Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Mostafa, M.M
Al-Ganainy, G.S
El-Khalek, A.M.Abd
and
Nada, R.H
2003.
Steady-state creep and creep recovery during transformation in Al–Zn alloys.
Physica B: Condensed Matter,
Vol. 336,
Issue. 3-4,
p.
402.
Abd El-Salam, F.
Abd El-Khalek, A.M.
and
Nada, R.H.
2007.
Effect of cyclic stress reduction on the creep behaviour of Al-40wt%Zn alloy.
Physica B: Condensed Matter,
Vol. 388,
Issue. 1-2,
p.
219.
El-Salam, F. Abd
Mostafa, M.M.
Wahab, L.A.
Mostafa, M.T.
and
El-Aziz, Sh. M. Abd
2008.
Enhanced creep parameters of Al–Zn alloy induced by cyclic stress reduction.
Materials Science and Engineering: A,
Vol. 474,
Issue. 1-2,
p.
230.
Abd El-Rehim, Alaa Farag
2008.
Effect of grain size on the primary and secondary creep behavior of Sn–3 wt.% Bi alloy.
Journal of Materials Science,
Vol. 43,
Issue. 4,
p.
1444.
Fawzy, A.
2009.
Creep properties of Ag–2wt% Cu alloy in the solid solution region.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds,
Vol. 486,
Issue. 1-2,
p.
768.
Mahmoud, M. A.
and
Abd El-Rehim, A. F.
2010.
The enhancement of creep in Al–22 wt% Ag alloy by cyclic stressing.
Journal of Materials Science,
Vol. 45,
Issue. 6,
p.
1579.
Nada, R.H.
El-Salam, F. Abd
Wahab, L.A.
and
Zahran, H.Y.
2012.
Frequency and temperature dependence on the creep characteristics of Al-5wt.% Zn alloy.
Materials Science and Engineering: A,
Vol. 543,
Issue. ,
p.
180.
Nada, R.H.
El-Salam, F.Abd
Wahab, L.A.
and
Zahran, H.Y.
2012.
Effect of In addition on the characteristics of Al–5wt.%Zn.
Materials Science and Engineering: A,
Vol. 532,
Issue. ,
p.
249.
Abd El-Rehim, A. F.
and
Mahmoud, M. A.
2013.
Transient and steady state creep of age-hardenable Al–5 wt% Mg alloy during superimposed torsional oscillations.
Journal of Materials Science,
Vol. 48,
Issue. 6,
p.
2659.
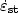 but decreased β values. The value of the
ratio γ (0.75−0.77) shows the high dependence of the steady creep on the transient
creep stage. The results were explained in view of the nature of the thermally induced
structures during aging and their mode of interaction with lattice defects generated by
the applied stress and the imposed oscillations. Grain boundary sliding and grain
boundary diffusion of Zn and Al are suggested as the rate controlling mechanisms for
both the transient and steady creep stages, respectively.
but decreased β values. The value of the
ratio γ (0.75−0.77) shows the high dependence of the steady creep on the transient
creep stage. The results were explained in view of the nature of the thermally induced
structures during aging and their mode of interaction with lattice defects generated by
the applied stress and the imposed oscillations. Grain boundary sliding and grain
boundary diffusion of Zn and Al are suggested as the rate controlling mechanisms for
both the transient and steady creep stages, respectively.