Epigenetics refers to the regulation of gene expression through processes that do not change DNA sequence. These changes usually occur in response to environmental conditions and are inheritable through cell division. DNA methylation is the most studied and most common epigenetic modification, influencing gene expression when reduced in promoter regions, the binding site of enzymes responsible for transcription, and increased in the body and 3’ end of genes(Reference Yu, Ware and Waterland1). In vertebrates, this is represented by a methyl group covalently bound to the carbon at the 5’ position of the pyrimidine ring of 5-methylcytosine (5mC) in a CpG dinucleotide (a cytosine followed by a guanine). Genome CpG density is low, with the majority of CpG being present in CpG islands (CGI) that are on average 1000 bp long(Reference Deaton and Bird2) and have a relatively high concentration of hypomethylated CpG dinucleotides.
Approximately 70% of annotated promoters are associated with CGI(Reference Saxonov, Berg and Brutlag3–Reference Lister, Pelizzola and Dowen5), including promoters of tissue-specific genes and developmental regulators(Reference Larsen, Gundersen and Lopez6,Reference Lokk, Modhukur and Rajashekar7) , with around 50% of the CGI in mice and humans located in transcription start sites(Reference Illingworth, Gruenewald-Schneider and Webb8). While the functionality of dynamic methylation patterns of the CGI has been more associated with repression of transposons (DNA sequences capable of moving from one location to another within the genome) and repetitive elements, imprinting (selective monoallelic expression), X-inactivation (inactivation of one copy of the X chromosome in females) and promoter accessibility to transcription factors (TCF)(Reference Edwards, Yarychkivska and Boulard9), most DNA methylation patterns are probably not biologically functional, making it difficult to create a causation link between DNA methylation, transcriptional activation and gene expression(Reference Lister, Pelizzola and Dowen5,Reference Edwards, O’Donnell and Rollins10) . However, most CGI promoters are protected against de novo methylation indicating a functional reason for its maintenance in a hypomethylated state. This is corroborated by the embryonic lethality of the knockout (KO) of the DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) genes Dnmt1 or Dnmt3b in mice and the early death of Dnmt3a-KO mice(Reference Okano, Bell and Haber11,Reference Li, Bestor and Jaenisch12) . The DNMT enzymes are responsible for the establishment and maintenance of methylation patterns on DNA while ten-eleven translocation (TET) enzymes are linked with DNA methylation regulation by catalysing the conversion of 5mC into 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), which is the first step of the demethylation process(Reference Tahiliani, Koh and Shen13,Reference Rasmussen and Helin14) .
In somatic cells, DNA methylation patterns are maintained through inheritance across mitoses with remarkable precision(Reference Wigler, Levy and Perucho15) and can even be maintained across generations. However, the maintenance of methylation status is not universal in all genomic regions, as some regions without apparent regulatory functions are heterogeneously methylated even in cell clones(Reference Lister, Pelizzola and Dowen5,Reference Edwards, O’Donnell and Rollins10) .
The binding of TCF, proteins that regulate transcription, can reduce the methylation level of local and flanking CGI(Reference Bestor, Edwards and Boulard4), making it difficult to prove causality between DNA methylation and gene expression. However, the fact that a difference in the methylation pattern reflects modifications of gene expression levels indicates that DNA methylation could be a marker for modification of transcriptional patterns due to environmental changes such as diet and microbiota composition. This review highlights evidence on how nutritional status, diet and microbiota influence intestinal functionality through DNA methylation (Fig. 1), including methodologies used to measure DNA methylation in intestinal tissue, links between DNA methylation and intestinal development, differentiation and maturation and the influence of microbiome modulation on the intestinal methylome.
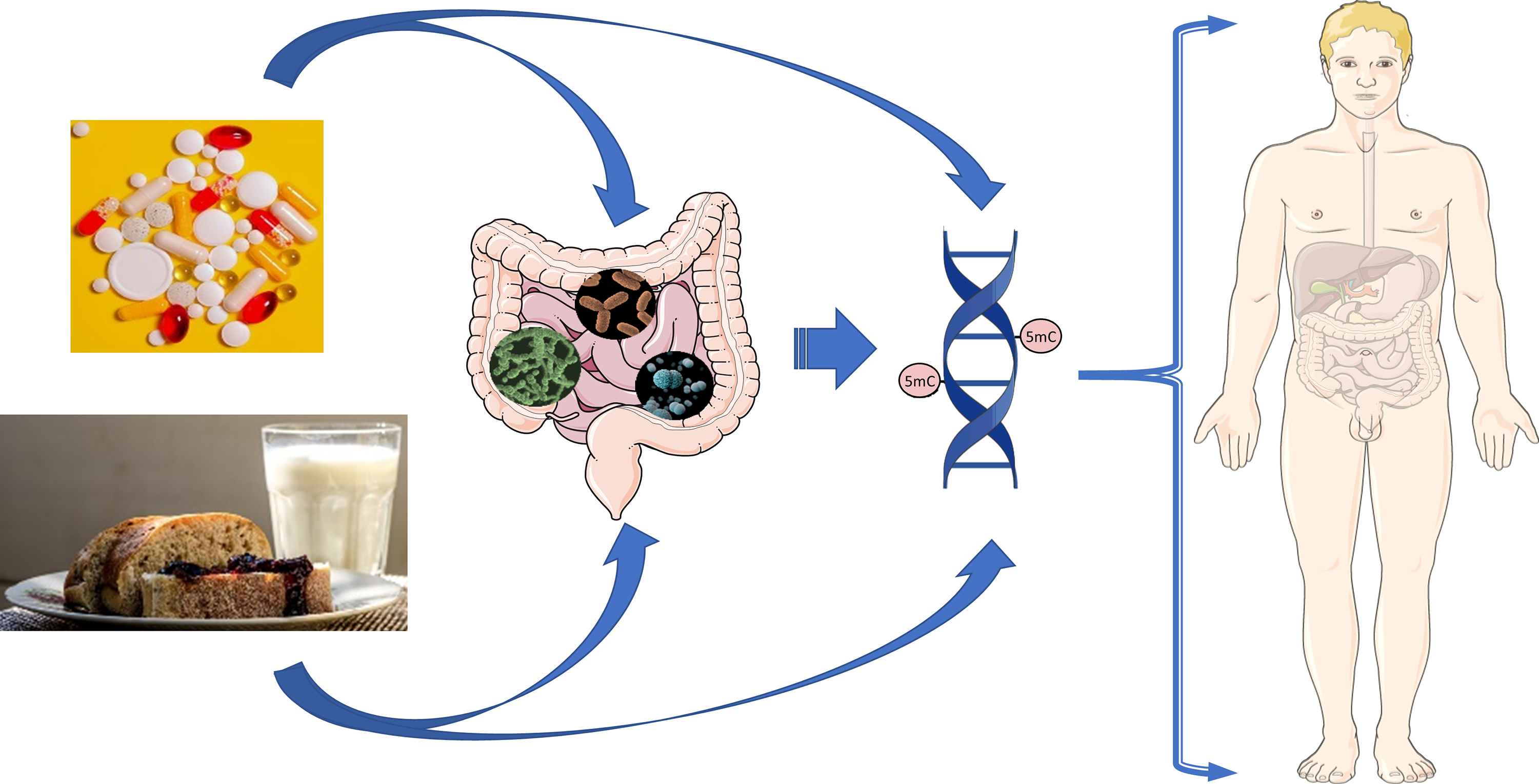
Fig. 1. Nutritional and microbial impacts on DNA methylation of the gastrointestinal tract.
Methodologies for the analysis of DNA methylation
Multiple methodologies have been used for the analysis of DNA epimodifications. As genome-wide approaches have become more viable and feasible due to improvements in DNA sequencing technology and analysis, epigenetic modification methodologies have also evolved to high-throughput technologies with single-base resolution.
The most used approaches for methylation profiling target one or a few genomic loci. Identifying CpG methylation on a sequence of defined length is frequently done by methylation-specific PCR (MSP)(Reference Herman, Graff and Myohanen16) or pyrosequencing(Reference Tost and Gut17). With either methodology, the DNA is first treated with bisulphite (BS) for the conversion of unmethylated cytosines into uracil and subsequently into thymines, which allows the identification of differently methylated loci(Reference Frommer, McDonald and Millar18). MSP utilises primers, small oligonucleotides complementary to the targeted region, that are specific for a methylated or unmethylated locus and the presence of a band determines the methylation status(Reference Herman, Graff and Myohanen16). One drawback is that only the region of the primers can be truly analysed and a CpG rich region is necessary to create primers specific enough to differentiate between methylated and unmethylated DNA. In BS pyrosequencing, the amplicon sequence can be analysed, which makes it a more quantitative and robust technique than MSP. Pyrosequencing entails sequencing-by-synthesis using pyrophosphate release to identify the nucleotide added to the sequence and therefore can quantify the ratio between cytosines and thymines at a given CpG position. It has also been extensively used as a validation technique for high-throughput methods(Reference Kraiczy, Nayak and Ross19–Reference Häsler, Feng and Bäckdahl25). MS-based approaches can also be used to analyse the methylation level at targeted regions(Reference Ehrich, Nelson and Stanssens26).
Global methylation quantification is the measure of the general level of DNA methylation without considering methylation changes at specific loci. Different techniques are used to investigate global methylation levels, such as pyrosequencing of Alu or long interspersed nuclear element 1 (LINE1) elements, luminometric methylation assay and HPLC. PCR-based methods estimate the methylation status of the most prevalent repetitive elements in the genome, Alu and LINE1, by pyrosequencing, where the cytosines:thymine ratio at a given CpG in LINE/Alu elements indicates the methylation status. Luminometric methylation assay uses the ratio of the digestion of unsensitive:sensitive isoschizomers to estimate the methylation status. Pyrosequencing LINE1 elements showed the smallest variation between samples and corresponded the best to results obtained by HPLC which is one of the most accurate methods to assess methylation(Reference Lisanti, Omar and Tomaszewski27). However, caution must be used in extrapolating evidence of methylation changes in LINE1 elements to global changes in specific conditions(Reference Yegnasubramanian, Haffner and Zhang28). High performance capillary electrophoresis and chromatography approaches separate methylated and unmethylated DNA by size, and both are quantified, but despite being considered the gold standard for methylation quantification, they usually require a large amount of DNA(Reference Ramsahoye29,Reference Armstrong, Bermingham and Bassett30) . MS also has high sensitivity and requires lower amounts of starting material(Reference Globisch, Münzel and Müller31,Reference Le, Kim and Fan32) .
For genome-wide methylation analysis, although microarray-based methodologies have been used extensively, they require whole genome amplification, which can insert sequence bias, and previous knowledge of the sequence for probe synthesis, but are much more cost-effective than next-generation sequencing approaches(Reference Yamashita, Hosoya and Gyobu33). This method has been progressively replaced by whole genome bisulphite sequencing (MethylC-seq) that now is considered the gold standard approach and can identify differently methylated regions (DMR) with single bp resolution. Whole genome bisulphite sequencing is done by sequencing of the whole genome after BS treatment and only one of the strands is analysed, although alternative protocols can analyse all four strands formed after the BS treatment(Reference Cokus, Feng and Zhang34).
The use of techniques to enrich samples with methylated cytosines or CpG-rich regions of the genome can be used together with genome-wide approaches such as microarrays or next-generation sequencing. The use of beads that have high affinity to 5mC to precipitate methylated regions (methylated DNA immunoprecipitation) of the genome(Reference Weber, Davies and Wittig35) is one enrichment technique. Methyl binding domain proteins can also be used to enrich methylated genome regions and although it can be used to compare regions between samples, it cannot assess single nucleotide methylation status(Reference Gebhard, Schwarzfischer and Pham36,Reference Selker, Tountas and Cross37) .
The use of methylation-sensitive discordant isoschizomers can be used in conjunction with microarrays and sequencing, in, for example, the HpaII tiny fragment enrichment by ligation-mediated PCR (HELP) assay and reduced representation bisulphite sequencing, respectively, usually with the intent to enrich CpG containing areas. The HELP assay(Reference Khulan, Thompson and Ye38) has also been used together with sequencing, and in this way it has similar CpG coverage to reduced representation bisulphite sequencing. HELP-tagging is a modification of the methyl-sensitive cut counting assay that uses the HpaII restriction enzyme, with a normalisation step using reads formed by non-methylation-sensitive MspI cleavage. This approach works for CpG rich sites, as well as more CpG depleted regions in the genome, and compares reads formed by MspI or HpaII digestion to estimate the methylation at each of these sites(Reference Suzuki, Jing and Lia39).
Reduced representation bisulfite sequencing(Reference Gu, Smith and Bock40–Reference Meissner, Mikkelsen and Gu42) uses restriction enzymes that have its recognition site in CpG dinucleotides and is insensitive to methylation (usually MspI); therefore, each fragment will contain two CpG (one on each end). After digestion and size selection of the fragments, the samples are BS treated to convert unmethylated cytosines into thymines and then sequenced. Reduced representation bisulphite sequencing is one of the most popular methylation assay techniques because it can be used to analyse 80% of the CGI and 60% of the promoters(Reference Bock, Tomazou and Brinkman43). But as the other BS-based methods, it cannot distinguish between methylcytosine and hydroxymethylcytosine. A more complete review on these and other methods for methylation analyses can be found at Tost and Gut(Reference Tost and Gut44).
DNA methylation and intestinal development and proliferation maintenance
The intestinal tract is the organ in mammals responsible for digestion of food for nutrient extraction and absorption and for excretion of digestion and metabolic waste. It is exposed to the external environment and is in constant and intimate contact with micro-organisms in a symbiotic manner.
The small intestine, where most nutrients are absorbed under neurological and endocrine regulation, is a hollow tube lined by a mucosal layer consisting of a single layer of epithelial cells that are the physical barrier between the commensal bacteria and the interior of the host body. These epithelial cells are a heterogeneous population and are being constantly renewed by the division of intestinal stem cells (ISC) located in the intestinal crypts. Other self-renewal cell populations, such as haematopoietic stem cells, have been shown to have progressive changes in DNA methylation in a cell-specific manner(Reference Lipka, Wang and Cabezas-Wallscheid45).
Intestinal development undergoes transitional stages before and after birth, with the postnatal period being crucial for proper intestine and immune system maturation in response to microbial colonisation, oral nutrition, weaning and nutrient availability(Reference Rakoff-Nahoum, Kong and Kleinstein46–Reference Pan, Sommer and Falk-Paulsen49). Differences in both gene expression and DNA methylation patterns in the intestines were observed during the transitions between fetal, suckling, weaning and adult life periods(Reference Rakoff-Nahoum, Kong and Kleinstein46,Reference Yu, Gadkari and Zhou50) , and differences between intestinal sections in response to maturation were also observed. Regional identity between the different intestinal sections has also been linked to stable DNA methylation signatures observed in paediatric and adult human intestinal epithelial organoids, with fetal-derived organoids presenting dynamic methylation changes suggestive of in vitro maturation(Reference Kraiczy, Nayak and Howell51). Notably, most genes that are differentially expressed at the transcriptional level between the suckling and weaning periods stabilise expression levels after weaning, suggesting that early life transitional states can influence gene expression in adult intestines(Reference Rakoff-Nahoum, Kong and Kleinstein46). Intrauterine growth restriction can also cause DNA methylation abnormalities(Reference Hu, Hu and Gong52), which could contribute to the gastrointestinal dysfunctions presented by infants with very low birth weight.
Crypts are responsible for cell proliferation and turnover rate of the intestines and go through maturation in the early postnatal period. Using Dnmt1 KO mice, Yu et al. observed a large variance in the methylome of colonic stem cells of intestinal crypts in mice during the suckling period, especially during maturation, the transition from fetal ISC to adult ISC, compared with differentiation, when the stem cell is turned into different types of epithelial cells(Reference Yu, Gadkari and Zhou50). The methylation occurred mainly as hypermethylation in CGI associated with gene bodies and the 3’ end of genes. Dnmt1 KO mice presented severe intestinal abnormalities and an 80% mortality rate, indicating that DNA methylation is indeed important to intestinal maturation and that dysregulation of methylation patterns in the early postnatal period can lead to an immature intestinal tract. Furthermore, the reduced methylation at the 3’ end of genes in the KO mice was associated with reduced gene expression. Corroborating with the study of Yu et al., Forn et al., using amplification of inter methylated sites sequencing (AIMS-Seq), found only few differences (only 1.65% of the amplicons) between differentiated villi cells and ISC in the small intestines of mice with hypermethylation being the vast majority of the changes(Reference Forn, Díez-Villanueva and Merlos-Suárez53).
Other studies have demonstrated the importance of DNMT1 and methylome establishment during the normal maturation and differentiation processes of ISC, confirming differences between methylomes during maturation and differentiation(Reference Elliott, Sheaffer and Schug54,Reference Sheaffer, Kim and Aoki55) . They observed a tendency for decreased methylation during differentiation and that DMR were enriched at CGI and CpG shores with the majority (61%) of DMR hypomethylated during differentiation being at intronic regions. A correlation between loss of methylation in promoter, 3’ untranslated region and first intron and increased expression level was observed, occurring mainly in genes associated with small intestine metabolism.
The DMR that gain methylation through differentiation were associated with signalling pathways important to ISC function such as wingless and Int-1 signalling pathways (Wnt) and overlap with binding sites for transcriptional factors in ISC such as caudal type homeobox 2 (CDX2)(Reference Sheaffer, Kim and Aoki55). Sheaffer suggests that hypomethylation coordinates the binding of TCF; however, Bestor et al. and others(Reference Mummaneni, Yates and Simpson56,Reference Matsuo, Silke and Georgiev57) propose that the binding of transcriptional factors causes the hypomethylation on the motif regions. Kaaij et al. also related the binding of a TCF with hypomethylation, in this case TCF4, which the author suggests contributes to DMR formation during differentiation of small intestine leucine-rich repeat-containing receptor 5 positive cells (Lgr5+ cells), a marker of ISC(Reference Kaaij, van de Wetering and Fang58). Comparing fetal and paediatric intestinal epithelial cells, Kraiczy et al. found that in human ileum and colonic cells, the potentially regulatory DMR frequently overlap transcription start sites and that these DMR were enriched in pathways involved with embryonic, tissue and intestine development. In regulatory DMR-associated genes, the expression was inversely related to promoter DNA methylation. Age was also inversely related to methylation of innate immunity genes and positively correlated with those genes’ expression levels.
Differences in methylation level in enhancers and promoters of genes related to ISC function were observed and although intestinal DNMT1 ablation in adult mice intestines can cause alternative methylation patterns in enhancers and delay the differentiation process (by extension of the cryptic zone), it seems to have milder effects compared with early life KO(Reference Yu, Gadkari and Zhou50,Reference Elliott, Sheaffer and Schug54,Reference Sheaffer, Kim and Aoki55,Reference Kaaij, van de Wetering and Fang58) . Perinatal ablation of DNMT1 caused loss of nascent villi due to hypomethylation and premature differentiation and apoptosis(Reference Elliott, Sheaffer and Schug54) due to DNA damage and genomic instability in progenitor cells linked to hypomethylation. Corroborating this, genes associated with cell cycle were expressed at lower levels in the DNMT1-/- ablated cells along with up-regulation of P21, a gene expressed due to DNA damage and associated with cell cycle arrest(Reference Elliott, Sheaffer and Schug54). Interestingly, Kaaij et al. could not find many DMR in transcription start sites due to differentiation of Lgr5+ inter villi epithelial cells in adult intestines. Instead, they observed that there was considerably stable methylation status between the two cell types, which could corroborate the fact that DNMT-1 and de novo methylation is more important during development than differentiation, hence the milder effects of DNMT1 in adult mice and stabilisation of gene expression after weaning.
Elliott et al. investigated the milder effect of Dnmt1 KO in adult mice and found that it was being compensated for by a higher expression of Dnmt3b within 2 months of Dnmt1 KO, and that a KO of both Dnmt1 and Dnmt3b in intestines causes high mortality in adult mice, indicating compensatory process(Reference Elliott, Sheaffer and Kaestner59).
These results were then validated in vitro where perinatal organoid formation and maintenance required DNMT1 but this was not true for organoids from adult crypts(Reference Elliott, Sheaffer and Kaestner59). Another interesting result in this paper was the increase in expression of the Lysozyme 1 and 2 genes in the Dnmt1-/- intestinal cells compared with wild-type controls. This indicates a premature differentiation of Paneth cells. In addition, other genes related to Paneth cells were up-regulated in the mutant cells. However, staining did not corroborate these findings since few cells in progenitor regions were differentiated. The effect of methylation in Paneth cells might indicate a slow ongoing process instead of a fast morphophysiological modification. In contrast, studies addressing DNA methylation and ageing surprisingly found many genomic regions associated with genes that gained or lost methylation in the intestines over time in humans(Reference Maegawa, Hinkal and Kim20,Reference Ahuja, Li and Mohan60) and that some of these patterns are partially conserved in mice in spite of their short lifespan(Reference Maegawa, Hinkal and Kim20,Reference Kellermayer, Balasa and Zhang22) . Methylome alterations due to ageing in colonic epithelium were also related to greater susceptibility to inflammatory bowel disease in young adults(Reference Kellermayer, Balasa and Zhang22). Due to extensive references on the connection between inflammatory bowel disease and DNA methylation, we will not comment on this topic in this review, focusing instead on the impact of dietary supplementation and nutritional status in the intestinal methylome.
Studies focusing on smooth muscle cells have also demonstrated a critical role of DNA methylation on their differentiation, phenotype and expression patterns(Reference Hu, Gharaee-Kermani and Wu61–Reference Jorgensen, Berent and Ha63). Jorgensen et al., in particular, demonstrated that smooth muscle cell-specific KO of Dnmt1 in mice led to 20% reduction in global methylation and loss of mature smooth muscle cells. Furthermore, the KO animals presented shorter intestines and a rapid postnatal intestinal dilation beginning at day 10 after birth and leading to death on day 21 by intestinal ischaemia or perforation. They also observed a reduction in expression of TET family genes while DNMT3A protein increased, suggesting a compensatory effect similar to what was observed in other cell types(Reference Elliott, Sheaffer and Kaestner59).
Not only DNMT are responsible for methylation pattern regulation. TET1, which mediates the demethylation process by conversion of 5mC into 5hmC, was also studied as a possible ISC methylation regulator during development. Comparing Lgr5+ and differentiated villi cells, the levels of 5hmC were much higher in progenitor cells in genes associated with Wnt signalling and in ISC markers such as Olfm4 and Lgr5(Reference Kim, Sheaffer and Choi64). Genes that were expressed only in differentiated cells presented high levels of 5hmC in villi cells. Interestingly, the differentiated cells had an 8-fold increase in the total 5hmC level compared with the Lgr5+ cells. The expression level of Tet1 was much higher in Lgr5+ cells compared with differentiated cells and the opposite was true for the Tet2 and Tet3 genes. Using Tet1 mutant mice, it was shown that the mutant mice were growth retarded and that the mutation caused significant lethality in the early postnatal period compared with wild-type littermates(Reference Kim, Sheaffer and Choi64). Also, in the intestinal tissue, villi height and the number of progenitor cells in the crypts were significantly reduced in the Tet1-/- mice, indicating that the Tet1 gene is important for cell proliferation. Organoid budding and size were also decreased in the cultures derived from Tet1-/- intestines. Overall, 5hmC enrichment at the Wnt target site is essential for gene expression of Wnt target genes in Lgr5+ cells and that the depletion of the Tet1 gene product decreased the level of 5hmC and therefore decreased the expression level of those genes. The conversion of the 5mC into 5hmC is an important regulatory mechanism for the expression of Wnt target genes during intestinal postnatal maturation. Kraiczy et al. observed that Tet1 gained methylation and reduced expression through development(Reference Kraiczy, Nayak and Ross19).
A recent study investigating 5hmC observed dynamic changes during differentiation of mouse progenitor adult ISC into epithelium specialised cells(Reference Uribe-Lewis, Carroll and Menon65). Interestingly, 5hmC in progenitors did not correlate with transcripts levels while a positive 5hmC × gene expression correlation was observed after differentiation. Furthermore, ~60% of the 5hmC were intragenic and 5% of the intergenic 5hmC were located with 5 kb of a transcription start site with the gain of 5hmC upon differentiation occurring mainly in intergenic regions. Gene ontology analysis of the genes containing significant changes in 5hmC was enriched for cell metabolism and cell–cell interaction while intergenic 5hmC was assigned to the closest gene and those were enriched for organ morphogenesis, cell signalling and DNA template processes.
Overall, the importance of DNA methylation on early life intestinal development is notable. The regulation of intestinal maturation is being driven at least in some part by DNA methylation with the differentiation process being less dependent on methylation modifications. Also, it is interesting to note the association between methylation level differences during the growth/ageing processes, mostly with hypomethylation either locally in the first case or globally in the later.
Microbiota composition influence on intestinal DNA methylation and development and ‘functionality’
Intestinal commensal bacteria colonisation in the postnatal period influences physiology, morphology and functionality of the intestinal tissue(Reference Sommer and Bäckhed66,Reference Buchon, Broderick and Chakrabarti67) and can affect gene expression of the host, as shown in many studies comparing germ-free (GF) and conventionally raised animals(Reference Comelli, Simmering and Faure68–Reference Sun, Zhong and Du72) and reviews on the topic(Reference Sommer and Bäckhed66,73,Reference Richards, Burns and Alazizi74) . The link between microbiota and intestinal renewal has also been found in species that have historically less evidence of DNA methylation such as Drosophila(Reference Buchon, Broderick and Poidevin75), indicating that DNA methylation status may be an acquired regulation during evolution. Also, epigenetic reprogramming of host genes has been demonstrated during microbial and virus infections and has been associated with malignant progression of cancer(Reference Oka, Sato and Ouchida76,Reference Paschos and Allday77) .
Microbiota effects on host physiology can be associated with bacterial metabolites, such as butyrate, a by-product predominantly from Firmicutes metabolism, that potentially influences host gene expression by histone chromatin modifications(Reference Aoyama, Kotani and Usami78). Fermentation of dietary fibre by bacterial populations in the colon produces butyrate that is the main source of energy to colonocytes. Also, the regulatory function of butyrate as an inhibitor of histone deacetylase is consequently associated with open chromatin and accessibility to transcriptional machinery(Reference Delage and Dashwood79) linking butyrate to increases in gene expression and indirectly to decreases in DNA methylation(Reference Sheaffer, Kim and Aoki55,Reference Eden, Hashimshony and Keshet80) . Besides butyrate production, intestinal microbiota produce B vitamins and folate, metabolites that participate in one-carbon metabolism of the host, both as methyl donors (MD) and co-factors, potentially influencing constitution of the methylome since they cannot be synthesised by humans(Reference Kau, Ahern and Griffin81).
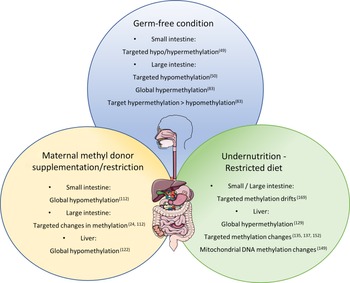
Corroborating the fact that the lack of bacteria in the intestinal tract can induce methylome modification of the intestinal epithelium, Yu et al. compared identical lines of mice in axenic or conventional (CV) conditions(Reference Yu, Gadkari and Zhou50). They observed an abnormal DNA methylation profile, specifically hypomethylation of CpG nucleotides in GF mice at 21 and 100 days of life, while on day 0, methylation patterns were indistinguishable between GF and CV mice. Interestingly, the hypomethylation was not global and did not affect genome repetitive elements, suggesting a specificity to the regulation of DNA methylation by the intestinal microbiota. Hypomethylated CGI in GF mice were related to lower expression of genes associated with intestinal maturation and that, for some genes, the expression level was increased to levels comparable to CV mice after the reconstitution of the commensal bacteria by faecal microbiota transplant.
Pan et al. also investigated the influence of microbiota colonisation at different life stages on the methylome of small intestine epithelial cells(Reference Pan, Sommer and Falk-Paulsen49). They observed that the influence of microbial presence on DNA methylation was detected early after birth and global methylation level increased subtlety over time. The number of differently methylated positions between CV and GF animals was ten times greater (1496 differently methylated positions) in the first week after birth than in week 4 and weeks 12/16, which corroborates with the idea that microbial colonisation has great impact on gut function during early life, when differently methylated positions were also enriched in promoter regions. However, adult mice (12/16 weeks) presented greater number of differently expressed genes (79) containing differently methylated positions compared with only 17 in week 1. Furthermore, both Tet3 and Dnmt3a expression levels were altered by microbiota presence in week 1 and week 12/16 after birth.
Interestingly, the intestinal adaptation of preterm piglets to microbiota colonisation and milk enteral feeding was shown to involve DNA methylation changes and occurred mostly in the first month of life, with the global hypermethylation of preterm intestines observed within the first 5 days of life normalising to the levels of the term intestine by the 26th day after birth(Reference Pan, Thymann and Gao82). Methylation differences observed in the five postnatal days between preterm and term in mid intestine affected Wnt signalling and lipopolysaccharide-binding protein-toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) pathways, indicating cell proliferation and immune alterations in the preterm gut.
In a more recent study, Ansari et al. observed a global hypomethylation in colonic crypts when comparing CV to GF mice accompanied by a subtle change in gene promoters(Reference Ansari, Raddatz and Gutekunst83). Analysing low-methylated regions representing potentially active regulatory regions, they observed a greater number of hypomethylated low-methylated regions (12 983) in the CV mice with only 3115 hypermethylated when compared with the GF animals. Furthermore, the majority (78.2%) of low-methylated regions associated with changes in gene expression were hypomethylated and from those, 300 were linked with significantly increased expression and were enriched for the binding sites of forkhead box A, kruppel like factor and activator protein 1 TCF. These findings suggest a much more intricate role of bacteria–host interaction on DNA methylation and regulation of gene expression. It also shows that the microbiota helps to regulate intestinal maturation and homoeostasis through DNA methylation, possibly controlling TCF binding sites.
Takahashi and colleagues observed that the methylation profile of the TLR4 gene was different in CV and GF mice with the 5’ end of the gene being considerably hypomethylated in the intestinal epithelial cells of the large intestine of GF mice(Reference Takahashi, Sugi and Nakano84). Interestingly, Tlr4 expression was not associated with its methylation status in the small intestine, suggesting that the bacterial load in large intestine could be an important factor for bacterial regulation of Tlr4 gene expression and that there is a complementary regulatory process for Tlr4 expression in the small intestine.
Both microbiota shifts and difficulties in discriminating commensal from pathogenic bacteria can play a role in regulating host functionality. Host recognition of bacterial populations and its link with DNA methylation, gene expression and host physiology were further corroborated with the use of TLR2 KO mice(Reference Kellermayer, Dowd and Harris23). The Tlr2 KO mice had different expression levels of genes associated with immune response correlated with changes in DNA methylation and were combined with shifts in colonic microbial populations with Firmicutes being less abundant and Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes more abundant in the KO mice. Interestingly, the diversity was much higher for the bacteria present within the Tlr2 KO mice, compared with the much more closely clustered wild-type samples, indicating a more consistent control of microbiota population diversity by the presence of TLR2.
Interestingly, in a study from Bhat et al., neither probiotics nor E. coli exposure alone alters global DNA methylation in Caco-2 cells despite changes in histone acetylation(Reference Bhat, Kumari and Kapila85). However, when cells treated with probiotic strains of Lactobacilli were challenged with E. coli, the result was global hypermethylation, indicating that interactions within microbiota populations also influence host functionality.
Although many studies focus on changes in microbiome composition due to different conditions, such as nutritional status (reviewed by Million et al.; Castaner et al.; Blanton et al.)(Reference Million, Diallo and Raoult86–Reference Blanton, Barratt and Charbonneau88), diet (reviewed by Singh et al.)(Reference Singh, Chang and Yan89), antibiotic use (reviewed by Iizumi et al.)(Reference Iizumi, Battaglia and Ruiz90) and pathological conditions (reviewed by Wang et al.)(Reference Wang, Yao and Lv91), only few look for associations between shifts in bacterial populations and DNA methylation status of the host despite observed changes in gene expression. Therefore, new research on the regulatory mechanisms, including DNA methylation, that bacterial populations use to impact host function can help to determine the important microbial–host interactions that influence physiological and pathological processes.
Dietary supplementation and DNA methylation
The association between diet and the intestinal microbial population has been extensively studied(Reference Krautkramer, Kreznar and Romano92,Reference Zhang, Ju and Zuo93) . Gene expression modifications and epigenetic alterations in different tissues and developmental stages due to host gene expression directly or indirectly associated with diet and nutritional status have also been extensively demonstrated (reviewed by Jiménez-Chillarón et al.)(Reference Jiménez-Chillarón, Díaz and Martínez94). However, the effects of dietary interventions on the intestinal tract epigenome are not well established and the molecular mechanisms regulating the change in transcription level in response to intake modifications or microbiota manipulations have still to be elucidated for a large part of the observed events. For instance, Krautkramer et al. demonstrated that the microbiota induces histone modification in the host tissue, including liver and colon, in a diet-dependent manner, suggesting modulation of bacterial population and function due to nutrient availability(Reference Krautkramer, Kreznar and Romano92). This was confirmed by including SCFA to the diet of GF mice and observing a rescue of the expression level and chromatin modification to levels compared with colonised mice.
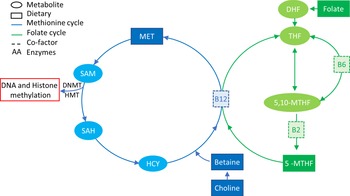
DNA methylation deposition requires not only the presence of DNMT enzymes but also the presence of methyl groups that are supplied by the one-carbon metabolic pathway (Fig. 2) that is dependent on nutrition(Reference Mudd, Brosnan and Brosnan95,Reference Stover96) . The major source of methyl groups for multiple cellular methylation processes (DNA, RNA, protein and lipid methylation) through the action of methyltransferases is S-adenosylmethionine, derived from one-carbon metabolism, which is dependent on multiple substrates, factors/co-factors such as B12, B6, folate, methionine and betaine(Reference Van den Veyver97,Reference Kominsky, Keely and Macmanus98) . The intake of some of these nutrients, also known as MD, has been shown to have systemic effects on methylation, such as folate intake restoring methylation status of blood cells of patients with hyperhomocysteinaemia, a disease that characterised by an unbalanced one-carbon cycle that results in global hypomethylation(Reference Ingrosso, Cimmino and Perna99).
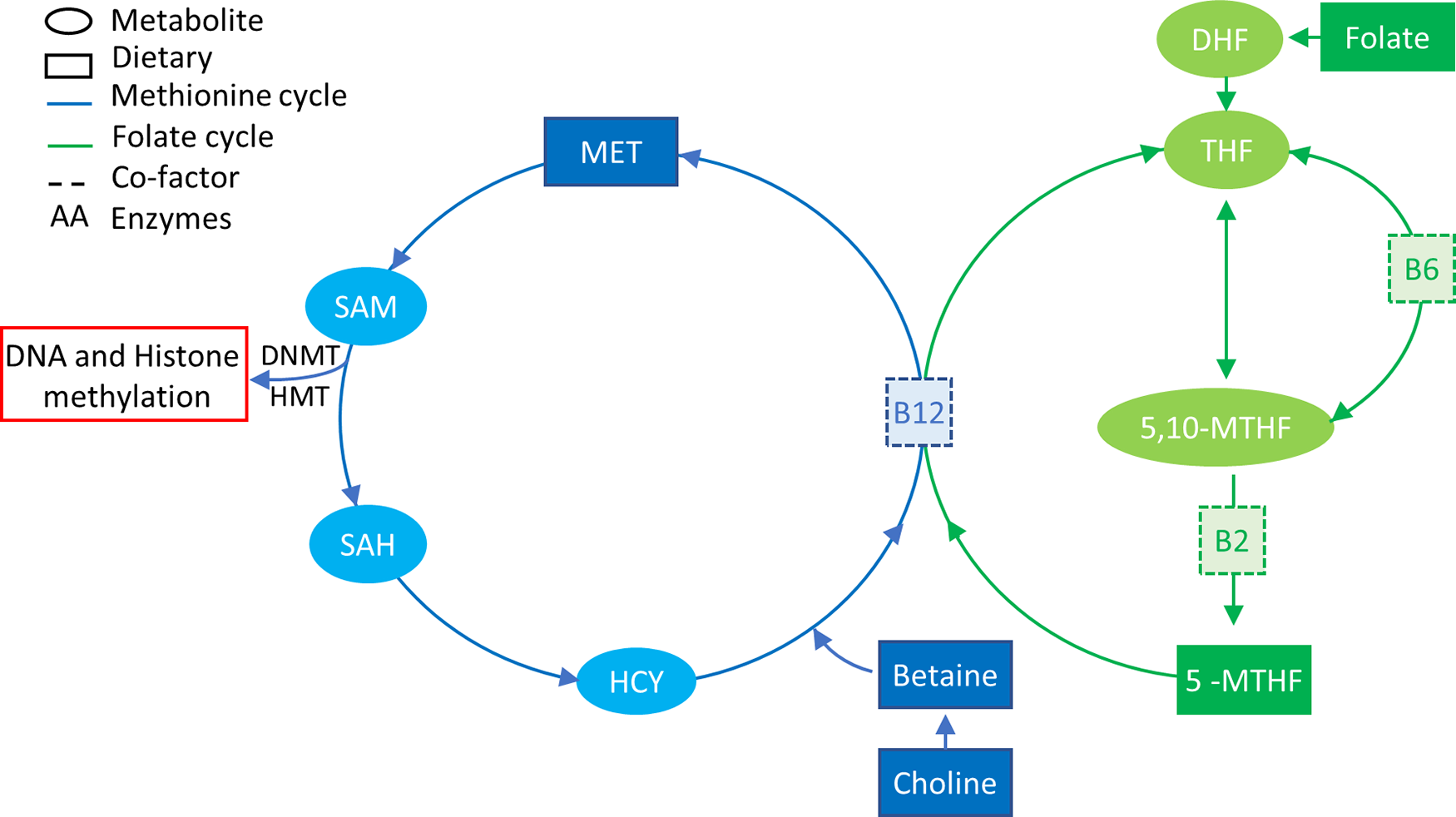
Fig. 2. One-carbon metabolism. The methionine cycle is represented in blue and the folate cycle is represented in green. Square boxes represent nutrients supplied in the diet. Choline and betaine are part of the resource pool of methionine together with homocysteine (HYC). B12 is a co-factor for the conversion of 5-MTHF, which is a result of a series of folate reductions into THF, freeing one methyl group for the conversion of HCY into MET. MET in turn is converted to SAM that donates a methyl group to DNA/histone methylation when it is converted to SAH. 5-MTHF, 5-methyl tetrahydrofolate; 5,10-MTHF, 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate; DHF, dihydrofolate; DNMT, DNA methyltransferase; HMT, histone methyltransferase; HYC, homocysteine; MET, methionine; SAH, S-adenosyl homocysteine; SAM, S-adenosyl methionine; THF, tetrahydrofolate.
Early nutritional effects on metabolism and disease predisposition have been observed on multiple occasions and extensively studied(Reference Jiménez-Chillarón, Díaz and Martínez94,Reference Lucas100,Reference Vansant101) . One of the mechanisms by which nutrition can establish these long-lasting modifications is via DNA methylation as shown with the maternal MD supplementation of yellow agouti mice(Reference Waterland and Jirtle102). The MD diet altered the coat colour of the offspring due to DNA methylation of the transposable element inserted in the agouti gene, indicating that dietary exposure in pregnancy or early life can have significant and long-lasting effects on metabolism and disease susceptibility in different organs of the offspring including the intestines. Policies for supplementation with folic acid for pregnant women to prevent open neural tube defects(Reference Persad, Van Den and Dubé103), the increase in the use of MD supplementation, especially in developed countries, and long-lasting effects of maternal diet on the DNA methylation of the offspring(Reference El, Schneider and Lehnen104–Reference Keleher, Zaidi and Shah109) encouraged the investigation into transgenerational risks and effects of maternal supplementation with MD(Reference Van den Veyver97).
Morphological changes due to MD supplementation/deficiency have also been observed in the intestines. Silva et al. found sporadic regions throughout the small intestine with increased crypt depth in the offspring of dams submitted to a methyl deficient diet during gestation until weaning(Reference Alves da Silva, de Castro Oliveira and Di Rienzi110). The MD deficient offspring also had a decrease in jejunal and faecal microbial α-diversity and lower relative abundance of Bacteriodales and higher abundance of Lactobacillales. Interestingly, they also observed target hypomethylation of glycosylation genes in enteroids cultured in methyl deficient media(Reference Alves da Silva, de Castro Oliveira and Di Rienzi110). Furthermore, DNA methylation levels of two repetitive elements were measured and only one (IAP) was hypomethylated in the MD deficient enteroids, disregarding global hypomethylation and contradicting the one-carbon metabolism theory.
The one-carbon metabolism theory suggests that a reduced intake of dietary MD would induce a global hypomethylation due to decreased resources for formation of methyl groups, and the opposite would also be true, with an increase in DNA methylation due to a dietary supplementation of MD. This is corroborated by studies like the one from Choi et al., which describe a 35% reduction in DNA methylation in colonic genome of rats after vitamin B12 deficiency(Reference Choi, Friso and Ghandour111), and from McKay et al. that observed global hypomethylation in the small intestine of offspring of dams submitted to a low folate diet during pregnancy and lactation(Reference McKay, Waltham and Williams112).
However, local hyper and hypomethylation were observed in studies with MD supplementation contradicting the idea that DNA methylation would decrease or increase in a random, dysregulated manner. Schaible et al., for instance, found that supplementation of the maternal diet with a combination of MD such as B12, folate and choline can alter the establishment of DNA methylation in mice as observed at postnatal day 30 (P30) and P90(Reference Schaible, Harris and Dowd24). They observed fifty-nine hypermethylated regions and ninety-six hypomethylated ones, with more than 50% hypomethylated loci localised on the X chromosome. The changes in methylation were combined with an increase in the susceptibility to acute colitis induced by dextran sodium sulphate associated with changes in gene expression. Eighteen of the 155 DMR were associated with change in expression of a flanking gene, including the PPARα gene, which showed decreased methylation level and increased expression. Finally, they also assessed the mucosa-associated microbiome of the offspring and found a significant separation at the genus level at P30 that is rescued by P90 with Bacteroidetes and Clostridia being overrepresented, and Lactobacillus underrepresented in early life of MD-exposed offspring.
Maternal diet can also influence the DNA methylation level of the PPARα promoter in the liver of the offspring(Reference Lillycrop, Phillips and Jackson113,Reference Lillycrop, Phillips and Torrens114) , with protein-restricted diet having 26% less methylation than the controls and folic acid rescuing the methylation status(Reference Lillycrop, Phillips and Torrens114), corroborating with the findings of Schaible et al.. In the murine fetal gut, a low folate maternal diet reduced the methylation in the Zn transporter gene solute carrier 39 member 4 (Slc39a4), but did not cause changes in the methylation of insulin-like growth factor 2 and oestrogen receptor 1(Reference McKay, Wong and Relton115). Paternal folic acid deficient and supplemented diet throughout life also impacted DNA methylation levels of imprinted genes in the brain and in the placenta and increased postnatal–preweaning pup death(Reference Ly, Chan and Aarabi116), as was observed by Ly et al.
Despite the fact the important epigenetic modification occurs in colonic mucosa during paediatric development as shown by Kellermayer et al. (Reference Kellermayer, Balasa and Zhang22), Schaible et al. did not observe an increase to colitis susceptibility when the mice were exposed to MD supplementation from P30 to P80, suggesting that the in utero effect is more important than postnatal dietary exposure. These results were in agreement with the findings from Mir et al. that, in spite of not analysing the DNA methylation status, observed a 25% increase in mortality in the MD group offspring, with males being more susceptible to colitis(Reference Mir, Nagy-Szakal and Dowd117). The sex difference might be related to the finding of Schaible et al. that a high percentage of hypomethylated regions due to maternal MD were localised on the X chromosome. Trasler and colleagues also did not observe changes in global methylation in the colon of mice predisposed to intestinal adenoma formation (Apc+/Min) submitted to a low folate diet from weaning to 13 weeks of age with or without reductions in Dnmt1 expression due to heterozygous gene KO(Reference Trasler, Deng and Melnyk118).
It is noteworthy that the impact of methyl deficient/supplemented diets on DNA methylation is organ specific, as observed in studies focusing on liver and brain DNA methylation in rats under dietary restriction of methionine, choline and folic acid. In these studies, global hypomethylation was observed in the liver(Reference Pogribny, Ross and Wise119) and genome hypermethylation in the brain(Reference Pogribny, Karpf and James120). Ly et al. 2016 also observed that maternal supplementation with folic acid during the second and third week of gestation or throughout pregnancy decreased global methylation in the brain, while no global alterations were observed in the liver, colon or kidney of the offspring pups(Reference Ly, Ishiguro and Kim121).
The tumour suppressor gene p53, generally mutated or dysregulated in cancer, showed an increase in DNA methylation in its promoter in liver and colon mucosa following selenomethionine diet supplementation(Reference Zeng, Yan and Cheng122). Global DNA methylation was decreased in the liver of rats fed with extra selenomethionine, while the selenomethionine-deficient animals had global hypermethylation. This was not true for colon mucosa, where the selenomethionine intake did not significantly influence global methylation status. Using a modelling approach to identify variables that had the strongest association with gene-specific methylation, Tapp et al. observed greater correspondence between age and methylation level in males than in females and that correlation was weak and slightly negative for LINE-1 elements, indicating a subtle age-related hypomethylation(Reference Tapp, Commane and Bradburn123). Plasma folate and red cell folate correlated with the methylation of some of the genes in a sex-dependent manner. A similar trend was observed with plasma selenium that presented a positive correlation with methylation in males but a negative correlation in females. Interestingly, neither B12 nor homocysteine had a significant correlation with methylation status.
Other diet supplementations, not directly associated with one-carbon metabolism, have also been shown to influence DNA methylation in intestinal tissue. One example was the association of epigallocatechin-3-gallate, the catechin of green tea, to a regulatory effect on DNMT enzymes(Reference Remely, Ferk and Sterneder124). It has also been shown to inhibit DNMT in multiple cells including colon cell lines(Reference Morris, Moseley and Cabang125). Despite that the majority of epigallocatechin-3-gallate is absorbed in the small intestine, the administration of epigallocatechin-3-gallate resulted in a shift in microbiota population in the colon of mice, resulting in a decrease in acetic and butyric acids(Reference Unno, Sakuma and Mitsuhashi126) suggesting a modulation of energy metabolism. Remely et al. found that the methylation of CGI associated with the promoter region of multL homolog 1 (MLH1) in the colon increased with ECGC intervention to a greater extent than with a high fat diet, with or without ECGC(Reference Remely, Ferk and Sterneder124). In fact, a high fat diet coupled with ECGC decreased the methylation level of this CGI. Dnmt1 gene expression was lower in the colon of mice fed a high fat diet, but the expression level was rescued when ECCG was added to the diet. CpG in the promoter region of Dnmt1 were hypermethylated when ECGC was added to either high fat or control diets.
Organ-specific effects were also observed with dietary supplementation of nutrients outside one-carbon metabolism. Day et al. observed DNA methylation changes in the prostate of rats but not in the liver after diet supplementation with the soya phyto-oestrogen genistein(Reference Kevin Day, Bauer and Desbordes127). This was similar to the findings of Guerrero-Bosagna et al., where continuous pre- and postnatal genistein and daidzein exposure did not alter hepatic methylation level in the promotor region of the gene α-actin (Acta1), but it caused hypermethylation in the pancreas(Reference Guerrero-Bosagna, Sabat and Valdovinos128).
All this evidence suggests that the diet can affect the methylation status systemically and locally in the intestinal tract, representing both a risk and a protective function for specific disease pathologies. The consequences of food and nutrient intake on the molecular mechanisms regulating gene expression and consequently the function of the intestines should be further studied as an easy and affordable way of preventing and treating pathological conditions/states.
Nutritional status and DNA methylation
Extreme nutritional status, such as undernutrition and obesity, has been reported to influence DNA methylation in different organs with a potential impact on the health of individuals as parental dietary conditions also effect the metabolism and methylation level in offspring. Maternal nutrition has been shown to influence the state of DNA methylation in offspring in several animal models. In rats and mice, it has been reported that maternal malnutrition due to protein deficiency resulted in stable global hypermethylation until adulthood in the liver of the offspring(Reference Rees, Hay and Brown129). Methylation changes at specific loci in the liver(Reference Lillycrop, Phillips and Jackson113,Reference Lillycrop, Phillips and Torrens114,Reference Coupé, Amarger and Grit130–Reference Altmann, Murani and Schwerin138) , pancreas(Reference Sandovici, Smith and Nitert139), amygdala(Reference Nätt, Barchiesi and Murad140), adrenal gland(Reference Bogdarina, Welham and King141,Reference Bogdarina, Haase and Langley-Evans142) , hypothalamus(Reference Coupé, Amarger and Grit143) and adipose tissue(Reference Claycombe, Uthus and Roemmich144,Reference Jousse, Parry and Lambert-Langlais145) were also reported correlating with changes in gene expression. Likewise, low protein feeding caused paternal transgenerational effects in mice, including various DNA methylation changes in the offspring’s liver(Reference Carone, Fauquier and Habib137). In utero undernutrition increased obesity and glucose resistance in mice and interestingly, the female offspring of male mice submitted to in utero undernutrition also developed glucose intolerance which was linked to DNA methylation alteration on the liver X receptor alpha (Lxrα) gene in the liver, the same methylation signature found on the sperm of the F1 mice(Reference Martínez, Pentinat and Ribó135). Accordingly, Radford et al. found that in utero undernutrition changes the germline methylome of the male offspring with a prevalence of hypomethylation and enrichment of DMR in nucleosome retaining regions, and part of the alteration is resistant to embryo methylation reprogramming(Reference Radford, Ito and Shi146). However, Ivanova et al. found that the liver DMR identified in mice treated with maternal or early postnatal protein restriction did not significantly affect imprinted genes, indicating that expression of imprinted genes is not particularly influenced by maternal or early life nutrition(Reference Ivanova, Chen and Segonds-Pichon147).
Maternal diet during pregnancy was also shown to impact methylation status in species other than rodents. The offspring of sows under dietary protein restriction during pregnancy developed changes in DNA methylation in CGI flanking metabolic genes, such as PPARα, in the liver(Reference Altmann, Murani and Schwerin148). Maternal low-protein diet also affected mitochondrial DNA methylation in the liver of piglets(Reference Jia, Li and Cong149) and muscle GLUT type 4 (GLUT4) promoter methylation level(Reference Wang, Cao and Yang150). Energetic restriction in baboons during early pregnancy resulted in global hypomethylation in fetal kidneys and in late gestation resulted in global hypermethylation in fetal kidneys and frontal cortex(Reference Unterberger, Szyf and Nathanielsz151). Hepatic epigenetic modification was also observed in baboon fetus due to maternal malnutrition(Reference Nijland, Mitsuya and Li152–Reference Waterland, Kellermayer and Laritsky154). Tobi et al. found hypomethylation at the insulin-like growth factor 2 locus and other genes in leucocytes of women that were affected by famine during the peri-conception period and that the difference of methylation in some of the genes was sex specific(Reference Heijmans, Tobi and Stein153–Reference Tobi, Lumey and Talens157).
Dietary interventions can also influence epigenome changes in early/adult life specially during dietary transitions. Post-weaning malnourishment in mice caused global hypomethylation in the thalamus and hypothalamus with methylation profiling in the thalamus identifying DMR (both hypomethylated and hypermethylated) in genes associated with neuronal development or psychiatric diseases, including nine genes related to long-term potentiation(Reference Weng, Zhou and Liu158). Peter et al. found associations between the blood DNA methylation profile associated with severe malnutrition in early childhood and impairments in attention and cognition(Reference Peter, Fischer and Kundakovic159). A study in India searched for correlation between DNA methylation in LINE1 sites in DNA from blood cells of children from 5 to 12 years old with malnourishment indices such as Z-score, BMI and blood vitamin concentration (B12 and folic acid) and found that the DNA methylation at LINE1 elements relates inversely to retinol levels in the blood(Reference Narayan and Dangi160).
Ageing is usually associated with global hypomethylation combined with hypermethylation at specific loci, which is also the methylation profile linked to cancer (reviewed by Klutstein et al.)(Reference Klutstein, Nejman and Greenfield161). Energetic restriction can potentially reverse age-related abnormal DNA methylation, increasing genomic stability(Reference Vaquero and Reinberg162,Reference Li, Liu and Tollefsbol163) in a possible explanation as to why it is considered the most powerful mechanism to increase lifespan in different animal models(Reference Vaquero and Reinberg162,Reference Wilson, Smith and Mag164–Reference Waki, Tamura and Sato168) . Rhesus monkeys exposed to chronic 30% energetic restriction had a reduction in the age-related methylation drift in their blood compared with ad libitum fed controls(Reference Maegawa, Lu and Tahara169). The same study found that in mice with 40% energetic restriction, similar but more evident results were observed across multiple tissues. Furthermore, fifteen genes that showed an age-related drift in methylation in the blood of the monkeys were analysed in various tissues including the small and large intestine, and an even larger methylation drift was seen in the large intestine with the selected genes also showing age-related clustering in both the small and large intestines indicating a marked effect of diet on the DNA methylation profile in these tissues.
High-fat diets and maternal overnutrition and obesity during gestation also influence the DNA methylation levels of the offspring in tissues including the brain(Reference Vucetic, Kimmel and Totoki170,Reference Ramamoorthy, Allen and Davies171) , liver(Reference Dudley, Sloboda and Connor172–Reference Seki, Suzuki and Guo174), blood(Reference Sharp, Salas and Monnereau175) and adipose tissue(Reference Borengasser, Zhong and Kang176). Contrastingly, Li et al. found that offspring of obese female mice presented widespread but subtle alterations in their hepatic DNA methylation profile and suggested that healthy postnatal feeding would be enough to prevent metabolic dysfunctions in the offspring(Reference Li, Young and Maloney177). This is in agreement with Moody et al. that showed evidence that postnatal diet can reverse the methylation effects in the liver caused by a high fat maternal diet(Reference Moody, Chen and Pan178). As with undernutrition, in rats, female offspring of high fat-fed males presented with programmed βcell dysfunction despite the fact of not being exposed to a high-fat diet during development(Reference Ng, Lin and Laybutt179) and the alteration was accompanied by DNA methylation changes. There is also evidence that obesogenic diets combined with obesity-associated microbiome modulate colonic gene expression through epigenetic modifications other than DNA methylation(Reference Qin, Roberts and Grimm180). Maternal and paternal obesity have also been associated with DNA methylation changes in fetal blood and placenta at specific loci(Reference El, Schneider and Lehnen104,Reference Li, Young and Maloney177,Reference Bouchard, Thibault and Guay181,Reference Soubry, Schildkraut and Murtha182) .
Chronic high-fat diet in mice (from weaning to 20 weeks of age) changed promoter methylation status of genes associated with food intake in brain tissue(Reference Vucetic, Kimmel and Totoki170,Reference Vucetic, Kimmel and Reyes183) , which could explain the establishment of obesity and obesity-related diseases. Neonatal overfeeding has also been associated with changes in DNA methylation in the hypothalamus of rats and was associated with decreased expression of genes associated with the metabolic syndrome(Reference Ramamoorthy, Allen and Davies171,Reference Plagemann, Harder and Brunn184,Reference Plagemann, Roepke and Harder185) . There has also been work relating DNA methylation profiles (especially in blood) with BMI, waist circumference and body composition. In an epigenome-wide study using blood samples from human subjects(Reference Sayols-Baixeras, Subirana and Fernández-Sanlés186), it was observed that validated, differently methylated CpG associated with genes or coding regions explained 14.18% of the BMI score and 16.73% of the waist circumference variability. Interestingly, from the 95 loci with CpG significantly associated with BMI, only ten were genes previously associated with BMI from a genome-wide association study. Using blood samples from preschool children, Rzehak et al. found specific DNA methylation variants associated with BMI, fat mass and fat-free mass(Reference Rzehak, Covic and Saffery187).
Noticeably, the link between extreme nutritional status and developmental programming has been extensively studied, especially in the liver, brain and adipose tissue, while information regarding the intestines is still lacking. However, if nutritional supplementation and microbiome colonisation have organ-specific effects, it is not farfetched that the effects of obesity and undernutrition in these tissues do not reflect what would be observed in the intestinal tract and the different sections of the small and large intestine.
Although morphophysiological changes in the intestines due to malnutrition have been shown(Reference Lopez-Pedrosa, Torres, Fernandez, Rios and Gill188), including in swine models for childhood undernutrition(Reference Garas, Feltrin and Hamilton189), the molecular aspects underlying these changes have not been understood. Furthermore, there have been few efforts towards analysing DNA methylation profile changes in the intestines, especially the small intestines, due to extreme nutritional status. As the point of adaptation between nutritional intake and immune protection, changes in the intestinal tract could potentially be related to systemic effects of dietary manipulations. The known effects of nutritional status on the epigenome of the intestinal tract are limited and could be the key to explain how dietary intervention can systemically influence host physiology.
Conclusions
It is easy to see how information on the molecular effects of how diet and nutritional status directly influence the intestine and how the interplay between nutrient intake/nutritional status and commensal bacteria influences host health and their long-lasting effects on metabolism and disease predisposition is still lacking. The use of diet to manipulate host physiology to better respond to pathological or adverse conditions such as undernutrition, chronic inflammatory diseases and diarrhoea could be used once the mechanisms behind the interactions between diet, microbiota and host are understood. As observed in this review, DNA methylation can help to link environmental shifts to host function, but there is still a long way to go in describing the actions of bioactive nutrients and foods that could benefit host health. The links between intestinal and nutritional biology need to be better defined in order to answer clinically relevant questions. For instance, could diet/microbiota modulation be an effective and precise approach to manipulate intestinal cell function against specific medical conditions? At what stage of life would these alterations need to occur and are they sustainable over time? Specifically, the role of epigenetics as a conductor makes it a crucial point of study to deepen our knowledge of intestinal adaptation to nutritional challenges and discover its translational potential in precession medicine.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) and the Science without Borders program for financially supporting the author R. M. P. CNPq had no role in the design, analysis or writing of this article. The authors’ responsibilities were as follows: R. M. P. and E. A. M. conceptualized the review topic; R. M. P. collected and curated the data; both authors drafted and reviewed the manuscript; R. M. P. had primary responsibility for the final content; and both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.