Introduction
Dry bean is a leguminous crop commonly produced in arid and semiarid climates of the Northern High Plains. Dry bean was planted on 48,600 ha in Nebraska and 537,600 ha in the United States in 2019 (USDA 2019). To achieve optimum soil temperature for germination and emergence, dry bean is planted later in the season compared to corn (Zea mays L.), sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.), and soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] (Balasubramanian et al. Reference Balasubramanian, Vandenberg and Hucl2004). Due to late planting of dry bean, early-emerging annual weed species such as kochia [Bassia scoparia (L.) A.J. Scott] and common lambsquarters (Chenopodium album L.) are less problematic (Werle et al. Reference Werle, Sandell, Buhler, Hartzler and Lindquist2014). Late season–emerging weeds, such as Amaranthus and Solanum species, are the primary competitors in dry bean production (Ogg and Dawson Reference Ogg and Dawson1984), interfering with crop growth and development and resulting in yield and quality reductions (Amini et al. Reference Amini, Alizadeh and Yousefi2014; Blackshaw Reference Blackshaw1991). Without effective weed control, dry bean yield in the state of Nebraska would be reduced by an estimated 59%, compared with 71% nationally (Soltani et al. Reference Soltani, Dille, Gulden, Sprague, Zollinger, Morishita, Lawrence, Sbatella, Kniss, Jha and Sikkema2017).
Palmer amaranth is a summer annual broadleaf species that has become troublesome in agronomic crop production systems across many regions of the United States (Ward et al. Reference Ward, Webster and Steckel2013), including the western region of Nebraska known as the Panhandle (Sarangi and Jhala Reference Sarangi and Jhala2018). Palmer amaranth is a dioecious species, native to the southwestern United States and Mexico (Sauer Reference Sauer1957). It is highly competitive in agronomic cropping systems due to its ability to emerge over long periods of time during the growing season (Jha and Norsworthy Reference Jha and Norsworthy2009) and its rapid rate of growth (Jha et al. Reference Jha, Norsworthy, Riley, Bielenberg and Bridges2008). Palmer amaranth can grow at a rate of 0.21 cm GDD−1 (growing degree day, base 10 C) (Horak and Loughin Reference Horak and Loughin2000) and can produce up to 600,000 seeds per female plant (Keeley et al. Reference Keeley, Carter and Thullen1987). Palmer amaranth achieves optimum germination at fluctuating soil temperatures near 30 C (Steckel et al. Reference Steckel, Sprague, Stoller and Wax2004), which favors late-season emergence. Palmer amaranth interference in dry bean has not previously been investigated; however, other Amaranthus species can be competitive and significantly reduce yield in dry and snap bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) (Aguyoh and Masiunas Reference Aguyoh and Masiunas2003; Amini et al. Reference Amini, Alizadeh and Yousefi2014).
Palmer amaranth is becoming a widespread issue in the Panhandle of Nebraska and is challenging to control in dry bean due to a lack of effective postemergence herbicide options. In dry bean production fields, both PPI and preemergence residual herbicides are the basis of weed control (Blackshaw et al. Reference Blackshaw, Molnar, Muendel, Saindon and Li2000; Wilson and Sbatella Reference Wilson and Sbatella2014). As PPI and preemergence herbicides cannot provide season-long weed control, postemergence herbicides are usually applied between the first and fifth trifoliate growth stage, depending on residual activity of PPI and preemergence herbicides applied. Common broadleaf postemergence herbicides in dry bean include imazamox and bentazon (Nissen and Kniss Reference Nissen and Kniss2015; Wilson Reference Wilson2005). Palmer amaranth is widely resistant to acetolactate synthase (ALS)-inhibiting herbicides in Nebraska (Sarangi and Jhala Reference Sarangi and Jhala2018) as well as in other states (Sprague et al. Reference Sprague, Stoller, Wax and Horak1997), making imazamox an ineffective control option. Bentazon has low activity on Amaranthus species and thus does not provide effective control when applied alone (Anonymous 2017).
Fomesafen, a protoporphyrinogen oxidase–inhibiting herbicide, is an alternative POST herbicide that can provide effective control of Amaranthus species in dry bean (Wilson Reference Wilson2005); however, due to label restrictions, fomesafen is not an option for most dry bean growers in western Nebraska. Corn is the most common rotational crop following dry bean in western Nebraska, and fomesafen requires an 18-mo rotation restriction to corn (Anonymous 2021).
If dry bean planting is delayed, the emergence of Palmer amaranth may be better aligned with the period of time that PPI and preemergence herbicides are still active in the soil, providing increased control of late-emerging weed species when fomesafen is not an option for producers. The influence of planting time has been investigated in crops similar to dry bean, such as soybean, tepary bean (Phaseolus acutifolius A. Gray), and faba bean (Vicia faba L.). For example, Gunsolus (Reference Gunsolus1990) identified potential benefits in weed control by delaying soybean planting. Buhler and Gunsolus (Reference Buhler and Gunsolus1996) observed that delayed planting reduced weed density and yield loss when no weed control measures were utilized; however, time of planting did not affect yield when a herbicide was applied. Delayed planting in soybean has also been shown to limit yield potential (De Bruin and Pedersen Reference De Bruin and Pedersen2008). Bhardwaj et al. (Reference Bhardwaj, Rangappa and Hamama2002) found that delaying the planting of tepary bean from May 29 to mid-June resulted in a 15% yield reduction. Khalil et al. (Reference Khalil, Wahab, Rehman, Muhammad, Wahab, Khan, Zubair, Shah, Khalil and Amin2010) observed a gradual decrease in yield as the planting of faba bean was delayed by 15-d intervals.
Growing degree days (GDD) are a method of determining accumulated heat units in a growing season and useful in determining crop development over time. In the Panhandle region of western Nebraska there are 2,400 to 2,800 GDD (base 10 C) accumulated each growing season (Klein and Lyon Reference Klein and Lyon2011). Most dry bean cultivars grown in the Panhandle require 1,550 to 1,700 GDD to mature, which in a typical growing season can be accumulated in 83 to 90 calendar days (Ostdiek Reference Ostdiek2009). In the Northern High Plains production region, dry bean is normally planted between May 20 and June 10 to ensure that the crop reaches full maturity before the first frost (Pearson et al. Reference Pearson, Brick and Smith2015).
Growers in the Panhandle region are looking for best management practices for late-emerging weeds such as Palmer amaranth in dry bean production fields. Herbicide options are limited, so integrating cultural practices, such as manipulating planting time in combination with herbicides, may provide improved control. There is no information in the scientific literature comparing the efficacy of PPI and preemergence herbicides and their effect on late-emerging weeds as influenced by dry bean planting date. The objective of this experiment was to evaluate effect of planting date and herbicide programs on control of Palmer amaranth in dry bean. It was hypothesized that delayed planting would increase late-season weed control by allowing residual herbicides to be active later in the growing season, but that benefits in improved weed control may be offset by lower dry bean yield. To our knowledge, this is the first paper assessing control of Palmer amaranth in dry edible bean. Therefore, results will be useful to scientists and dry bean growers.
Materials and Methods
Site Description
Field experiments were conducted during the 2017 and 2018 growing seasons at the University of Nebraska–Lincoln’s Panhandle Research and Extension Center near Scottsbluff, NE (41.89°N, 103.68°W). Soil type was a Tripp sandy loam (mesic Aridic Haplustolls), with a pH of 8.1, 42% sand, 37% silt, and 21% clay, and 2.1% organic matter in 2017, and a pH of 7.7, 65% sand, 18% silt, and 17% clay, and 1.2% organic matter in 2018. Common weed species at the research site include common lambsquarters, kochia, Palmer amaranth, and hairy nightshade [Solanum villosum (L.) Mill.]. Kochia and Palmer amaranth populations present at the experiment location are resistant to ALS-inhibiting herbicides. Dry fertilizer was spread in both years before planting, providing 112 kg ha−1 nitrogen and 45 kg ha−1 phosphorus. Irrigation was provided throughout the growing season via an overhead lateral move sprinkler irrigation system, with 330 and 280 mm irrigation applied during the growing seasons of 2017 and 2018, respectively. The preceding crops were corn and sugar beet in 2016 and 2017, respectively. The entire experiment area was tilled in the fall of 2017 to level the soil surface after sugar beet harvest. In western Nebraska, no- or reduced-tillage practices are often used when dry bean is planted under center-pivot irrigation, in which case a preemergence herbicide is used. When dry bean is planted under gravity- or furrow-irrigated fields, PPI herbicides are the standard practice. Therefore, tillage conducted in the growing season only occurred in plots receiving a PPI herbicide, and all other treatments were planted no-till, to simulate standard grower practice.
Experimental Design and Treatments
The experiments were designed as a two-factor randomized compete block arranged in a split-plot design with four replications. Main plot treatment was dry bean planting date, while the subplot factor was herbicide treatment. Subplot size was 3.4 m by 7.6 m. ‘Sinaloa’ (ADM Seedwest, P.O. Box 1470, Decatur, IL 62525) an indeterminate upright pinto cultivar was planted in rows spaced 56 cm apart at a population of 210,000 plants ha−1 with two dry bean planting dates, referred to as standard and delayed planting. In 2017, the standard and delayed planting dates were on June 1 and June 15, respectively. In 2018, the standard planting date was on June 13, and the delayed planting date was June 29. The 2018 planting time was delayed compared with 2017 as a result of wet and cold weather early in the cropping season and is reflective of grower practices in 2018, when delayed planting occurred region-wide.
Herbicide treatments consisted of imazamox + bentazon applied postemergence, EPTC + ethalfluralin applied PPI, pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P applied preemergence, as well as both of the PPI and preemergence treatments applied with the addition of imazamox + bentazon applied postemergence. The rate of each herbicide and pertinent product information is listed in Table 1. Nontreated and weed-free controls were also included in each replicate. Weed-free control plots were maintained weed-free by hand pulling and hoeing weeds two times per week throughout the growing season. PPI treatments were applied 1 d before planting and incorporated with a Howard® HR-30 rotavator (Kongskilde Agriculture, Roholmsvej 19, DK-2620 Albertslund, Denmark) to a depth of 5 cm immediately after application. Preemergence herbicide treatments were applied the same day as planting, and the entire study received 1.3 cm of overhead irrigation within 24 h to incorporate preemergence treatments. All postemergence herbicide treatments contained 18 g of ammonium sulfate L−1 and Preference® (Land O’Lakes, 4001 Lexington Avenue N, Arden Hills, MN 55126) nonionic surfactant at a concentration of 1% v/v. Herbicides were applied with a CO2-pressurized backpack sprayer equipped with TeeJet® 11002 AIXR nozzles (TeeJet® Technologies, Spraying Systems, P.O. Box 7900, Wheaton, IL 60187). Nozzle spacing was 51 cm and calibrated to deliver 140 L ha−1 of spray solution. Glyphosate (1,261 g ae ha−1) was applied within 1 h after planting to control early-emerging weeds such as kochia and common lambsquarters in all plots that did not receive a PPI treatment. Early-season weeds were controlled with tillage in PPI treatments. Postemergence herbicides were applied at different times depending on the dry bean planting date. The postemergence herbicides in standard and delayed dry bean planting time were applied on June 26 and July 10 in 2017 and July 13 and July 25 in 2018, respectively. Dry bean were at the V3 growth stage at the time of postemergence application, and Palmer amaranth was near 3 to 6 cm in height in both years.
Table 1. Herbicide products and application rates for field experiments conducted near Scottsbluff, NE, in 2017 and 2018. a
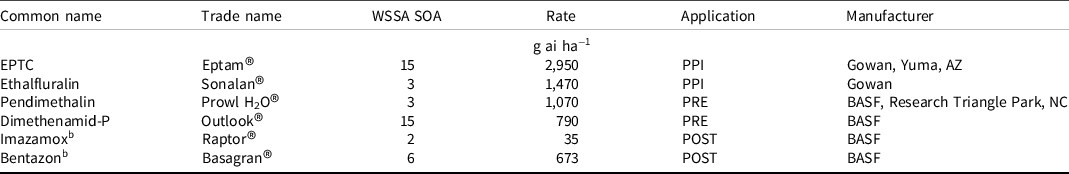
a Abbreviations: WSSA SOA, Weed Science Society of America herbicide site of action; POST, postemergence; PPI, preplant incorporated; PRE, preemergence.
b Herbicides applied POST included 18 g ammonium sulfate L−1 and 1% v/v non-ionic surfactant (NIS).
Data Collection
Weed control was estimated visually on a scale of 0% to 100% based on the density of weeds present in the plot; 100% indicated no weeds were observed. Weed density by species was assessed at 3 wk after postemergence herbicide application for the respective planting date, and all plots had a final weed control assessment at harvest. Weed density and biomass by species were recorded at harvest from two randomly placed 1.0-m2 quadrats per plot. Weed biomass was oven-dried for 48 h at 49 C and then weighed.
Dry bean harvest occurred on September 8 and 20 in 2017 and September 19 and October 1 in 2018 for standard and delayed plantings, respectively. Dry bean was hand harvested from 6 m per row from each plot to obtain yield. Beans were allowed to air-dry before being threshed by a Zurn 150 plot combine (Zurn Harvesting, Kapellenstrasse 1, D-74214 Schontal-Westernhausen, Germany), which was used as a stationary thresher. Yields were adjusted to a standard moisture of 15%.
Statistical Analysis
Data from both years of the experiment were analyzed utilizing R software (R Core Team 2019). ANOVA was performed on dry bean yield and weed control ratings, and mean separation was performed with Tukey’s HSD using the ExpDes v. 1.2.0 package (Ferreira et al. Reference Ferreira, Cavalcanti and Nogueira2014). Weed density and biomass were analyzed utilizing a generalized linear mixed model (GLMM) with a quasipoisson error distribution, fit utilizing the Lme4v. 1.1-21 package (Bates et al. Reference Bates, Maechler, Bolker, Walker, Christensen, Singmann, Dai, Scheipl, Grothendieck, Green and Fox2019). Significance of GLMM models was assessed with a likelihood-ratio chi-square test performed using the car v. 3.0.10 package (Fox et al. Reference Fox, Weisberg, Price, Adler, Bates, Baud-Bovy, Bolker, Ellison, Firth, Friendly, Gorjanc, Graves, Heiberger, Krivitsky and Laboissiere2020). Tukey’s HSD was used to determine separation of treatments, utilizing the multcomp v. 1.4-10 package as a post hoc test for GLMM procedures (Hothorn et al. Reference Hothorn, Bretz, Westfall, Heiberger, Schuetzenmeister and Scheibe2019).
Results and Discussion
Palmer amaranth was the only weed species present at the research site in 2017. In 2018 Palmer amaranth was the predominant weed species, along with moderate to low infestations of common lambsquarters, hairy nightshade, and kochia. Common lambsquarters, hairy nightshade, and kochia were not sufficiently evenly distributed throughout the experimental area to allow meaningful analysis. Palmer amaranth control ratings were combined for both years of the experiment, because there was no year-by-treatment interaction. The main effect (standard or delayed dry bean planting) had no effect on Palmer amaranth control; subplot effect (herbicide treatments) was significant (Table 2). EPTC + ethalfluralin followed by (fb) imazamox + benazon controlled Palmer amaranth 98% at 3 wk after postemergence herbicide application (WAT) and at harvest (Table 3). At 3 WAT, EPTC + ethalfluralin and pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P fb imazamox + bentazon controlled Palmer amaranth 84% and 93%, respectively, and control at harvest was 90% for both treatments. Palmer amaranth control with imazamox + bentazon and pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P was 56% and 66%, respectively, at 3 WAT, and 36% and 52% at harvest (Table 3).
Table 2. Significance of main effects analyzed with ANOVA in experiments conducted near Scottsbluff, NE, in 2017 and 2018. a
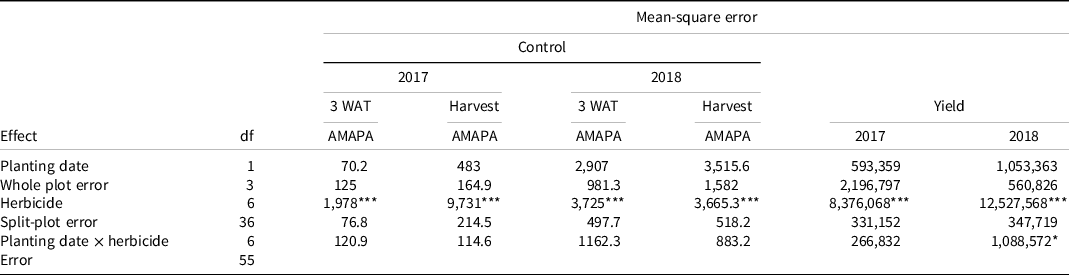
a Abbreviations: AMAPA, Palmer amaranth; df, degrees of freedom; POST, postemergence; WAT, weeks after POST treatment.
*P = 0.05–0.01.
*** P ≤ 0.001.
Table 3. Effect of herbicide program on control of Palmer amaranth at 3 wk after treatment and at dry bean harvest in field experiments conducted near Scottsbluff, NE, in 2017 and 2018. a
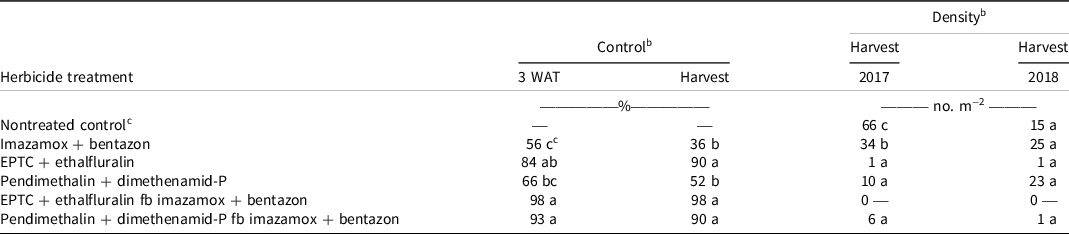
a Abbreviations: fb, followed by, indicating a later application; POST, postemergence; WAT, weeks after POST treatment.
b Means followed by the same letter are not statistically different at an alpha of 0.05.
c Nontreated control and weed-free control were removed from analysis due to lack of variance.
EPTC + ethalfluralin provided effective control of Palmer amaranth; control was not improved when followed by imazamox + bentazon applied postemergence. As only the PPI treatments were tilled, it is not possible to separate the benefits of tillage compared with EPTC + ethalfluralin. However, EPTC + ethalfluralin applied PPI provided greater control of Palmer amaranth than pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P applied preemergence in both years of this experiment.
Pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P controlled Palmer amaranth 52% at dry bean harvest, compared with 90% control with pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P fb imazamox + bentazon, indicating that the postemergence herbicides are providing a level of additional control (Table 3). The efficacy of imazamox applied postemergence for Palmer amaranth control would depend on the level of ALS resistance present in the Palmer amaranth population. The Palmer amaranth population at the experiment location is segregating for ALS resistance, as evidenced by 90% control with pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P followed by a postemergence application of imazamox + bentazon. However, imazamox + bentazon applied postemergence did not provide an acceptable level of weed control (90% or greater).
Palmer amaranth Density and Biomass
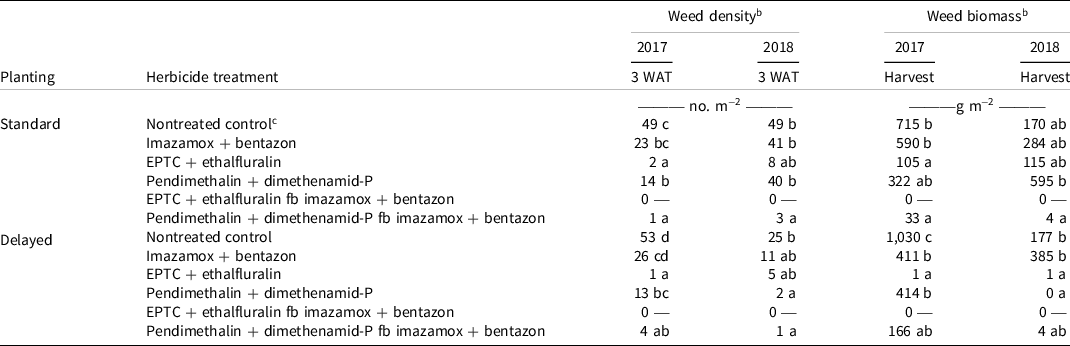
Palmer amaranth density at 3 WAT was affected by planting timing, herbicide treatment, and an interaction of the two treatment factors (Table 4). Delayed planting reduced Palmer amaranth density at 3 WAT in 2018; however, this effect was not present at dry bean harvest. At 3 WAT, Palmer amaranth density in plots that received no herbicide was 49 plants m−1 in standard planting compared with 25 plants m−1 in delayed planting (Table 5). All herbicide treatments, except imazamox + bentazon, reduced Palmer amaranth density compared with the nontreated control within the delayed planting treatment (Table 5). In both years of the experiment, EPTC + ethalfluralin fb imazamox + bentazon had zero Palmer amaranth present at both assessment dates. This treatment was omitted from the GLM to improve residual distributions, due to lack of variance within the treatment. Both treatments containing EPTC + ethalfluralin and pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P fb imazamox + bentazon had the lowest Palmer amaranth density for both planting timings (Table 5). In 2018, pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P had significantly greater Palmer amaranth density in the standard planting timing compared with the delayed (Table 5).
Table 4. Significance of main effects analyzed with generalized linear mixed model in experiments conducted near Scottsbluff, NE, in 2017 and 2018. a
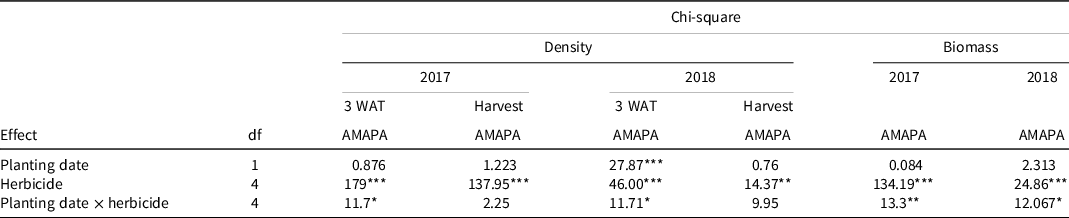
a Abbreviations: AMAPA, Palmer amaranth; df, degrees of freedom; POST, postemergence; WAT, weeks after POST treatment.
*P = 0.05–0.01.
** P = 0.01–0.001.
*** P ≤ 0.001.
Table 5. Effect of planting date and herbicide program on Palmer amaranth density and biomass in dry bean in field experiments conducted near Scottsbluff, NE, in 2017 and 2018. a
a Abbreviations: fb, followed by, indicating a later application; POST, postemergence; WAT, weeks after POST treatment.
b Means followed by the same letter are non-statistically different at an alpha of 0.05.
c Weed-free control was removed from analysis due to lack of variance.
Palmer amaranth density at dry bean harvest time was not affected by planting timing in either year (Table 4). In 2017, all herbicide treatments reduced Palmer amaranth density compared with the nontreated control (Table 3). The postemergence-only treatment, imazamox + bentazon, had a higher density of Palmer amaranth at harvest compared with all other herbicide treatments. In 2018, herbicide treatment was a significant factor in the GLMM model; however, the post hoc test did not separate differences in Palmer amaranth density.
In both years, there was an interaction between herbicide treatment and planting timing affecting Palmer amaranth biomass (Table 4). As is the case for the density data, the treatment of EPTC + ethalfluralin fb imazamox + bentazon had zero Palmer amaranth biomass at harvest time. Due to lack of variance, this treatment was removed from the analysis to improve error distribution.
In 2017, all herbicide treatments reduced Palmer amaranth biomass, with the exception of imazamox + bentazon in the standard planting treatment (Table 5). Within standard planting, both treatments containing EPTC + ethalfluralin and pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P fb imazamox + bentazon resulted in the lowest Palmer amaranth biomass. In the delayed planting treatment, both treatments containing EPTC + ethalfluralin resulted in the lowest Palmer amaranth biomass (Table 5).
In 2017, the delayed planting nontreated control produced significantly greater Palmer amaranth biomass than the standard planting (Table 5). This agrees with research performed by Keeley et al. (Reference Keeley, Carter and Thullen1987), who found that Palmer amaranth planted in July produced greater biomass than Palmer amaranth planted in June when plants were harvested 12 wk after planting. These growth and emergence times are comparable to this experiment and illustrate the Palmer amaranth emergence differences between standard and delayed planting. This early increase in biomass from later-emerging Palmer amaranth could also be attributed to longer daylengths during the early development of the plant (Keeley et al. Reference Keeley, Carter and Thullen1987).
In 2018, there was again an interaction between planting timing and postemergence herbicide treatment with respect to Palmer amaranth biomass. Within standard planting, the pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P treatment produced the highest Palmer amaranth biomass (Table 5). This is explained by the nontreated and imazamox + bentazon treatments having other weed species present, such as common lambsquarters and kochia competing with Palmer amaranth. When the soil activity of the pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P treatment dissipated, Palmer amaranth was the primary emerging weed species, and hence produced the greatest biomass.
Within the delayed planting treatment, in 2018, all herbicide treatments provided Palmer amaranth biomass reduction compared with the nontreated control, except for the imazamox + bentazon treatment. In 2018, the pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P treatment provided significantly greater Palmer amaranth biomass reduction in delayed planting compared with standard (Table 5). This reduction in Palmer amaranth biomass could be attributed to the planting date being near the end of June in 2018, which is near the end of the planting window to allow dry bean adequate time to mature.
Dry Bean Yield
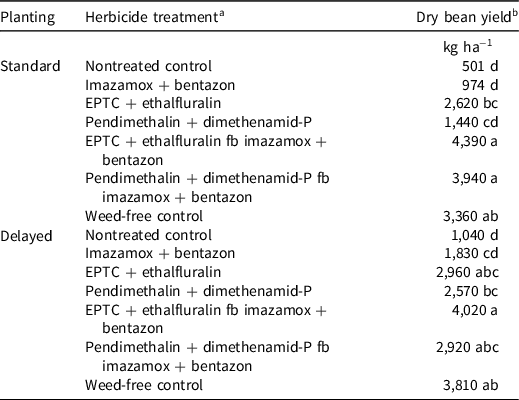
In 2017, there was no effect of planting timing on dry bean yield (Table 2). All herbicide treatments resulted in increased dry bean yield compared with the nontreated control (Table 6). Imazamox + bentazon and pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P were the two lowest-yielding herbicide treatments. Pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P fb imazamox + bentazon and both treatments containing EPTC + ethalfluralin resulted in the highest yields. EPTC + ethalfluralin performed similarly to EPTC + ethalfluralin fb imazamox + bentazon, indicating that EPTC + ethalfluralin is providing superior weed control as a residual herbicide (Table 6). The weed-free control produced a lower yield in comparison to the highest-performing herbicide treatments (Table 6). In the 2017 growing season, there were extreme amounts of Palmer amaranth emergence that continued late into the growing season. Hand weeding the weed-free plots did not provide enough weed control to prevent yield loss compared with plots treated with herbicides to prevent weed emergence.
Table 6. Effect herbicide program on dry bean yield in 2017 in field experiments conducted near Scottsbluff, NE.

a Abbreviation: fb, followed by, indicating later application.
b Means followed by the same letter are non-statistically different at an alpha of 0.05.
In 2018, there was again no main effect of planting timing on yield; however, there were interactions present between herbicide treatment and planting timing (Table 2). Within standard planting, EPTC + ethalfluralin fb imazamox + bentazon, pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P fb imazamox + bentazon, and hand weeded were the highest-yielding treatments. Within delayed planting, EPTC + ethalfluralin, EPTC + ethalfluralin fb imazamox + bentazon, pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P fb imazamox + bentazon, and hand-weeded were the highest-yielding treatments (Table 7). In 2018, Palmer amaranth density was significantly lower 3 wk after postemergence application for pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P in the delayed planting versus standard, as was Palmer amaranth biomass (Table 5). However, differences in Palmer amaranth density and biomass in the delayed vs. standard planting treatments that received pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P preemergence in 2018 did not result in differences in yield.
Table 7. Effect of planting date and herbicide program on dry bean yield in 2018 in field experiments conducted near Scottsbluff, NE.
a Abbreviation: fb, followed by, indicating later application.
b Means followed by the same letter are non-statistically different at an alpha of 0.05.
Delayed planting of dry bean is not likely to reduce yield potential as long as there are ample GDD accumulated for the crop to reach full maturity. However, there was limited benefit from delayed planting in regard to weed control. Only in 1 yr was there improved weed control from delayed planting when utilizing pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P. A grower using pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P as a residual herbicide program could potentially benefit by prioritizing fields with greater infestation of Palmer amaranth to be planted later than fields with less weed pressure. Both EPTC + ethalfluralin and pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P provided effective Palmer amaranth control as residual herbicides and will be critically important in managing Palmer amaranth in dry bean. However, EPTC + ethalfluralin, applied PPI, provided the highest control, as pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P required a postemergence application to reach a similar level of control. This paper is the first comparison of EPTC + ethalfluralin and pendimethalin + dimethenamid-P for Palmer amaranth control available in the literature. While differences in herbicide efficacy may be explained by tillage rather than the active ingredient applied, this information may be useful to dry bean growers who have the option of using either herbicide program.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Nebraska Dry Bean Commission for providing funding for this research. The authors thank Peter Sikkema for providing help in reviewing an early version of this article. No conflicts of interest have been declared.










