Published online by Cambridge University Press: 04 June 2008
We report on the effect of thickness on the structural and electrical properties of permalloy thin films Ni81Fe19 (Py). Permalloy films were deposited onto Si(100) substrates at room temperature using a KrF (wavelength of 248 nm, pulse duration of 30 ns) excimer laser at a fluence of 3 J/cm2. The thickness ranges from 25 nm to 250 nm. The micrographs reveal the formation of irregular droplets with dimensions between 4.6 μm and 0.24 μm. We show that all samples presented a strong $ \langle 100 \rangle$ 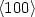 texture. The lattice constant (a) monotonously increases with increasing thickness. Also, we note that for thickness below 127 nm, the lattice constant (a) is lower than the bulk value, however, for thickness more than 127 nm, (a) is higher than $a_{\rm bulk} $
texture. The lattice constant (a) monotonously increases with increasing thickness. Also, we note that for thickness below 127 nm, the lattice constant (a) is lower than the bulk value, however, for thickness more than 127 nm, (a) is higher than $a_{\rm bulk} $ 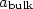 . The grain size increases from 30 nm to 54 nm as the thickness increases from 45 nm to 250 nm. The different contributions to the electrical resistivity are investigated as a function of the Py thickness.
. The grain size increases from 30 nm to 54 nm as the thickness increases from 45 nm to 250 nm. The different contributions to the electrical resistivity are investigated as a function of the Py thickness.