The optical properties (refractive index and optical energy gap) were studied as a
function of film thickness, substrate temperature and heat-treatment temperature for
structurally, compositionally and morphologically well characterized CdI2 films grown
by thermal evaporation. The variation of residual stress in the film (determined by X-ray diffraction), grain size (D), refractive index (n) and optical energy gap (Eg) was
observed to be different in the above three cases. Combining the results of all three
experiments, the grain size dependence of n and Eg was derived. Variation of n with
grain size may be attributed to the changing packing density of crystallites with grain
size and its distribution consistent with SEM results. Eg was found to decrease with D
non-linearly and the data fits well with the equation of the type either $E_{\rm g}(D)=3.61-0.023D-0.0034D^2$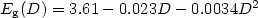 or $E_{\rm g}(D)=3.59-\frac{0.075 D^2}{(2+D)}\cdot$
or $E_{\rm g}(D)=3.59-\frac{0.075 D^2}{(2+D)}\cdot$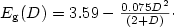 The variation of Eg with D could be attributed as due to the defect densities in the film.
The variation of Eg with D could be attributed as due to the defect densities in the film.