A proposed causal association between childhood trauma and later psychosis has raised much debate within the psychiatric literature over recent years. Reference Read, van Os, Morrison and Ross1–Reference Spauwen, Krabbendam, Lieb, Wittchen and van Os6 With some notable exceptions, Reference Janssen, Krabbendam, Bak, Hanssen, Vollebergh, De Graff and van Os5,Reference Spauwen, Krabbendam, Lieb, Wittchen and van Os6 the literature to date has been open to the risk of recall bias as most studies were based on treatment samples and used retrospective assessment of trauma. Although a number of studies indicate that individuals with psychotic disorders are no less likely to be accurate in recalling abusive experiences than the general population, Reference Meyer, Muenzenmaier, Cancienne and Struening7,Reference Read, Agar, Argyle and Aderhold8 some researchers still voice reliability concerns. Reference Morgan and Fisher2 One solution to this methodological problem is to examine the association between childhood trauma and psychosis in a population-based sample of people who have not yet had contact with the mental health services. The account of trauma is therefore unbiased by diagnosed outcome. We analysed data from a population-based sample of adolescents recruited from schools in Dublin, Ireland, to investigate whether there was an association between childhood traumatic experiences and the presence of psychotic symptoms. Research on long-term outcomes suggests there are increased rates of adult psychotic illness among adolescents reporting psychotic symptoms. Reference Poulton, Caspi, Moffitt, Cannon, Murray and Harrington9 Therefore, adolescents who report psychotic symptoms can be conceptualised as a ‘high-risk’ group for psychotic illness and this paradigm can be used to explore early risk factors for psychosis vulnerability. We wished to examine a range of traumatic experiences among such a cohort to investigate the relationship between psychotic symptoms in adolescence and childhood trauma.
Method
Participants
The Challenging Times study Reference Lynch, Mills, Daly and Fitzpatrick10,Reference Lynch, Mills, Daly and Fitzpatrick11 was established to investigate the prevalence of psychiatric disorders among Irish adolescents aged 12–15 years. The study was carried out in the geographical catchment area of a child and adolescent mental health team in North Dublin with a population of 137 000. After describing the study to participants, written informed consent was obtained from their parent or guardian. In brief, 743 pupils (52% of the total school population in that area) were screened for psychiatric symptoms using the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire Reference Goodman12,Reference Goodman, Ford, Simmons, Gatward and Meltzer13 and the Children's Depression Inventory. Reference Kovacs14 Eight primary schools were selected using a stratified random sampling technique, stratified in order to approximate the socio-economic profile of the geographical area population. Overall, 140 adolescents scored above threshold on these instruments, indicating high risk of having mental health problems. Of these, 117 (84%) agreed to attend a full psychiatric interview. A comparison group of 173 adolescents, matched for gender and school were also invited to attend, of whom 94 (54%) agreed.
Ethical approval for the study was granted by the medical ethics committee of the Mater Misericordiae University Hospital, Dublin, Ireland. The study was supported by the multidisciplinary child and adolescent mental health team covering the geographical area. The protocol ensured that any child who was deemed to be in need of a clinical service could be referred to the team.
Interview instrument
The interview schedule used in this study was the Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia for School-Aged Children, Present and Lifetime Versions (K–SADS). Reference Kaufman, Birmaher, Brent, Rao and Ryan15 The K–SADS is a well-validated, semi-structured research diagnostic interview for the assessment of all Axis 1 psychiatric disorders in children and adolescents. Children and parents were interviewed separately, both answering the same questions. Interviews were conducted by two psychologists and one psychiatrist who were trained in the use of the K–SADS. Interrater reliability for the K–SADS was estimated as >90% in this study. Reference Lynch, Mills, Daly and Fitzpatrick11
Exposure measurement
As part of the K–SADS interview the following childhood traumatic experiences were assessed. Interviews were conducted with parents and children separately.
Childhood abuse
Both child physical and sexual abuse were assessed as part of the K–SADS interview. Children were asked the following questions in relation to physical abuse: ‘When your parents got mad at you, did they hit you? Have you ever been hit so that you had bruises or marks on your body, or were hurt in some way? What happened?’ They were asked the following questions in relation to sexual abuse: ‘Did anyone ever touch you in your private parts when they shouldn't have? What happened? Has someone ever touched you in a way that made you feel bad?’.
Parents were asked the same questions appropriately modified. A disclosure of physical or sexual abuse from the parent was taken as evidence of a history of child abuse, regardless of whether it was also disclosed by the child. There were no cases where the parent disputed the occurrence of abuse that had been disclosed by the child.
Domestic violence
Exposure to domestic violence was assessed in the post-traumatic stress disorder section: ‘Some kids’ parents have a lot of nasty fights. They call each other bad names, throw things, and threaten to do bad things to each other. Did your parents ever get in really bad fights? Tell me about the worst fight you remember your parents having. What happened?'. Again, parents were asked the same questions, appropriately modified. A disclosure of physical violence between parents/step-parents from the parent was taken as evidence of a history of domestic violence. There were no cases where the parent disputed the occurrence of domestic violence that had been disclosed by the child.
Bullying
Bullying was assessed as part of the K–SADS Social Relations section; parents and children were specifically asked: ‘Have you ever been bullied?’ and ‘Have you ever been accused of being a bully?’. A positive response from either the parent or child was taken as evidence of a history of being a bully or being a victim of bullying. The ‘victim of bullying’ group included all those who responded positively to being bullied (regardless of whether they were also perpetrators of bullying). The ‘perpetrator of bullying’ group included all those who responded positively to being bullies (regardless of whether they were also victims of bullying).
Outcome measures
The Psychosis section of the K–SADS asks about the child's experience of hallucinations and delusions. Screen questions are detailed in the Appendix. Responses to these questions were recorded on the interview sheet. Three psychiatrists (M.H., F.L. and M.C.) and one psychologist (I.K.) examined these responses and concurred that the symptoms seemed genuine in content. All psychotic experiences were reported by the child. In no case did the parents report such symptoms in their child.
Socio-economic status and family history of psychiatric illness
Socio-economic status of each participant was determined using parental occupation assessed according to the Irish Social Class Scale. 16 We divided the sample into two major groups according to social class: the first group contained socio-economic status groups 1 and 2 (professional/managerial) and the second group contained groups 3–7: (non-manual skilled, skilled manual, semi-skilled manual, unskilled manual and unemployed). The K–SADS interview includes a routine screening section for family history of psychiatric illness, which was used in the present study.
Statistical analysis
First, we used chi-squared tests to compare the socio-demographic and clinical characteristics of adolescents reporting psychotic symptoms with adolescents who did not report such symptoms. Second, we used logistic regression analyses to examine the association between the outcome measure, experiencing psychotic symptoms, and the exposures: child physical and sexual abuse, exposure to domestic violence and bullying (victimisation or perpetration). We report univariate associations in terms of odds ratios, along with 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) and P-values, adjusted for gender and socio-economic status. Third, in order to control for the effect of comorbid psychiatric illness, we used a regression analysis stratified by the presence of psychiatric disorder. All analyses were carried out using STATA version 8.2 for Windows.
Results
Of the 211 children interviewed, 83 (39%) received a DSM–IV 17 Axis 1 diagnosis following K–SADS interview. The most common disorders diagnosed were depressive disorders. No participants received a formal diagnosis of a psychotic illness. Fourteen participants (6.6%) reported experiencing psychotic symptoms, primarily auditory and visual hallucinatory experiences. Adolescents who reported psychotic symptoms were significantly more likely to receive an Axis 1 psychiatric diagnosis than were adolescents who reported no such symptoms (71.4% v. 37.1%; χ2=5.4, d.f.=1, P=0.02). Specifically, the diagnoses of the 14 adolescents who reported psychotic symptoms included eight depressive disorders, two conduct disorders, two phobic disorders, two attention-deficit hyperactivity disorders, and one each of post-traumatic stress disorder, overanxious disorder, oppositional defiant disorder, tic disorder and separation anxiety disorder.
Adolescents who reported psychotic symptoms were more likely to be male (71.4%, psychotic symptoms group v. 45.2%, comparison group; χ2=3.3, d.f.=1, P=0.07), and from high socio-economic groups (professional/managerial) (64.3% v. 38.1%; χ2=3.5, d.f.=1, P=0.06) than the adolescents who did not report any symptoms. There were no differences between the groups for family history of psychiatric illness (χ2=0.12, d.f.=1, P=0.73).
Table 1 shows that adolescents reporting psychotic symptoms were six times more likely to have experienced child physical abuse than adolescents who did not report such symptoms and were ten times more likely to have witnessed domestic violence in their homes. These findings were statistically significant. Adolescents who reported psychotic symptoms were four-times more likely to have experienced child sexual abuse but, given the low absolute numbers of those who reported sexual abuse (n=4), this difference was not statistically significant. Adolescents with psychotic symptoms were not significantly more likely to have been victims of bullying but were significantly more likely to be bullies than adolescents who did not report such symptoms. Figure 1 shows the percentages of participants in each group who experienced the given traumatic events.

Fig. 1 Percentage of adolescents with and without psychotic symptoms reporting traumatic experiences. * P<0.05.
Table 1 Associations between psychotic symptoms in adolescence and early life traumatic experiences in (A) the whole sample (n=211) and (B) just adolescents with a history of psychiatric disorder (n=84) a
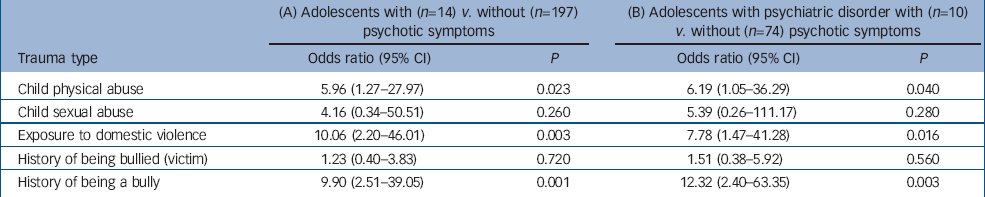
| (A) Adolescents with (n=14) v. without (n=197) psychotic symptoms | (B) Adolescents with psychiatric disorder with (n=10) v. without (n=74) psychotic symptoms | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trauma type | Odds ratio (95% CI) | P | Odds ratio (95% CI) | P | ||
| Child physical abuse | 5.96 (1.27–27.97) | 0.023 | 6.19 (1.05–36.29) | 0.040 | ||
| Child sexual abuse | 4.16 (0.34–50.51) | 0.260 | 5.39 (0.26–111.17) | 0.280 | ||
| Exposure to domestic violence | 10.06 (2.20–46.01) | 0.003 | 7.78 (1.47–41.28) | 0.016 | ||
| History of being bullied (victim) | 1.23 (0.40–3.83) | 0.720 | 1.51 (0.38–5.92) | 0.560 | ||
| History of being a bully | 9.90 (2.51–39.05) | 0.001 | 12.32 (2.40–63.35) | 0.003 | ||
a. All findings adjusted for gender and socio-economic status
There was a high level of comorbidity between reported psychotic symptoms and other childhood psychiatric disorder in this sample. Therefore, we considered that the traumatic experiences identified could be associated with general psychopathology rather than showing any specificity to psychotic symptoms. To test this hypothesis, we carried out a further analysis confined to those adolescents who received psychiatric diagnoses following interview. The prevalence of childhood traumatic experiences among adolescents with a diagnosed psychiatric disorder who also displayed psychotic symptoms (n=10) was compared with the prevalence among adolescents with diagnosed psychiatric disorder who did not display psychotic symptoms (n=73). Table 1 shows that the association between psychotic symptoms and traumatic experiences remained statistically significant after controlling for psychiatric disorders.
Discussion
Our results show significant associations between psychotic symptoms in early adolescence and reports of child physical abuse, exposure to domestic violence and involvement in bullying. We did not find a significant association with child sexual abuse but the reported rate of sexual abuse in our sample as a whole was low. There is an emerging literature on the association between adverse childhood experiences and positive psychotic symptoms, and this literature has focused mainly on child physical and sexual abuse. Reference Read, van Os, Morrison and Ross1,Reference Morgan and Fisher2 We have extended these findings to exposure to domestic violence and bullying, which have been rarely studied to date. Reference Bebbington, Bhugra, Brugha, Singleton, Farrell, Jenkins, Lewis and Meltzer4
Traumatic experiences and mechanisms of risk for psychosis
Theories proposed to explain how exposure to childhood abuse may increase the risk of psychotic symptoms have drawn on findings that severe stress at a young age appears to result in catecholamine deregulation and hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis dysfunction. Reference Read, Perry, Moskowitz and Connolly18 It has been shown that adult female victims of child physical and sexual abuse demonstrate persistent sensitisation of the pituitary–adrenal and autonomic stress response. Reference Heim, Newport, Heit, Graham, Wilcox, Bonsall, Miller and Nemeroff19 This process may create a diathesis that renders the individuals' mental health vulnerable to stress and may place them at greater risk of future psychiatric illness, including psychosis. Reference Walker and DiFiori20,Reference Cotter and Pariante21
Although direct evidence is lacking, witnessing domestic (interparental) violence may well invoke similar stress-induced neurodevelopmental changes as those evidenced in victims of childhood physical and sexual abuse. It is known that multiple behavioural, emotional, social and psychological effects are associated with childhood exposure to domestic violence. Reference Jaffee, Moffitt, Caspi, Taylor and Arseneault22,Reference Osofsky23 A correlation between marital discord and child urinary dopamine levels has also been reported, Reference Gottman and Katz24 which may indicate a process of dopamine sensitisation. Reference Cougnard, Marcelis, Myin, De Graaf, Vollebergh, Krabbendam, Lieb, Wittchen, Henquet, Spauwen and Van Os25
Complementary theories suggest that the cognitive schema formed as a result of traumatic experiences increase risk of psychosis Reference Read, van Os, Morrison and Ross1 . These are characterised by negative schematic models of the self and the world. Abusive experiences, for example, may teach the victim that people are dangerous, ultimately leading to paranoid ideation and the appraisal of normal events as threatening. Reference Kuipers, Garety, Fowler, Freeman, Dunn and Bebbington26–Reference Birchwood, Meaden, Trower, Gilbert and Plaistow28
Bullying and psychosis
In the context of our findings on child physical abuse and exposure to domestic violence, our findings regarding bullying were somewhat counterintuitive. We found that adolescents who reported psychotic symptoms were not significantly more likely to have been victims of bullying than the remainder of the sample. This finding is contradictory to a number of studies that reported a significant association between psychotic symptoms and being a victim of bullying. Reference Lataster, van Os, Drukker, Henquet, Feron, Gunther and Myin-Germeys29,Reference Campbell and Morrison30 There are a number of possible explanations for this discrepancy. First, there were high reported baseline rates of bullying victimisation in our whole sample (34%), which is likely to have reduced our ability to find an effect of victimisation. We did not have sufficient information on the nature of the victimisation experiences to allow subdivision by severity of victimisation. It is worth noting that, of those identified as bullies in the psychotic symptom group, the majority (80%) were also victims of bullying and would fit the definition of ‘bully/victim’ rather than the typical bully profile. In fact, children who fit the definition of bully/victim appear to be at particularly high risk of psychotic experiences, as 50% of the bully/victims in the study reported psychotic symptoms. Research is beginning to address the factors associated with bully/victim status. Reference Veenstra, Lindenberg, Oldehinkel, DeWinter, Verhulst and Ormel31,Reference Arseneault, Walsh, Trzesniewski, Newcombe, Caspi and Moffitt32 Compared with ‘pure’ victims, they tend to develop more pervasive and more severe psychological and behavioural outcomes, even after controlling for adjustment problems existing prior to the bully/victim behaviours. Reference Arseneault, Walsh, Trzesniewski, Newcombe, Caspi and Moffitt32 Studies suggest that bully/victims come from homes where the parents are less involved and more likely to be hostile and rejecting. Reference Bowers, Smith and Binney33
Physical abuse and exposure to domestic violence may be common risk factors for both the development of psychotic symptoms and the development of bullying behaviour. Children who have witnessed domestic violence or who have been victims of physical abuse may model their own behaviour on such acts of aggression. It could also be hypothesised that underlying genetic factors may influence antisocial and violent behaviour both in the parents and in the child. However, we found no significant relationship between being a bully and experiencing physical abuse and/or domestic violence. More research is needed to clarify what role bullying behaviour may play in the development of psychotic symptoms.
Strengths and limitations
This study has a number of strengths. First, it was population-based and all participants were attending mainstream schools. The detailed clinical interviews provided a comprehensive evaluation of the prevalence of experiences of trauma. Second, parents were interviewed in every instance and this collateral information was particularly valuable regarding child abuse and exposure to domestic violence. Parents, when reporting traumas, were unaware that their offspring had reported psychotic symptoms. Furthermore, most studies on psychosis that have investigated child abuse have been conducted with adults. There is, therefore, a significant intervening time period between the abuse events and assessment of these events. In our study the assessment is much closer to the time of abuse events. All of these factors reduce the possibility of recall bias, which has been identified as a significant problem in the literature to date. Reference Morgan and Fisher2
One limitation is that the Challenging Times study was not designed specifically to identify psychotic symptoms. This may have resulted in less sensitivity in detecting weaker symptoms with an underestimation of symptom prevalence in this sample. Another important limitation is the cross-sectional nature of the study. Our ability to draw causal conclusions between traumatic experiences and psychotic symptoms is limited by a lack of clear temporal information. If psychotic symptoms preceded trauma in only a couple of the cases this would have serious implications since the numbers with psychotic symptoms is small. However, our data from parental interviews show that exposure to domestic violence, at least, occurred from a very young age, typically less than 5 years old.
The questions on sexual abuse in the interview instrument involve a somewhat narrow definition of abuse and the ambiguity of these questions may partially explain the low sexual abuse rates reported in this study. One study, based on self-report questionnaires, has suggested that sexual abuse (or, more specifically, ‘unwanted sexual experiences’) is, in fact, more common among adolescents who report having experienced psychotic symptoms. Reference Campbell and Morrison30 Although the present study was population based, it does not represent a true population cohort since one of the two groups was selected for being ‘at risk’ of psychiatric problems, based on screening measures. However, we have controlled for psychiatric disorders in our analysis. There was also a higher than expected refusal rate among the comparison group. Although the overall sample size was large, there were small numbers with the symptoms of interest and with the experiences of interest (particularly sexual abuse). For these reasons, replication of our findings is warranted.
Early life traumatic events and psychosis
Clearly not all individuals who experience severely traumatic events in childhood go on to develop a psychotic disorder. Disease causation is a dynamic process and should be considered in terms of a pathway over a life course rather than in terms of a certain set of risk factors at a point in time. Reference Cannon and Clarke34 Other ‘environmental’ risk factors for schizophrenia, such as obstetric complications, Reference Clarke, Harley and Cannon35 urbanicity Reference Krabbendam and van Os36 or cannabis use, Reference Caspi, Moffitt, Cannon, McClay, Murray, Harrington, Taylor, Arseneault, Williams, Braithwaite, Poulton and Craig37 may have cumulative or interactive effects on psychosis risk. None the less, this paper adds to the evidence that traumatic childhood events may be part of a cascade that leads to the development of psychotic symptoms and may ultimately contribute to the onset of psychotic illness.
Appendix
K–SADS Psychosis sectionReference Kaufman, Birmaher, Brent, Rao and Ryan 15 (reprinted with permission)
Hallucinations:
Sometimes children, when they are alone, hear voices or see things, or smell things and they don't quite know where they come from. Has this ever happened to you? Tell me about it.
Has there ever been a time you heard voices when you were alone? What did you hear?
Have you ever heard someone call your name when there was no one around?
What kind of things did you hear?
Did you ever hear music which other people could not?
Has there ever been a time when you saw things that were not there?
What about shadows or other objects moving?
Did you ever see ghosts? When?
Did this only happen at night while you were trying to sleep, or did it happen in the daytime too?
What did you see? Has there ever been a time when you had an unusual smell about yourself?
Delusions
Do you know what imagination is? Tell me.
Has there ever been a time your imagination played tricks on you?
What kinds of tricks? Tell me more about them.
Did you have any ideas about things that you didn't tell anyone because you are afraid they might not understand? What were they?
Did you believe in things that other people didn't believe in? Like what?
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a Clinician Scientist Award to M.C. (CSA/2004/1) from the Health Research Board (Ireland). L.A. is supported by a Career Scientist Award from the Department of Health (UK). We thank Ms Carla Mills and Ms Irene Daly for their roles in conducting clinical interviews for this study. The original Challenging Times study was funded by Friends of the Children's University Hospital (Dublin), the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention, HSE Northern Area and the Mater Misericordiae University Hospital.





eLetters
No eLetters have been published for this article.