Health research plays a major role in advancing science and in providing solutions for health problems. Imbalances in health research output in terms of populations and disease burden addressed have been noted (Reference HortonHorton, 2003; Canadian Medical Association Journal, 2004; Reference Rochon, Mashari and CohenRochon et al, 2004; Reference Paraje, Sadana and KaramParaje et al, 2005) and aptly labelled ‘Western medical journals and the 10/90 problem’ (Canadian Medical Association Journal, 2004). In comparison with the burden imposed by mental disorders (13% of global burden of diseases), mental health is an underresearched health area. In a study on global significance of health research by Rochon et al (Reference Rochon, Mashari and Cohen2004), only 2.44% of clinical trials on 25 leading contributors to global burden of diseases targeted mental disorders. Geographical disproportions have also been recorded and commented upon in mental health research; only about 6% (or less) of publications are from low- and middle-income countries (Reference Patel and SumathipalaPatel & Sumathipala, 2001; Reference Parker and ParkerParker & Parker, 2002; Reference Saxena, Maulik and SharanSaxena et al, 2004; Reference TyrerTyrer, 2005). Here we examine mental health literature within internationally accessible health literature for geographical distribution over a 10-year period.
METHOD
The 4061 health-related journals indexed in the ISI Web of Science database (1992-2001) were searched for all publications on mental health, mental disorders and services for mental health. The ISI database does not exhaustively list internationally accessible literature but its listing of institutional affiliation of all authors, a feature that is not offered by other databases (including Medline), which list the affiliation of only one author, makes it uniquely suited for assessment of geographical contribution to publications.
The list of keywords included global terms such as behaviour, psychology, psychiatry, psychosocial, mental health, mental disorders, mental development, intellectual disability; specific terms such as organic brain syndrome, dementia, drug abuse, psychosis, schizophrenia; and service-related terms such as mental healthcare, psychiatric hospital, psychiatric services, halfway home, residential psychiatric care, and community mental health. (Complete list available from authors on request.) The final set of keywords was selected by an iterative process that yielded a precision value of 94% and recall value of 93% (precision: proportion of relevant articles among those retrieved; recall: proportion of articles in a random sample of mental health journals that were retrieved by the search strategy).
The countries of origin for each publication were determined by the fractional counting method (assigning an equal fraction of each publication to all listed countries).
RESULTS
Out of 3 288 252 health-related publications available in the ISI database (1992-2001), only 117 449 (3.57%) were related to mental health. There was very low variability in the proportion of mental health to health-related publications across the 10-year period (2.95%-3.86%).
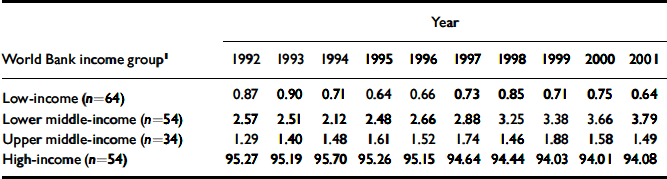
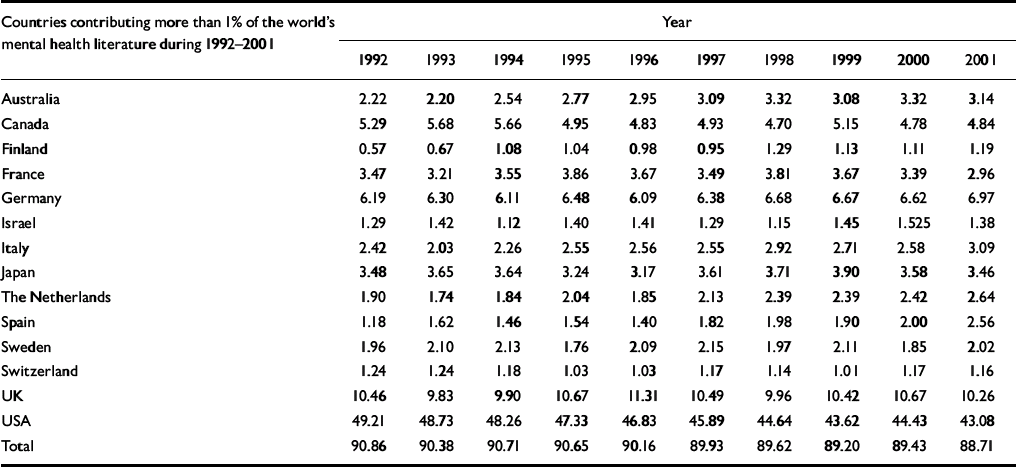
All high-income countries (see World Bank (2003) criteria), with 15% of the world's population, contributed 94%; low- and middle-income countries, with more than 85% of the world's population, contributed 6% to internationally accessible mental health literature (Table 1). The USA and UK, with 5.6% of the world's population, contributed more than 50%; 14 leading high-income countries (with more than 1% contribution for the majority of years under consideration), including the USA and UK, with 12.9% of the world's population (<7% of all countries) contributed 90% (see data supplement to the online version of this paper). Fifty-one countries (more than a quarter) among those listed as member states of the World Health Organization (WHO) were virtually unrepresented (<0.001% of internationally accessible mental health publications in any year) in the database (data not shown). Some of the unrepresented countries are mid-sized countries with populations above 5 million (e.g. Chad, Guinea, Haiti, Honduras, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Rwanda and Somalia). The contribution from the USA decreased from 49% to 43% over the 10-year time period.
Table 1 Percentage of world production of mental health publications (total n=117449) according to World Bank income groups
| Year | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| World Bank income group 1 | 1992 | 1993 | 1994 | 1995 | 1996 | 1997 | 1998 | 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | |||||||||
| Low-income (n=64) | 0.87 | 0.90 | 0.71 | 0.64 | 0.66 | 0.73 | 0.85 | 0.71 | 0.75 | 0.64 | |||||||||
| Lower middle-income (n=54) | 2.57 | 2.51 | 2.12 | 2.48 | 2.66 | 2.88 | 3.25 | 3.38 | 3.66 | 3.79 | |||||||||
| Upper middle-income (n=34) | 1.29 | 1.40 | 1.48 | 1.61 | 1.52 | 1.74 | 1.46 | 1.88 | 1.58 | 1.49 | |||||||||
| High-income (n=54) | 95.27 | 95.19 | 95.70 | 95.26 | 95.15 | 94.64 | 94.44 | 94.03 | 94.01 | 94.08 | |||||||||
1. Economies are divided according to 2002 gross national income (US$) per capita: low-income countries, $735 or less; lower middle-income countries, $736-$2935; upper middle-income countries, $2936-$9075; high-income countries, $9076 or more.
Data supplement 1 Percentage of world production of mental health publications (total n=117449): breakdown of contributions by countries contributing more than 1% of the literature
| Countries contributing more than 1% of the world's mental health literature during 1992-2001 | Year | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1992 | 1993 | 1994 | 1995 | 1996 | 1997 | 1998 | 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | ||||||||||
| Australia | 2.22 | 2.20 | 2.54 | 2.77 | 2.95 | 3.09 | 3.32 | 3.08 | 3.32 | 3.14 | |||||||||
| Canada | 5.29 | 5.68 | 5.66 | 4.95 | 4.83 | 4.93 | 4.70 | 5.15 | 4.78 | 4.84 | |||||||||
| Finland | 0.57 | 0.67 | 1.08 | 1.04 | 0.98 | 0.95 | 1.29 | 1.13 | 1.11 | 1.19 | |||||||||
| France | 3.47 | 3.21 | 3.55 | 3.86 | 3.67 | 3.49 | 3.81 | 3.67 | 3.39 | 2.96 | |||||||||
| Germany | 6.19 | 6.30 | 6.11 | 6.48 | 6.09 | 6.38 | 6.68 | 6.67 | 6.62 | 6.97 | |||||||||
| Israel | 1.29 | 1.42 | 1.12 | 1.40 | 1.41 | 1.29 | 1.15 | 1.45 | 1.525 | 1.38 | |||||||||
| Italy | 2.42 | 2.03 | 2.26 | 2.55 | 2.56 | 2.55 | 2.92 | 2.71 | 2.58 | 3.09 | |||||||||
| Japan | 3.48 | 3.65 | 3.64 | 3.24 | 3.17 | 3.61 | 3.71 | 3.90 | 3.58 | 3.46 | |||||||||
| The Netherlands | 1.90 | 1.74 | 1.84 | 2.04 | 1.85 | 2.13 | 2.39 | 2.39 | 2.42 | 2.64 | |||||||||
| Spain | 1.18 | 1.62 | 1.46 | 1.54 | 1.40 | 1.82 | 1.98 | 1.90 | 2.00 | 2.56 | |||||||||
| Sweden | 1.96 | 2.10 | 2.13 | 1.76 | 2.09 | 2.15 | 1.97 | 2.11 | 1.85 | 2.02 | |||||||||
| Switzerland | 1.24 | 1.24 | 1.18 | 1.03 | 1.03 | 1.17 | 1.14 | 1.01 | 1.17 | 1.16 | |||||||||
| UK | 10.46 | 9.83 | 9.90 | 10.67 | 11.31 | 10.49 | 9.96 | 10.42 | 10.67 | 10.26 | |||||||||
| USA | 49.21 | 48.73 | 48.26 | 47.33 | 46.83 | 45.89 | 44.64 | 43.62 | 44.43 | 43.08 | |||||||||
| Total | 90.86 | 90.38 | 90.71 | 90.65 | 90.16 | 89.93 | 89.62 | 89.20 | 89.43 | 88.71 | |||||||||
DISCUSSION
Mental health research publications form a much smaller fraction of health research publications in comparison with the relative burden of mental illness (Reference Rochon, Mashari and CohenRochon et al, 2004; present study). Currently priorities for health research are established by a combination of explicit and implicit means. Priorities may be affected by the personal scientific interests of researchers, the priorities of those who serve as reviewers for grants and the philanthropic interests of those who privately fund research, the availability of researchers or institutions that specialise in a subject area, government policy, stakeholder lobbying and media interest, and the profit potential of the research (Reference Jorm, Griffiths and ChristensenJorm et al, 2002). Mental health research has obviously received low priority, as exemplified by the fact that the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) of Australia spent only 8.9% of its funds on mental health research compared with the 19.1% contribution of mental disorders to disease burden in Australia (Reference Jorm, Griffiths and ChristensenJorm et al, 2002). Similarly, the scientific interests of editors, reviewers, researchers and readers (subscribers), and overall context of publishing could also play a role in the underrepresentation of mental health publications in general health journals. A widespread acceptance of mental health as an issue deserving attention, a perception that mental health research can be scientific and advocacy for mental health research are needed to improve the current situation. Some noteworthy efforts have been made in this direction. The World Health Report 2001 (WHO, 2001) and a report of the Surgeon General (US Department of Health & Human Services, 1999) have called for greater support for mental health research.
It is evident that the 10/90 divide in health research output (Canadian Medical Association Journal, 2004; Reference Paraje, Sadana and KaramParaje et al, 2005) also holds true for the mental health field. A very limited amount (6%) of internationally accessible mental health literature emanates from low- and middle-income countries. The very slight increase observed in the production of middle-income countries is negated by the decrease in the already low production of low-income countries.
Earlier studies of a limited number of publications in terms of journals (<10) and time periods covered (2 years) reported similar findings (Reference Patel and SumathipalaPatel & Sumathipala, 2001; Reference Parker and ParkerParker & Parker, 2002). Limited access to information, lack of advice on research design and statistics, difficulty in writing in a foreign language, overall material, financial, policy and infrastructural constraints, and limited appreciation by editorial offices of the research needs of, and realities in, low- and middle-income countries may constitute barriers that impede publication of mental health research from these countries in widely accessible journals (Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 2004).
The fact that the proportional decrease in the contribution of the USA was balanced by an increase in mental health publications from other high-income countries suggests that the 10/90 divide is not going away and that active efforts are required to improve the mental health research situation in low- and middle-income countries. The results of this study highlight the need to improve the research infrastructure and capacity to conduct and disseminate mental health research in general, and in particular in low- and middle-income countries. The WHO has called for a substantial increase in investment in mental health research capacity, particularly in low- and middle-income countries (WHO, 2003). A joint statement issued recently by editors of scientific journals publishing mental health research and the WHO summarised the existing unsatisfactory state regarding publication of mental health research and offered some steps to correct these imbalances (Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 2004). The present study confirms that the 10/90 divide in mental health research has remained undiminished over 10 years; hence the urgent need to implement the steps suggested by the joint statement.
Acknowledgement
We thank Professor Grant Lewison, Department of Information Science, City University, London for serving as a scientific advisor during finalisation of the search strategy for this project.





eLetters
No eLetters have been published for this article.