke and Williams1999). This 9-item self-report questionnaire assesses how bothered participants have been by a range of depression symptoms. Items are rated on a 4-point Likert scale and responses are summed. Total scores range from 0 to 27, with higher scores indicating higher levels of depression. Scores of 0–4 indicate minimal depression severity, scores of 5–9 indicate mild depression severity, scores of 10–14 indicate moderate depression severity, scores of 15–19 indicate moderately severe depression severity, and scores of 20–27 indicate severe depression (Kroenke et al., Reference Kroenke, Spitzer and Williams2001). The PHQ-9 has demonstrated good reliability and validity (Martin et al., Reference Martin, Rief, Klaiberg and Braehler2006; Spitzer et al., Reference Spitzer, Kroenke and Williams1999).
Parent anxiety was assessed using the Generalised Anxiety Disorder Questionnaire (GAD-7; Spitzer et al., Reference Spitzer, Kroenke, Williams and Löwe2006). This 7-item self-report questionnaire assesses how bothered participants have been by a range of anxiety symptoms. Items are rated on a 4-point Likert scale and responses are summed. Total scores range from 0 to 21, with higher scores indicating higher levels of anxiety. Scores of 0–4 indicate minimal anxiety severity, scores of 5–9 indicate mild anxiety severity, scores of 10–14 indicate moderate anxiety severity, and scores of 15–21 indicate severe anxiety (Spitzer et al., Reference Spitzer, Kroenke, Williams and Löwe2006). The GAD-7 has demonstrated good reliability and validity (Löwe et al., Reference Löwe, Decker, Müller, Brähler, Schellberg, Herzog and Herzberg2008; Spitzer et al., Reference Spitzer, Kroenke, Williams and Löwe2006).
Parent quality of life related to the child’s skin condition was assessed using an adapted version of the Family Dermatology Life Quality Index (FDLQI; Basra et al., Reference Basra, Sue-Ho and Finlay2007). For the current study, the phrase ‘relative/partner’s skin disease’ was changed to ‘child’s skin disease’. This self-report questionnaire consists of 10 items that are rated on a 4-point Likert scale (ranging from ‘not at all’ to ‘very much’) and are summed. Total scores range from 0 to 30, with higher scores indicating poorer quality of life. In a sample of 210 parents of children with eczema or psoriasis, the mean FDLQI score was 12.7 (SD=7.7) (Heapy et al., Reference Heapy, Norman, Emerson, Murphy, Bögels and Thompson2021). The FDLQI has demonstrated good reliability and validity (Basra et al., Reference Basra, Sue-Ho and Finlay2007).
Child measures
Children’s quality of life related to their skin condition was assessed using the Children’s Dermatology Life Quality Index (CDLQI; Lewis-Jones and Finlay, Reference Lewis-Jones and Finlay1995). This self-report questionnaire consists of 10 items that are rated on a 4-point Likert scale (ranging from ‘not at all’ to ‘very much’) and are summed. Total scores range from 0 to 30, with higher scores indicating poorer quality of life. In a sample of 180 children with eczema or psoriasis, the mean CDLQI score was 10.0 (SD=7.2) (Heapy et al., Reference Heapy, Norman, Emerson, Murphy, Bögels and Thompson2021). The CDLQI has demonstrated good reliability and validity (Lewis-Jones and Finlay, 1995). The cartoon version of the measure, which has demonstrated similar psychometric properties to the standard version, was used for those children in the current study who were 10 years old or younger (Holme et al., Reference Holme, Man, Sharpe, Dykes, Lewis-Jones and Finlay2003).
Intervention evaluation
An evaluation questionnaire assessed parents’ experiences of the intervention (based on Bögels and Restifo, Reference Bögels and Restifo2013). Quantitative data were collected on parents’ perceived change or benefits of the intervention (e.g. ‘Do you feel you’ve got something of lasting value of importance as a result of taking the training?’), home practice adherence (e.g. ‘How many times a week on average did you practise the meditation exercises during the course?’), and importance of each element of the intervention (e.g. ‘Sitting meditation in the group’). Parents also provided qualitative written responses about their experiences of the intervention (see Supplementary material for details of the evaluation form).
Procedure
Parents were first interviewed for their eligibility. In this interview, parents identified two target idiographic measures of parenting stress with the help of the interviewer. These measures were sent to them each day using an online text message service (ConnectTxt). Parents responded to the questions with numerical scores by replying to the text message. Participants completed paper copies of the standardised questionnaires. Parents attended the mindful parenting groups at the University of Sheffield. Children did not attend the groups. Parents completed the intervention evaluation form after the eighth session. Ethical approval was attained from the University of Sheffield, Psychology Department ethics committee.
Intervention description
The Mindful Parenting intervention followed the manual developed by Bögels and Restifo (Reference Bögels and Restifo2013). This group intervention consisted of eight weekly sessions and one follow-up session. Each session lasted three hours and parents were taught how to apply mindfulness to themselves and their parenting. Parents were encouraged to carry out home practice each week based on the content of each session. Each session involved a review of the home practice, a formal meditation practice (e.g. a bodyscan meditation), a mindful parenting exercise (e.g. observing your child with beginners mind), and group discussion around a theme (e.g. responding vs reacting to parenting stress).
Treatment fidelity
The intervention was led by an accredited mindfulness teacher who had completed advanced mindful parenting teacher training. The mindfulness teacher received three supervision sessions over the course of the intervention from one of the developers of the mindful parenting intervention, Professor Susan Bögels. Two sessions were video-recorded at random for fidelity review using the Mindfulness-Based Interventions Teaching Assessment Criteria (MBI:TAC; Crane et al., Reference Crane, Eames, Kuyken, Hastings, Williams, Bartley and Surawy2013), by Professor Susan Bögels. Six elements of the mindfulness teaching were assessed using criteria ranging from 1 (‘incompetent’) to 6 (‘advanced’).
Statistical analyses
Daily responses to idiographic measures were graphed in Microsoft Excel and inspected for trend, variability and consistency of data patterns (Morley, Reference Morley2017).
Idiographic data were analysed with Tau-U (Parker et al., Reference Parker, Vannest, Davis and Sauber2011) using an online calculator (Vannest et al., Reference Vannest, Parker, Gonen and Adiguzel2016). Tau-U examines percentage of data non-overlap between each of the study phases (baseline, intervention, follow-up). Baseline scores were first assessed for trend and any significant trend was corrected for. Weighted averages were also calculated for each idiographic measure using the same online calculator.
Changes in scores on secondary outcome measures (IEM-P, PSI-SF-4, FDLQI, PHQ9, GAD-7, CDLQI) between baseline, intervention, and follow-up, were investigated using Jacobson’s reliable change index (Jacobson and Truax, Reference Jacobson and Truax1991). This method demonstrates statistically reliable improvement or deterioration in standardised questionnaires. Reliable change criteria were calculated using means and standard deviations of the measures found in existing research data. The analyses were carried out using the Leeds Reliable Change Calculator (Morley and Dowzer, Reference Morley and Dowzer2014).
Quantitative scores from the intervention evaluation form were presented; qualitative responses were counted.
Results
Participant characteristics are presented in Table 1 (with additional information contained in the table found in the Supplementary material). From baseline to follow-up, perceived skin severity reduced in four children (1, 2, 6 and 7), stayed the same in one child (4), and increased in two children (3 and 5). Itch severity reduced in four children (1, 5, 6 and 7), stayed the same in one child (2), and increased in two children (3 and 4). The number of body areas affected by the skin condition reduced in three children (1, 6 and 7), stayed in the same in three children (2, 3 and 4) and increased in one child (5).
Idiographic measures
Visual analysis
See Figs 1 and 2 for the graphs of each parent’s idiographic stress responses. The mean of daily responses for each week are displayed (see Supplementary materials for graphs of daily responses).
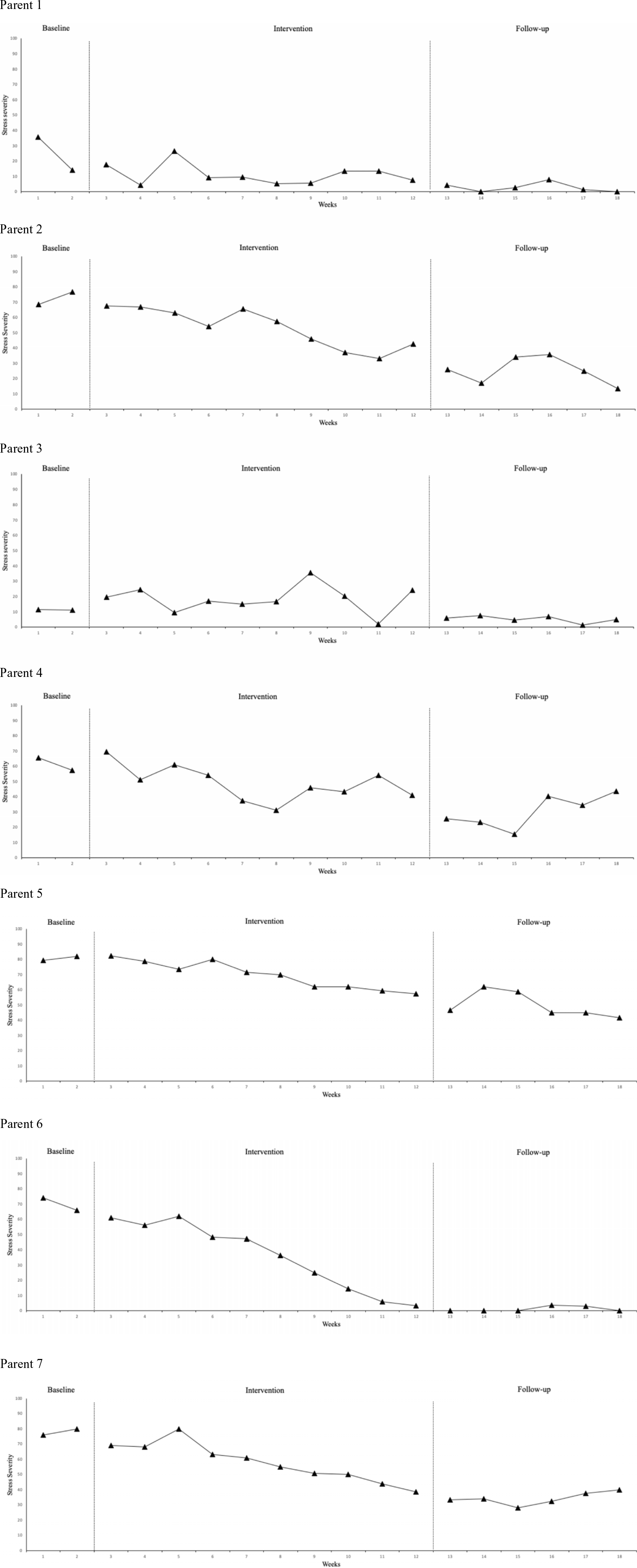
Figure 1. Weekly averages of daily scores for decrease-framed idiographic parenting stress questions (i.e. something the participant wanted to decrease; e.g. ‘how stressed did you feel when you last applied treatment to [child]?’). Higher scores indicate higher levels of parenting stress. Parents reported practising mindful exercises for the following average number of times each week: 1–2 times per week (Parents 1, 3 and 5); 3–4 times per week (Parents 2, 4 and 7); 5–7 times per week (Parent 6).
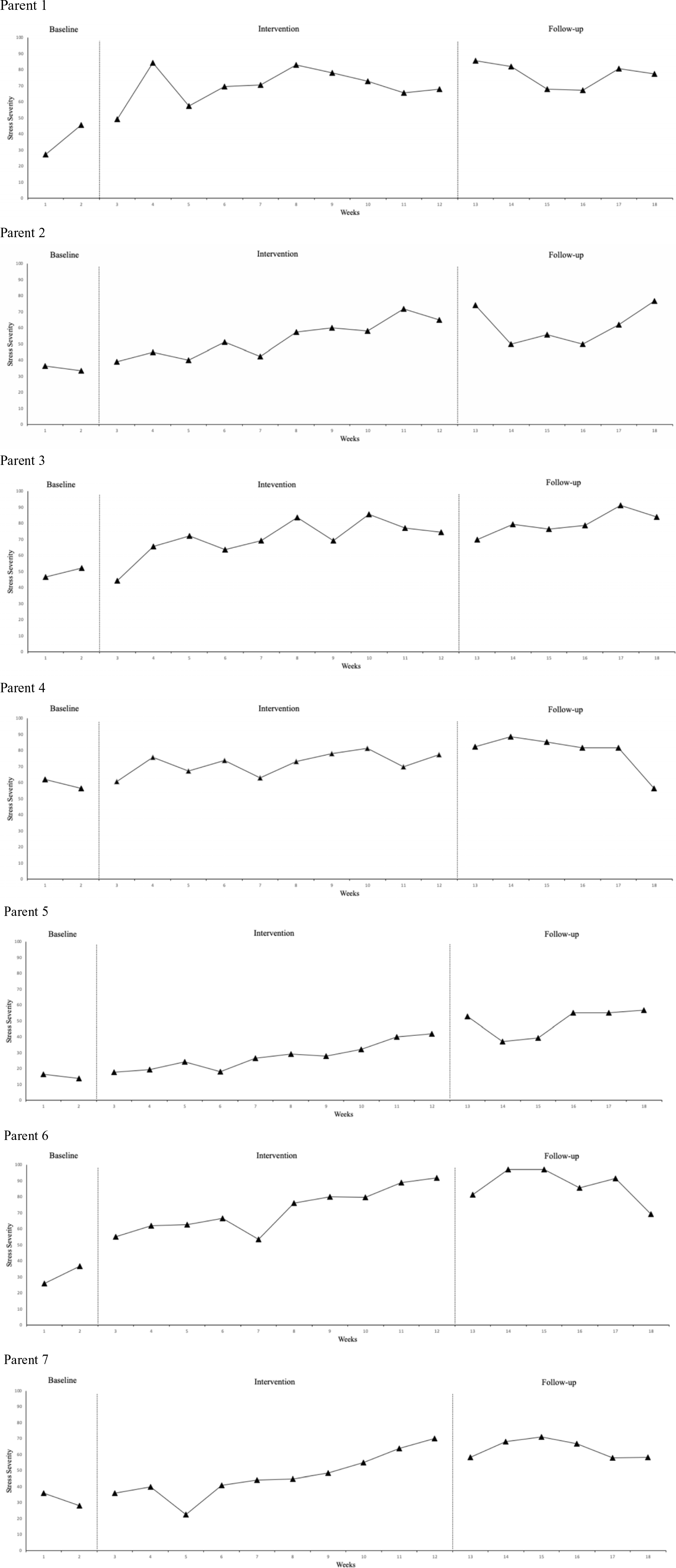
Figure 2. Weekly averages of daily scores for increase-framed idiographic parenting stress questions (i.e. something the parent wanted to increase; e.g. ‘how calm did you feel with [child] during your last daily cream routine?’). Higher scores indicate lower levels of parenting stress. Parents reported practising mindful exercises for the following average number of time each week: 1–2 times per week (Parents 1, 3 and 5); 3–4 times per week (Parents 2, 4 and 7); 5–7 times per week (Parent 6).
Question 1 – Decrease-framed idiographic parenting stress
Six of the parent participants (1, 2, 4, 5, 6 and 7) demonstrated a downward trend and reduction in the severity of their decrease-framed idiographic measure of parenting stress relative to the baseline phase across post-control phases. For Parent 1, however, this trend may have begun late in the baseline period, or early in the intervention period, and then maintained at floor level. For Parent 3 it was less clear whether there was any change in severity or trend across phases. Five of the parents (1, 2, 3, 4 and 6) showed moderate or high variability in scores in the baseline period; this reduced across post-control phases for parents 1, 3 and 6, but did not change for parents 2 and 4. Two of the parents (5 and 7) showed low variability in scores across all phases.
Question 2 – Increase-framed idiographic parenting stress
All parent participants demonstrated an improvement in the severity of their idiographic measure of parenting stress (question 2) relative to baseline phase across post-control phases.
All parents demonstrated an upward trend in idiographic measure of parenting stress (question 2) across post-control phases. Two of the parents (1 and 6) showed high variability in scores in the baseline period, but this reduced across post-control phases. Three of the parents (2, 3 and 4) showed moderate variability in scores and this did not change across phases. Two of the parents (5 and 7) showed low variability in scores across all phases.
Tau-U analysis
Four of the parent participants (2, 5, 6 and 7) demonstrated significant improvements in their decrease-framed (question 1) idiographic measure of parenting stress from baseline to intervention. Weighted average of all parents also demonstrated an overall significant improvement in parenting stress (question 1) from baseline to intervention.
All parents demonstrated significant improvements in their increase-framed (question 2) idiographic measures of parenting stress from baseline to intervention. Weighted average of all parents also demonstrated an overall significant improvement in parenting stress (question 2) from baseline to intervention.
All parents, across both questions, demonstrated significant improvement in their idiographic measures of parenting stress from baseline to follow-up (see Table 2). Weighted averages of both questions also demonstrated overall significant improvements in both idiographic measures.
Table 2. Tau-U results for each parent participant

1 Baseline trend corrected.
Standardised measures of quality of life and distress
Jacobson reliable change
The following scores were considered as reliable change for each measure: IEM-P=9; PSISF-4=15; PHQ-9=6; GAD-7=4; FDLQI=6; CDLQI=5 (see Table 3 for a summary).
Table 3. Scores at four time points across the intervention, on measures of mindful parenting, parenting stress, parent depression, parent anxiety, parent quality of life, and child quality of life
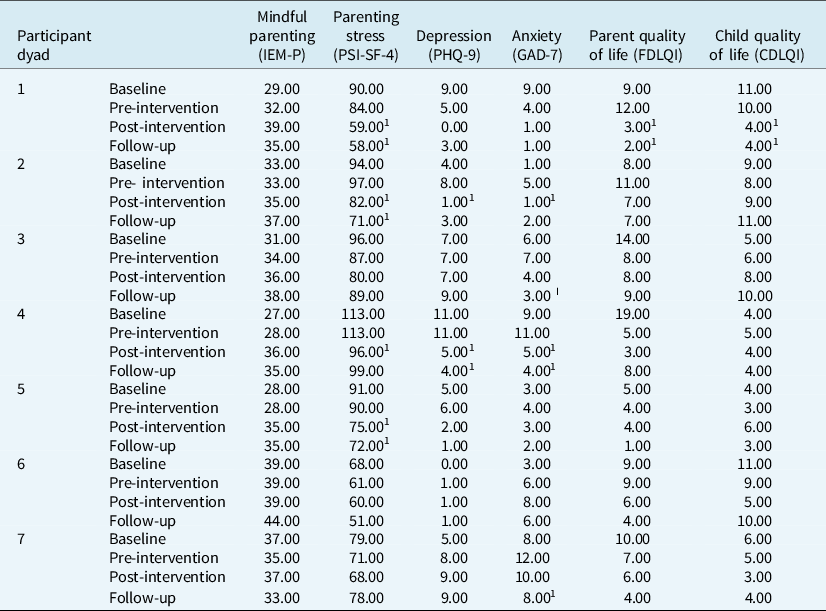
1 Indicates reliable improvement from pre-intervention score (none of the participants showed deterioration in scores from pre-intervention to post-intervention or follow-up). Possible range of questionnaire scores: PSI-SF-4 (36–180); IEM-P (10–50); PHQ-9 (0–27); GAD-7 (0–21); FDQLI (0–30); CDLQI (0–30). Higher scores indicate higher levels of parenting stress, mindful parenting, depression and anxiety. Higher scores indicate poorer parent and child quality of life.
None of the parents showed improvement in mindful parenting from pre-intervention to follow-up. Three of the parents (1, 2 and 5) showed reliable improvement in parenting stress (PSI-SF-4) from pre-intervention to follow-up. In addition, only Parent 4 showed reliable improvement in depression from pre-intervention to follow-up, and Parents 3, 4 and 7 showed reliable improvements in anxiety. Only Child 1 showed reliable improvement in quality of life from pre-intervention to follow up. None of the participants showed reliable deterioration in any of the measures.
Feasibility and acceptability
Participant retention
No participants dropped out from the intervention.
Treatment fidelity
The mindfulness teacher was rated 5 overall (‘proficient’) and scored 4 (‘competent’) or higher in each domain, confirming treatment fidelity.
Intervention evaluation
All parent participants reported that they took something of lasting value from the intervention and reported making changes in parenting. The ‘3-minute breathing space’ from the intervention was rated as being the most important technique parents learnt. None of the parents reported any negative changes due to the intervention. On average, for home practice, three parents (1, 3 and 5) reported practising 1–2 times per week; three parents (2, 4 and 7) reported practising 3–4 times a week; and 1 parent (6) reported practising 5–7 times a week. When parents were asked how important the intervention had been to them on a scale from 0 (‘not at all’) to 10 (‘extremely’), all participants scored 7 or above.
Qualitative responses
Three parent participants provided comments on the intervention content; two were positive (e.g. ‘The course content was interesting and relevant’) and one was a suggested improvement (‘Sometimes felt there could have been more content to accompany some of the sessions – more background maybe’). Three parents provided comments on the way information was presented; all were positive (e.g. ‘The combination of handouts, flipcharts, roleplay, instructions, chat and instruction was great’). Six parents provided comments on the homework expectation; all were suggested improvements (e.g. ‘I found the amount of different tasks difficult to manage/overwhelming’). Five parents provided comments on the handout content; four were positive (e.g. ‘Useful – I will refer back to these’) and one was a suggested improvement (e.g. ‘More evidence probably needed to be provided for people to go with the “schemas”’).
One further comment was provided by a parent: ‘The course was more challenging than I had anticipated, physically and emotionally draining! But so worthwhile, I’ve had experiences that will stay with me forever! My daily interactions with my children are very different and I am so grateful for that’ (see Supplementary material for further evaluation results).
Discussion
We investigated the effectiveness, feasibility and acceptability of a Mindful Parenting intervention on children with eczema or psoriasis and their parents. To achieve this, we adopted a single-case experimental design and measured parent and child wellbeing variables across a baseline period, the Mindful Parenting intervention, and follow-up period. Most parents showed improvements in idiographic measures of parenting stress from baseline to post-intervention, and all showed improvements from baseline to follow-up. In addition, six of the seven parent–child dyads showed some improvement in wellbeing from pre-intervention to post-intervention; that is, a reduction in scores on the standardised measures of either parenting stress, depression, anxiety, or an increase in quality of life. Feasibility and acceptability of the intervention were demonstrated by treatment fidelity, adherence to home practice, no participant drop-out, and positive evaluation form responses. Overall, the Mindful Parenting intervention was effective, feasible and acceptable for parents of children with eczema or psoriasis.
Our key finding was that the Mindful Parenting intervention reduced parenting stress related to raising a child with eczema or psoriasis. This reduction is probably due to a combination of factors targeted by the intervention, such as increased self-care, acceptance, effective responding to the child’s needs, and decreased reactivity to the child’s behaviour and emotions (Bögels et al., Reference Bögels, Lehtonen and Restifo2010; Emerson and Bögels, Reference Emerson and Bögels2017). Parents who incorporate the lessons of the intervention into their life, for example, may be more likely to spend time alone, relaxing, when feeling highly stressed. They may also be more likely to understand and support their child, rather than scold or criticise, when they are non-compliant with treatment regimens, which in turn leads to less conflict and less stress. Indeed, mindful parenting interventions have been shown to improve parent–child relationships (Shorey and Ng, Reference Shorey and Ng2021). In line with previous findings, reductions in parenting stress were larger at the end of the 6-week follow-up period than at the end of the intervention period, suggesting the beneficial effects of the intervention continue beyond the end of formal teaching (Burgdorf et al., Reference Burgdorf, Szabó and Abbott2019). This finding is encouraging and suggests that the intervention may provide sustained, long-term benefits. In addition, the current findings suggest a relationship between mindful practice and parenting stress. Parent 6 practised most regularly (5–7 times per week) and showed some of the largest reductions in parenting stress, whereas Parent 1 practised least regularly (1–2 times per week) and showed the smallest reductions in parenting stress. However, the small sample prevents strong conclusions from being drawn.
Mindful parenting did not increase in any parents from pre-intervention to post-intervention or follow up – a surprising finding when considering that this is the target for the intervention, and parenting stress decreased. It is possible that the intervention reduced parenting stress through an alternative mechanism to mindful parenting; for example, through regular, scheduled support from other parents. But if true, it is difficult to explain why parenting stress reduced more during the follow-up period than the intervention period, after contact with the group had ceased. More likely, this finding might be explained by the 10-item mindful parenting questionnaire used, which has demonstrated only adequate reliability and validity and may lack the sensitivity to detect changes in mindful parenting (IEM-P; Duncan, Reference Duncan2007). Future studies of mindful parenting interventions should measure mindful parenting using a more reliable and valid questionnaire, such as the adapted 29-item Interpersonal Mindfulness in Parenting Scale (IM-P; de Bruin et al., Reference de Bruin, Zijlstra, Geurtzen, Zundert, Weijer-Bergsma, Hartman and Bögels2012).
Most parent–child dyads also showed some benefit of the intervention on their wellbeing. That is, six of the seven parent–child dyads showed a decrease in the standardised measures of either parenting stress, depression or anxiety, or an increase in parent or child quality of life from pre-intervention to post-intervention or follow-up. This finding is unsurprising when considered alongside the evaluation feedback: all parents reported positive changes in dealing with the emotions of parenting, and all reported taking something of lasting value from the intervention. In those cases where improvements in wellbeing were not evident, this reflected low pre-intervention scores of participants, which left little or no room for improvement. For example, the findings suggest the intervention did not improve most children’s quality of life. However, the average pre-intervention child quality of life score was only 6.3 (from a maximum score of 30) and Child 5 scored 3 on the quality of life questionnaire, meaning a reliable reduction of 5 was impossible. Indeed, the child with the poorest quality of life (Child 1) did show improvement from pre-intervention to follow-up. Overall, the intervention was beneficial for families and this was more apparent in those with poorer baseline wellbeing.
Limitations and future directions
The small sample in this study limits the generalisability of the findings. Nevertheless, adopting a single-case experimental design is an appropriate step in rigorously investigating the effectiveness, feasibility and acceptability of the Mindful Parenting intervention in this population. Furthermore, as our methodology allowed for the measurement of idiographic, and therefore personally meaningful, outcomes, our findings are arguably particularly important in demonstrating the potential effectiveness of the intervention. Clearly, future studies should investigate the Mindful Parenting intervention in larger samples through randomised controlled trials. Participants in the current study were all highly educated, highly motivated (as they volunteered for the study), white British, and mostly female. In addition, although inclusion criteria specified that parents must be experiencing parenting stress, several parents reported low baseline levels of parenting stress on the standardardised or idiographic questionnaires, thereby limiting the relevance of the findings to highly distressed parents. Future randomised controlled trials should therefore investigate the intervention’s effectiveness in more diverse, and distressed, samples. In addition, it would be useful for future trials to assess other potential mechanisms of change, such as hopefulness and normalising of difficulties.
Most children showed some improvement in their skin condition from baseline to follow-up: either reductions in perceived skin severity, reductions in itch intensity, or reductions in the number of areas affected by the skin condition. However, these data were descriptive and therefore inferences cannot be drawn about the impact of the intervention on the child’s skin condition. Future large-scale studies would benefit from assessing perceived skin severity, objective skin severity (i.e. clinician rated) and treatment adherence, to investigate whether mindful parenting improves children’s skin through improved treatment management. Future studies may also benefit from assessing other child variables, such as depression and anxiety.
Finally, based on the evaluation feedback from participants, future mindful parenting interventions should be adapted to reduce the perceived demands of home practice on participants, for example by offering short (10 and 20 min) as well as long (30 or 40 min) audios of guided meditations. In addition, given the intensity of the intervention, future studies should examine whether the method of delivery might be altered to reduce the demands on both parents and service providers and provide greater access to this type of intervention, for example by offering the intervention in two face-to-face sessions with four online sessions in the middle, in order to reduce the amount of travelling and being away from home.
Conclusions
In conclusion, mindful parenting appears to be a potentially valuable intervention capable of reducing parent identified targets of stress, for some parents of children with eczema or psoriasis. Replicating these findings in a randomised controlled trial could benefit the large number of families worldwide who experience the negative consequences of living with childhood skin conditions.
Supplementary material
To view supplementary material for this article, please visit https://doi.org/10.1017/S1352465822000170
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author (A.R.T.). The data are not publicly available due to their containing information that could compromise the privacy of research participants.
Acknowledgements
The intervention was provided by Jane Mitchell, Mindfulness Practitioner. We would like to thank Jane for delivering the mindful parenting intervention.
Author contributions
Connor Heapy: Formal analysis (equal), Investigation (equal), Methodology (equal), Project administration (equal), Writing – original draft (equal), Writing – review & editing (equal); Paul Norman: Conceptualization (equal), Data curation (equal), Formal analysis (equal), Funding acquisition (equal), Investigation (equal), Methodology (equal), Project administration (equal), Supervision (equal), Writing – original draft (equal), Writing – review & editing (equal); Lisa-Marie Emerson: Conceptualization (equal), Funding acquisition (equal), Investigation (equal), Methodology (equal), Project administration (equal), Supervision (equal), Writing – original draft (equal), Writing – review & editing (equal); Ruth Murphy: Funding acquisition (equal), Investigation (supporting), Project administration (supporting), Supervision (supporting), Writing – original draft (supporting), Writing – review & editing (supporting); Susan Bögels: Investigation (supporting), Methodology (supporting), Supervision (supporting), Writing – original draft (equal), Writing – review & editing (equal); Andrew Thompson: Conceptualization (lead), Formal analysis (equal), Funding acquisition (lead), Investigation (equal), Methodology (equal), Project administration (equal), Supervision (equal), Writing – original draft (equal), Writing – review & editing (equal).
Financial support
The study was funded by a grant from the Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Association (PAPAA). The research team acknowledges the support of the National Institute for Health Research Clinical Research Network (NIHR CRN).
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethics statements
The authors confirm that they have abided by the Ethical Principles of Psychologists and Code of Conduct as set out by the BABCP and BPS. Ethical approval was obtained via the UK NHS ethics system and confirmation of this is available on request. All participants provided informed consent to participate in the study as required by UK NHS ethics.








Comments
No Comments have been published for this article.