Article contents
Excited state absorption of pump and laser radiations in NYAB non-linear crystal operating at 1.3 µm for visible laser light generation
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 April 2000
Abstract
Excited state absorption of laser (≅ 1.3 µm, corresponding to the
$^4{\rm F}_{3/2}\to {}^{4}I_{13/2}$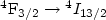 laser channel) and pump (790-860 nm) radiation have been
investigated in Nd doped YAl3(BO3)4 non-linear laser crystal. Laser gain slope efficiency
measurements as a function of pump wavelength have been used to estimate the excited state absorption of
pump radiation. On the other hand, excited state absorption cross-section in the 1300−1400 nm
wavelength range has been measured by using two beam spectroscopy. We have obtained that excited state
absorption cross-section for pump radiation is negligible whereas around 1.3 µm it is comparable to
the stimulated emission cross-section from 4F3/2 state, so that the net gain cross-section
becomes negative for certain wavelengths.
laser channel) and pump (790-860 nm) radiation have been
investigated in Nd doped YAl3(BO3)4 non-linear laser crystal. Laser gain slope efficiency
measurements as a function of pump wavelength have been used to estimate the excited state absorption of
pump radiation. On the other hand, excited state absorption cross-section in the 1300−1400 nm
wavelength range has been measured by using two beam spectroscopy. We have obtained that excited state
absorption cross-section for pump radiation is negligible whereas around 1.3 µm it is comparable to
the stimulated emission cross-section from 4F3/2 state, so that the net gain cross-section
becomes negative for certain wavelengths.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © EDP Sciences, 2000
References
- 4
- Cited by


