Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 November 2000
Charge diffusion in thin ${\rm Al}_2{\rm O}_3$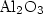 layers has been investigated by Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM).
The layers were made by anodic oxidation of Al plates, in order to obtain plane and homogeneous
amorphous oxides of known thicknesses. Under dry-nitrogen atmosphere, the charges are deposited
by contact electrification: a deposit voltage is applied between the Al substrate of the layer and the
metallized AFM tip brought to contact with the oxide. This process is perfectly controllable and
reproducible, the quantity of charges deposited being proportional to the deposit voltage.
Afterwards the tip is lifted up and scans the surface of the oxide in order to observe the diffusion of
the deposited charges. Two behaviors were observed for the diffusion process depending on the
thickness and on the deposit voltage. These results are interpreted by introducing an inhomogeneous
trap distribution in the layer, the diffusion process being considered mainly as diffusion by hopping
transport in the bulk.
layers has been investigated by Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM).
The layers were made by anodic oxidation of Al plates, in order to obtain plane and homogeneous
amorphous oxides of known thicknesses. Under dry-nitrogen atmosphere, the charges are deposited
by contact electrification: a deposit voltage is applied between the Al substrate of the layer and the
metallized AFM tip brought to contact with the oxide. This process is perfectly controllable and
reproducible, the quantity of charges deposited being proportional to the deposit voltage.
Afterwards the tip is lifted up and scans the surface of the oxide in order to observe the diffusion of
the deposited charges. Two behaviors were observed for the diffusion process depending on the
thickness and on the deposit voltage. These results are interpreted by introducing an inhomogeneous
trap distribution in the layer, the diffusion process being considered mainly as diffusion by hopping
transport in the bulk.