Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 October 2009
We report on microstructures of HfAl2O5 gate dielectric film grown on Si substrate with a Ti capping layer treated with rapid thermal annealing process. X-ray reflectivity, atomic force microscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy are used to investigate the sample. Results show that a Six (SiO $_{2})_{(1-x)}$ 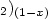 layer naturally forms at the interface between the HfAlO layer and the Si substrate in the as-grown sample. With the help of the Ti capping layer on the HfAlO/Si, the annealing treatment can effectively remove the Six (SiO $_{2})_{(1-x)}$
layer naturally forms at the interface between the HfAlO layer and the Si substrate in the as-grown sample. With the help of the Ti capping layer on the HfAlO/Si, the annealing treatment can effectively remove the Six (SiO $_{2})_{(1-x)}$ 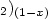 interface layer, which enhances the capacitance of the dielectric film. On the other side, the annealing process roughens the interfaces of the sample, which brings into the increase of the leakage current. Higher temperature of the annealing treatment results in rougher interfaces. Thus, the annealing temperature should be chosen properly to improve the capacitance of the film, before the interface roughening works to increase the leakage current. In this way, the dielectric and structural properties of the samples can be optimized.
interface layer, which enhances the capacitance of the dielectric film. On the other side, the annealing process roughens the interfaces of the sample, which brings into the increase of the leakage current. Higher temperature of the annealing treatment results in rougher interfaces. Thus, the annealing temperature should be chosen properly to improve the capacitance of the film, before the interface roughening works to increase the leakage current. In this way, the dielectric and structural properties of the samples can be optimized.