In recent years we have shown in south India that spontaneous dyskinesia is common in chronically ill, community-dwelling, never-treated people with schizophrenia (McCreadie et al, Reference McCreadie, Thara and Kamath1996, Reference McCreadie, Latha and Thara1997). As a result of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings (Reference McCreadie, Thara and PadmavathiMcCreadie et al, 2002a ) we have suggested recently that there may be a subgroup of schizophrenia, namely schizophrenia with dyskinesia and striatal pathology. We have now moved on to examine the first-degree relatives of our patients. If there is indeed a subgroup of schizophrenia, might movement disorders be more common in first-degree relatives of people with schizophrenia and dyskinesia than in first-degree relatives of those with schizophrenia and no dyskinesia? We have examined this question in the present study and also examined the prevalence of parkinsonism. It has been suggested already that schizotypal traits (Reference Silverman, Siever and HorvathSilverman et al, 1993) and neurological signs (Reference Kinney, Woods and Yurgelun-ToddKinney et al, 1986; Reference Ismail, Cantor-Graae and McNeilIsmail et al, 1998) may be more common in first-degree relatives.
METHOD
Background
The study was carried out in and around the village of Thiropuror 40 km south of Chennai (Madras) in south India. Here there is an outreach centre run by SCARF (Schizophrenia Research Foundation, Chennai, India), a non-governmental organisation specialising in research and community care of people with schizophrenia. Community mental health workers, trained to recognise major mental illness, bring to the centre individuals from villages within a 20 km radius for assessment and treatment.
Subjects
First-degree relatives of people with schizophrenia were recruited in two ways. First, we had already identified and examined never-treated people with schizophrenia from previous studies in 1997 (Reference McCreadie, Thara and PadmavathiMcCreadie et al, 2002a ) and 2000 (Reference McCreadie, Padmavathi and TharaMcCreadie et al, 2002b ). In August 2001 their first-degree relatives were identified in the villages and examined in their homes. Second, also in August 2001, we recruited from the villages newly identified people with schizophrenia and their first-degree relatives, specifically for this study.
As before, people with schizophrenia were recruited if they fulfilled the DSM–IV criteria for schizophrenia (American Psychiatric Association, 1994) and had never received antipsychotic medication. The diagnosis was made through mental state assessment, using the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia (Reference Kay, Fiszbein and OplerKay et al, 1987), and a history was obtained from those with schizophrenia and their relatives. The diagnosis was made by one of three psychiatrists (R.T., R.P. or T.N.S.), all of whom had a postgraduate qualification in psychiatry and had been practising clinicians for more than 15 years. People with schizophrenia were excluded if there was a history of seizures. None of the people with schizophrenia was misusing street drugs and none had ever received psychotropic medication. Analgesics and antipyretics were taken as needed.
None of the relatives included had a history of schizophrenia, any psychotic illness, seizures or brain injury. Also, none had ever taken psychotropic medication or abused alcohol or drugs. Those included were parents, siblings and children aged 18 years and over.
The study was approved by the ethical review board at SCARF. Written consent was inappropriate because almost all subjects were illiterate. All people with schizophrenia and their relatives gave informed consent, witnessed by a SCARF staff member. Oral consent was recorded in the case record of the person with schizophrenia.
Assessment
Relatives and newly identified people with schizophrenia (see above) were assessed for the presence of dyskinesia using the Abnormal Involuntary Movements Scale (AIMS; US Department of Health, Education and Welfare, 1976). This assesses movements in seven areas of the body and in each area movements are assessed on a five-point scale ranging from 0 (absent) to 4 (severe). A total score (AIMS 1–7) can also be obtained. Probable dyskinesia is said to be present if movements are rated as ‘mild’ (=2) in at least two areas, or ‘moderate’ (=3) in at least one area (Reference Schooler and KaneSchooler & Kane, 1982). In addition to dyskinesia, parkinsonism was assessed using the Simpson and Angus scale (Reference Simpson and AngusSimpson & Angus, 1970). This assesses ten areas and in each area the score ranges from 0 (absent) to 4 (severe). A total score also can be obtained (PARK 1–10). Parkinsonism is said to be present if the mean score is > 0.3 (Reference Simpson and AngusSimpson & Angus, 1970).
The following information about people with schizophrenia was also known or recorded: gender, age and length of illness (as estimated from first appearance of positive psychotic symptoms). In the case of relatives, in addition to gender, age, relationship to the person with schizophrenia, and the use of alcohol and/or tobacco was recorded – two factors that may be associated with dyskinesia in the general population (Reference Nilsson, Waller and RosengreenNilsson et al, 1997).
Blindness
All assessments of dyskinesia and parkinsonism were made by one psychiatrist (R.G.McC.). With regard to the relatives and people with schizophrenia who had been identified in the previous studies (McCreadie et al, Reference McCreadie, Thara and Padmavathi2002a , Reference McCreadie, Padmavathi and Thara b ), he was completely blind as to which relative was related to which person with schizophrenia. With regard to relatives of newly identified people with schizophrenia specifically recruited for the present study, there were two groups: for those who lived in the same house as the person with schizophrenia, he always rated the relatives before the person with schizophrenia; for those who lived in a different place to the person with schizophrenia, he was blind as to who was related to whom.
Statistical analysis
We made an a priori decision to report the following results in relatives: the median AIMS 1–7 score, the proportion with at least ‘mild’ movements in at least one area, the proportion with probable dyskinesia (Reference Schooler and KaneSchooler & Kane, 1982), the median PARK 1–10 score, the proportion with a score of at least 2 in at least one area and the proportion with parkinsonism (Reference Simpson and AngusSimpson & Angus, 1970).
It was originally agreed that we would compare the prevalence of movement disorders in all relatives of people with schizophrenia with and without probable dyskinesia and with and without parkinsonism. However, during our collation of results an authoritative report of the prevalence of neurological signs in siblings of people with schizophrenia was published (Reference Egan, Hyde and BonomoEgan et al, 2001), which stated that in order to avoid inflating the degrees of freedom, only one selected sibling per family was used for group comparisons. Also, if only one sibling was used, each patient would make the same contribution to the results. Thus, in the interests of transparency, we report an analysis of the comparison between siblings but also make reference to an analysis of all relatives.
Differences between groups were measured by χ2, Fisher's exact, Mann–Whitney and t-tests, as appropriate. Multivariate analysis explored the significance of predictor variables. Two-sided significance tests were used.
RESULTS
We recruited 181 relatives of 70 people with schizophrenia. Those with schizophrenia and probable dyskinesia (n=23) were significantly older than those without dyskinesia (n=47) (Table 1). Nineteen people with schizophrenia (27%) had parkinsonism and six (3%) had mild movements in at least one area.
Table 1 Demographic and clinical data for patients with schizophrenia, with and without dyskinesia
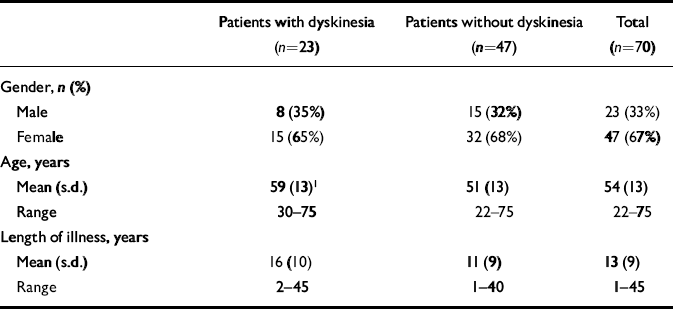
| Patients with dyskinesia (n=23) | Patients without dyskinesia (n=47) | Total (n=70) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, n (%) | |||
| Male | 8 (35%) | 15 (32%) | 23 (33%) |
| Female | 15 (65%) | 32 (68%) | 47 (67%) |
| Age, years | |||
| Mean (s.d.) | 59 (13)1 | 51 (13) | 54 (13) |
| Range | 30-75 | 22-75 | 22-75 |
| Length of illness, years | |||
| Mean (s.d.) | 16 (10) | 11 (9) | 13 (9) |
| Range | 2-45 | 1-40 | 1-45 |
Comparison of siblings
Dyskinesia
One sibling, the nearest in age to the person with schizophrenia, was identified for each person with schizophrenia (49 siblings in total; 21 people with schizophrenia had no siblings). When siblings of people with schizophrenia and dyskinesia were compared with siblings of those with schizophrenia but no dyskinesia there were no significant differences in gender distribution (Table 2) or proportions smoking or drinking alcohol. Siblings of people with schizophrenia and dyskinesia were significantly older, had a higher total AIMS 1–7 score and more had mild movements in at least one area (Table 2 and Fig. 1). Two of the four siblings with probable dyskinesia were siblings of people with schizophrenia and probable dyskinesia.
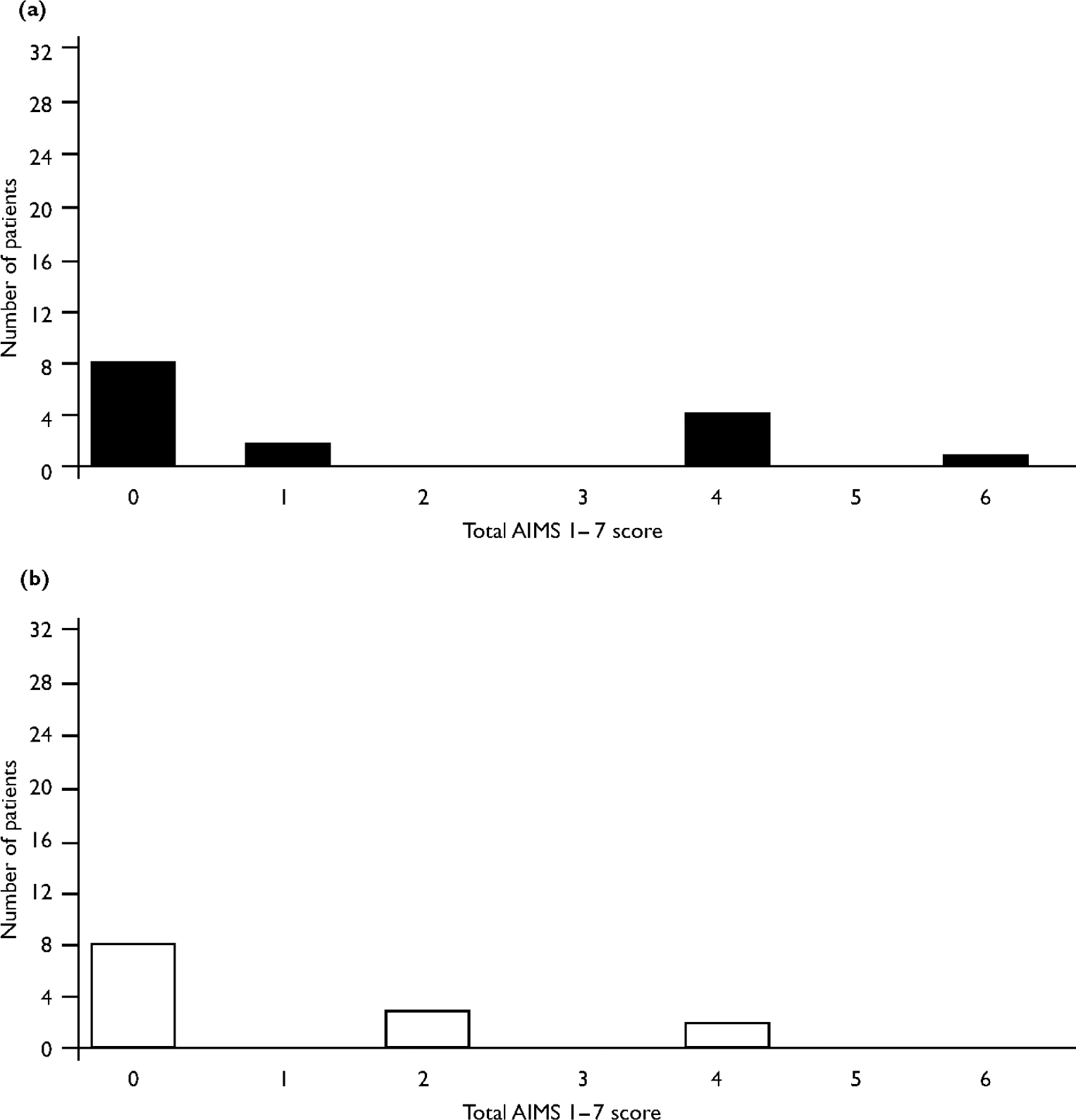
Fig. 1 Dyskinesia scores of siblings of patients (a) with and (b) without spontaneous dyskinesia.
Table 2 Demographic and clinical data for siblings of patients with schizophrenia, with and without dyskinesia
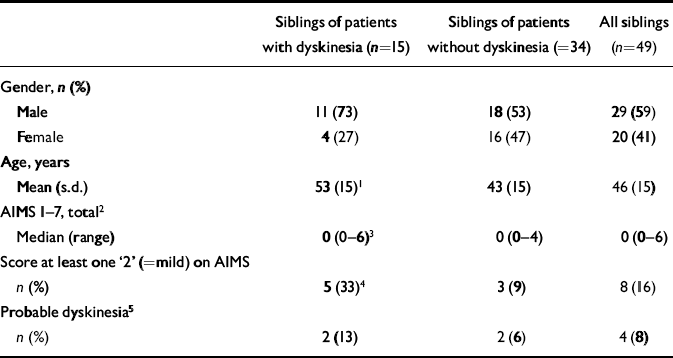
| Siblings of patients with dyskinesia (n=15) | Siblings of patients without dyskinesia (=34) | All siblings (n=49) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, n (%) | |||
| Male | 11 (73) | 18 (53) | 29 (59) |
| Female | 4 (27) | 16 (47) | 20 (41) |
| Age, years | |||
| Mean (s.d.) | 53 (15)1 | 43 (15) | 46 (15) |
| AIMS 1-7, total2 | |||
| Median (range) | 0 (0-6)3 | 0 (0-4) | 0 (0-6) |
| Score at least one ‘2’ (=mild) on AIMS | |||
| n (%) | 5 (33)4 | 3 (9) | 8 (16) |
| Probable dyskinesia5 | |||
| n (%) | 2 (13) | 2 (6) | 4 (8) |
Multiple linear regression was used to examine the simultaneous effect of two predictor variables – sibling age and dyskinesia status – of people with schizophrenia on a dependent variable – the sibling total AIMS 1–7 score. The dyskinesia status of people with schizophrenia remained independently significantly associated with the sibling total AIMS 1–7 score (P=0.02). Logistic regression was used to examine the effect of the same two predictor variables on the presence of mild movements in at least one area (the dependent variable). The dyskinesia status of people with schizophrenia remained independently significantly associated with the presence of mild symptoms in at least one area in siblings (P=0.05).
Parkinsonism
When siblings of those with schizophrenia and parkinsonism were compared with siblings of those with schizophrenia but no parkinsonism (14 and 35, respectively) there were no significant differences in gender distribution, age, proportions smoking or drinking alcohol, median parkinsonism score, proportions with a score of at least 2 in one area and proportions with parkinsonism.
All relatives
Twenty-five relatives (14%) had mild dyskinetic movements in at least one body area and six (3%) had parkinsonism. As with the siblings, differences between all relatives of people with schizophrenia with and without dyskinesia and with and without parkinsonism were examined. The statistically significant differences were the same as with the siblings but with the following exception: there was no difference in the age of relatives of those with schizophrenia with and without dyskinesia.
DISCUSSION
Methodological strengths
Some of the methodological issues in this study are similar to those of our previous studies and have been discussed before (Reference McCreadie, Thara and PadmavathiMcCreadie et al, 2002a ). Briefly, we are confident that those with schizophrenia, although ill for many years, and their relatives had not been exposed to antipsychotic medication. The SCARF team has been working in the Thiropuror area for more than 6 years and the health workers drawn from the villages know the families well, especially details about health conditions and treatment. Patients reviewed by SCARF members and diagnosed with schizophrenia are offered antipsychotic medication, but many refuse. There are no mental health services in this region except for the outreach programme of SCARF. Antipsychotics are not available in any of the local stores; therefore it is improbable that any of those with schizophrenia and their relatives would have received any antipsychotic medication, except through SCARF.
We are also satisfied that the abnormal movements rated were indistinguishable from tardive dyskinesia. The rater (R.G.McC.) has had extensive experience in the use of the AIMS scale in tardive dyskinesia and has made more than 1500 ratings using this scale.
Methodological limitations
There are, however, limitations to our study. Those with schizophrenia who were eventually recruited to the study had first to agree to come with outreach workers to the SCARF centre for assessment. They had to agree to be examined by clinicians and then, in one study (Reference McCreadie, Thara and PadmavathiMcCreadie et al, 2002a ), travel with their relatives to the city (up to 100 km) for an MRI scan. All this demanded a high degree of cooperation from those with schizophrenia and their families. We cannot be certain, therefore, that those individuals with schizophrenia are representative of the large numbers of never-treated people with schizophrenia in and around Thiropuror.
Also, we did not examine all first-degree relatives of patients. Some had left the village to work in the city and some female siblings who had married were living in distant places.
Another limitation is that the diagnosis of schizophrenia was made on clinical grounds, albeit by experienced clinicians, using the PANSS assessment and history from those with schizophrenia and their families. A structured diagnostic interview was not carried out.
With regard to assessment, a strength is that all ratings of movement disorders were made by the same psychiatrist. A potential drawback to the assessment is that in those with schizophrenia recruited specifically for the present study, although the rater, in his assessment of relatives, was blind to the dyskinesia status of those with schizophrenia, he was not always blind to the dyskinesia status of the relatives when he rated the person with schizophrenia.
Dyskinesia
When the siblings of those with schizophrenia with and without dyskinesia were compared, we found dyskinetic movements to be significantly more common and more severe in the siblings of those with schizophrenia and dyskinesia. We believe that this is the first study to report this finding. In contrast, a study of dyskinesia in treated individuals with schizophrenia and neuroleptic-naïve siblings (Reference Ismail, Cantor-Graae and McNeilIsmail et al, 2001) found little co-occurrence of dyskinesia in the siblings and the person with schizophrenia in the same family. Another study (Reference Egan, Hyde and BonomoEgan et al, 2001), using the AIMS, found a higher dyskinesia rating in siblings when compared with normal controls, but the significance level was reduced (P=0.06) when subjects who were taking neuroleptics or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors were excluded.
If spontaneous dyskinesia in schizophrenia runs in families, then either environmental or genetic factors may be responsible. With regard to the environment, all those with schizophrenia and their relatives were recruited from the same group of villages in south India, with very similar lifestyles and dietary habits. However, one possible environmental factor studied in tardive (drug-induced) dyskinesia is obstetric complications. One small study (Reference Cantor-Graae, Ismail and McNeilCantor-Graae et al, 2000; Reference Ismail, Cantor-Graae and McNeilIsmail et al, 2001) found that the rate of obstetric complications was increased by 65% in siblings with signs of dyskinesia compared with those having no signs. We now plan to examine further the obstetric histories of never-treated individuals with schizophrenia and their siblings with and without dyskinesia.
With regard to genetic factors, in those with schizophrenia with and without spontaneous dyskinesia we have already reported no variations in the dopamine D3 receptor gene (Reference Lovlie, Thara and PadmavathiLovlie et al, 2001), a variation found in those with schizophrenia with and without tardive dyskinesia (Reference Lerer, Segman and FangerauLerer et al, 2002).
Parkinsonism
There were no significant differences in parkinsonian symptoms when siblings of those with schizophrenia with and without parkinsonism were compared. The findings, therefore, do not suggest any familial basis to parkinsonian symptoms.
Our present results suggest that spontaneous dyskinesia but not parkinsonism runs in families and is further evidence that there may be a subgroup of schizophrenia, namely schizophrenia with dyskinesia. A previous study (Reference McCreadie, Thara and PadmavathiMcCreadie et al, 2002a ) suggests that such patients may have striatal pathology. Whether genetic factors are responsible for both the schizophrenic illness and the dyskinesia or whether environmental factors contribute to the latter is not yet known.
Clinical Implications and Limitations
CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS
-
▪ Dyskinetic movements are more common in relatives of people with schizophrenia who themselves have dyskinesia than in relatives of those without dyskinesia.
-
▪ The same is not true for parkinsonism.
-
▪ These findings are further evidence that there may be a subgroup of schizophrenia, namely schizophrenia with dyskinesia and striatal pathology.
LIMITATIONS
-
▪ The high degree of cooperation demanded from those with schizophrenia and their families means that we cannot be certain that those with schizophrenia are representative of the large numbers of never-treated people with schizophrenia in south India.
-
▪ Not all first-degree relatives were examined.
-
▪ We cannot say whether environmental or genetic factors are responsible for spontaneous dyskinesia in schizophrenia.
Acknowledgements
We thank the patients and their relatives for their continuing cooperation, Mr J. R. Ayankaran for help in identifying subjects, Miss H. Barrington for statistical advice and Mrs S. Farrington for secretarial assistance.






eLetters
No eLetters have been published for this article.