Article contents
Optimisation of a corrugation-pitch-modulated DFB laser structure with inhomogeneous coupling coefficient for stable single longitudinal mode operation
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 30 October 2009
Abstract
This paper shows that a suitable design of a corrugation-pitch-modulated (CPM) distributed-coupling-coefficient (DCC) distributed feedback (DFB) laser structure can strongly improve the mode selectivity $(\mathfrak{G})$ 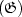 and the flatness $(\mathfrak{F})$
and the flatness $(\mathfrak{F})$ 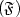 of DFB laser structures in order to ensure the required criteria for single longitudinal mode operation ( $\mathfrak{G}$
of DFB laser structures in order to ensure the required criteria for single longitudinal mode operation ( $\mathfrak{G}$ 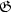 ≥ 0.25 and $\mathfrak{F}$
≥ 0.25 and $\mathfrak{F}$ 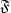 ≤ 0.05), through an extended range of current injection. It is shown that a symmetric structure should be used in order to accomplish the requirements imposed by the modern optical communication systems.Photon and carrier rate equations have been used in order to evaluate the performance of the proposed laser structure in the above-threshold regime. The variations of $\mathfrak{G}$
≤ 0.05), through an extended range of current injection. It is shown that a symmetric structure should be used in order to accomplish the requirements imposed by the modern optical communication systems.Photon and carrier rate equations have been used in order to evaluate the performance of the proposed laser structure in the above-threshold regime. The variations of $\mathfrak{G}$ 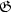 , $\mathfrak{F}$
, $\mathfrak{F}$ 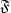 , the lasing wavelength, the emitted power (P) and the side-mode-suppression-ratio (SMSR) with the current injection (I) have been evaluated.For I = 5 I th , where I th is the laser threshold current, substantial improvements in $\mathfrak{G}$
, the lasing wavelength, the emitted power (P) and the side-mode-suppression-ratio (SMSR) with the current injection (I) have been evaluated.For I = 5 I th , where I th is the laser threshold current, substantial improvements in $\mathfrak{G}$ 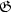 (3.8 times better), in $\mathfrak{F}$
(3.8 times better), in $\mathfrak{F}$ 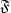 (2 times better), in P (15% higher) and in the SMSR (about 3.4 dB higher) are achieved in the proposed CPM-DCC-DFB laser when compared to an optimised CPM-DCC-DFB laser referred elsewhere. The improvements are even better when compared to the standard QWS-DFB laser.
(2 times better), in P (15% higher) and in the SMSR (about 3.4 dB higher) are achieved in the proposed CPM-DCC-DFB laser when compared to an optimised CPM-DCC-DFB laser referred elsewhere. The improvements are even better when compared to the standard QWS-DFB laser.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © EDP Sciences, 2009
References
- 7
- Cited by


