Article contents
Structural and vibrational properties of Cu(1 1 0)-2 × 1-Pd surface alloy
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 30 January 2012
Abstract
Investigations of surface alloys are important in various applications such as that of heterogeneous catalysis, where the electronic structure and geometric arrangement of the surface atoms strongly influence the reactions taking place on the surface. So, a deeper understanding of the physical and chemical phenomena associated with the creation of surface alloys appears to be essential in order to further progress in catalysis. In this paper, we present the calculation of vibrational properties of the Cu(1 1 0)-2×1-Pd surface alloy formed by depositing Pd atoms onto the Cu(1 1 0) surface substrate. The surface phonon frequencies and local vibration density of state (LDOS) are calculated with the use of the matching theory. New surface modes have been found on the Cu(1 1 0)-2×1-Pd surface alloy along the directions of high-symmetry ΓX¯$ \overline{{\Gamma X}}$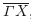 , XS¯$ \overline{{XS}}$
, XS¯$ \overline{{XS}}$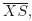 , SY¯$ \overline{{SY}}$
, SY¯$ \overline{{SY}}$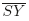 and YΓ¯$ \overline{Y\mathrm{\Gamma }}$
and YΓ¯$ \overline{Y\mathrm{\Gamma }}$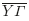 of the two-dimensional Brillouin zone, in comparison with the clean surface Cu(1 1 0). From the calculated local phonon densities of states (LDOS) we find that the layer DOS start to settle at the fourth layer, where there are only small differences with the bulk DOS spectrum.
of the two-dimensional Brillouin zone, in comparison with the clean surface Cu(1 1 0). From the calculated local phonon densities of states (LDOS) we find that the layer DOS start to settle at the fourth layer, where there are only small differences with the bulk DOS spectrum.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © EDP Sciences, 2012
References
- 4
- Cited by


