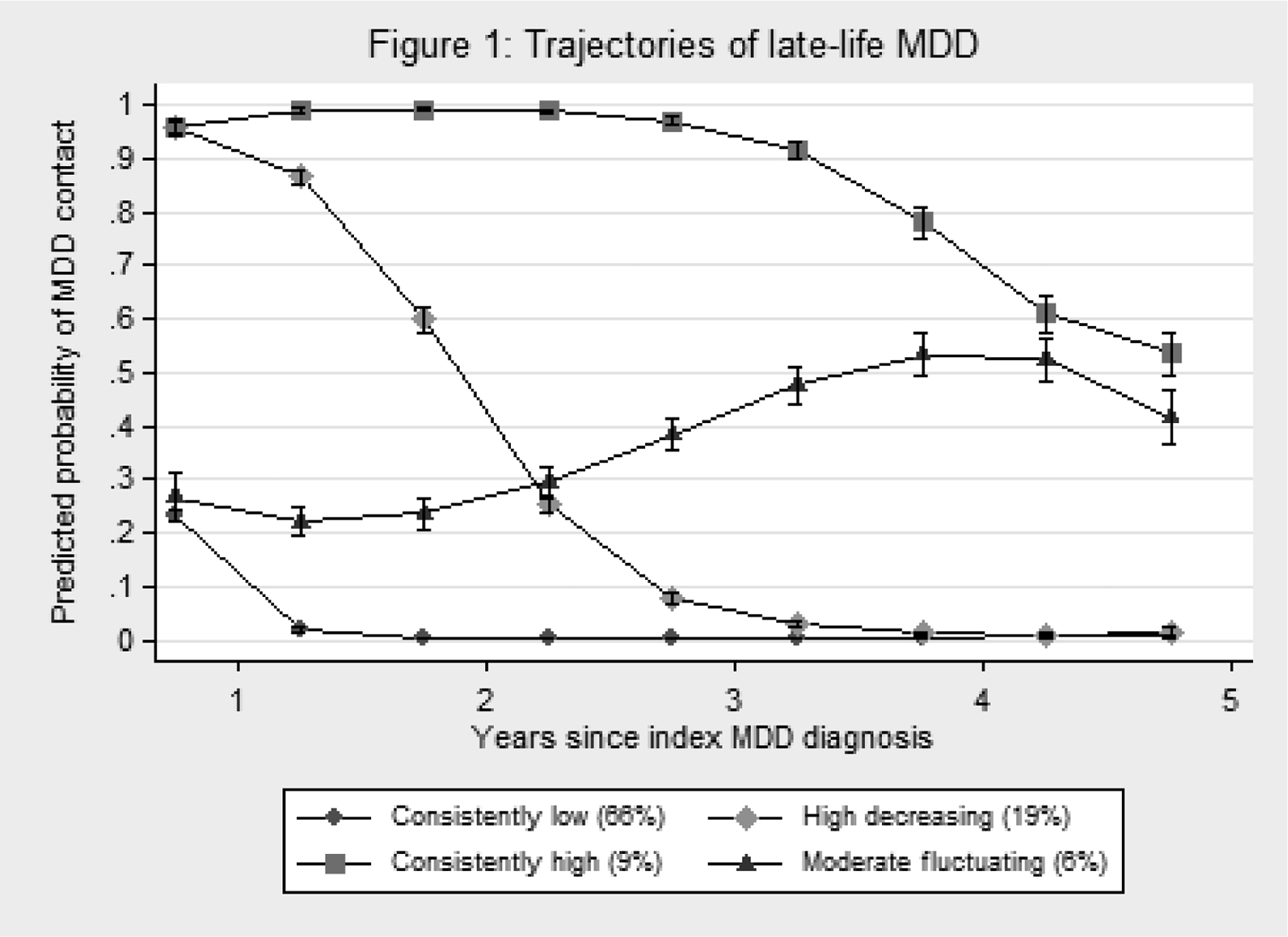
Fig. 1 Trajectories of late-life MDD.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 23 March 2020
To examine 5 years trajectories of secondary-treated late-life major depressive disorder (MDD), and evaluate whether pre-existing cerebrovascular disease and related risk factors are associated with more severe trajectories of late-life MDD.
Data were obtained from Danish registers. The sample included 11,184 adults ≥ 60 at index MDD diagnosis. Trajectories of in or outpatient contact at psychiatric hospitals for MDD over the 5 years period following index MDD diagnosis were modeled using latent class growth analysis. Risk factors included cerebrovascular disease, cardiovascular disease, hypertension, diabetes, and vascular dementia defined based on hospital diagnoses and prescription medications, demographic characteristics and characteristics of the index MDD diagnosis.
The final model included classes with consistently low (66%), high decreasing (19%), consistently high (9%) and moderate fluctuating (6%) probabilities of contact at a psychiatric hospital for MDD during the 5 year period following the index MDD diagnosis (Fig. 1). Older age, greater severity, inpatient treatment and > 12 antidepressant prescriptions within 5 years of the index MDD diagnosis predicted membership in more severe trajectory classes. Cerebrovascular disease and related risk factors were not associated with trajectory class membership.
A substantial proportion (34%) of individuals diagnosed with MDD in late-life require specialized psychiatric treatment for extended periods of time. We found no evidence that cerebrovascular disease or related risk factors predicted course trajectories in secondary-treated late-life MDD.
The authors have not supplied their declaration of competing interest.

Fig. 1 Trajectories of late-life MDD.

Fig. 1 Trajectories of late-life MDD.
Comments
No Comments have been published for this article.