It is estimated that on average 15.6% pregnant women (95% CI 15.4–15.9) and 19.8% (95% CI 19.5–20.0) women who have recently given birth in low- and lower-middle-income countries (LMIC) experience a common mental disorder (CMD) including depression and anxiety. Reference Fisher, de Mello, Patel, Rahman, Tran and Holton1 These rates are substantially higher than those reported in high-income countries: 10% in pregnancy and 13% postnatally. Reference Hendrick2,Reference O'Hara and Swain3 These differences are attributed to the higher rates of exposure to individual and multiple risks and lack of access to protective factors for CMD that women living in resource-constrained settings can experience. Common correlates of perinatal CMD among women identified in cross-sectional studies in resource-constrained settings are socioeconomic disadvantage, unintended or unwelcome pregnancy, being younger, being unmarried, lacking intimate partner empathy and support, experiencing intimate partner violence, having insufficient emotional and practical support, having hostile in-laws, giving birth to a female baby, having a history of mental health problems, low education level and not having a secure income. Reference Fisher, de Mello, Patel, Rahman, Tran and Holton1,Reference Howard, Oram, Galley, Trevillion and Feder4,Reference Lund, Breen, Flisher, Kakuma, Corrigall and Joska5 There is, however, little evidence from longitudinal studies in these settings. Few have used diagnostic tests to examine whether common mental disorders apparent in advanced pregnancy or in the early postpartum period persist, worsen or diminish over the subsequent year and what factors are associated with these outcomes. The aims of this study were to determine, first, the incidence of and recovery from CMD among rural Vietnamese women, and second, the risk and protective factors associated with these outcomes in the first year after giving birth.
Method
The study was a population-based prospective study of a cohort of women who were in the last trimester of pregnancy or had recently given birth. Data were collected in two surveys: the baseline survey (S1) at recruitment and the follow-up survey (S2) when the women’s children were aged 15 months. The baseline survey was conducted in rural and urban provinces. The design and results of the baseline survey have been reported elsewhere. Reference Fisher, Tran, La, Kriitmaa, Rosenthal and Tran6,Reference Tran, Tran, La, Lee, Rosenthal and Fisher7 In brief, the prevalence of CMD (29.9%, 95% CI 25.2–34.7) was the same among women who were in advanced pregnancy and those who had recently given birth, but in the rural Ha Nam province it was more than double that in the national capital, Hanoi (OR = 2.17, 95% CI 1.19–.93).
Ha Nam province is located approximately 50 km south of Hanoi; it is a typical Red River delta province. It was selected because it is accurately representative of rural provinces in Vietnam and was willing to collaborate in research about women’s and children’s health. This province has both highland and lowland areas with a population of 0.8 million persons. The average annual per capita income was approximately USD850 in 2013; that is in the middle-income group in Vietnam. As is characteristic of rural Vietnam, most people rely on subsistence agriculture, principally rice farming. The healthcare system in this province follows the standard of rural Vietnam in that every commune has a health centre that is responsible for primary healthcare and implementation of national public health programmes. It is estimated that more than 99% of women have at least one antenatal healthcare visit and give birth in a medical facility. Mental health is not considered either in antenatal care or in primary postnatal healthcare in Vietnam.
Participants and recruitment
Participants in this study were recruited through a two-stage sampling procedure. First, six of a total 116 communes in Ha Nam were randomly selected by an independent statistician using the ‘select’ command in Stata version 11. A commune is the primary local government administrative unit in Vietnam; each has a health centre and a population of 5000–10 000 residents. Inclusion criteria for participants were:
-
(a) living in one of the selected communes;
-
(b) being at least 32 weeks pregnant with a single fetus or being the mother of a singleton infant 4–6 weeks old;
-
(c) being registered with the commune health centre;
-
(d) being able to provide informed consent to participate.
There were approximately 35–45 eligible women in each commune. In the second stage, all women who met inclusion criteria were informed of the study and invited to participate.
Data sources
Data were collected by study-specific structured questions and locally validated standardised psychometric measures. Common mental disorders were assessed at S1 and S2 by psychiatrist-administered Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis I Disorders (SCID-I) modules for major depressive episode, generalised anxiety and panic disorder. Reference First, Gibbon, Spitzer and Williams8 This is the demonstrated gold standard for diagnosis of mood disorders in diverse cultural settings and countries. Reference Gorman, O'Hara, Figueiredo, Hayes, Jacquemain and Kammerer9
Quality of intimate partner relationship was evaluated at S2 by the 24-item Intimate Bonds Measure (IBM), Reference Wilhelm and Parker10 which yields scores on two subscales: the Care subscale assesses perceived sensitivity, warmth, emotional responsiveness, trust, physical gentleness and capacity for companionship, and the Control subscale assesses perceived coerciveness, exertion of power or dominance and extent of criticism. Scores on each subscale range from 0 to 36, with higher scores on the Control subscale indicating less optimal and on the Care subscale more optimal quality of relationship. The Vietnamese validation of the IBM demonstrated that it was meaningful and comprehensible to Vietnamese women and sensitive to relevant aspects of relationship with the intimate partner. Reference Fisher, Tran, Biggs and Tran11 It has an identical factor structure to the original measure.
The quality of the woman’s relationship with her own mother and mother-in-law was ascertained at S2 by single study-specific fixed-choice questions assessing trust and affection in these relationships. Practical sharing of the unpaid workload experienced by the woman in the first year after childbirth was ascertained at S2 by three fixed-choice questions to assess how much assistance she received with care for the baby during the day, care for the baby during the night and household tasks.
Women’s experiences of past and current interpersonal violence were assessed by study-specific questions. Childhood sexual abuse was assessed at S1 as any unwanted sexual encounter with an adult, and physical abuse as being beaten or otherwise physically mistreated by a parent or other person in authority before the age of 16 years. Experiences of intimate partner violence were assessed at S2 in two dimensions: fear of the partner (an indicator of emotional abuse), or any experience of being hit, slapped, kicked, dragged, choked or punched (physical abuse) during the past year.
Reproductive health and current pregnancy were assessed by study-specific questions at S1 including numbers of prior miscarriages and stillbirths, numbers of living children, birth spacing, and if this pregnancy was unintended or unwelcome.
Child variables were collected at S2 including gender, age, common health problems (e.g. fever, cough) in the past 2 weeks, and whether the child had ever been admitted to hospital for treatment. Sociodemographic variables were collected by study-specific questions at S1 and included age and marital, educational and occupational status. Household wealth was assessed by the World Bank household wealth index method, Reference Tran12 calculated from the information about 17 household characteristics, services and durable assets.
Procedure
As completion of self-report questionnaires is unfamiliar, data were collected by face-to-face individual interviews and recorded on paper forms, which is preferred. All interviews were conducted in private rooms at commune health centres by trained health research interviewers from the Research and Training Centre for Community Development (RTCCD). Author B.L., a senior Vietnamese psychiatrist from the RTCCD TuNa mental health clinic, administered the SCIDs in separate individual interviews at both assessment points: the first was in November and December 2006 and the second in January and February 2008.
Statistical analysis
The probabilities and 95% confidence intervals of the changes of maternal mental health status (having any CMD v. no CMD) were calculated (see Fig. 1). In order to examine the factors associated with the incidence of CMD in the first year after childbirth, a multiple logistic regression model was constructed that included only women who were healthy (not having a diagnosable CMD) at S1. The outcome variable was coded 1 as being diagnosed with any CMD (new cases of CMD) at S2 and 0 as healthy at S2 (healthy at both time points). A second multiple logistic regression model was constructed that included only women who were diagnosed with any CMD at S1, to examine the factors associated with recovery from CMD at S2. In this model the outcome variable was coded 1 as healthy at S2 (changing from CMD at S1 to healthy at S2) and 0 as being diagnosed with any CMD at S2 (persistent CMD). These models were built using a stepwise backward elimination method in which the significance level of P<0.1 is required to permit inclusion of a variable into the final model. Covariates included in these initial models were based on the findings of our previous studies in Vietnam, Reference Fisher, Tran, La, Kriitmaa, Rosenthal and Tran6,Reference Fisher, Tran, Duc Tran, Dwyer, Nguyen and Casey13 and evidence about perinatal CMD among women from other LMIC. Reference Fisher, de Mello, Patel, Rahman, Tran and Holton1,Reference Howard, Oram, Galley, Trevillion and Feder4,Reference Lund, Breen, Flisher, Kakuma, Corrigall and Joska5 These included sociodemographic characteristics (maternal age, education level and current occupation, and the child’s gender and age at the follow-up survey); the number of living children; whether or not the participant had an affectionate and trusting relationship with own mother and/or with her mother-in-law; had experienced childhood maltreatment and/or fear of or physical abuse by her intimate partner in the past year; whether the pregnancy had been unintended or unwelcome; birth spacing; past experience of miscarriage or stillbirth; support experienced with care of the baby during the day and overnight, and housework; interval between giving birth and resuming income-generating work and income security. They also included scores for standardised measures including the IBM Control and Care subscale scores and the Household Wealth Index. Finally, all analyses controlled for whether participants were in advanced pregnancy or the early postpartum period when they completed the baseline survey. Data analyses were performed in Stata version 12 for Windows.
Ethics approval
Approvals to conduct the study were provided by the Vietnam Medical Association Ethics and Scientific Committee and the University of Melbourne’s Health Sciences Human Research Ethics Committee (HREC 050793). All participants were provided with an oral and written plain language description of the study; those who could write signed a consent form, others provided a thumbprint or verbal consent witnessed by an independent observer. The consent procedure was approved by the ethics committees.
Results
Overall, 234 of 255 eligible women (91.8%) agreed to participate and provided data at S1. Of these, 211 women (90.1%) provided complete data in the follow-up survey and were included in the analyses reported here. The baseline characteristics of women who did not provide data at S2 and were therefore not included in this study were not significantly different from those for whom complete data were available.
The characteristics of the sample (Table 1) were similar to those of other studies of perinatal health among women in rural Vietnam. Reference Tran, Tran, La, Lee, Rosenthal and Fisher7,Reference Hanieh, Ha, Simpson, Casey, Khuong and Thoang14 Among the 211 participants the age ranged from 20 years to 44 years, most had completed Year 9 as the highest education level, and most generated income through agricultural or manual work. No women endorsed any experience of childhood sexual violence.
Common mental disorders
On the basis of the SCID interviews it was established that the proportion of women with symptoms meeting diagnostic criteria
Table 1 Sociodemographic characteristics, reproductive health, intimate relationships and exposure to violence of 211 women
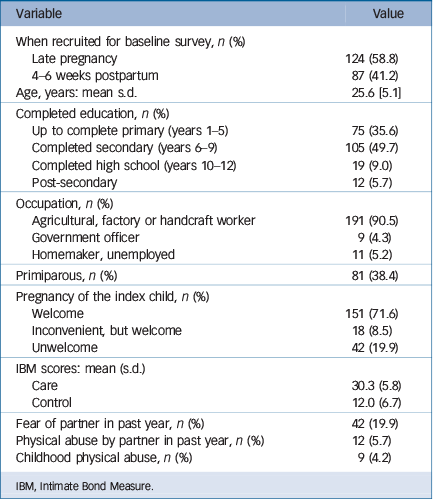
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| When recruited for baseline survey, n (%) | |
| Late pregnancy | 124 (58.8) |
| 4–6 weeks postpartum | 87 (41.2) |
| Age, years: mean s.d. | 25.6 [5.1] |
| Completed education, n (%) | |
| Up to complete primary (years 1–5) | 75 (35.6) |
| Completed secondary (years 6–9) | 105 (49.7) |
| Completed high school (years 10–12) | 19 (9.0) |
| Post-secondary | 12 (5.7) |
| Occupation, n (%) | |
| Agricultural, factory or handcraft worker | 191 (90.5) |
| Government officer | 9 (4.3) |
| Homemaker, unemployed | 11 (5.2) |
| Primiparous, n (%) | 81 (38.4) |
| Pregnancy of the index child, n (%) | |
| Welcome | 151 (71.6) |
| Inconvenient, but welcome | 18 (8.5) |
| Unwelcome | 42 (19.9) |
| IBM scores: mean (s.d.) | |
| Care | 30.3 (5.8) |
| Control | 12.0 (6.7) |
| Fear of partner in past year, n (%) | 42 (19.9) |
| Physical abuse by partner in past year, n (%) | 12 (5.7) |
| Childhood physical abuse, n (%) | 9 (4.2) |
IBM, Intimate Bond Measure.
for at least one CMD including depression, anxiety and comorbid depression and anxiety disorders almost halved from the baseline to the follow-up assessment (Table 2). The same pattern occurred in every subtype of CMD. There was no difference in prevalence between the pregnant and postpartum groups within the cohort at S1 or S2. The transition diagram (Fig. 1) presents the probabilities of the changes of mental health status from baseline to follow-up. More than two-thirds of women with CMD at baseline had recovered by the follow-up assessment. The probability (incidence) of a woman who was healthy at baseline having symptoms meeting diagnostic criteria for a CMD at follow-up (0.13, 95% CI 0.08–0.19) was significantly lower than the probability of a woman having a CMD at baseline and also experiencing at least one CMD at follow-up (0.30, 95% CI 0.20–0.40).
Regression analyses
The results of the backward stepwise logistic regression analysis of the incidence of CMD among women who were healthy at baseline are shown in Table 3. Low IBM Care subscale scores (less optimal intimate partner relationship), low household wealth index (poorest quintile) and having experienced physical abuse in childhood were associated with developing a CMD in the first year after giving birth. Having a trusting and affectionate relationship with her own mother was a protective factor. Incidence of CMD also appeared to be more likely among women whose infant had been admitted to hospital during the prior year (P = 0.06, approaching the significant level).
Factors associated with recovery from CMD in the first year postpartum were examined in the second backward stepwise logistic regression analysis (Table 4). Women who had a period of heightened care from others for at least 1 month postpartum before resuming usual activities were more likely to recover from CMD than women who did not receive this care and had to resume household tasks and income-generating work within a
Table 2 Common mental disorders among the women at baseline (late pregnancy or early postpartum) and at follow-up 1 yearlater (n = 211)

| Baseline n (%) |
Follow-up n (%) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Any mental disorder | 71 (33.6) | 39 (18.5) |
| Major depression | 36 (17.1) | 18 (8.5) |
| Generalised anxiety and/or panic disorder | 25 (11.8) | 16 (7.6) |
| Comorbid depression and anxiety disorder | 10 (4.7) | 5 (2.4) |
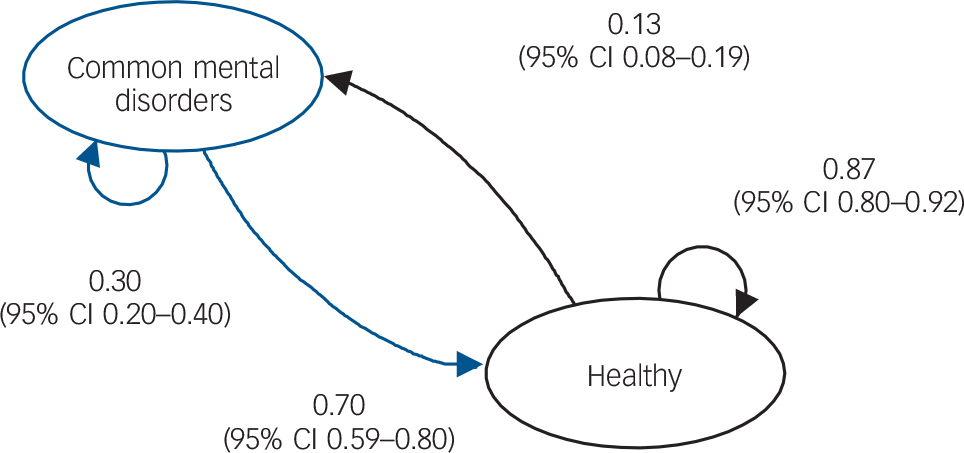
Fig. 1 Transition diagram of the states of maternal mental health from late pregnancy or early postpartum to 1 year after childbirth (path coefficients are probabilities).
Table 3 Multiple logistic regression model predicting the incidence of common mental disorders 1 year after childbirth among women free from disorders at baseline
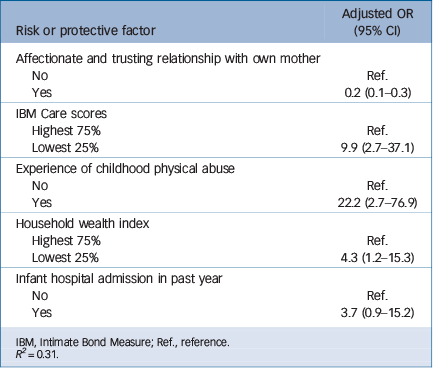
| Risk or protective factor | Adjusted OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|
| Affectionate and trusting relationship with own mother | |
| No | Ref. |
| Yes | 0.2 (0.1–0.3) |
| IBM Care scores | |
| Highest 75% | Ref. |
| Lowest 25% | 9.9 (2.7–37.1) |
| Experience of childhood physical abuse | |
| No | Ref. |
| Yes | 22.2 (2.7–76.9) |
| Household wealth index | |
| Highest 75% | Ref. |
| Lowest 25% | 4.3 (1.2–15.3) |
| Infant hospital admission in past year | |
| No | Ref. |
| Yes | 3.7 (0.9–15.2) |
IBM, Intimate Bond Measure; Ref., reference.
R 2 = 0.31.
Table 4 Recovery by 1 year postpartum among women experiencing common mental disorders at baseline: multiple logistic regression

| Risk or protective factor | Adjusted OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|
| Time to resume usual responsibilities | |
| < 30 days after childbirth | Ref. |
| 30 days or more after childbirth | 14.4 (3.1–31.2) |
| Experienced IPV in past year | |
| No | Ref. |
| Yes | 0.25 (0.06–0.51) |
| Having support with household work and infant care | |
| No | Ref. |
| Yes | 3.4 (1.1–12.7) |
IPV, intimate partner violence; Ref., reference.
R 2 = 0.26.
month of giving birth. Women who experienced IPV in the first year postpartum were less likely to recover than women who did not experience IPV. Sharing the practical household work was associated with recovery.
Discussion
This is to our knowledge the first study to date to examine changes in psychiatrist-diagnosed common mental disorders among women prospectively in the first year after giving birth in an LMIC. We took into account a comprehensive range of risk and protective factors identified in studies of postnatal CMD in LMIC as well as those specific to the study population. Subgroup analyses of mental health status 15 months after giving birth among women who were or were not experiencing CMD at baseline allowed us to distinguish the specific factors associated with the incidence of and recovery from such disorders in the first postpartum year. We acknowledge that the relatively small sample size might limit study power to detect associations among risk and protective factors and the outcomes if the effect sizes were small. We aimed to detect factors that had large effect sizes that could inform public health interventions in LMIC. We also acknowledge that in using single questions to ascertain prior experiences of childhood maltreatment and intimate partner violence, rather than using more detailed lists of abusive behaviours, we are likely to have underascertained experiences of family violence among participants.
Recovery factors
There was a significant spontaneous decline in the point prevalence of CMD among women from the perinatal period to 1 year postpartum. Overall 70% (95% CI 59–80) of women who experienced a perinatal CMD recovered in the following year. None received formal mental healthcare. The factors that contributed to recovery from CMD were having a sustained period of mandated rest and heightened postpartum care before having to resume usual responsibilities, not having experienced intimate partner violence in the prior year and having practical support with household work and infant care. These findings are similar to existing evidence from Vietnam and other LMICs. Reference Fisher, de Mello, Patel, Rahman, Tran and Holton1,Reference Fisher, Tran, La, Kriitmaa, Rosenthal and Tran6 A short postpartum interval prior to resuming usual responsibilities was associated with higher rates of clinically significant depressive symptoms among women 6–8 weeks postpartum in the south of Vietnam. Reference Fisher, Morrow, Ngoc and Anh15 Experience of intimate partner violence has not been assessed in most prior research on perinatal CMD in LMICs, but, there is consistent evidence in the studies that have ascertained this exposure that it constitutes a serious risk. Reference Fisher, de Mello, Patel, Rahman, Tran and Holton1,Reference Howard, Oram, Galley, Trevillion and Feder4 Although intuitively likely, this is the first study to demonstrate in an LMIC that having other family members share the practical work of household tasks and infant care was associated with better postnatal mental health outcomes among women.
Development of mental disorder
Despite the decline discussed above, there was a considerable incidence of CMD in the first year after giving birth (13%, 95% CI 8–19). We are not aware of any previous studies in LMIC that have reported data on the incidence of CMD in women in the first year postpartum. However, a study in Italy of 1066 women reported the incidence of depression assessed by a diagnostic tool in the first year after giving birth as being 6.8%. Reference Banti, Mauri, Oppo, Borri, Rambelli and Ramacciotti16 Gavin et al reviewed studies conducted in high-income countries up to March 2004 which had used diagnostic interviews to establish point prevalence or incidence of depression among women in the postpartum year. Reference Gavin, Gaynes, Lohr, Meltzer-Brody, Gartlehner and Swinson17 They reported a rate after the seventh postpartum month similar to the Italian study (6.5%). The difference between the incidence we found and the results of studies in high-income countries indicates that differences in prevalence of risk factors between these settings are relevant.
In our study the experience of childhood maltreatment and experiencing the intimate partner as providing little care, sensitivity, kindness or affection and the chronic stress of household poverty were risks for the incidence of CMD in the first year postpartum. Having an affectionate and trusting relationship with the woman’s own mother was protective. These factors have been reported as the correlates of perinatal CMD among women in Vietnam, Reference Fisher, Morrow, Ngoc and Anh15,Reference Fisher, Tran, Biggs, Dang, Nguyen and Tran18 and in other LMIC. Reference Fisher, de Mello, Patel, Rahman, Tran and Holton1,Reference Howard, Oram, Galley, Trevillion and Feder4,Reference Lund, Breen, Flisher, Kakuma, Corrigall and Joska5 The first year after giving birth is an especially demanding developmental phase for a woman as she adjusts to the work of caring for an infant and managing a household in which an infant lives. Women’s needs for care and support from others are heightened and those whose partners are neither encouraging nor willing to share this work fairly are placed in a vulnerable predicament. It is worsened if they are living with severe economic difficulties, which we have shown in this setting are associated with deep distress about food insufficiency and inability to purchase healthcare or medicine for the baby. Childhood maltreatment is known to have new psychological significance for women when they themselves become mothers and can identify with their dependent infants, and often experience distress in becoming aware that their caregivers were not protective when they were themselves young children. Conversely, women who trusted their own mothers and experienced them as helpful and kind were at a low risk of developing CMD in this period.
Public health implications
There is growing evidence of the adverse effect of exposure to maternal perinatal CMD on infant health and development in LMIC. Reference Howard, Oram, Galley, Trevillion and Feder4,Reference Rahman, Bunn, Lovel and Harrington19–Reference Tran, Tran, Simpson, Tran, Nguyen and Hanieh22 There is increasing recognition that mental disorders among women who are pregnant or have recently given birth is a major public health problem in these resource-constrained settings. Interventions to address them can be implemented effectively by trained, supervised community-based health workers, but only have an impact on early childhood development when it is targeted directly. Reference Rahman, Fisher, Bower, Luchters, Tran and Yasamy23 In addition to a focus on symptom reduction through cognitive-behavioural therapy, a direct focus on evidence-informed risk factor reduction is crucial and likely to have a much greater population impact. The data reported here provide further evidence about the most significant modifiable factors for postnatal mental health problems among women and have important implications for policy-making and public health. They indicate that rather than focusing only on women there is a need to educate men who are pregnancy partners or the fathers of very young children about the importance of their behaviour towards women. Countries that have retained a strong traditional divide in the roles and responsibilities of women and men can use this evidence to challenge stereotypes about the division of household labour and the care of young children and emphasise the value to families, communities and societies when these responsibilities are shared fairly between women and men. Interpersonal violence including childhood maltreatment and intimate partner violence is destructive of the recipients’ mental health. Interpersonal violence is especially problematic during the perinatal life phase when women are confined to the domestic domain and have more limited access to protective opportunities such as interactions with peers and participation in income-generating work. Reference Fisher, Tran, Biggs, Dang, Nguyen and Tran18 These data reinforce the importance of perinatal specific strategies for the reduction of intimate partner violence. Reference Howard, Oram, Galley, Trevillion and Feder4 They also emphasise the psychological benefits to women of having access to their own mothers as they acquire the skills of infant care and adjust to the work of mothering. This is more difficult when women relocate on marriage to live in their parents-in-laws’ household, but as restrictions placed on women’s freedom to travel outside households are diminishing, enabling them to have frequent access to their own mothers warrants consideration.
To date there has been no public health intervention to prevent or ascertain and treat perinatal CMD among women in Vietnam. We recently translated, adapted and field-tested in rural Vietnam the Thinking Healthy Programme, Reference Rahman, Malik, Sikander, Roberts and Creed24 which was developed to reduce perinatal CMD among women in rural Pakistan using specific cognitive-behavioural therapy strategies to assist women to modify maladaptive thinking styles and to increase problem-solving capabilities. The results of the pilot study indicate that this programme is acceptable, comprehensible and salient to pregnant women in this setting and can be administered to small groups in the commune health centre rather than just to individual women in home visits. Reference Fisher, Nguyen, Mannava, Tran, Dam and Tran25 We are investigating the suitability of other programmes which have been demonstrated in randomised controlled trials in other settings to be effective in preventing or reducing CMD among women.
Clinical implications
Modifiable social factors, including the quality of a woman’s relationships with her intimate partner and her own mother, are central to women’s mental health from early pregnancy through the postpartum year. Interventions should include these people and address their knowledge and skills directly, emphasising the importance of their provision of emotional support and their involvement in the work of infant care and household tasks.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Myer Foundation and Monash University who funded the research. They are also grateful to the research staff from the Research and Training Centre for Community Development in Hanoi who collected the data, the commune health workers in Hanoi and Ha Nam who assisted with recruitment and the participants who contributed their time and experiences.








eLetters
No eLetters have been published for this article.