No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 23 December 2010
The temperature dependence of the electrical conductivity before and after gamma irradiation of hydrogenated amorphous silicon (a-Si:H) films, prepared by the hot wire method, at a dose of 2 kGy of 60Co gamma irradiation are presented and discussed. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) measurements provide useful information on the characteristics of bond configurations in a-Si:H before and after gamma irradiation. The conductivity increased and the bond configurations changed significantly after gamma irradiation. The results are explained by the filling of shallow donor states and variation of bond type due to migration of hydrogen atoms under the effect of irradiation. The behaviour of the conductivity is consistent with a hopping mechanism. The temperature dependence of the conductivity of a-Si:H exhibits a $T^{-1/4}$ 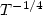 law, instead of the $T^{-1/2}$
law, instead of the $T^{-1/2}$  law, after gamma irradiation.
law, after gamma irradiation.