Published online by Cambridge University Press: 09 December 2019
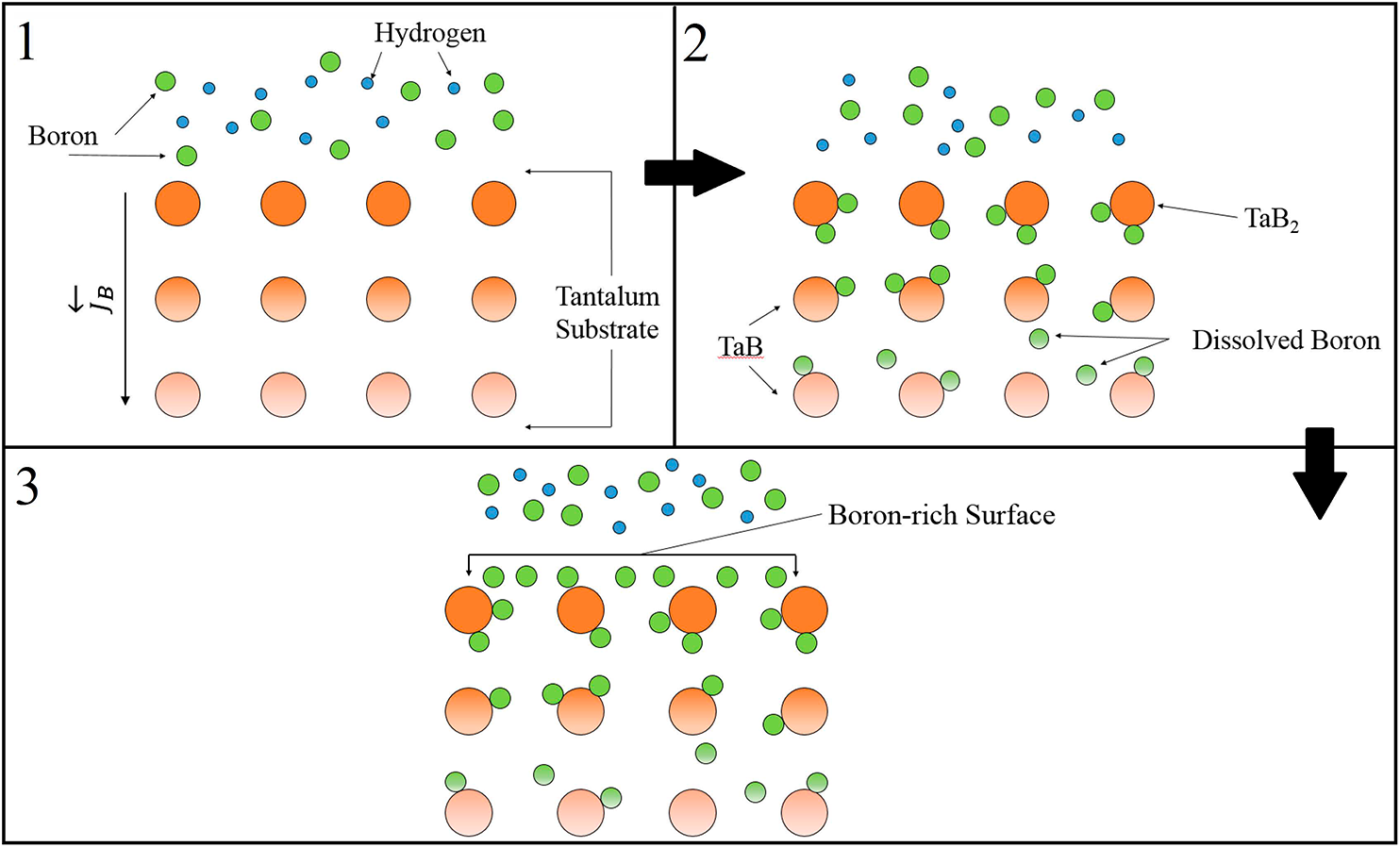
Microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition (MPCVD) was used to diffuse boron into tantalum using plasma initiated from a feedgas mixture containing hydrogen and diborane. The role of substrate temperature and substrate bias in influencing surface chemical structure and hardness was investigated. X-ray diffraction shows that increased temperature results in increased TaB2 formation (relative to TaB) along with increased strain in the tantalum body-centered cubic lattice. Once the strained tantalum becomes locally supersaturated with boron, TaB and TaB2 precipitate. Additional boron remains in a solid solution within the tantalum. The combination of precipitation and solid solution hardening along with boron-induced lattice strain may help explain the 40 GPa average hardness measured by nanoindentation. Application of negative substrate bias did not further increase the hardness, possibly due to etching from increased ion bombardment. These results show that MPCVD is a viable method for synthesis of superhard borides based on plasma-assisted diffusion.
A previous error in this article was corrected, please see doi:10.1557/jmr.2019.400.
Please note a has been issued for this article.