Weight gain and changes in body composition can follow a diagnosis of breast cancer and treatment( Reference Vance, Mourtzakis and McCargar 1 ) and increases the risk of cancer recurrence and other obesity-related disorders comorbidities and has a negative effect on quality of life.( Reference Chen, Lu and Zheng 2 ) There is limited data concerning dietary intakes made by women after a cancer diagnosis,( Reference Vance, Campbell and McCargar 3 ) particularly early in the treatment trajectory when changes are likely to be initiated. The aim of this study was to investigate self-reported changes in dietary intake in early stage breast cancer during the first year following treatment.
Thirty-one women with early stage breast cancer were recruited from a local hospital clinic and studied at baseline (pre-treatment) and thereafter at 3, 6 and 12 months. The mean age of the women was 62.3 (42–85) years; BMI at baseline was 28.0 (20–40.9) kg/m2; 25 of the women were post-menopausal. At each time point dietary data was collected using 4-day weighed diet diaries. Nutrient intakes were analysed using dietary analysis software (NetWISP v4.0, Tinuviel Software, Warrington, UK). All the women completed the study.
Overall the mean body weight remained unchanged by 12 months. However within the group 55 % (n = 17) of the women had lost > 2 kg (maximum weight loss 12.1 kg), 26 % (n = 8) had gained >2 kg (maximum weight gain 6.2 kg) and 6 women (19 %) had stable weight. A significant reduction in dietary energy was observed by 12 months (P < 0.01). Whilst there were significant declines in both dietary carbohydrate and protein at 3 (P < 0.05) and 12 months (P < 0.01), total fat intake remained unchanged.
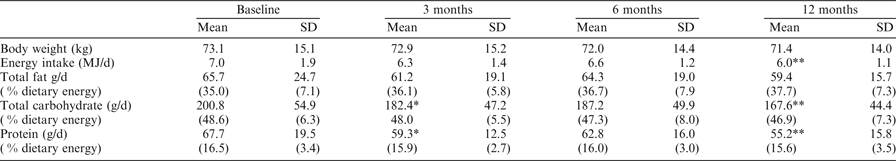
Mean value was significantly different from baseline. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01
These results show that the majority of these breast cancer patients lost weight after the first year following treatment reflected in reductions in energy, total carbohydrate and protein intakes, but not total fat. The data would suggest that studies should not solely focus on mean weight gain but consider individual weight trajectories including weight loss and stable weight. More research is needed to understand dietary patterns in the early phase post treatment for breast cancer to encourage women to follow healthy behaviours that could reduce the risk of cancer recurrence, and potentially improve their prognosis and survival.


