Introduction
Compared to most areas on Earth, the vast continent of Antarctica has been, except for the most recent decades, a minor focus of scientific exploration. Yet what is already known about Antarctica demonstrates that, despite its remote location, it plays a significant role in the global climate system. Encircled by some of the world’s most biologically productive oceans, Antarctica is the largest reservoir of fresh water on the planet, a major site for the production of the cold deep water that drives ocean circulation, a major player in Earth’s albedo dynamics, and an important driving component for atmospheric circulation. Thus, Antarctica plays a critical role in the dynamic linkages that couple the spatially and temporally complex components of Earth’s climate system. While the complexity of the global climate system is now widely appreciated, the details of its functioning are still poorly understood. In the Northern Hemisphere and portions of the Southern Hemisphere, direct observational and instrumental records exist only for the last ∼2000 and ∼100 years, respectively. Except at a small handful of coastal sites, observational and instrumental records in Antarctica cover only the last 40–50 years.
The Antarctic Oscillation (AAO), also referred to as the High Latitude Mode, and the Southern Hemisphere Annular Mode (Reference KidsonKidson, 1988; Reference Thompson and WallaceThompson and Wallace, 2000; Reference Thompson and SolomonThompson and Solomon, 2002) are expressions of the statistically dominant temporal variability over the extratropical regions of the Southern Hemisphere. The AAO is a near-zonally symmetric seesaw in atmospheric mass between high and mid-latitudes and is characterized by variations in the strength and extent of the subpolar wind maximum (the polar vortex). Its manifestation in the mean sea-level pressure field is revealed in the US National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) Re-analyses (NNR) covering the period 1948–2001 (Reference Thompson and WallaceThompson and Wallace, 2000; www.jisao.washington.edu) (Fig. 1a). Over at least the period of the instrumental era, the AAO is a prominent feature. Warming (expanding) Hadley circulation in the tropics acts to increase the strength of the zonal mean circulation, leading to a strengthening of the polar vortex and consequent isolation of the polar regions, while tropical cooling (shrinking) acts to weaken the polar vortex, allowing more meridional flow and a stronger connection between polar and mid-latitude regions (Reference ShulmeisterShulmeister and others, 2004).
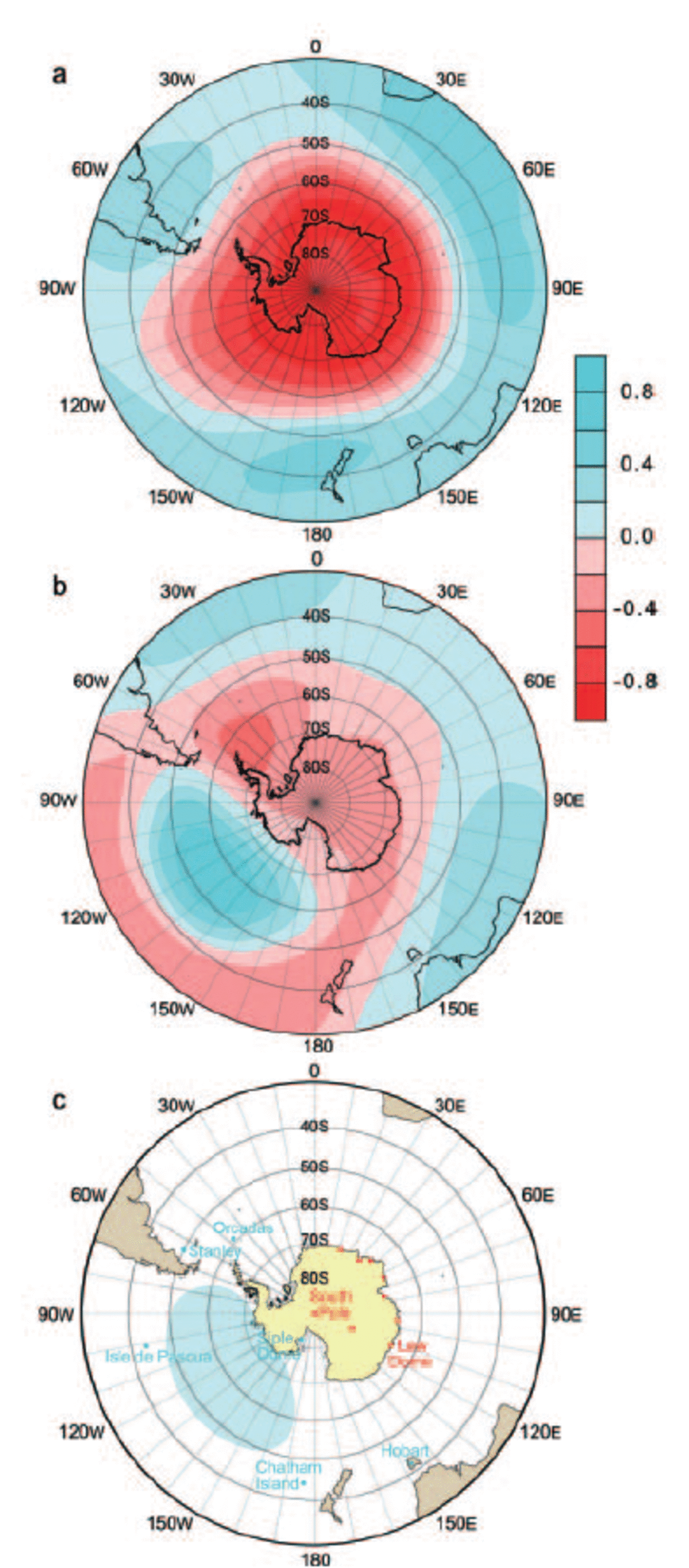
Fig. 1. (a) EOF1 and (b) EOF2 of the Southern Hemisphere extratropical 850 hPa Z (plotted as correlations) taken from www.jisao.washington.edu (Reference Thompson and WallaceThompson and Wallace, 2000; Reference Thompson and SolomonThompson and Solomon, 2002). (c) Regions and sites where sea-level pressure is strongly correlated with either DSS Na (red dots) or SD Na (blue area; SD designated by blue dot), plus location of South Pole (red dot at South Pole).
Although the AAO is a prominent mode of variability, it is supplemented by wave patterns across, for example, the Pacific/South American sector (Reference Mo and HigginsMo and Higgins, 1998; Reference Renwick and RevellRenwick and Revell, 1999). NNR calculations reveal a seesaw between the South Pacific and Antarctica across to the southwestern Atlantic that represents the second dominant mode of circulation for the extratropics (Reference Thompson and WallaceThompson and Wallace, 2000) (Fig. 1b). Persistence and position of the Amundsen Sea Low (ASL), the South Pacific component of the seesaw, is associated with meridional circulation south of New Zealand imposed by the presence of the Australian land mass (Reference Sturman and TapperSturman and Tapper, 1996; Reference Hurrell, van Loon, Shea, Karoly and VincentHurrell and others, 1998). The Pacific–South American (PSA) mode of this seesaw may be forced by anomalous tropical heating (convection) associated both with the El-Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle and with shorter-term intra-seasonal variability (Reference Kiladis, Mo, Karoly and VincentKiladis and Mo, 1998; Reference Mo and HigginsMo and Higgins, 1998). The PSA has a strong influence on blocking anticyclone activity across the southeast Pacific.
The present-day climate of the Antarctic exhibits significant regional complexity that is closely linked to changes in global climate (Reference Yuan, Cane and MartinsonYuan and others, 1996). Slight cooling of much of the Antarctic ice sheet, observed from in situ and satellite temperature measurements during the period 1979– 98 (Reference ComisoComiso, 2000), contrasts with warming over the Antarctic Peninsula during the same period (Reference Jacobs and ComisoJacobs and Comiso, 1997). They may also be linked to alternating warm and cold anomalies and associated changes in sea-ice extent around the continent, consistent with the presence of eastward-propagating temperature patterns generated by the Antarctic Circumpolar Wave (ACW) (Reference White and PetersonWhite and Peterson, 1996). An associated feature, the Antarctic Dipole (ADP), characterized by out-of-phase relationships in sea-ice extent, temperature and sea-level pressure, between Atlantic and Pacific sectors, is connected with extratropical features such as ENSO (Reference Chiu, Street-Perrott, Beran, Ratcliffe and RidelChiu, 1983; Reference CarletonCarleton, 1989; Reference Simmonds and JackaSimmonds and Jacka, 1995; Reference Ledley and HuangLedley and Huang, 1997; Reference Peterson and WhitePeterson and White, 1998; Reference HarangozoHarangozo, 2000; Reference YuanYuan and Martinson, 2000, Reference Yuan and Martinson2001; Reference Schneider and SteigSchneider and Steig, 2002). It has also been suggested that changes in ozone in the lower stratosphere trigger changes in the acceleration of the westerly winds surrounding Antarctica, thus affecting tropospheric trends in temperature (Reference Thompson and SolomonThompson and Solomon, 2002). However, to understand the significance of trends and other climate changes on time-scales longer than interannual, and to potentially predict future changes in atmospheric circulation and temperature over Antarctica requires examination of climate series that are longer than available instrumented records. Such records are available from ice cores recovered from Earth’s largest storehouse of annually resolved climate records, the Antarctic.
To contribute to the understanding of past climate over the extratropical regions of the Southern Hemisphere, we utilize three of the highest-resolution (sub-annual) ice-core records (Fig. 1c) available from West (Siple Dome) and East Antarctica (Law Dome and South Pole). Siple Dome (SD; 81˚39' S, 148˚49'W; elevation 650 m; mean annual accumulation rate 13.3 cm ice equivalent a–1) is located on the Siple Coast, in the Pacific Ocean sector of West Antarctica. Law Dome (Dome Summit South (DSS); 66˚46' S, 112˚48' E; elevation 1370 m; mean annual accumulation rate 60 cm ice equivalent a–1) is located in Wilkes Land, in the Indian Ocean sector of East Antarctica (Reference Morgan, Wookey, Li, van Ommen, Skinner and FitzpatrickMorgan and others, 1997). SD and DSS ice cores both have annually dated (Reference Van Ommen and MorganVan Ommen and Morgan, 1996; Reference Kreutz, Mayewski, Pittalwala, Meeker, Twickler and WhitlowKreutz and others, 2000) proxies for changes in sea-level pressure and temperature. The South Pole (elevation 2814 m; mean annual accumulation rate 8 cm ice equivalent a–1) ice core contains an annually dated proxy for El Niño frequency covering the last 500 years (Reference Meyerson, Mayewski, Kreutz, Meeker, Whitlow and TwicklerMeyerson and others, 2002).
Variability in Atmospheric Circulation
To assess variability in atmospheric circulation, we examine sea-level pressure ice-core calibrated proxies developed from the SD and DSS ice cores (Fig. 2).
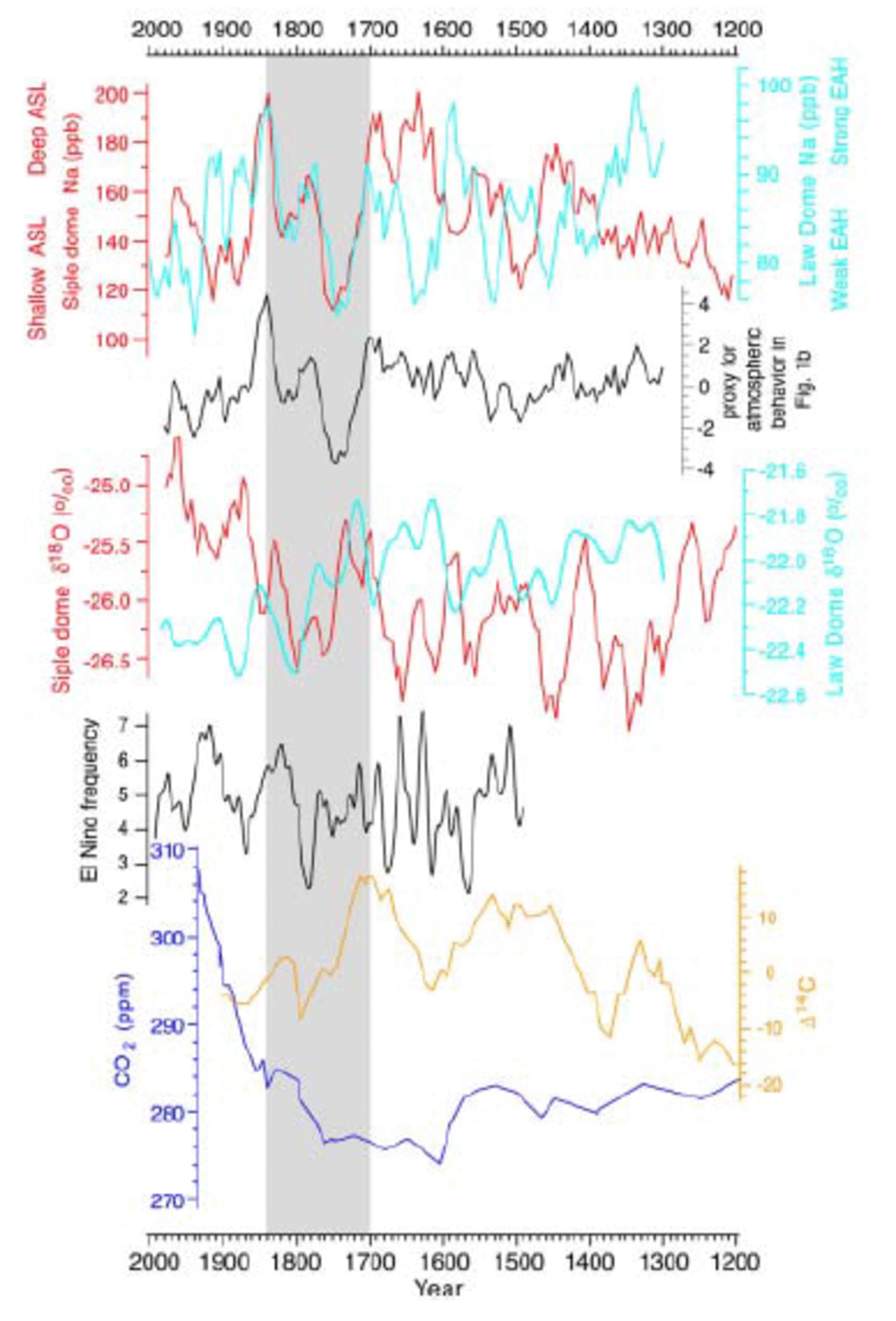
Fig. 2. A 25 year running mean of SD and DSS Na (ppb) used as a proxy for the ASL and EAH, respectively, with estimated sea-level pressure developed from calibration with the instrumental and NCEP re-analysis (based on Reference Kreutz, Mayewski, Pittalwala, Meeker, Twickler and WhitlowKreutz and others, 2000; Souney and others, 2002). EOF2 (Fig. 1b) proxy (normalized units) based on adding normalized DSS Na plus normalized SD Na. 25 year running mean SD and DSS δ18O (‰) used as a proxy for temperature, with estimated temperature developed from calibration with instrumental mean annual and seasonal temperature values Reference Van Ommen and Morgan(Van Ommen and Morgan, 1997; Reference SteigSteig and others, 2000). Frequency of El Niño polar penetration based on calibration between the historical El Niño frequency record (Reference Quinn, Neal and Antúnez de MayoloQuinn and others, 1987; Reference Quinn, Neal, Bradley and JonesQuinn and Neal, 1992) and SP MS (Reference Meyerson, Mayewski, Kreutz, Meeker, Whitlow and TwicklerMeyerson and others, 2002). Δ14C series used as an approximation for solar variability (Reference Stuiver and BraziunasStuiver and Braziunas, 1993). CO2 from DSS ice core (Reference Etheridge, Steele, Langenfelds, Francey, Barnola and MorganEtheridge and others, 1998).
Higher (lower) levels of sea-salt deposition (represented by Na) at SD are coincident with higher (lower) levels of austral winter–spring cyclone intensity in one of the major quasi-stationary lows in the circumpolar trough, the ASL (Reference Kreutz, Mayewski, Pittalwala, Meeker, Twickler and WhitlowKreutz and others, 2000). Annual values of Na in the SD ice core are anticorrelated (r = –0.32 (annual series) to –0.51 to –0.75 (3 year smoothed series); p < 0.001) with September– October–November SLP changes throughout much of the South Pacific (including New Zealand, South America and the Antarctic Peninsula) (Fig. 1c) over the period of ice-core and instrumental overlap (1900–95) (Reference Kreutz, Mayewski, Pittalwala, Meeker, Twickler and WhitlowKreutz and others, 2000).
Higher (lower) levels of sea-salt deposition (represented by Na) at DSS are associated with high (low) sea-level pressure changes from coastal and interior East Antarctic locations (Reference Souney, Mayewski, Goodwin, Morgan and van OmmenSouney and others, 2002) and with increased (decreased) wind speeds at Casey Station, coastward of DSS (Reference Curran, van Ommen and MorganCurran and others, 1998). The high sea-salt loading of the poleward-moving air masses is coincident with the austral winter minimum in sea ice (June). The correlation is best for June because there is at this time an available source of sea salt from open water and also energetic air–sea exchange allowing entrainment of sea-salt aerosols. Annual values of Na in the DSS ice core are well correlated (r = 0.35–0.636; r average for 11 stations (Fig. 1c); p < 0.05) with winter (June correlation highest) sea-level pressure over East Antarctica during the period of ice-core and instrumental overlap (1957–96), providing a proxy for the East Antarctic High (EAH) (Reference Souney, Mayewski, Goodwin, Morgan and van OmmenSouney and others, 2002).
The SD and DSS proxies for the ASL and EAH, respectively, were resampled using a 25 year running mean in order to examine multi-decadal scale variability (Fig. 2). Testing demonstrated that use of the 25 year running mean did not introduce phasing artifacts into the data. Comparison between the location of the instrumental-ice-core calibration sites (Fig. 1c) and the regional distribution of the first two primary modes of temporal behavior at 850 hPa (Fig. 1a and b, after Reference Thompson and WallaceThompson and Wallace, 2000) demonstrates that the instrumental-ice-core calibration sites are distributed throughout regions representative of two major Southern Hemisphere extratropical circulation seesaws: (1) the AAO (Fig. 1a), and (2) the ASL–EAH and associated PSA (Fig. 1b).
Between AD 1200 and 1700, long-term, multi-centennial scale trends in the ASL and EAH are inverse, with the EAH generally weakening and the ASL generally intensifying (Fig. 2). These trends suggest poleward migration of the circumpolar trough consistent with solar-insolation-induced deglaciation of Antarctica over the last several thousand years. During this same period the ASL and EAH also display inverse behavior at the multi-decadal scale (Fig. 2). This seesaw pattern maintained between the ASL and EAH from AD 1200 to 1700, at centennial to multi-decadal time-scales, is suggestive of the atmospheric seesaw mode calculated from the AD 1948–2001 NCEP re-analysis data seen in Figure 1b.
There is a prominent departure from Figure 1b-style behaviour, ASL and EAH seesaw, during the period AD 1700– 1850. During this time the EAH is strong (weak) when the ASL is deep (shallow). The EAH and ASL are weakest∼AD 1750 and strongest ∼AD 1850, relative to the full record. We suggest that between AD 1770 and 1850 the South Pacific (and perhaps the entire Southern Ocean) and Antarctica experienced a mode switch. Decreased Na concentrations ∼AD 1700 may be a consequence of dramatically increased extent and duration of sea ice and, as a consequence, significant loss of exposed Na source area. Alternately, the decreased Na concentrations may mark a period of weakened ASL and EAH and therefore reduced incorporation of Na. Increased Na levels ∼AD 1850 suggest decreased sea-ice extent and duration and/or strengthened ASL and EAH. Following the AD 1700–1850 mode switch, the multidecadal scale behavior of the ASL and EAH returns to its pre-AD 1700 mode.
To assess past variability in temperature between coastal sites in East and West Antarctica we examine the δ18O ice-core proxy for temperature derived from the SD and DSS ice cores (Fig. 2). The average form of the seasonal δ18O curve at DSS is calibrated with measured temperature at the site, resulting in the relationship 0.44‰˚C–1 (Reference Morgan and van OmmenMorgan and Van Ommen, 1997; Reference Van Ommen and MorganVan Ommen and Morgan, 1997). For the calibration between SD δ18O and temperature we utilize a relationship available for the western side of the Ross Ice Shelf derived from the Taylor Dome ice core of 0.5‰˚C–1 (Reference SteigSteig and others, 2000).
Examination of the 25 year running mean values for the SD and DSS ice-core temperature proxies demonstrates that these two sites differ in their long-term, multi-centennial scale trends over most of the record. This difference in long-term temperature trend is not necessarily maintained at the multi-decadal scale as is the case for the pre-AD 1700 and post-AD 1850 portions of the ASL and EAH proxy record. For SD the lowest temperatures (up to –3˚C relative to AD 1900) are AD 1350 and ∼AD 1450, and for DSS the lowest temperatures (close to –2˚C relative to AD 1900) are early and late 19th century. SD temperatures fluctuate throughout the record, but rise in general from AD 1650 to the present. DSS temperatures fluctuate through much of the record, but decline from ∼AD 1400 to the present.
During the early phase of the AD 1700–1850 atmospheric mode switch, coastal West and East Antarctic temperatures decline in general together. Background SD temperature rises almost monotonically as of ∼AD 1800–50. The second warmest period in the SD record is in the late 19th century (up to +1˚C relative to AD 1900) and the warmest (up to +2˚C relative to AD 1900) in the mid-20th century. In contrast, temperatures at DSS since the mid-19th century are close to the lowest over the record period. Recent differences between SD and DSS temperatures may be attributed to the influence of 20th-century warming at low latitudes since low-latitude temperature changes may propagate to West Antarctica through the strong teleconnection between the tropical and the southern Pacific (Reference Gereaud and BattistiGereaud and Battisti, 1999). This process may have little influence, and may even promote cooling, in East Antarctica due perhaps to enhanced downwelling of cooler stratospheric source air over East Antarctica.
El Niño Frequency
A 500 year long annually dated record of methanesulfonate (MS) from the SP ice core, calibrated with and comparable to the historical El Niño event record (Reference Quinn, Neal and Antúnez de MayoloQuinn and others, 1987; Reference Quinn, Neal, Bradley and JonesQuinn and Neal, 1992), is utilized as a proxy for the frequency of polar penetration of El Niño events (Reference Meyerson, Mayewski, Kreutz, Meeker, Whitlow and TwicklerMeyerson and others, 2002). The switch to longer periods of El Niño recurrence close to AD 1850, is coincident with the middle of the AD 1700–1850 mode switch and the onset of rise in temperatures at SD and in general globally. This switch in recurrence of El Niño event penetrations to South Pole further supports a strong link between the tropical Pacific and West Antarctica.
Discussion and Conclusions
The ASL (an approximation of EOF2 mode of the temporal behavior at 850 hPa in the Southern Hemisphere) and the EAH (an approximation of EOF1 mode of the temporal behavior at 850 hPa in the Southern Hemisphere) have operated in a seesaw mode both during the instrumental era (Fig. 1b) and at multi-decadal to multi-centennial scales throughout much of the 700 year period recorded by the DSS and SD ice cores. This behavior was disrupted during a mode switch from AD 1700 to 1850 that affected a large portion of the extratropical regions of the Southern Hemisphere. Examination of other paleoclimate records verifies that this climate disruption occurred throughout the Southern Hemisphere, as evidenced by: a shift in circulation at Taylor Dome, Ross Sea region, East Antarctica; drier and colder conditions based on a speleothem record from Cold Air Cave, South Africa (Reference Lee-ThorpLee-Thorp and others, 2001); and colder conditions based on an ice core from Huascarán ice cap, Peru (Reference ThompsonThompson and others, 1995). The mode switch started during a period of globally distributed cooling, coincident with a 10 ppmv drop in the DSS ice-core CO2 record (Reference Etheridge, Steele, Langenfelds, Francey, Barnola and MorganEtheridge and others, 1998), and at the height of the Maunder Minimum, identified in the Δ14C proxy for solar variability (Reference LingenfrelteLingenfelter, 1963; Reference O’BrienO’Brien, 1979; Reference Stuiver and BraziunasStuiver and Braziunas, 1993) (Fig. 2). During the mode switch, atmospheric circulation patterns were characterized by greater than normal variability relative to the remainder of the record. Increased climate variability appears to be a common theme during cold periods, based on the examination of glacial/interglacial scale records of change in atmospheric circulation (Reference MayewskiMayewski and others, 1994).
Generally lower temperature from AD 1350 to the early 19th century in coastal West Antarctica is coincident with increased values of Δ14C (Fig. 2) (decreased solar variability) and the onset of a globally distributed cool event, referred to in some regions as the Little Ice Age. Both SD and DSS approximations for coastal West and East Antarctic temperatures, respectively, decrease during the early phase of the AD 1700–1850 mode switch, supporting the idea of increased sea-ice extent (decreased open-ocean source for Na) as a cause for the dramatic drop in Na levels in these areas.
SD temperature starts to rise in the early 19th century, at the end of the atmospheric mode switch. The rise in temperature is coincident with an increased frequency of El Niño events that penetrate as far south as the South Pole. Both the late 19th- and a 20th-century increase in SD temperature (of +2˚C) are coincident with rise in CO2 (Fig. 2), and the latter with the trend in instrumental observations of a 0.17˚C warming in the Southern Ocean over the second half of the 20th century (Reference GilleGille, 2002). Recently reported decreases in temperature over East Antarctica, for the last few decades (Reference ComisoComiso, 2000; Reference DoranDoran and others, 2002), are consistent with the decrease in temperature at DSS recorded since the mid-19th century. The juxtaposition of warming at SD with ASL values that are within the range of natural variability of the last 700 years suggests that atmospheric circulation is not the sole cause for the warming. However, the low elevation of West Antarctica relative to East Antarctica makes it suitable for the penetration of lower-tropospheric warming events and the intensified frequency of penetration of El Niño events.
Superimposed on the general trends in the SD and DSS proxies for atmospheric circulation and temperature described above are a series of highly significant periodicities (p < 0.01) close to 2–8 years and 10–12 years (Reference Kreutz, Mayewski, Pittalwala, Meeker, Twickler and WhitlowKreutz and others, 2000; Reference Souney, Mayewski, Goodwin, Morgan and van OmmenSouney and others, 2002) suggestive of ACW and ENSO phenomena and solar cycles, respectively, plus a series of multi-decadal periodicities that may offer insight into other atmospheric teleconnections and potential climate forcings. More high-resolution, annually dated records similar to those being collected by the International Trans-Antarctic Scientific Expedition (ITASE) (Reference Mayewski and GoodwinMayewski and Goodwin, 1997) are required to assess the implications of these periodic structures. ITASE ice cores will also help to determine changes in the position of the ASL and EAH over time that cannot be assessed in this study. Examination of paleoclimate archives that capture pre-instrumental-era behavior of major modes of Southern Hemisphere atmospheric circulation are essential to the insight needed to assess the dynamic range and forcing of the global climate system.
Acknowledgements
Support for this research was provided by US National Science Foundation (NSF) Office of Polar Programs (OPP) and Earth System History (ESH) grants NSF OPP 0096305, NSF OPP 00996299 and NSF ESH 0096331.




