Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 May 2006
ZnO thin films have been deposited on Si(111) substrates at different positions of the focusing lens by pulsed laser deposition (PLD) of a ZnO target in an oxygen atmosphere. The strong influence of the position of the focusing lens on the deposition rate, crystallinity, surface morphology and optical properties of the deposited ZnO thin films are studied. The results show that the ZnO thin films deposited at lens-target distance $(D_{l-t}) =59.5$ 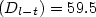 cm (the focal length is 70 cm) have the highest deposition rate and crystalline quality. The photoluminescence (PL) spectrum with the strongest ultraviolet (UV) peak and blue peak is observed in this condition. Moreover, the results of scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and selected area electron diffraction (SEAD) indicate that the films deposited at this lens position show the transition from monocrystalline to polycrystalline. Perfect monocrystalline ZnO films are obtained only when D l-t is changed in the range from 63 cm to the focus position.
cm (the focal length is 70 cm) have the highest deposition rate and crystalline quality. The photoluminescence (PL) spectrum with the strongest ultraviolet (UV) peak and blue peak is observed in this condition. Moreover, the results of scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and selected area electron diffraction (SEAD) indicate that the films deposited at this lens position show the transition from monocrystalline to polycrystalline. Perfect monocrystalline ZnO films are obtained only when D l-t is changed in the range from 63 cm to the focus position.