1. INTRODUCTION AND SCALING ARGUMENTS
Textbook treatments of glacier sliding based on pioneering work by Weertman (Reference Weertman1957); Nye (Reference Nye1969); Kamb (Reference Kamb1970) describe how glacier motion is facilitated through a combination of ice deformation over larger bed obstacles, and the process of melting and refreezing across smaller obstacles that is referred to as regelation (Cuffey and Paterson, Reference Cuffey and Paterson2010). In these treatments, the rate of regelation is limited by the conduction of latent heat across the obstacle in response to changes in melting temperature that accompany variations in ice pressure. Here, we follow the classical scaling arguments for the rate of regelation (e.g. Fowler, Reference Fowler2011) to demonstrate that the permeability between the ice and the obstacle, which limits the rate at which water can flow, requires that significant local differences arise between the ice and liquid pressures. When the pressure in a liquid differs from that imposed on its adjacent solid (more precisely, the first invariant of the stress tensor), the theory of premelting describes how equilibrium is achieved at a temperature that differs from the bulk melting temperature that holds when the pressures in the two phases are the same (Dash and others, Reference Dash, Rempel and Wettlaufer2006). Taking premelting into account, we modify the Kamb (Reference Kamb1970) treatment of sliding and demonstrate both that the rate of regelation is faster than previously thought, and that the effects of pressure melting and refreezing are typically of negligible importance in comparison to melting and refreezing sourced to variations in effective stress.
We begin with the scaling for conduction of the latent heat due to the refreezing of water. The rate of regelation v R is linked to the time required to transport volumetric latent heat ![]() $\rho_{i} {\cal L}$ by conduction at effective thermal conductivity K from the downstream side of small obstacles, where the melting temperature is elevated slightly, to the upstream side, where higher ice pressures cause the melting temperature to be depressed. For obstacles of wavelength λ, scaling considerations suggest that energy transport requires
$\rho_{i} {\cal L}$ by conduction at effective thermal conductivity K from the downstream side of small obstacles, where the melting temperature is elevated slightly, to the upstream side, where higher ice pressures cause the melting temperature to be depressed. For obstacles of wavelength λ, scaling considerations suggest that energy transport requires
where ΔT is the (negative) difference in melting temperature between the upstream and downstream sides. Conventionally, this melting temperature difference is linked to the (positive) difference in ice pressure ΔP i between the upstream and downstream sides through the Clapeyron slope, i.e. ΔT = −C 0ΔP i, with
where T m ≈ 273 K is a reference melting temperature, and ρ i and ρ l are the ice and liquid densities; C 0 is sensitive to the air-content dissolved in the liquid (e.g. Röthlisberger and Lang, Reference Röthlisberger, Lang, Gurnell and Clark1987; Clarke, Reference Clarke2005), with reported values ranging between 9.8 × 10−8 K Pa−1 (saturated) and 7.4 × 10−8 K Pa−1 (pure). Where this description of phase equilibrium is valid, it follows that the regelation velocity scales as
As noted above, the equilibrium between liquid water and ice tracks along the Clapeyron slope of the bulk phase diagram only when the ice and liquid pressures are equal to each other along their common interface so that ΔP i = ΔP l. Considerations of mass conservation constrain the difference in liquid pressure between the upstream and downstream sides that is required to drive transport of liquid with viscosity μ, whereupon
Here, the resistance to flow at low Reynolds number is characterized by effective permeability Π; for example, Darcy flow through a porous medium with the permeability Π or an equivalent Poiseuille flow through a liquid film of thickness δ, which can be described with Π = δ2/12. Substituting in for the regelation velocity scaling from the energy transport argument that led to Eqn (1) suggests that
Since the melting temperature difference between the upstream and downstream sides falls along the Clapeyron slope so that ΔT = −C 0ΔP i only when ΔP l = ΔP i, the special case in which regelation is driven by pressure melting alone holds when the permeability to liquid transport is
Taking nominal values of μ = 1.8 × 10−3 Pa s, K = 2 W m−1 K−1, ![]() ${\cal L}= 3.3\times 10^5\,{\rm J}\,{\rm kg}^{-1}$, and treating the case of pure water so that ρ l = 103 kg m−3 and C 0 = 7.4 × 10−8 K Pa−1, implies that Π0 ≈ 1.6 × 10−18 m2, which in the case of thin film flow corresponds with δ0 ≈ 4.4 nm.
${\cal L}= 3.3\times 10^5\,{\rm J}\,{\rm kg}^{-1}$, and treating the case of pure water so that ρ l = 103 kg m−3 and C 0 = 7.4 × 10−8 K Pa−1, implies that Π0 ≈ 1.6 × 10−18 m2, which in the case of thin film flow corresponds with δ0 ≈ 4.4 nm.
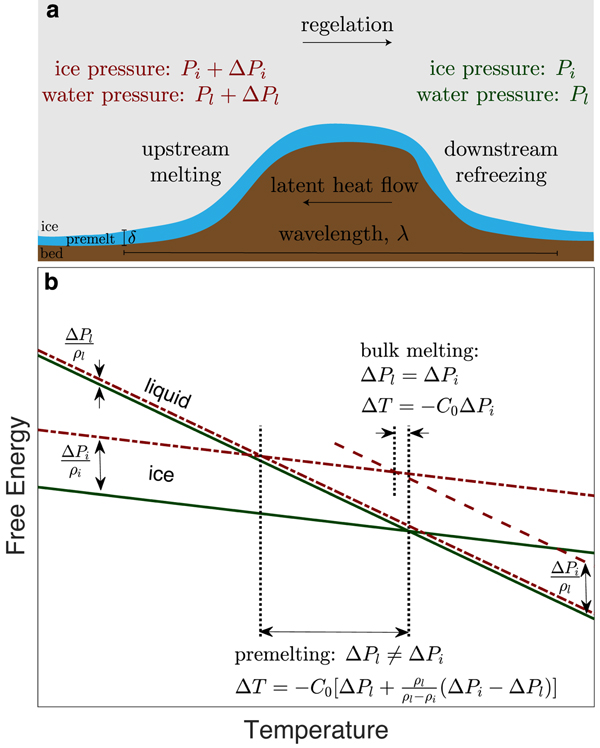
Permeabilities as low as Π0 are uncommon in surficial geological materials. Moreover, when the proximity between ice and mineral substrates δ is reduced below the micron scale, the intermolecular forces that cause premelting (e.g. Dash and others, Reference Dash, Fu and Wettlaufer1995, Reference Dash, Rempel and Wettlaufer2006; Wettlaufer and Worster, Reference Wettlaufer and Worster2006) enable significant load transfers between the ice and mineral surfaces so that the ice pressure exceeds the liquid pressure, with their difference identified as the effective stress N = P i − P l. Hence, for the idealized case of sliding over a completely impermeable bed with all liquid transport confined within an interfacial film, we infer that the film thickness δ0 implied by mass-balance constraints is inconsistent with the central assumption of regelation by pressure melting alone, which holds that P i = P l and N=0. Instead, the generalized Clapeyron equation (see Fig. 1) must be invoked to describe the changes in melting temperature that result from variations in both liquid pressure and effective stress as (cf. Rempel, Reference Rempel2008, Eqn (1))
where each of these quantities (i.e. ΔT, ΔP l, ΔN = ΔP i − ΔP l) represents the difference between values on the upstream and downstream sides of bed obstacles. Substituting Eqn (7) into Eqn (1) gives a regelation velocity of

Fig. 1. Generalized Clapeyron conditions for regelation. (a) Schematic of regelation past a bump. (b) Gibbs free energy per molecule of ice and liquid water. The ice lines are more shallow because ice has a lower specific entropy than liquid. Separate lines for a given substance correspond to different pressures. Intersections of ice and liquid lines correspond to phase equilibria. Consider the intersection of the two green lines (e.g. at the pressure conditions on the downstream side of a bump): at temperatures below the phase equilibrium temperature, ice has the lower free energy, and above the melting temperature, liquid prevails due to its lower free energy. The red lines show the free energy in each phase when pressure is elevated as labeled. If the ice and liquid pressures both increase by the same amount, the melting temperature decreases along the Clapeyron slope with the intersection between the dashed and the dot-dashed red lines. If, however, the ice and liquid pressures are perturbed by different amounts (e.g. at the pressure conditions on the upstream side of a bump), the melting temperature decrease can be much larger, as shown by the intersection of the two dot-dashed red lines.
In the typical case where Π ≫ Π0 from Eq. (6) efficient liquid drainage is expected to diminish liquid pressure variations so that ΔP i ~ (Π/Π0)ΔP l ≫ ΔP l, and in this limit Eqn (8) implies a regelation velocity of
For pure water, Eqn (9) suggests that v R is ρ l/(ρ l − ρ i) ≈ 12 times faster than predicted by conventional treatments, which rely upon temperature differences that result from pressure melting alone (cf. Eqn (3)). The enhanced regelation speed predicted by Eqn (9) is the primary finding of this work.
2. LINEARIZED ICE FLOW OVER WAVY TOPOGRAPHY
Further insight can be gained by revisiting the detailed analysis provided by Kamb (Reference Kamb1970) for regelation (at velocity v R) and ‘plastic’ deformation (at velocity v p) over a rough glacier bed, while making the minor extensions required to describe how the water pressure P l varies independently from the ice pressure P i. The details of this calculation are provided in the Supplementary Information. The interface we consider is described by
for area element A, Fourier spectrum a, and horizontal wavenumbers h (along flow) and k (perpendicular to flow). We account for the transport of heat and ice of viscosity η as in Kamb (Reference Kamb1970), while assuming that liquid flow follows Darcy's law and that the interface is at its melting temperature everywhere, as given by Eqn (7). This results in a modified version of Kamb's expression relating the shear stress τ and sliding velocity v = v R + v P, given by
where ℓ2 = h 2 + k 2, and the characteristic wavenumbers ℓ0 and ![]() $\ell _\Pi $ are defined by
$\ell _\Pi $ are defined by
The length scale 2π/ℓ0 is the transition wavelength at which the conduction of latent heat required by regelation and the deformation of ice over an obstacle offer equal resistance, whereas ![]() $2\pi /\ell _\Pi $ marks distances for which the liquid transport needed to accommodate regelation imposes a significant impediment. Since reasonable permeability estimates satisfy Π ≫ ρ iΠ0/[(ρ l − ρ i)], a comparison of the limiting wave numbers under such conditions yields
$2\pi /\ell _\Pi $ marks distances for which the liquid transport needed to accommodate regelation imposes a significant impediment. Since reasonable permeability estimates satisfy Π ≫ ρ iΠ0/[(ρ l − ρ i)], a comparison of the limiting wave numbers under such conditions yields ![]() $\ell _\Pi ^2\ll \ell _0^2$, implying that liquid transport plays a negligible role in restricting regelation. Hence, as in conventional treatments of regelation due to pressure melting (Weertman, Reference Weertman1957; Nye, Reference Nye1969; Kamb, Reference Kamb1970; Gudmundsson, Reference Gudmundsson1997), the relative importance of plastic deformation to regelation in controlling sliding speed depends on a comparison between the topographic wavelength 2π/ℓ and the transition wavelength 2π/ℓ0. Importantly, the transition wavelength is governed by considerations of heat flow, and because liquid transport is relatively efficient, variations in ice pressure produce commensurate variations in effective stress. The resultant perturbations to the melting temperature (see Fig. 1) cause the transition wavelength to be
$\ell _\Pi ^2\ll \ell _0^2$, implying that liquid transport plays a negligible role in restricting regelation. Hence, as in conventional treatments of regelation due to pressure melting (Weertman, Reference Weertman1957; Nye, Reference Nye1969; Kamb, Reference Kamb1970; Gudmundsson, Reference Gudmundsson1997), the relative importance of plastic deformation to regelation in controlling sliding speed depends on a comparison between the topographic wavelength 2π/ℓ and the transition wavelength 2π/ℓ0. Importantly, the transition wavelength is governed by considerations of heat flow, and because liquid transport is relatively efficient, variations in ice pressure produce commensurate variations in effective stress. The resultant perturbations to the melting temperature (see Fig. 1) cause the transition wavelength to be ![]() $\sqrt {(\rho _l-\rho _i)/\rho _l}\approx 3.5$ times larger than would be expected if the phase behavior were governed by pressure melting alone. For example, adopting the nominal parameter values given above and assigning an ice viscosity of η = 10−13 Pa s leads to 2π/ℓ0 ≈ 3 m.
$\sqrt {(\rho _l-\rho _i)/\rho _l}\approx 3.5$ times larger than would be expected if the phase behavior were governed by pressure melting alone. For example, adopting the nominal parameter values given above and assigning an ice viscosity of η = 10−13 Pa s leads to 2π/ℓ0 ≈ 3 m.
Of particular interest here, for interfaces with roughness only at wavelengths small enough that ![]() $\ell ^2\gg \ell _0^2 + \ell _\Pi ^2$ so that plastic deformation is negligible (i.e. v ≈ v R), Eqn (11) reduces to
$\ell ^2\gg \ell _0^2 + \ell _\Pi ^2$ so that plastic deformation is negligible (i.e. v ≈ v R), Eqn (11) reduces to
where Π0 is defined as in Eqn (6). In the special case where Π = Π0 we note that the term in parentheses on the right tends to unity so that the relationship between τ and v predicted by treatments that set P i = P l and consider pressure melting alone (e.g. Weertman, Reference Weertman1957; Nye, Reference Nye1969; Kamb, Reference Kamb1970) is recovered; with Π ≫ Π0, for a given basal shear stress τ the regelation velocity predicted by Eqn (13) is a factor of ρ l/(ρ l − ρ i) ≈ 12 greater.
3. IMPLICATIONS
In attempting to validate aspects of his treatment of glacier sliding Kamb (Reference Kamb1970, see §17) compared his predicted transition wavelength to field observations and found evidence suggesting that conventional theory underestimated 2π/ℓ0. In revising expectations of the transition wavelength upwards by a factor of 3.5, the current treatment may yield an explanation for this discrepancy and is promising for efforts to map basal roughness at the resolution of the Weertman (Reference Weertman1957) ‘controlling obstacles’. Perhaps more important than such quantitative improvements is the enhanced recognition of the importance of the effective stress in basal dynamics, and particularly basal thermodynamics. Though the role of subglacial water pressure in controlling sliding behavior through its effects on subglacial mechanics is well established in a variety of contexts (Lliboutry, Reference Lliboutry1968; Iken and Bindschadler, Reference Iken and Bindschadler1986; Tulaczyk and others, Reference Tulaczyk, Kamb and Engelhardt2000; Schoof, Reference Schoof2010), its importance in affecting the ice–liquid equilibrium temperature and premelting (Dash and others, Reference Dash, Rempel and Wettlaufer2006) has arguably been under-appreciated (Alley and others, Reference Alley1997).
Here, we have demonstrated that liquid transport near the basal interface (primarily as a consequence of premelting rather than the density difference that determines the sign of the Clapeyron slope) causes an order of magnitude increase to the speed of regelation. Indeed, because effective stress variations drive melting and refreezing in the same qualitative manner in any system where a solid is wetted by its own melt (i.e. premelting takes place), this suggests a more general role for regelation as a viable mechanism for accommodating slip over small obstacles in diverse geological systems where pressure melting cannot occur because the melt is less dense than its solid. In the glacial context, we anticipate that effective-stress-driven changes in melting temperature are likely to be common causes of basal melting and refreezing, possibly even supercooling (e.g. Röthlisberger and Lang, Reference Röthlisberger, Lang, Gurnell and Clark1987; Alley and others, Reference Alley, Lawson, Evenson, Strasser and Larson1998; Lawson and others, Reference Lawson1998; Creyts and Clarke, Reference Creyts and Clarke2010). Evidence has been given that the thermo-mechanical feedbacks made possible by premelting and variations in effective stress are instrumental in limiting both the range of observed glacier driving stresses (Meyer and others, Reference Meyer, Downey and Rempel2018) and the occurrence of regions amenable to stick-slip behavior (Lipovsky and others, Reference Lipovsky2019). This adds further emphasis to the importance of basal liquid transport for understanding glacier dynamics (e.g. Clarke, Reference Clarke2005; Iverson, Reference Iverson2010).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank Tim Creyts, Neal Iverson, Brad Lipovsky, Elisa Mantelli, Brent Minchew, Kiya Riverman, Olga Sergienko and Christian Schoof for discussions; we appreciate the guidance of scientific editor Ian Hewitt, and the constructive comments of Martin Lüthi and an anonymous reviewer; we also acknowledge financial support from NSF-1603907.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
The supplementary material for this article can be found at https://doi.org/10.1017/jog.2019.33