A comparative nonlinear characterization is carried out between the nonlinear
behavior of a composite and the piezoceramic used to obtain it. This study is necessary for
using the composite in power transducer applications, as in the Non Destructive Testing
(NDT) by ultrasonic waves at high frequencies (300 kHz−800 kHz). Measurements of the
losses and the resonator stiffness variations have also been done. Both these effects, as well as
the possibility of the frequency hysteresis, show different behavior in the composites, since
the increases in the ceramics are different from those in the composites. In this study two
measure methods are used; principally the motional impedance increase with the motional
current measurements. The results obtained are normalized in order to make them
independent of the resonator size, and thus make the comparison between the composite and
the ceramic easier. The figure of the mechanical loss tangent tg $\delta_{\rm m}$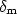 versus the mean strain
$\langle S \rangle $
versus the mean strain
$\langle S \rangle $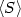 shows that the losses can be greater in the ceramic than in the composite for soft ceramics.
The dependence behavior of the losses versus the mean strain shows that hard composite
transducers have lower losses and higher strains than the soft ones. However, these losses in
hard composites are higher than those in the bulk ceramic transducers.
shows that the losses can be greater in the ceramic than in the composite for soft ceramics.
The dependence behavior of the losses versus the mean strain shows that hard composite
transducers have lower losses and higher strains than the soft ones. However, these losses in
hard composites are higher than those in the bulk ceramic transducers.