Approximately 60 sets of triplets are born in Australia every year (Australian Bureau of Statistics, 2013), many of which are conceived with the assistance of artificial reproductive techniques (ART). Strategies to reduce the risk of high order multiple pregnancy include reducing the number of embryos transferred per in vitro fertilisation (IVF) cycle (Pfeifer et al., Reference Pfeifer, Fritz, McClure, Adamson, Barnhart, Catherino and La Barbera2012) and transfer of a day 5 blastocyst instead of a day 3 embryo, which increases conception rates. Nevertheless, transfer of a day 5 blastocyst means that cleavage will inevitably result in monochorionic (MC) twins. Blastocyst transfer is associated with a three-fold increase in monozygotic (MZ) twinning compared to day 3 transfer (Chang et al., Reference Chang, Lee, Jee, Suh and Kim2009). It has been estimated that at least 5% of day 5 blastocysts may result in monochorionic twins (Skiadas et al., Reference Skiadas, Missmer, Benson, Gee and Racowsky2008). Dichorionic quadriamniotic quadruplets are an uncommon outcome following double blastocyst transfer, but dichorionic triamniotic (DCTA) triplets — composed of a MC pair and a singleton — occur more frequently.
Counseling couples who are found to have DCTA triplets is complex. Although the perinatal benefit of multifetal pregnancy reduction in trichorionic triamniotic triplets continues to be disputed (Wimalasundera, Reference Wimalasundera2010), the presence of a MC pair substantially increases risk. This is due to the added perinatal loss and preterm birth in the setting of MC complications, particularly twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) and selective intrauterine growth restriction (sIUGR). Early reduction of the MC pair to a singleton pregnancy in DCTA triplets is generally recommended, with improved perinatal outcomes compared to either unreduced DCTA triplets (Skiadas et al., Reference Skiadas, Missmer, Benson, Acker and Racowsky2010), or reduction of one MC twin to maintain a DC twin pregnancy (Li et al., Reference Li, Chen, Yang, Yang, Ma, Liu and Qiao2013).
Nevertheless, Evans rightly observed that ‘fetal reduction of any number is emotionally and morally troubling for couples, even when couples make educated decisions after an extensive consent’ (Evans & Britt, Reference Evans and Britt2010). This is perhaps particularly so following prolonged infertility treatment that has been arduous and expensive. It would help inform this decision if there were a reliable early predictor for later complications in the monochorionic pair. While early mid-trimester ultrasound may detect congenital abnormality or early twin oligohydramnios sequence (TOPS; Lewi et al., Reference Lewi, Jani, Boes, Donne, Van Mieghem, Gucciardo and Deprest2007), there is no reliable first trimester test for TTTS, whether TOPS, characteristically occurring in the mid-trimester, or twin anemia polycythemia sequence (TAPS), mostly a third trimester phenomenon. There is also no reliable predictor of sIUGR likely to result in extreme preterm birth, hence couples are forced to make a decision regarding multifetal reduction in early pregnancy on the basis of uncertain numerical risks.
Continuing pregnancies require intense ultrasound surveillance, which can be more challenging due to fetal crowding, so such diagnoses may be delayed or missed entirely. Decisions regarding invasive treatment for MC complications need to weigh up the proposed benefits to the twins with the potential risks posed to the singleton ‘innocent bystander’. Here we present a case of a continuing DCTA triplet pregnancy complicated by TAPS requiring intrauterine transfusion to achieve safe prolongation of pregnancy at critical gestation.
Case Study
A 31-year-old primigravid woman conceived DCTA triplets following double embryo transfer with IVF for prolonged infertility. She was counseled regarding the maternal and perinatal risks associated with DCTA triplets, but did not wish to consider multifetal pregnancy reduction. First trimester ultrasound confirmed the chorionicity and early anatomy survey appeared normal, with each triplet at low risk for aneuploidy. At 15 weeks, 2-weekly ultrasound surveillance commenced for evidence of TTTS. Growth discordance of 8 days was noted between both twins and the singleton at 19 weeks, but this remained stable, with normal fetoplacental Dopplers, and no evidence of TOPS.
At 28 weeks gestation, the middle cerebral artery peak systolic velocities (MCA-PSV) were noted to be consistently discordant in the monochorionic twins. The smaller twin had a MCA-PSV 2.1 MoMs and the larger twin had a MCA-PSV 0.81 MoMs, consistent with TAPS (Table 1).
TABLE 1 Twin Anemia Polycythemia Sequence Staging (Slaghekke et al., Reference Slaghekke, Kist, Oepkes, Pasman, Middeldorp, Klumper and Lopriore2010)

Cervical shortening was noted in association with increased uterine tightenings, and so the patient was administered corticosteroids and admitted to hospital. The MCA-PSV discordance persisted, and uterine activity settled, so an intraperitoneal transfusion (IPT) to the donor twin was performed in an attempt to increase gestational age for all three triplets. A single uncomplicated IPT of 40 mls was performed, with normalisation of the MCA-PSV in the presumed donor within 24 hours (Figure 1).
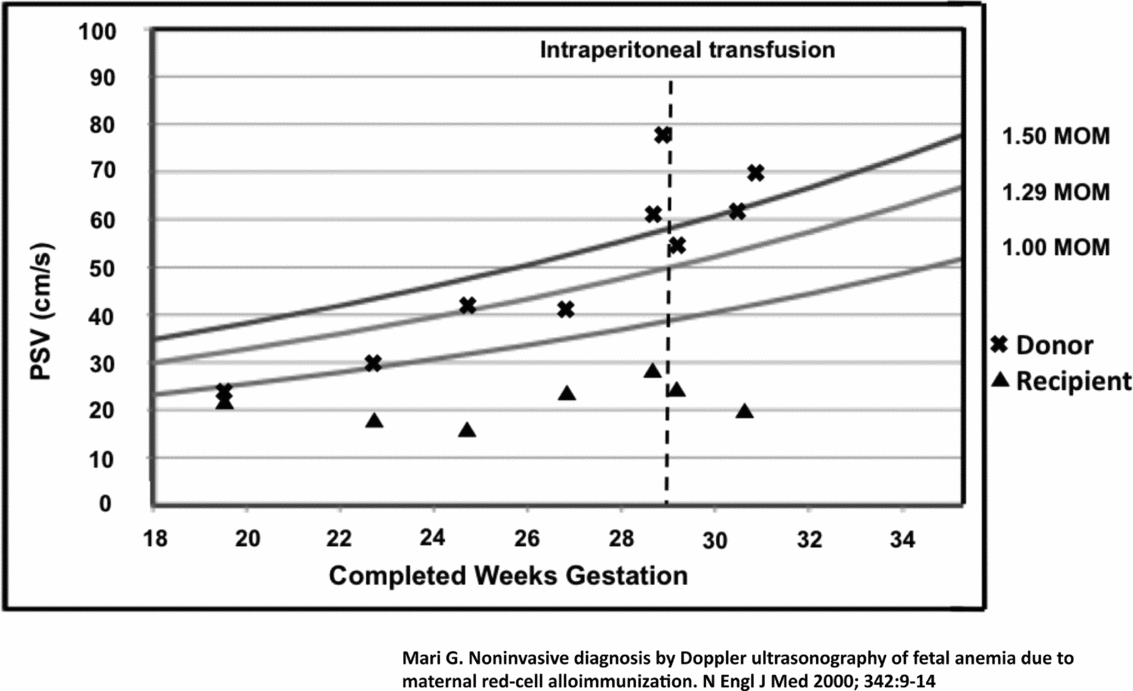
FIGURE 1 Middle cerebral artery peak systolic velocity in the monochorionic twins before and after intrauterine transfusion (Mari et al., Reference Mari, Deter, Carpenter, Rahman, Zimmerman, Moise and Blackwell2000). From The New England Journal of Medicine, Mari et al. (Reference Mari, Deter, Carpenter, Rahman, Zimmerman, Moise and Blackwell2000), Noninvasive Diagnosis by Doppler Ultrasonography of Fetal Anemia Due to Maternal Red-Cell Alloimmunization, 342, 9–14 Copyright © (2000) Massachusetts Medical Society. Reprinted with permission from Massachusetts Medical Society.
The pregnancy continued uneventfully for a further 17 days. At 30 weeks 6 days, the MCA discordance recurred, and the patient was symptomatic with preterm contractions. Given the ongoing uterine activity, a further intra-uterine transfusion was considered inadvisable, and delivery occurred by caesarean section following antenatal administration of magnesium sulphate for neuroprotection.
The triplets were all born in good condition, with the birth weight of the donor and recipient female twins 1,055 g and 1,315 g respectively, and the singleton male 1,435 g. The diagnosis of recurrent TAPS was confirmed postnatally, with the Hb of the donor twin, 111 g/L (reticulocyte count 496), and the recipient twin, 232 g/L (reticulocyte count 251); reticulocyte count ratio 1.98. The hemoglobin concentration of the unaffected singleton was normal (168 g/L). Histopathology of the placenta confirmed the chorionicity, the presence of small anastomoses between the monochorionic twins, and pallor of the donor twin placental territory. The donor twin needed no ventilation support, although the recipient twin required continuous positive airway pressure for 13 days, and the singleton for 2 days. The infants were finally discharged home in healthy condition at 38 weeks 4 days corrected gestational age. Recent pediatric follow-up at 17 months corrected gestational age has confirmed normal physical and neurodevelopment in all three triplets.
Discussion
TTTS complicates approximately 15% of all monochorionic twin pregnancies (Lewi et al., Reference Lewi, Jani, Boes, Donne, Van Mieghem, Gucciardo and Deprest2007). TTTS may be subdivided into TOPS, occurring in approximately 10% of MC twins, and TAPS, responsible for the remaining 5%. TOPS is often an acute presentation in the mid-trimester, characterized by hypervolemia, cardiac overload and polyhydramnios in the recipient twin, and hypovolemia and oligohydramnios in the donor. In contrast, TAPS is characterised by a significant inter-twin hemoglobin discordance without amniotic fluid discordance. It is associated with a low volume, gradual intertwin transfusion across small placental anastomoses, generally presenting insidiously and later in pregnancy (Slaghekke et al., Reference Slaghekke, Kist, Oepkes, Pasman, Middeldorp, Klumper and Lopriore2010). TAPS is the less common variant of TTTS, occurring spontaneously in 3–5% of all monochorionic twins, but in up to 13% cases after selective laser photocoagulation of placental vessels for TOPS (Robyr et al., Reference Robyr, Lewi, Salomon, Yamamoto, Bernard, Deprest and Ville2006). This is due to failure of surgical dichorionization, with small vessels missed or not apparent at the time of initial surgery, allowing a small inter-twin transfusion to persist. A recent randomized controlled trial has confirmed a significant reduction in post-laser TAPS using the Solomon technique, where the entire length of the vascular equator is coagulated, rather than just the visually identified placental anastomoses, thus more effectively dichorionizing the placental bed (Slaghekke et al., Reference Slaghekke, Favre, Peeters, Middeldorp, Weingertner, van Zwet and Lopriore2014). This study reported a reduction in both post-laser TAPS (16% vs. 3%; OR 0.16, 95% CI 0.05–0.49), and recurrent TOPS (1% vs. 7%; 0.21, 0.04–0.98) using this modified technique.
The outcome of TAPS is highly variable, ranging from double intra-uterine fetal death to an incidental postnatal finding, and the diagnosis may thus be established by either antenatal or postnatal criteria. Antenatal diagnosis is achieved with Middle Cerebral Artery Peak Systolic Velocity (MCA-PSV) discordance in monochorionic twins, with an MCA-PSV >1.5 MoMs in the anemic donor in association with MCA-PSV <1.0 MoMs in the recipient (Slaghekke et al., Reference Slaghekke, Kist, Oepkes, Pasman, Middeldorp, Klumper and Lopriore2010). To ensure timely antenatal diagnosis of TAPS, MCA-PSV should be incorporated into surveillance regimens of all monochorionic twins. Postnatal diagnosis includes a hemoglobin discordance of >80 g/L, and at least one of: (1) reticulocyte count ratio (>1.7), where the reticulocyte count of the donor is divided by that of the recipient. An elevated reticulocyte ratio reflects the donor's established response to pre-existing anemia, precluding an acute event, such as intrapartum TTTS to account for the hemoglobin discordance; or (2) confirmed small diameter (<1 mm) vascular anastomoses on histological examination of the placenta. In an attempt to quantify the severity of TAPS, a five-stage antenatal and postnatal scoring system has been proposed (Table 1), which loosely parallels the Quintero staging of TOPS.
While the overall survival of TAPS is reported to be 74% (De Musso et al., Reference De Musso, Chalouhi, Al Ibrahim, Essaoui, Stirnemann, Salomon and Ville2013), the optimal treatment remains unclear. Treatment options include laser photocoagulation of placental anastomoses, intrauterine transfusion to the donor (with or without partial exchange to the recipient), expectant management or delivery. The goal of intrauterine transfusion is to improve the condition of the donor in order to allow safe prolongation of the pregnancy. Nevertheless, there is a risk of worsening the recipient polycythemia, and intraperitoneal transfusion has thus been proposed as an alternative to intravascular transfusion, enabling slow restoration of the donor hematocrit, with less hemodynamic disturbance and risk of rapid inter-twin transfer of the transfused blood to the recipient (Herway et al., Reference Herway, Johnson, Moise and Moise2009). Partial exchange transfusion of the recipient has also been suggested as a means of reducing the complications of polycythemia, although it adds complexity to the procedure (Slaghekke et al., Reference Slaghekke, Kist, Oepkes, Pasman, Middeldorp, Klumper and Lopriore2010).
Laser photocoagulation of the placental bed is the only curative treatment, but this needs to be weighed against the risks of fetoscopic surgery, particularly preterm labour and preterm premature rupture of the membranes. In addition, laser photocoagulation for TAPS is technically more difficult, given the absence of polyhydramnios, and that all post-laser TAPS involve a second fetoscopic procedure. Nevertheless, a recent non-randomised series of 55 pregnancies complicated by spontaneous (33%) or post-laser (67%) TAPS has reported comparable perinatal survival for TAPS treated with primary laser (95%), compared with either IUT (85%) or expectant management (83%) (Slaghekke et al., Reference Slaghekke, Favre, Peeters, Middeldorp, Weingertner, van Zwet and Lopriore2014). This is despite the fact that: (1) TAPS stage was higher in those offered invasive treatment (IUT or laser); (2) treatment was performed significantly earlier in the laser compared to the IUT group, and (3) laser was associated with a significantly higher rate of PROM. These results assist in counseling families with TAPS-affected twins. Overall, they suggest that (1) severe midtrimester disease may be best managed with laser; (2) IUT may be an appropriate palliative treatment in persistent TAPS in the late second or early third trimester, and (3) expectant management with close observation and/or early delivery should be considered in late onset and/or less severe disease. The equation is less balanced in DCTA triplets, where the risks of in utero treatment need to be weighed against those of iatrogenic prematurity for not just the affected twins, but the unaffected singleton. We chose to perform a single intraperitoneal transfusion as a straightforward procedure to minimise the risk of extreme preterm birth to all three fetuses.
Conclusion
An unintended consequence of increasing blastocyst transfer for IVF is the increasing number of high order multiple pregnancies that include monochorionic twins. This case highlights the complexities in managing these pregnancies, and the need for increased surveillance for TTTS, including TAPS, so that timely treatment can be offered. Optimal management of these cases remains uncertain, but will be largely determined by disease severity and gestational age, weighing up the risks of in utero treatment against the burden of prematurity to both affected and unaffected fetuses. We conclude that despite the potential risks, in utero therapy has an important role in multiple pregnancies of mixed chorionicity, and can achieve safe prolongation of pregnancy at critical gestations.




