Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Akabli, H.
Rajira, A.
Almaggoussi, A.
and
Abounadi, A.
2010.
Study of theoretical intersubband absorption in a multilevel superlattice as a function of temperature and doping.
The European Physical Journal Applied Physics,
Vol. 52,
Issue. 2,
p.
20302.
Akabli, H.
Almaggoussi, A.
Abounadi, A.
Rajira, A.
Berland, K.
and
Andersson, T.G.
2012.
Intersubband energies in Al1−yInyN/Ga1−xInxN heterostructures with lattice constant close to aGaN.
Superlattices and Microstructures,
Vol. 52,
Issue. 1,
p.
70.
Rajira, A.
Akabli, H.
Almaggousi, A.
and
Abounadi, A.
2015.
The non parabolicity and the enhancement of the intersubband absorption in GaAs/GaAlAs quantum wells.
Superlattices and Microstructures,
Vol. 84,
Issue. ,
p.
192.
Moudou, Lhoucine
AL-Hattab, Mohamed
Bajjou, Omar
Boulghallat, Mustafa
Khenfouch, Mohammed
and
Rahmani, Khalid
2022.
Improvement of intersubband absorption in asymmetric quantum wells based on GaN/AlInN.
Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures,
Vol. 139,
Issue. ,
p.
115168.
Zhang, Zhi-Hai
and
Yuan, Jian-Hui
2022.
The nonlinear second harmonic generation and third harmonic generation in GaAs/GaAlAs exponentially confined quantum well: Electric and magnetic field effects.
Physica B: Condensed Matter,
Vol. 646,
Issue. ,
p.
414356.
Moudou, L’houcine
AL-Hattab, Mohamed
Rahmani, Khalid
Oublal, Essaadia
Maouhoubi, Ibrahim
Bajjou, Omar
Guerroum, Jamal
and
Chrafih, Younes
2024.
Temperature dependence analysis of intersubband absorption in asymmetric ZnO/MgZnO quantum wells: Potential for terahertz emission applications.
Journal of Luminescence,
Vol. 275,
Issue. ,
p.
120727.
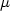 m operating wavelength.
m operating wavelength.