Published online by Cambridge University Press: 23 September 2021
We introduce a novel logic-based system for reasoning over data streams, which relies on a framework enabling a tight, fine-tuned interaction between Apache Flink and the 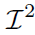 $${{\mathcal I}^2}$$
-DLV system. The architecture allows to take advantage from both the powerful distributed stream processing capabilities of Flink and the incremental reasoning capabilities of
$${{\mathcal I}^2}$$
-DLV system. The architecture allows to take advantage from both the powerful distributed stream processing capabilities of Flink and the incremental reasoning capabilities of 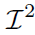 $${{\mathcal I}^2}$$
-DLV, based on overgrounding techniques. Besides the system architecture, we illustrate the supported input language and its modeling capabilities, and discuss the results of an experimental activity aimed at assessing the viability of the approach.
$${{\mathcal I}^2}$$
-DLV, based on overgrounding techniques. Besides the system architecture, we illustrate the supported input language and its modeling capabilities, and discuss the results of an experimental activity aimed at assessing the viability of the approach.
This work has been partially supported by the project “MAP4ID - Multipurpose Analytics Platform 4 Industrial Data”, N. F/190138/01-03/X44 and by the Italian MIUR Ministry and the Presidency of the Council of Ministers under the project “Declarative Reasoning over Streams” under the “PRIN” 2017 call (CUP H24I17000080001, project 2017M9C25L_001).