Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 December 2000
When the frequency of infrared light and the plasma frequency of highly doped n-GaAs
are in resonance (e.g. for a doping concentration
N = 7 × 1018cm−3 and a wavelength $\lambda=10.6 \mu$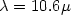 m), the free-electron induced optical nonlinearity is soundly pronounced. At such high doping concentrations it is necessary to extend the rigid quantum mechanical description of the free-electron induced nonlinearity to a multi-valley model. The central valley of GaAs was treated as a fully nonparabolic degenerated electron gas, whereas
the satellite valley was modeled as an anisotropic electron gas of arbitrary degeneracy.
The following intra- and intervalley absorption mechanisms were taken into account:
impurity assisted, thermal and hot polar optical phonon assisted intravalley absorption
on one hand and intervalley phonon assisted absorption in equivalent and nonequivalent
intervalley absorption on the other hand. The dependence of the different absorption and
energy relaxation mechanisms on the doping concentration, free electron heating,
optical power density and the equivalent LL-intervalley deformation potential are
discussed. We demonstrated for the first time that the behavior of the optical intervalley
nonlinearity, i.e. the nonlinear absorption and nonlinear intervalley transfer, strongly
depend on the equivalent LL-intervalley deformation potential. In the linear regime the
model calculations are in good agreement with experimental results.
m), the free-electron induced optical nonlinearity is soundly pronounced. At such high doping concentrations it is necessary to extend the rigid quantum mechanical description of the free-electron induced nonlinearity to a multi-valley model. The central valley of GaAs was treated as a fully nonparabolic degenerated electron gas, whereas
the satellite valley was modeled as an anisotropic electron gas of arbitrary degeneracy.
The following intra- and intervalley absorption mechanisms were taken into account:
impurity assisted, thermal and hot polar optical phonon assisted intravalley absorption
on one hand and intervalley phonon assisted absorption in equivalent and nonequivalent
intervalley absorption on the other hand. The dependence of the different absorption and
energy relaxation mechanisms on the doping concentration, free electron heating,
optical power density and the equivalent LL-intervalley deformation potential are
discussed. We demonstrated for the first time that the behavior of the optical intervalley
nonlinearity, i.e. the nonlinear absorption and nonlinear intervalley transfer, strongly
depend on the equivalent LL-intervalley deformation potential. In the linear regime the
model calculations are in good agreement with experimental results.