Article contents
High performance LTPS TFT with very large grains producedby sequential lateral crystallization
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 September 2005
Abstract
We report the structural and electrical properties of polycrystalline silicon on glass crystallized by using a CW Nd:YVO4 laser. Various microstructures appear on amorphous silicon after a scanning of the laser regardless of the crystallization process parameters such as laser power and scan speed. The crystallized region could be characterized by their grain size as 3 distinct regions; RTA-SPC (rapid thermal annealed-solid phase crystallization) region, small-grain region and SLC (sequential lateral crystallization) region with very large grains of ~10 μm. To verify its electrical properties, p-ch TFTs were fabricated on the 3 different regions. The characteristics of TFTs on SLC region were superior to those on other regions and average performances of SLC poly-Si TFTs were $u_{\rm fe} = 132$ 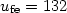 cm2/V s, $V_{\rm th} = -4.6$
cm2/V s, $V_{\rm th} = -4.6$ 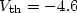 V, S.S. = 0.5 V/dec, and $I_{\rm off} =\,\sim 1$
V, S.S. = 0.5 V/dec, and $I_{\rm off} =\,\sim 1$ 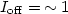 pA/μm at $V_{d} = -10$
pA/μm at $V_{d} = -10$ 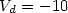 V, respectively.
V, respectively.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- The European Physical Journal - Applied Physics , Volume 31 , Issue 3 , September 2005 , pp. 165 - 168
- Copyright
- © EDP Sciences, 2005
References
- 7
- Cited by


