1. Introduction
The Northern and Southern Patagonia Icefields cover areas of 3950 km2 (Reference Rivera, Benham, Casassa, Bamber and DowdeswellRivera and others, 2007) and 12 550 km2 (Reference Skvarca, Marinsek and AniyaSkvarca and others, 2010), respectively, forming the largest temperate ice mass in the Southern Hemisphere. Recent studies report a significant mass loss of both icefields. Their contribution to global sea-level rise (SLR) was estimated to be +0.105 ±0.011 mm a- 1 from 1995 to 2000 (Reference Rignot, Rivera and CasassaRignot and others, 2003) and +0.067 ± 0 . 0 0 4 mm a- 1 from 2000 to 2012 (Reference Willis, Melkonian, Pritchard and RiveraWillis and others, 2012) from surface elevation changes. Results from the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) also revealed a significant contribution to SLR (Reference Chen, Wilson, Tapley, Blankenship and IvinsChen and others, 2007; Reference Jacob, Wahr, Pfeffer and SwensonJacob and others, 2012). There are 17 outlet glaciers terminating in the ocean on the western side, and 35 outlet glaciers terminating in lakes mainly on the eastern side (Reference Rignot, Rivera and CasassaRignot and others, 2003). Ice discharge through these calving glaciers plays a key role in the ice mass budget. In contrast to the recent intensive research activities focusing on drastic changes in calving glaciers in Alaska, Greenland and Antarctica (e.g. Reference O’Neel, Pfeffer, Krimmel and MeierO’Neel and others, 2005; Reference Howat, Smith, Joughin and ScambosHowat and others, 2008; Reference Pritchard, Arthern, Vaughan and EdwardsPritchard and others, 2009), only a few reliable observations have been carried out in Patagonia. This leaves considerable uncertainty concerning the future contribution of the Patagonia Icefields to sea-level rise. Observations of the front positions, ice thickness and flow velocities of calving glaciers in the Patagonia Icefields are instrumental in improving our understanding of the current status and future evolution of the Patagonia Icefields. It is necessary to increase the observational data on calving glaciers in terms of their front positions, ice thickness and ice flow velocity.
Several processes have been proposed as possible drivers of the rapid changes of calving glaciers observed in Greenland, Alaska and other regions. The first hypothesis starts with changes occurring at the terminus (e.g. retreat, thinning, disintegration of floating tongues, trigger reduction in along-flow resistive stresses) (Reference Joughin, Abdalati and FahnestockJoughin and others, 2004; Reference ThomasThomas, 2004; Reference Howat, Joughin, Tulaczyk and GogineniHowat and others, 2005). An imbalanced stress regime then leads to faster ice flow, thinning and steepening in surface slope that propagate rapidly upstream, resulting in further retreat of the glacier. Such a change in the stress regime may be controlled by basal overdeepening in a fjord (Reference Howat, Joughin and ScambosHowat and others, 2007; Reference Nick, Vieli, Howat and JoughinNick and others, 2009). Another important process is meltwater input to the glacier bed, which potentially changes glacier dynamics as elevated subglacial water pressure enhances basal ice motion (e.g. Reference Iken and BindschadlerIken and Bindschadler, 1986; Reference Iken and TrufferIken and Truffer, 1997; Reference SugiyamaSugiyama and others, 2011). The amount of meltwater increases under warming climate conditions, potentially resulting in glacier acceleration, thinning and retreat (Reference Zwally, Abdalati, Herring, Larson, Saba and SteffenZwally and others, 2002; Reference Parizek and AlleyParizek and Alley, 2004). Water surface conditions in front of a calving glacier also play a role. A likely interpretation of seasonal frontal variations observed at Greenland tidewater glaciers is the presence and disappearance of ice melange covering the ocean, which is controlled by sea surface temperature. (Reference JoughinJoughin and others, 2008; Reference Amundson, Fahnestock, Truffer, Brown, Luthi and MotykaAmundson and others, 2010; Reference Howat, Box, Ahn, Herrington and McFaddenHowat and others, 2010). These hypotheses proposed in previous studies are useful in interpreting the drivers of rapid changes in tidewater glaciers. For example, the retreat of many calving glaciers along the Greenland coast in 2002 and 2003 can be understood as a result of climatic and/or ocean forcing rather than the influences of surface and basal geometries (e.g. Reference Howat, Box, Ahn, Herrington and McFaddenHowat and others, 2010). Nevertheless, only a few studies have been carried out on freshwater calving glaciers so far, despite the fact that many of these have also undergone rapid retreat.
To study recent changes in a large calving glacier in Patagonia, we measured the front positions, surface elevation and ice velocity of Glaciar Upsala, one of the largest glaciers in the Southern Patagonia Icefield, using satellite images taken from 2000 to 2011. The migration of the frontal margin was tracked at 97–272 day intervals. The surface elevation change was obtained by comparing high-resolution digital elevation models (DEMs) derived from stereographic satellite image pairs. This paper reports recent rapid retreat, thinning and acceleration revealed by these analyses, and discusses the role of glacier dynamics in the observed drastic recession of Glaciar Upsala.
2. Study Site
Glaciar Upsala is located on the eastern side of the Southern Patagonia Icefield and is the third largest glacier in South America, at 840 km2 in area and 54 km in length, as measured in 2011 (Skvarca, unpublished data). It has flowed at a rate of >1600ma–1 near the terminus (Reference Skvarca, Raup and De AngelisSkvarca and others, 2003), discharging ice into Brazo Upsala of Lago (lake) Argentino, with an estimated calving flux of 0.47– 1.47 km3 a–1 (Reference Naruse, Aniya, Skvarca and CasassaNaruse and others, 1995) (Fig. 1a). From 1978 to 2000 it underwent rapid retreat (Reference Aniya and SkvarcaAniya and Skvarca, 1992; Reference Skvarca, Satow, Naruse and LeivaSkvarca and others, 1995, Reference Skvarca, De Angelis, Naruse, Warren and Aniya2002; Reference Naruse, Skvarca and TakeuchiNaruse and others, 1997; Reference Aniya, Dhakal, Park and NaruseAniya and others, 2000). During a retreat of 1200 m from 1990 to 1993, it thinned at an average rate of 11 m a–1 at the 1993 terminus position (Reference Skvarca, Satow, Naruse and LeivaSkvarca and others, 1995).

Fig. 1. (a) Landsat 7 ETM+ band 8 mosaic image of Southern Patagonia Icefield acquired on 14 October 2001. Study area is indicated by the box. (b) Frontal margins of Glaciar Upsala as observed from 7 July 2000 to 3 May 2011. Background is a Landsat 7 ETM+ band 1 image acquired on 3 May 2011. Boxes indicate ice velocity measurement sites. Surface elevation shown in Figure 6 was evaluated along the white line.
3. Methods
3.1. Glacier front position
We mapped glacier frontal margins from 7 July 2000 to 3 May 2011, using 22 images from the Landsat 7 Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus (ETM+), band 8, with a processing level of 1T (geometrically corrected data) (Table 1). The image resolution was 15 m, and an error associated with the uncertainty of the margin was about ±15 m. The cumulative distance of glacier retreat since July 2000 was measured by taking the northward displacement of the width-averaged calving front position.
Table 1. Satellite images used in this study
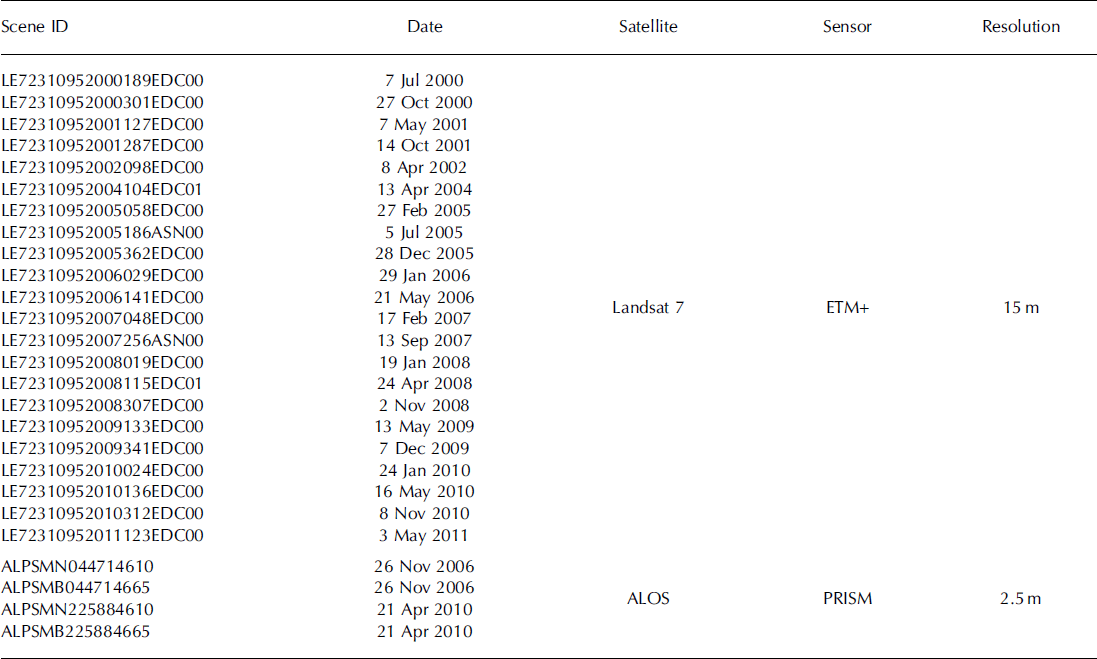
3.2. Ice velocity
Surface velocity was measured from 7 May 2001 to 3 May 2011 using 16 pairs of Landsat 7 ETM+ images (Table 1). Temporal separations of the image pairs were 97-272 days. We measured the velocity by tracking characteristic surface features such as crevasses and seracs. We defined three velocity targets within four survey sites defined by squares located at 2.7, 4.6, 6.0 and 7.7 km from the terminus (Fig. 1b). The velocity was calculated from the mean displacement of the three targets at each site. According to the image resolution (15 m), the error in the target location was ±11 m, corresponding to a velocity uncertainty of ±15-41 ma– 1 . Velocities obtained for the period 7 May-14 October 2001 agreed within 8% with the annual velocity reported for 2000/01 by Reference Skvarca, Raup and De AngelisSkvarca and others (2003).
3.3. Surface elevation
Changes in ice surface elevation from February 2000 to 26 November 2006, and to 21 April 2010 were measured by differentiating a DEM from the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) and those produced in this study. We produced DEMs for 26 November 2006 and 21 April 2010 by using stereo pairs of satellite images obtained by Panchromatic Remote-sensing Instruments for Stereo Mapping (PRISM) mounted on the Japanese Advanced Land Observing Satellite (ALOS) (Table 1). The nadir- and backward-looking images with a processing level of 1B2 (geometrically corrected data) were distributed with RPC (rational polynomial coefficient) files by the Remote Sensing Technology Centre of Japan (RESTEC). Root-mean-square errors of ALOS PRISM RPC were 0.5-10 m, and typically in the range 1-5 m. The accuracy of the elevation change presented in this paper relies on the quality of the DEMs generated from ALOS PRISM images. We processed the stereo images with the aid of the Leica Photogrammetric Suite (LPS) in the ERDAS IMAGINE workstation. After the generation of DEMs using an automated routine, we edited the elevation data referring to stereoscopic three-dimensional images by LPS. This manual correction process is important in order to improve the accuracy of the DEMs. More details of the DEM generation procedure are given by Reference Lamsal, Sawagaki and WatanabeLamsal and others (2011). The resolution of the ALOS DEMs was 10 m.
In addition to the ALOS DEMs, we used a DEM based on interferometric synthetic aperture radar measurements during SRTM in February 2000. This dataset covers an area from 60° N to 57° S (http://eros.usgs.gov/) with a 3" resolution and a geocoding accuracy of ±12.6 m (Reference FarrFarr and others, 2007). The resolution of the DEM after a projection on the studied area was 76m. The ALOS DEMs were interpolated at gridpoints of the SRTM DEM using a bilinear interpolation scheme to compute elevation changes.
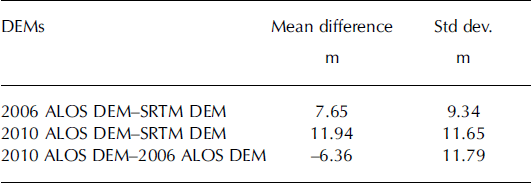
Errors in the DEMs were assessed by comparing elevations within 54 km2 rock outcrops surrounding Glaciar Upsala, where elevation changes are negligible. Mean elevation difference and standard deviations were computed for each pair of DEMs as listed in Table 2. The glacier surface has significantly more distinctive features than the neighbouring ice-free terrain, which is favourable for stereo image processing. Thus, we expect smaller errors on the glacier than the values estimated. Systematic errors were removed by correcting the ALOS DEMs for the elevation difference from the SRTM DEM averaged over the compared region. After this correction, random errors represented by the standard deviations were 9.3–11.8 m.
Table 2. Deviation of surface elevation from one DEM to the other evaluated over the rock outcrops neighbouring Glaciar Upsala
4. Results
4.1. Glacier retreat
Figure 1b shows the migration of the glacier front from 7 July 2000 to 3 May 2011. The front position was relatively stable until January 2008, particularly near the side margins. From January to November 2008, the eastern half of the glacier retreated by 1540 m and lost 1.78 km2 of ice. The western side retreated by a similar distance in the following years 2009 and 2010, whereas the front position at the eastern margin remained at approximately the same location over these 2 years. The glacier has retreated progressively, and in May 2011 reached the confluence area, where Glaciar Bertacchi merges with the main stream. The retreat distance from January 2008 to May 2011 was 2890 m.
Cumulative retreat distance since 2000 is shown in Figure 2. The retreat rate was 90ma–1 for the period May 2000–January 2008, followed by a sudden increase to a rate of 880 ma–1 from January 2008 to May 2011. The latest two images, taken in November 2010 and May 2011, give an even larger rate of 2000 m a–1. Seasonal signals are recognized in the retreat in 2009 and 2010. After a small advance over the May–December 2009 austral winter, the glacier retreated by 930 m during the December 2009–May 2010 summer. It advanced again by 250m during May–November 2010, followed by a 940m retreat from November 2010 to May 2011.
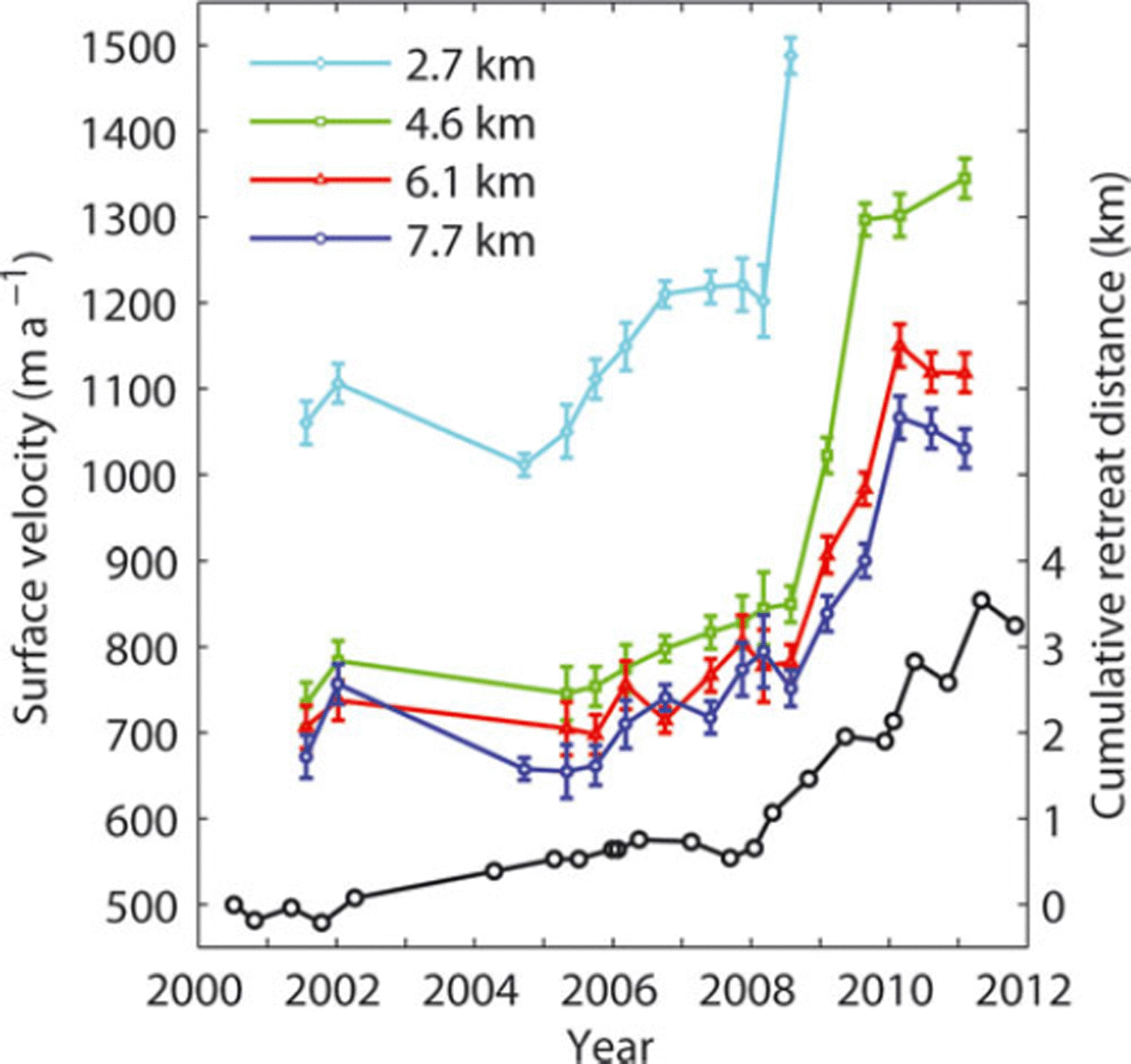
Fig. 2. Ice surface velocities of Glaciar Upsala between 7 May 2001 and 3 May 2011 measured at four locations along the glacier as indicated in Figure 1b (coloured lines to the left axis). The error bars were based on the estimated uncertainty in the feature-tracking method. Heavy crevasses at 2.7 km from the terminus after November 2008 prevented the tracking of surface features. Cumulative retreat distance since 7 July 2000 (black line to the right axis).
4.2. Ice velocity change
The rapid retreat since 2008 was associated with acceleration in the surface velocity (Fig. 2). In 2008, the velocity sharply increased at the four measurement sites. It increased by 24% at the lowermost site (2.7 km) from January to April. This change took place within a few months of the onset of rapid retreat and preceded the acceleration at the other sites. At the 4.6 km site, significant velocity change began after April 2008 and the ice accelerated by >50% by May 2009. Acceleration of a similar magnitude was observed at the upper two sites: 47% and 43% at the 6.0 and 7.7km sites, respectively. Acceleration ceased at the 4.6 km site after May 2009, while at the upper sites it lasted until December 2009. Velocities have remained steady since 2010 at the elevated level with respect to the pre-2008 velocity.
4.3. Surface elevation change
Surface elevation dropped significantly during the period including the rapid retreat and acceleration (Fig. 3a). From 26 November 2006 to 21 April 2010, ice surface elevation change averaged over the area was -45.7 m (-13.4 m a-1). The magnitude of the elevation change was greater near the terminus, but decreased down-glacier in the vicinity of the calving front at <200ma.s.l. (Fig. 4). The greatest change was observed at 1200 m from the calving front, corresponding to a rate of - 3 9 . 1 ma–1. If we assume the elevation change was due exclusively to ice thickness change, 5.90 km3 (1.73 km3 a-1) of ice was lost over the studied 129 km2.

Fig. 3. (a) The rate of surface elevation change over Glaciar Upsala between 26 November 2006 and 21 April 2010. The glacier margin was determined from the satellite image in 2010. (b) Same as (a) for the period February 2000 to 26 November 2006. The glacier margin was determined from the satellite image in 2006.
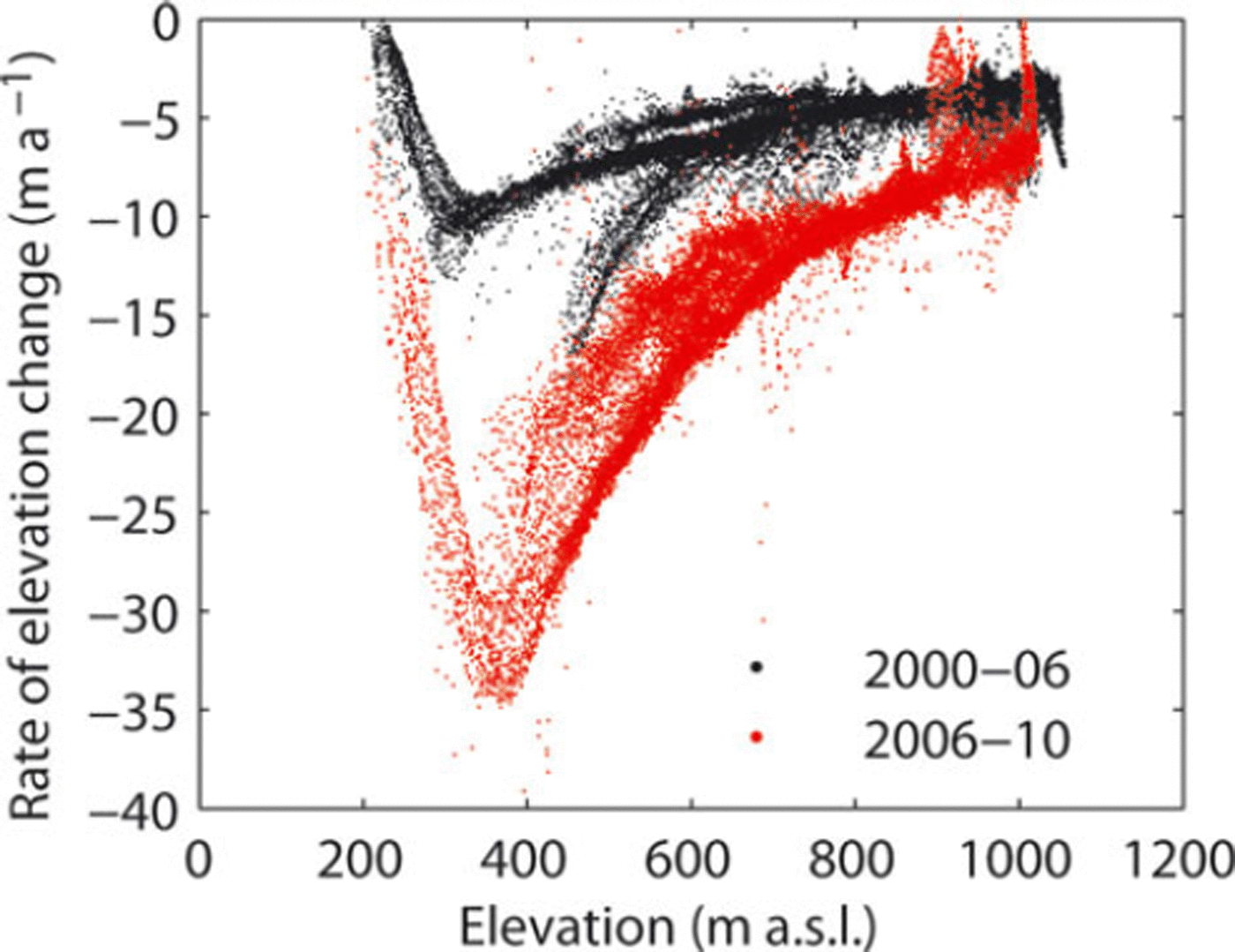
Fig. 4. The rate of surface elevation change over the regions shown in Figure 3a and b. The black and red dots represent elevation changes over the periods 2000–06 and 2006–10 respectively, evaluated at the gridpoints of the SRTM DEM. The elevation in the abscissa corresponds to the values in 2000 and 2006, respectively. across the glacier, i.e. initial retreat near the eastern margin from January to November 2008, followed by the larger ice loss in the middle and western side of the glacier, was due to a spatial pattern of the bedrock elevation. Similar irregular patterns of the calving front profile have been observed at Glaciar Upsala over the course of its retreat (Reference Aniya and SkvarcaAniya and Skvarca, 1992; Reference Skvarca, De Angelis, Naruse, Warren and AniyaSkvarca and others, 2002).
The elevation had been lowering even before the rapid retreat, but at a lower rate. From February 2000 to 26 November 2006, elevation change averaged over the area was -37.5 m (–4.7ma–1), which is equivalent to ice volume loss of 4.84 km3 (0.61 km3 a-1) over the studied 129 km2. This result indicated that the rate of change has increased by 185% from 2000-06 to 2006-10. Within 2000 m of the calving front, the magnitude of the change was greater near the side margins than in the central part of the glacier (Fig. 3b).
5. Discussion
Glaciar Upsala retreated throughout the 20th century (Reference Warren, Greene and GlasserWarren and others, 1995), and several major retreat events have been observed during recent decades. Nevertheless, the event revealed in this study is distinct from those reported in the past. The glacier retreated rapidly from 1981 to 1984 by 1.0 km at a rate of 150-525 m a - 1 , from 1990 to 1993 by 1.2 km at 400 m a- 1 , and from 1996 to 1999 by 1.5 km at 820 m a- 1 (Reference Aniya and SkvarcaAniya and Skvarca, 1992; Reference Skvarca, Satow, Naruse and LeivaSkvarca and others, 1995; Reference Naruse and SkvarcaNaruse and Skvarca, 2000). The 2.9 km retreat from 2008 to 2011 is greater than these previous observations in terms of magnitude and rate. The sudden transition from a period of relatively stable front position to rapid retreat in 2008 is similar to the observation in the 1980s. After small retreat and advance from 1968 to 1978 (230 m retreat over the period), the glacier went into a phase of rapid recession interrupted by periods of relatively slow retreat (Reference Naruse and SkvarcaNaruse and Skvarca, 2000). This transition cannot be attributed to climate change since no significant change has been observed on other glaciers of the Southern Patagonia Icefield (Reference AniyaAniya, 1999). In the case of the transition in 2008, monthly averaged air temperatures at Estancia Cristina (498580S, 738070W; 192 ma.s.l.), located ∼12km from Glaciar Upsala, were in 2008 and 2009 within the range of annual variation since 2001 (Fig. 5). The mean temperature has slightly increased over the past decade, but is not correlated with the retreat distance (Fig. 2) and does not show a remarkable transition in 2008. We collected this temperature dataset, recorded at hourly intervals, using an Ondotori Thermo Recorder, Model TR-52 (TASHIKA, JAPAN), installed at 2 m above the rock surface. Reference Naruse, Skvarca and TakeuchiNaruse and others (1997) argued that the temporally non-uniform recession of Glaciar Upsala was not related to climate variability, but was due to the change in the longitudinal stress exerted by the bedrock near the glacier front. Such a change takes place when the terminus retreats over a bedrock rise into deeper water along a reversed bed slope. Numerical studies also indicate that previously observed frontal variations of calving glaciers are primarily controlled by bedrock undulations (Reference Vieli, Jania and KolondraVieli and others, 2002; Reference Nick, Vieli, Howat and JoughinNick and others, 2009). It is also likely that the non-uniform retreat.
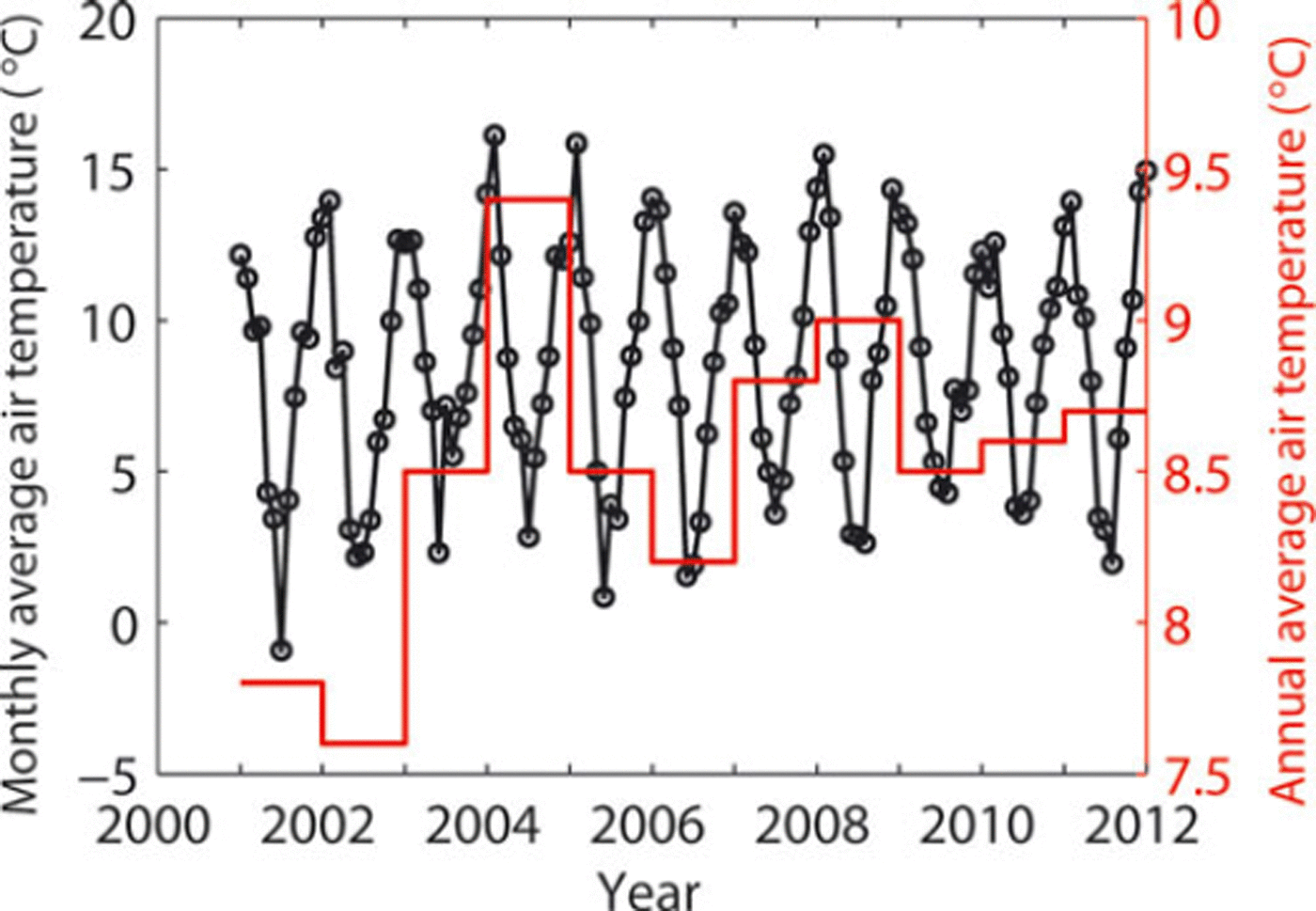
Fig. 5. Monthly average air temperatures from 2001 to 2012 at Estancia Cristina, located ∼12km from Glaciar Upsala.
In Patagonia, high-frequency ice velocity measurements are very rare, and acceleration associated with glacier retreat has never been resolved in the past. Our observations confirm the vital role of changing glacier dynamics in the evolution of calving glaciers in Patagonia and in the mass change of the icefields as suggested by Reference Rignot, Rivera and CasassaRignot and others (2003). The close agreement between the onsets of retreat and acceleration is consistent with the hypothesis that the speed-up was triggered by back-stress reduction due to the detachment of the ice front from a bedrock rise. According to the bathymetry of Brazo Upsala (Reference Skvarca, De Angelis, Naruse, Warren and AniyaSkvarca and others, 2002), the lake floor inclines ∼38 down-glacier from the 2000 ice front position to the 3 km lower reaches (Fig. 6). The bathymetry is available only up to the 2000 front position, but the lake is plausibly deepening up-glacier as an overdeepening is expected at the confluence area, where Glaciar Bertacchi merges from the west. Figure 7 shows details of speed-up propagation upstream and resulting changes in the flow regime. The speed-up began near the glacier front and subsequently propagated up-glacier, reaching a point 7.7 km behind the front within 1 year. Accordingly, the velocity gradient along the glacier first increased between the 2.7 and 4.6 km sites and later in the upper reaches. Longitudinal strain rate between the 2.7 and 4.6 km sites increased by 79% (from 0.19 a- 1 to 0.34 a-1) after April 2008, whereas the strain rate between the 4.6 and 7.7 km sites increased by 233% (from 0.03 a- 1 to 0.10 a-1) from April-November 2008 to November 2010-May 2011. Thus, ice was significantly thinning as a result of compressive vertical straining during these periods. These observations suggest that the initial acceleration results in ice thinning near the terminus, which steepens the ice surface and increases the driving stress, leading to acceleration in the upper reaches (Reference Nick, Vieli, Howat and JoughinNick and others, 2009). In fact, glacier surface inclination over the lower 10 km increased from 2.508 in 2006 to 2.698 in 2010, whereas it changed little from 2000 to 2006 (Fig. 6) Moreover, the thinning also enhances basal ice motion as the effective pressure decreases at the bed (Reference SugiyamaSugiyama and others, 2011).
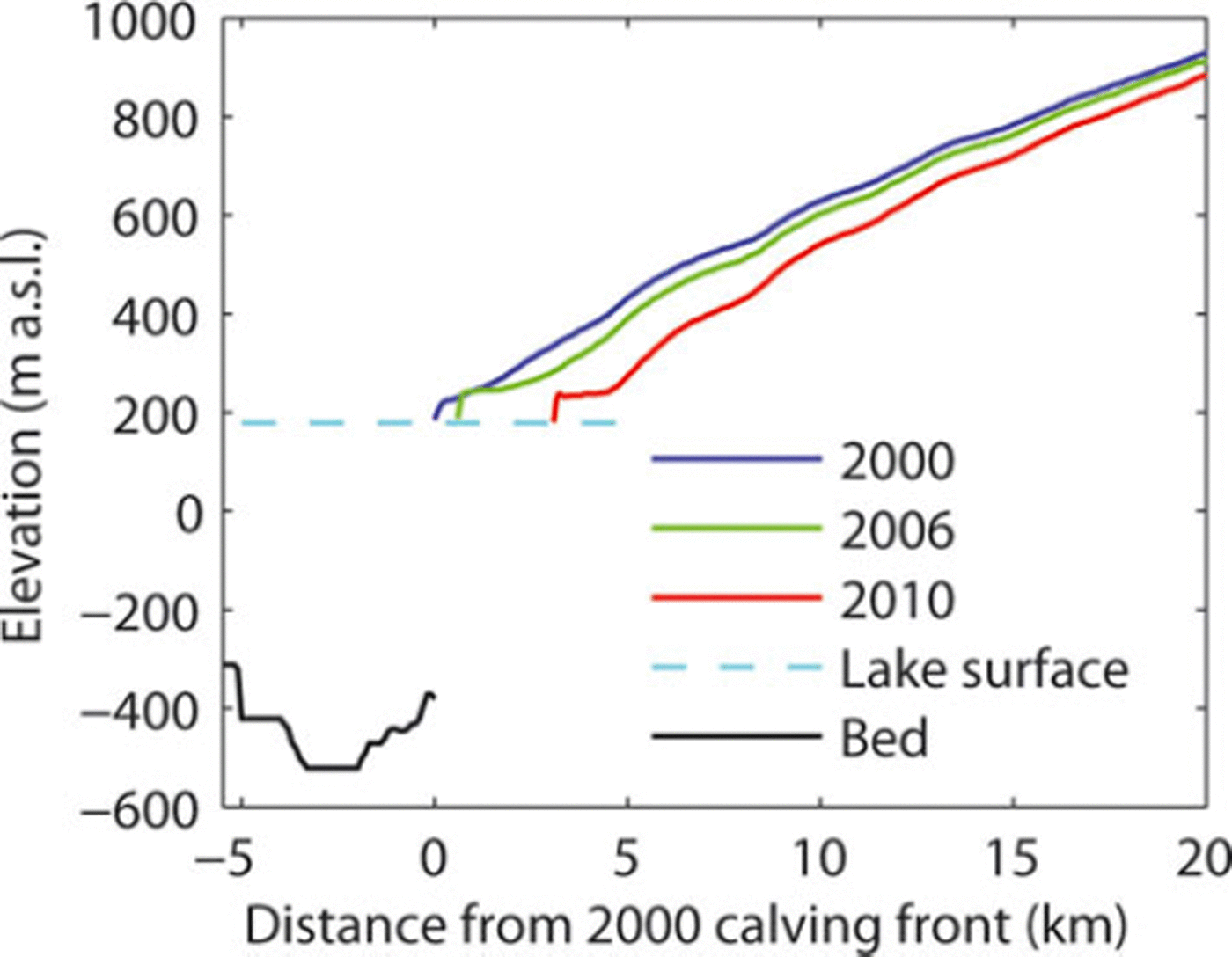
Fig. 6. Glacier surface elevation along the white line in Figure 1b. The black line indicates the lake bed elevation reported by Reference Skvarca, De Angelis, Naruse, Warren and AniyaSkvarca and others (2002).
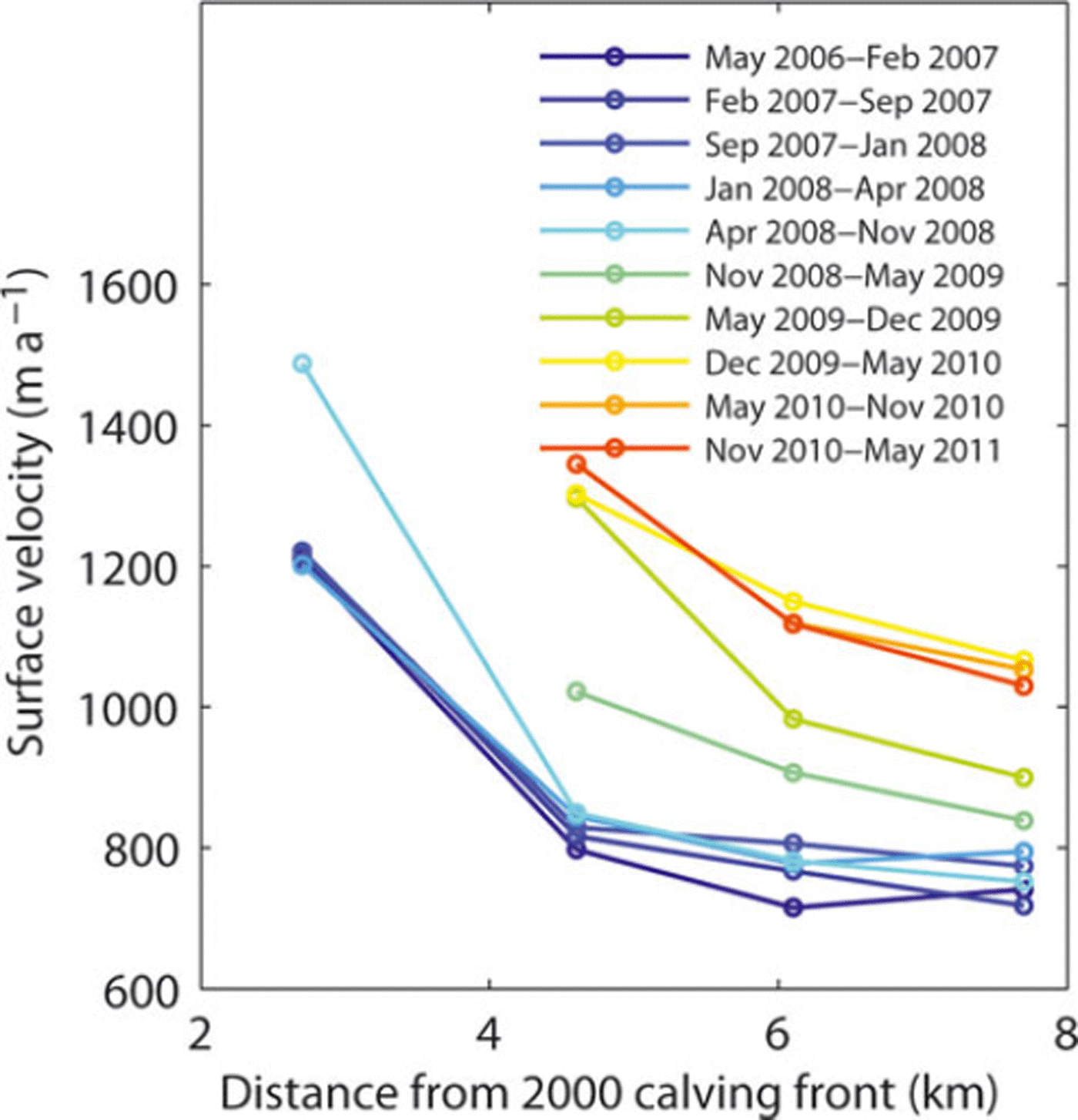
Fig. 7. Ice surface velocity measured from 2006 to 2011 at the locations indicated in Figure 1b.
Average surface elevation change of -11.1m a- 1 was measured previously at Glaciar Upsala during the 1990-93 retreat (Reference Skvarca, Satow, Naruse and LeivaSkvarca and others, 1995; Reference Naruse, Skvarca and TakeuchiNaruse and others, 1997). Because this measurement was performed at 1-2 km from the terminus where the largest change was expected, the rate of -13.4 m a- 1 from 2006 to 2010 as a mean for the region extending over 16km from the terminus is substantially larger. Surface ablation at the glacier front was estimated to be 14 ±2ma–1 , with annual variations of ± 2 m a - 1 (Reference Naruse, Skvarca and TakeuchiNaruse and others, 1997). Thus, mass-balance variation related to climate change cannot explain the observed elevation change. It is most likely that ice is thinning under the influence of the changing longitudinal strain rate caused by the velocity change (e.g. Reference Thomas, Abdalati, Frederick, Krabill, Manizade and SteffenThomas and others, 2003). A clear indication of the dynamically controlled ice thickness change was the elevation change peaking at 1.4 km from the 2011 front position (Figs 3a and 6). Presumably, the effect of the longitudinal velocity gradient, i.e. longitudinal strain rate, on the ice thickness change was greatest at this location. The reduction in elevation change near the terminus also suggested that part of the ice thinning might have been compensated for by uplift due to flotation. The possibility of a floating terminus has been pointed out previously, based on the bathymetry of the lake and height of the calving cliff (Reference Naruse and SkvarcaNaruse and Skvarca, 2000). The height of the ice cliff at the calving front was 51 m as measured with the 2010 DEM, which indicates that 516 m water depth is sufficient for terminus flotation. This condition is met if the lake floor slopes up-glacier from the 2000 terminus position.
Despite the difference between calving into fresh- or tidewater, our observations at Glaciar Upsala have many similarities with rapid changes reported in outlet glaciers of the Greenland ice sheet. Many tidewater calving glaciers in Greenland have shown a sudden transition from a quiescent phase to rapid retreat, thinning and acceleration during the last decade (e.g. Reference Rignot and KanagaratnamRignot and Kanagaratnam, 2006; Reference McFadden, Howat, Joughin, Smith and AhnMcFadden and others, 2011). One example is Helheim Glacier, the fastest-flowing outlet glacier along the eastern margin of the ice sheet (Reference Rignot, Braaten, Gogineni, Krabill and McConnellRignot and others, 2004). From 2001 to 2005, this glacier retreated at a rate of 1.8 km a- 1 , accelerated by 26% and thinned at a rate of 27 m a- 1 within 5 km of the terminus (Reference Howat, Smith, Joughin and ScambosHowat and others, 2008). Another example is Columbia Glacier, a fast-flowing outlet glacier in Alaska. Columbia Glacier began its rapid retreat in 1982, and the greatest retreat occurred in 1993 (1.2 km a-1). Velocity at the terminus increased from 5 md– 1 to >27md– 1 between 1980 and 2001. During the acceleration and retreat, the glacier thinned by >320m from 1982 to 2001 (Reference O’Neel, Pfeffer, Krimmel and MeierO’Neel and others, 2005). These values are comparable to those of Glaciar Upsala observed after 2008. Thus, collecting data from other calving glaciers and understanding the mechanism of their dynamic behaviour are of crucial importance for evaluating the current and future ice mass change in Patagonia.
6. Conclusions
We analysed satellite images acquired during the period 2000–11 to quantify recent changes in front position, ice speed and thickness of Glaciar Upsala, one of the largest freshwater calving glaciers in Patagonia. The results showed a clear transition in 2008 from a period of relatively stable front position (670m retreat from 2000 to 2008) to rapid recession (2890m retreat from 2008 to 2011). The retreat phase continues in 2011. The rate of retreat in 2008–10 was 880 m a–1, which is about ten times larger than in 2000–08, resulting in one of the most significant retreat events observed at this glacier. The rapid retreat was associated with ice flow acceleration, initiated near the calving front and propagated up-glacier. The glacier sped up by 20–50% in the region extending 7.7 km from the calving front. We also observed substantial ice thinning from 2006 to 2010, at a maximum rate of 39 ma–1 near the terminus, and a mean of 13.4 m a–1 over the area extending 16 km from the terminus. The rate of ice mass loss during this period was 1.73 km3 a–1, i.e. a total of 5.90 km3 during the 3.4 years within the analysed 129 km2. Our data indicate that the magnitude and the rate of glacier change at Glaciar Upsala are similar to those reported in large tidewater glaciers in Greenland. It is thus crucial to study the variations of other calving glaciers in order to quantify the ice mass loss of the Patagonia Icefields.
Acknowledgements
Landsat images were downloaded from http://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ and SRTM DEM from http://eros.usgs.gov/. We thank T. Yamanokuchi and T. Fukuda for help with the satellite data analysis. The manuscript was improved by the comments of R. Naruse and M. Aniya. This research was funded by the Japanese Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture through Grant-in-Aid 23403006 (2011–14) and the Global COE Program (Establishment of Center for Integrated Field Environmental Science). Financial support was also provided by Direccion Nacional del Antartico–Instituto Antartico Argentino through the project Ice–Climate Interaction and Glacier Dynamics on Antarctic Peninsula and Southern Patagonia. We thank N.E. Barrand and an anonymous reviewer for valuable comments, and the scientific editor, Tavi Murray, for handling the paper.











