In the original publication “Guidance for switching from off-label antipsychotics to pimavanserin for Parkinson’s disease psychosis: an expert consensus,” by Black et al. (Reference Black, Nasrallah and Isaacson2018), the authors regret the errors found in Table 1; Boxes 1, 3, and 4; and Figure 1. The correct Table 1, Boxes 1, 3, and 4, and Figure 1 are given below.
Table 1 Receptor binding affinities for select antipsychotic agents

+ weak binding affinity (100>Ki<1000)
++ moderate binding affinity (10>Ki<100)
+++ strong binding affinity (1>Ki<10)
++++ very strong binding affinity (Ki<1)
Abbreviations: 5-HT = serotonin; α = adrenergic; D = dopamine; H = histamine; M = muscarinic.
Ki (nM) values are derived from functional antagonist R-SATTM assays (ACADIA, San Diego, CA, USA).
“-” denotes no response.
Adapted from Hacksell et. al. Neurochem Res 2014; 39:2008-2017 and from data on file.
Box 1. Dosing tips for switching to pimavanserin from low-dose (≤ 100 mg) Quetiapine (see Figure 3)
Add full dose (34 mg) pimavanserin to current low dose (up to 100 mg) quetiapine for 4 weeks
Allows pimavanserin to reach steady state and the duration of treatment necessary to reach its delayed onset of therapeutic action
Then reduce quetiapine by 50% weekly until reaching 12.5 mg, then discontinue
If efficacy for PDP diminishes during quetiapine taper, can return to previous dose level and try tapering again in 1 week
Box 3. Dosing tips for switching to pimavanserin from low-dose (≤ 100 mg) Clozapine (see Figure 5)
Add full dose (34 mg) pimavanserin to continuing clozapine dose for 6 weeks
Then reduce clozapine by 6.25 mg weekly until discontinued and in no event, not less than 4 weeks of tapering
If efficacy for PDP diminishes during clozapine taper, can return to previous dose level and try tapering again in 1 week
Recommend not removing patient from clozapine registry for a few months in case clozapine must be restarted
Box 4. Dosing tips for switching to pimavanserin from high-dose (> 100 mg) Clozapine (see Figure 6)
Add full dose (34 mg) pimavanserin to continuing clozapine dose for 6 weeks
Then reduce clozapine by 25 mg weekly until discontinued and in no event, not less than 4 weeks of tapering
If efficacy for PDP diminishes during clozapine taper, can return to previous dose level and try tapering again in 1 week
Recommend not removing patient from clozapine registry for a few months in case clozapine must be restarted
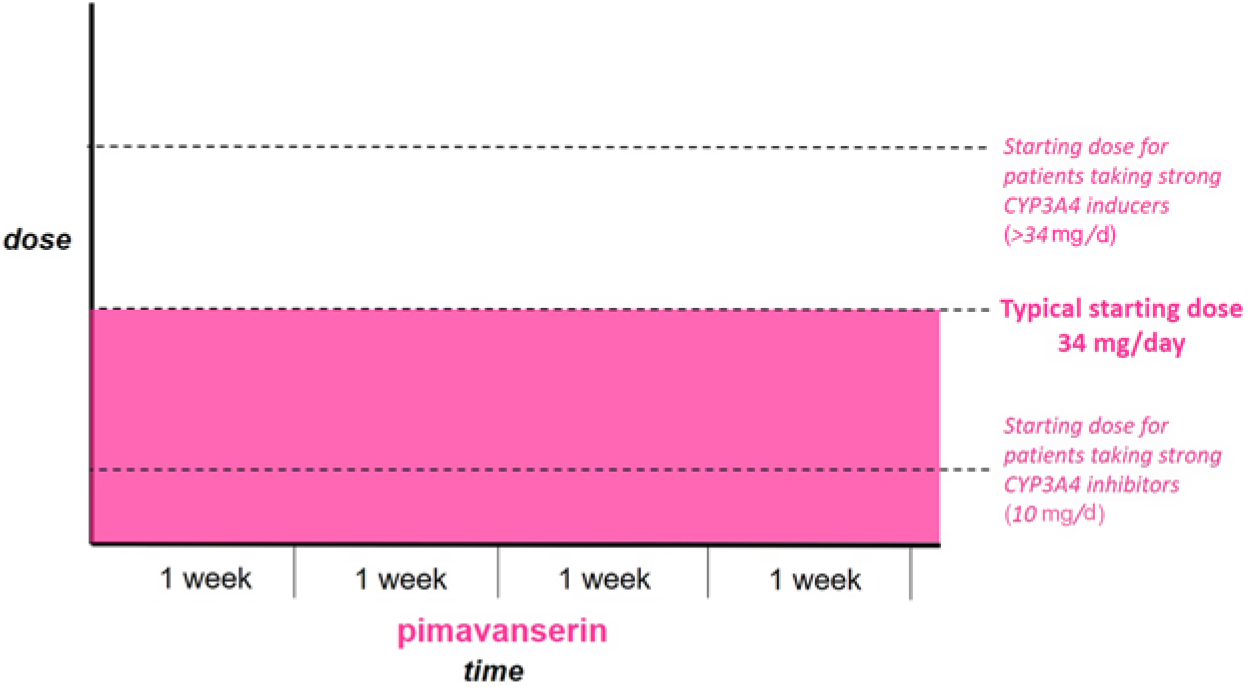
Figure 1 Patients not currently taking antipsychotic medication. Start full dose of Pimavanserin immediately.
In addition, the authors would like to make the following text corrections and clarifications:
Page 405:
The MDS EBM was published in 2011.
Page 406:
The doses in the early phase 2b/3 study were placebo, 8.5, and 34 mg/d.
The P-value for the hallucination and delusions subscales was 0.0012.
Sleep quality, caregiver burden, etc. were exploratory outcomes.
Page 407:
The QT prolongation for pimavanserin is 5-8 msec.
The original publication has been corrected to reflect these changes.




