Introduction
Brazil's biodiversity is protected by law, including the 1998 Environmental Crimes Law (Presidência da República do Brasil, 1998), which was a significant legal step for the protection of wildlife and for the punishment of perpetrators of wildlife crime. In Brazil wildlife crime includes keeping animals in captivity without legal permits, hunting and killing wild animals, removing animals from the wild, selling or exporting wildlife illegally, and abusing or mutilating animals (Presidência da República do Brasil, 2008). Keeping wild animals as pets is a practice deeply rooted in Brazilian culture (e.g. Alves et al., Reference Alves, Lima and Araújo2013), making surveillance and enforcement difficult and time-consuming. The official strategy for dealing with wildlife crime in Brazil is based predominantly on the command and control approach and is often inefficient (Regueira & Bernard, Reference Regueira and Bernard2012).
Brazil has a three-tiered political and administrative system, comprising the Federal government, states and municipalities, which together form the Federative Republic of Brazil (Presidência da República do Brasil, 1988). The 26 states and one federal district are semi-autonomous self-governing entities, with their own constitutions and governments, and the 5,570 municipalities are minor federal units, with autonomous local governments. According to the National Constitution, each administrative level should have its own executive agencies, including those for dealing with environmental issues (Presidência da República do Brasil, 1988). Until 2011, the National Institute of Environment and Renewable Natural Resources (Instituto Nacional do Meio Ambiente e dos Recursos Naturais Renováveis, IBAMA) was responsible for surveillance and enforcement of all administrative penalties involving wildlife crime in Brazil. This responsibility was transferred to state environmental agencies by Federal Law 140 (Presidência da República do Brasil, 2011a) but several states are not yet prepared to take full responsibility for their wildlife.
Success in tackling wildlife crime requires environmental legislation aligned with well-structured mechanisms for surveillance and de facto punishment (Brito & Barreto, Reference Brito and Barreto2005). Despite the existence of specific laws for wildlife protection in Brazil, their effectiveness is questionable (e.g. Alves & Pereira Filho, Reference Alves and Pereira Filho2007; Alves & Rosa, Reference Alves and Rosa2010; Regueira & Bernard, Reference Regueira and Bernard2012; Kuhnen & Kanaan, Reference Kuhnen and Kanaan2014), and the few data available indicate low rates of crime investigation, effective judgement, and punishment (Brito & Barreto, Reference Brito and Barreto2005, Reference Brito and Barreto2006; Barreto et al., Reference Barreto, Araújo and Brito2009a, Reference Barreto, Mesquita, Araújo and Britob). We use data on notifications of violations and on the payment of fines associated with wildlife crime, collected during a 12-year period in the state of Pernambuco, as a proxy for efficiency in tackling wildlife crime in Brazil. Pernambuco is a source and hub for trafficked animals in north-eastern Brazil, supplying illegal markets in the south and south-east (RENCTAS, 2001; Pereira & Brito, Reference Pereira and Brito2005; Regueira & Bernard, Reference Regueira and Bernard2012). The local framework for environmental surveillance and enforcement is similar to that in most other states, and thus our data may be indicative of the overall situation in the country.
Study area
Pernambuco state (98,311 km2) comprises 185 municipalities, with a total population of 9.2 million. Circa 3.6 million inhabitants are concentrated in the metropolitan area around the capital, Recife, where per capita income is USD 6,806 (IBGE, 2014). IBAMA has two offices in Pernambuco: the main one in Recife and a second in Salgueiro.
Methods
Under Brazil's law on access to information (Presidência da República do Brasil, 2011b) we submitted a request via IBAMA's citizen information system for all notifications of violations against wildlife (hereafter processes) recorded in Pernambuco state during January 2000–December 2012. We also searched for processes on IBAMA's database Public Consultation on Environmental Notifications and Embargoes.
The citizen information system returned 884 processes, and 15 others were added based on the search in the public consultation database. We analysed all 899 processes and discarded 96 because it was impossible to identify if they were directly related to wildlife crime (66), there were no data in the system (20), or the crimes were clearly not related to wildlife (10). Our final sample comprised 803 processes. We then used IBAMA's processes database to check the status of each process, extracting, if possible, the following data: process number; type of violation (as specified in Decree 6.514/2008; Presidência da República do Brasil, 2008); date of violation and value of the fine imposed; any reference to taxa and numbers of specimens; date of recording of the process in the database; date of the last process handling; processing status (concluded or in progress); duration of processing and/or conclusion; and payment status (paid, pardoned, expired or unknown). We considered as concluded all processes in which the fine had been paid, pardoned or expired, or those for which court proceedings had been issued to recover the fines. The payment status was considered unknown for processes that had been concluded but were under legal challenge, or for which it was not possible to determine whether the fine had been paid. All values were converted to USD based on the currency exchange rate of USD 1.00 = BRL 2.04 as of December 2012.
Results
We identified various problems with the data and, in some cases, a lack of information needed for appropriate handling of the processes: in 32 processes (3.99%) the date of entry in the database was incorrect; 29 processes (3.61%) did not include the name or document number of the transgressor; 17 (2.12%) indicated a fine of USD 0.00; 401 (49.94%) had no information on the taxon involved; and 355 (44.21%) did not indicate the number of specimens involved. The overall quality of the data has improved since 2008: 82.28% of the processes with data on taxa and 88.17% of those indicating the number of specimens are concentrated in the last 4 years of the sample.
We found 416 indications of taxa in 412 processes: 351 (84.38%) involved birds, 52 (12.50%) mammals, and 13 (3.12%) reptiles, crustaceans and fish. Keeping wild animals in captivity (35.12%), illegal trade in wildlife (12.20%), and mistreating animals (11.46%) were the most common crimes (Fig. 1).
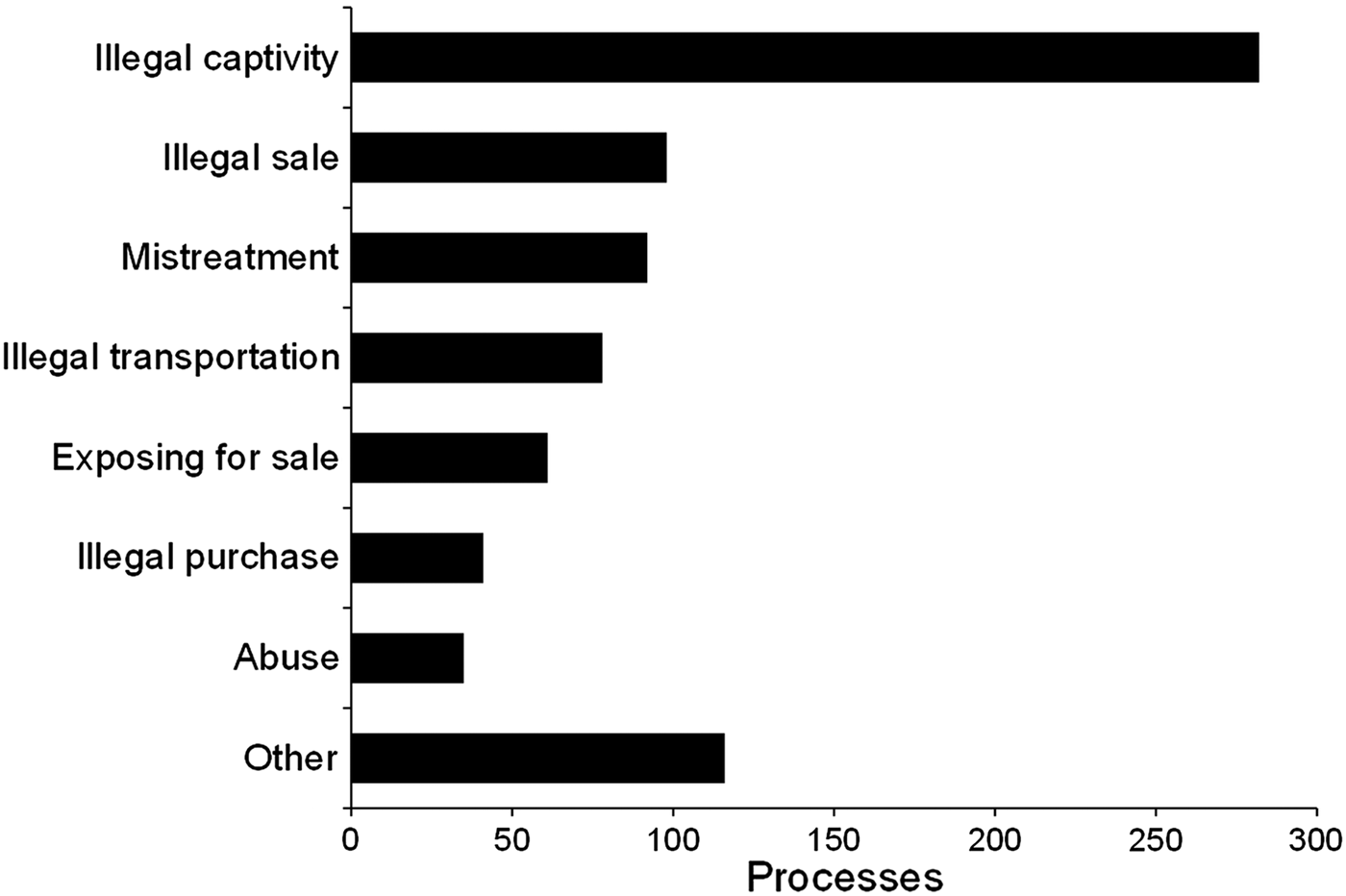
Fig. 1 Numbers of processes issued by Instituto Brasileiro do Meio Ambiente e dos Recursos Naturais Renováveis (IBAMA) against perpetrators of various types of wildlife crime in the state of Pernambuco, north-eastern Brazil, during January 2000–December 2012.
The number of processes varied from 17 in 2004 to 167 in 2012, with an annual mean of 66.91 (Fig. 2). The period 2008–2012 accounted for 69.36% of processes. The mean time between the date of issue of a process and its entry into the database varied from 1,509 days (2000) to 7 days (2009 and 2012). The mean time for completion of a process varied from 3,265 days (2000) to 191 days (2012; Fig. 3). Of the 803 processes considered, 501 (62.39%) were still in progress in December 2012 and 302 (37.61%) had been concluded. The oldest of the concluded processes, issued in 2000, had been in progress for 4,213 days. Ninety processes (17.96%) had been in progress for at least 5 years and, of these, 24 (26.67%) had been in progress for > 10 years.
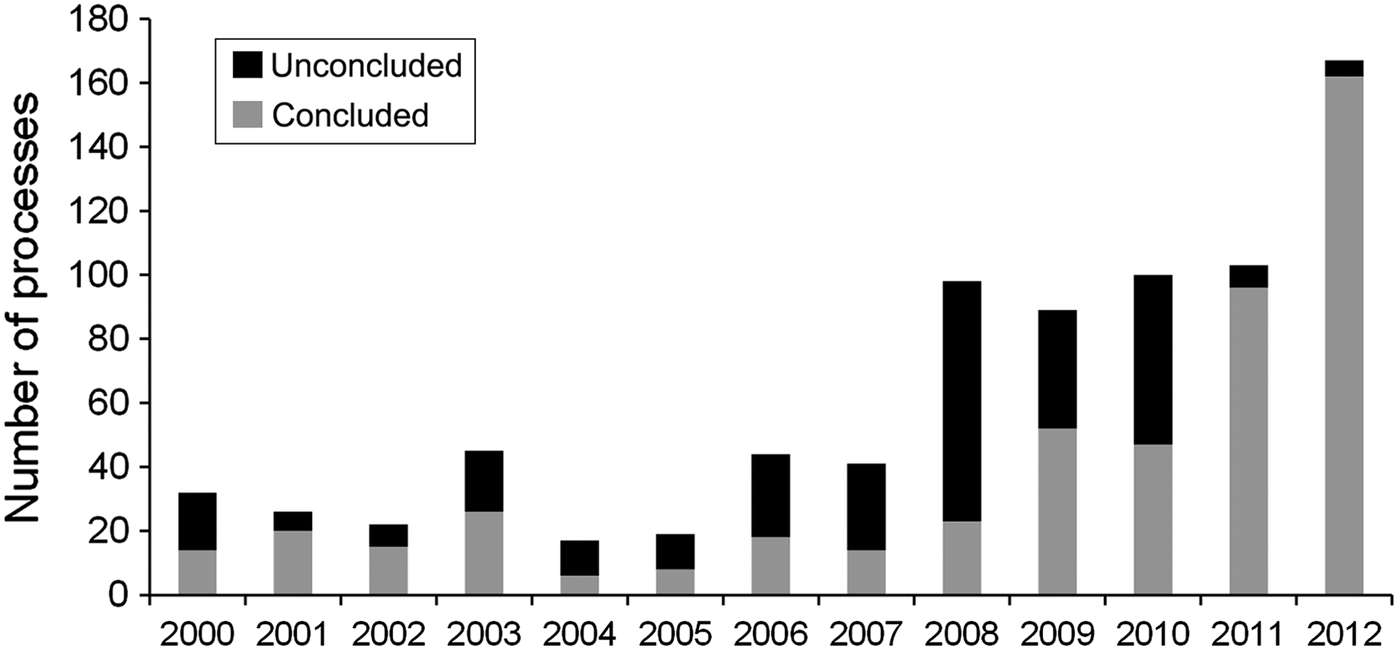
Fig. 2 Temporal distribution and status of 803 processes issued by IBAMA against perpetrators of wildlife crime in the state of Pernambuco, north-eastern Brazil, during January 2000–December 2012.
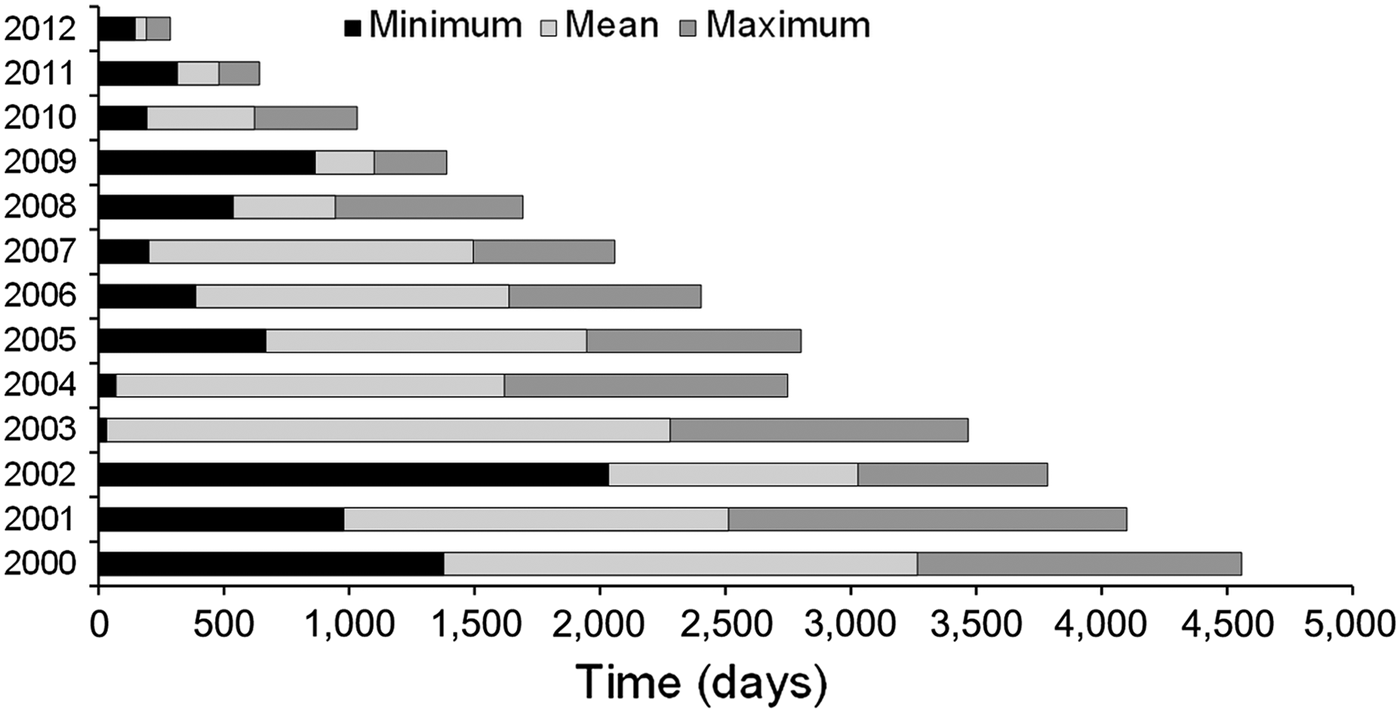
Fig. 3 Minimum, mean and maximum time (in days) for the conclusion of processes issued by IBAMA against perpetrators of wildlife crime in the state of Pernambuco, north-eastern Brazil, during January 2000–December 2012. Of 803 processes analysed only 302 had been concluded by December 2012.
During 2000–2012 USD 22,029,755 in fines were issued in Pernambuco for crimes against wildlife (Table 1). Fines varied from USD 500 (107 processes) to USD 5,170,000 (3). Of the 803 processes analysed 67 fines were paid (8.34%), 84 were pardoned (10.46%), nine expired (1.12%), and 142 were of unknown payment status (17.68%; Table 1). The amount paid in fines during the 12-year period was USD 232,911, just 1.06% of the total issued. Excluding 2011 and 2012, for which most of the processes were still in progress, the rate of success in the collection of fines varied from 0.33% (2001) to 38.56% (2003; Table 1). Sixty-nine percent of the fines paid were ≤ USD 980 (Fig. 4). In December 2012 IBAMA Pernambuco had 511 processes in progress (excluding those of unknown payment status), amounting to outstanding fines of USD 20,715,867.
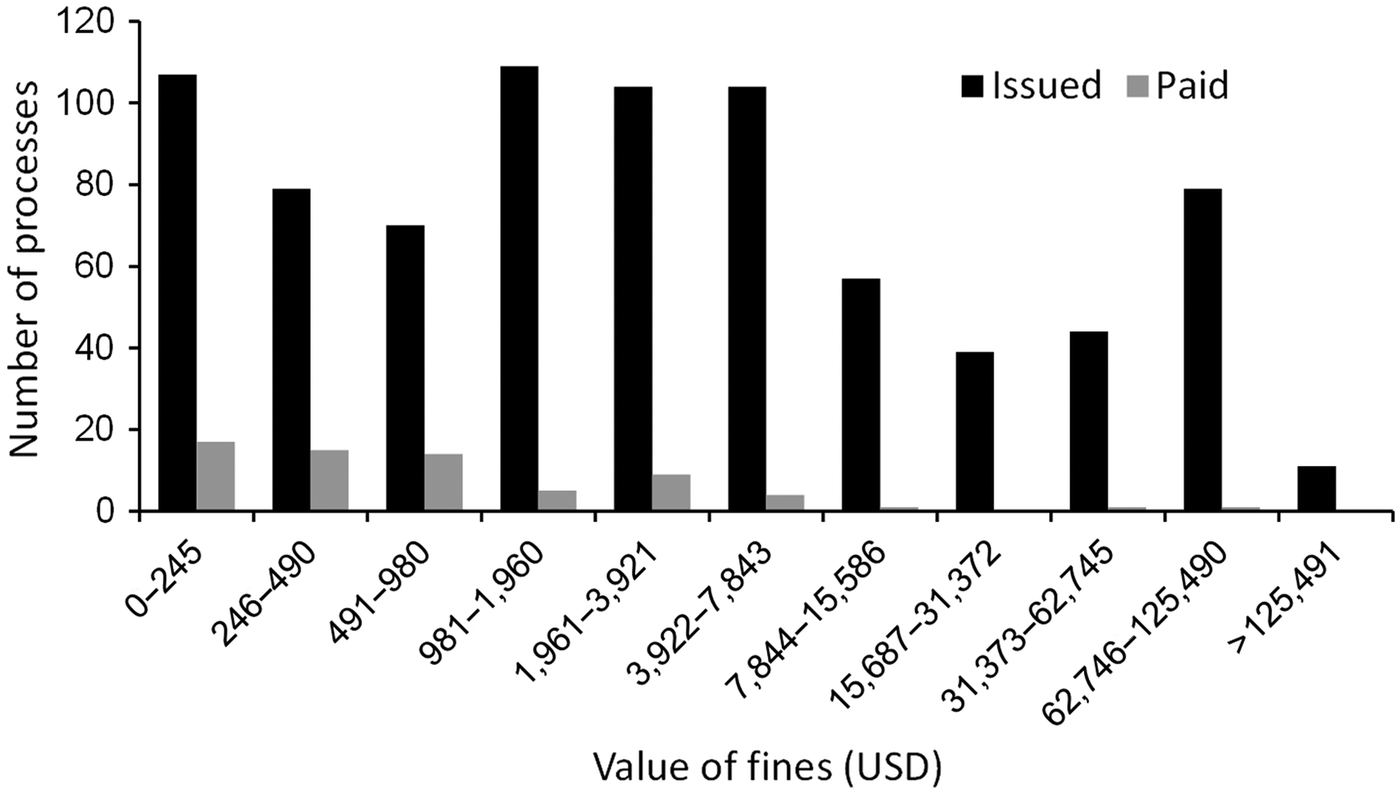
Fig. 4 Distribution of value of fines issued by IBAMA against perpetrators of wildlife crime in the state of Pernambuco, north-eastern Brazil, during January 2000–December 2012. Of 803 processes analysed only 67 fines had been paid by December 2012.
Table 1 Status of legal proceedings issued by Instituto Brasileiro do Meio Ambiente e dos Recursos Naturais Renováveis (IBAMA) in the state of Pernambuco, north-eastern Brazil, during January 2000–December 2012.
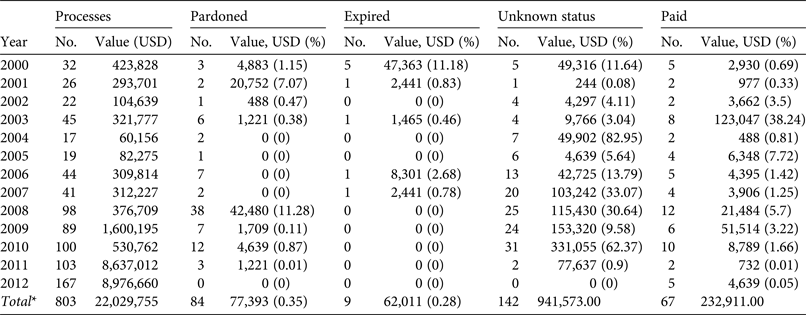
* Including concluded processes
Discussion
We found a significant degree of inefficiency in the federal system of surveillance and punishment of crimes against wildlife administered by IBAMA in Pernambuco state. Although enforcement has increased, the time frame for process handling and judgement in many cases still exceeds the legal limits. As a result the rate of collection of fines is low: of c. USD 22 million in fines issued during 2000–2012 only c. 1% was collected. This inefficiency is a consequence of a combination of errors in data entry, omissions of information necessary for the correct handling of processes, the slowness of the Brazilian justice system, and the public administration's lack of capacity to collect unpaid debts.
We found data entry errors in nearly 9% of the processes analysed, which can result in the cancellation of fines, although the overall quality has improved since 2008. Similar problems have been identified in other regions of Brazil. A study on illegal deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon revealed that 5% of 55 processes administered by IBAMA during 1999–2002 had data entry errors that resulted in the need to reissue the notification, or prevented prosecution (Brito & Barreto, Reference Brito and Barreto2006). In 2012 IBAMA adopted an electronic reporting system, which is contributing to the reduction of such errors (IBAMA, 2013).
Handling and judgement times were reduced progressively during 2000–2012, partly as a result of changes in legislation, with a reduction in the number of appeals allowed and the establishment of screening teams to deal with simpler processes (Presidência da República do Brasil, 2008; IBAMA, 2009). Despite such efforts there is a backlog of uncompleted processes and the judicial system continues to be slow. Environmental agencies often require the judiciary to collect fines on their behalf, and therefore slow trials result in low revenue (e.g. Barreto et al., Reference Barreto, Mesquita, Araújo and Brito2009b). Reports of the National Council of Justice (Conselho Nacional de Justiça) indicate that 92 million cases were processed by the Brazilian justice system in 2012, only 30% of which were completed (CNJ, 2013). The slow rate of progress has been attributed to various factors, including the probability of appeals, the lack of civil servants, judges and infrastructure, the state bureaucracy, the low level of digital processing, and limited budgets (Zampier, Reference Zampier2013).
Analyses of efficiency in the collection of fines are rare in the Brazilian federal government but should be adopted as a standard audit mechanism, to increase transparency in the public administration and improve the effectiveness of national enforcement bodies (TCU, 2013a). According to a study on deforestation in Pará state during 1999–2002 only 15% of 55 cases were concluded and paid (accounting for c. 3% of the total fines), whereas 74% of cases were sentenced but remained unpaid, accounting for 78% of the total fines (Brito & Barreto, Reference Brito and Barreto2006). In the state of Mato Grosso, analysis of 421 fines issued during 2005–2006 (229 by IBAMA and 192 by the State Secretary for the Environment) revealed that by March 2008 only 1% of the fines had been paid (Brito, Reference Brito2009). IBAMA's poor performance is recognized and its overall collection rate is one of the lowest among public agencies in Brazil. During 2008–2012 IBAMA had more fines issued than any other federal agency in Brazil (c. USD 8 billion; 35% of total federal fines) but its collection rate (0.6%) was the worst among 17 public agencies analysed (TCU, 2010, 2013b).
Such inefficiency has negative consequences for biodiversity. Firstly, the state is failing to collect taxes that could be used to fund environmental agencies and programmes. The Brazilian Ministry of Environment, which funds IBAMA, has one of the smallest budgets of Brazil's ministries and has undergone consecutive budget cuts since 2006 (Menezes & Chagas, Reference Menezes and Chagas2012). During 2005–2010, throughout the country, IBAMA issued nearly USD 314 million in fines for crimes against fauna, but during the same period it received < 2% of that amount in fines paid (Bennett, Reference Bennett2012). Failing to realize such important sources of funding is unwise, considering cuts in budgets for conservation programmes and the creation and maintenance of protected areas (Bruner et al., Reference Bruner, Gullison and Balmford2004; McCarthy et al., Reference McCarthy, Donald, Scharlemann, Buchanan, Balmford and Green2012; Hanson & McNair, Reference Hanson and McNair2014).
Secondly, such a low rate of revenue is indicative of bad governance in the environmental sector, which may have a direct impact on the success of conservation efforts (Smith et al., Reference Smith, Muir, Walpole, Balmford and Leader-Williams2003). Environmental governance should be a priority, given Brazil's dependence on the agribusiness and mining sectors, which have significant environmental impacts. Instead, however, there have been reversals in long-standing environmental achievements (e.g. Schwartzman et al., Reference Schwartzman, Moutinho and Hamburg2012; Novaes & Souza, Reference Novaes and Souza2013; Bernard et al., Reference Bernard, Penna and Araújo2014).
More importantly, poor governance sends the wrong message to society (that crimes against wildlife may be committed with impunity) and this may influence the decision-making of potential offenders (Gordon et al., Reference Gordon, Iglesias, Semeshenko and Nadal2009). A lack of will to prosecute may stem from the fact that illegal activities such as hunting and keeping wild birds are strongly rooted in local culture in some areas (Alves & Pereira Filho, Reference Alves and Pereira Filho2007; Regueira & Bernard, Reference Regueira and Bernard2012; Alves et al., Reference Alves, Lima and Araújo2013). If the law were enforced it would result in a high number of prosecutions. Historically, however, there has been an erroneous view that crimes against wildlife are minor and therefore warrant light sentences. Furthermore, with the possibility of pardoning or conversion of fines, transgressors may go unpunished (Barreto & Mesquita, Reference Barreto and Mesquita2009). In this way the Brazilian justice system fails to convey the message that biodiversity has an intrinsic and irreplaceable value that should be considered and respected.
Other studies have suggested that it is difficult for surveillance and enforcement systems against wildlife crime to function correctly in places where the culture is poorly aligned with conservation, and there is a need to seek alternative solutions, such as market-based mechanisms, social marketing or education (Jepson & Ladle, Reference Jepson and Ladle2005, Reference Jepson and Ladle2009). It may be necessary to focus surveillance and enforcement on threatened species and key personnel involved in wildlife trafficking.
In 2011 legal responsibility for surveillance and enforcement of administrative penalties involving flora, fauna and environmental licensing was transferred from IBAMA to state and municipal environmental agencies (Presidência da República do Brasil, 2011a). Such decentralization could be expected to have positive effects on conservation of ecosystems, by empowering local authorities to protect their natural resources. However, we believe this move will be deleterious to conservation in Brazil. Pernambuco and several other states are not yet prepared to take full responsibility for enforcement against wildlife crime, lacking qualified personnel and/or the necessary infrastructure facilities. Since 2007 IBAMA has accelerated the closure of several of its offices (e.g. Clark, Reference Clark2011; Farias, Reference Farias2011; IBAMA, 2012), transferring responsibility for enforcement to states or, in some cases, unprepared municipalities. The transition has given rise to territorial and temporal gaps in a system of surveillance and enforcement that is already insufficient to safeguard the country's biodiversity. To prevent further damage we recommend that the transfer of responsibilities from IBAMA should be conducted gradually, only after states and municipalities have acquired the necessary expertise, qualified personnel and infrastructure.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Department of Zoology at Universidade Federal de Pernambuco for supporting our research, Maria Eduarda Larrazabal and Felipe Pimentel Lopes de Melo for their role in evaluating EMS's BSc honours thesis, and Richard Ladle and Rômulo Alves for their constructive comments.
Biographical sketches
Ednaldo da Silva's studies focus on environmental sciences and, in particular, on quantifying the impact of wildlife crime. Enrico Bernard leads the Laboratory of Applied Biodiversity Conservation Science at the Department of Zoology, Federal University of Pernambuco, and his interests are focused on conservation biology.







