Research highlights persistent inequalities in both experiences and outcomes for people from minority ethnic groups when compared with White British patients in contact with psychiatric services. 1,2 There is a lack of engagement, poorer access to effective services and psychological interventions, more conflict between patients and staff, fears about reliance on emergency contacts with the police and the criminal justice system, and ethnic variations in the use of drug treatments. Reference Bansal, Bhopal, Netto, Lyons, Steiner and Sashidharan3–Reference Mangalore and Knapp5 The overrepresentation of specific ethnic groups in specialist psychiatric care contrasts with lower use of primary care and public health interventions. 1,2 These findings are mirrored in the USA, Canada, Australia and other European countries. One explanation for these inequalities is that the quality of therapeutic communication between patient and practitioner is poorer for minority ethnic groups. Therapeutic communication refers to any conversation (face-to-face or technology-assisted) that seeks to improve therapeutic outcomes through understanding and engagement. For example, communications can provide information to deal with uncertainty or reassurance and changes to the care to remedy dissatisfaction. Communications about diagnosis and assessment questions can also be helpful for patients who may fear what is happening and that no one can help. Therapeutic communications can also include discussion of treatment expectations, showing understanding and empathy as well as psychological interventions that rely on conversation and challenging cognitive bias. A stronger therapeutic alliance is one process through which good communication can lead to improved outcomes for patients. Reference Priebe, Richardson, Cooney, Adedeji and McCabe6 Effective communication is central to psychiatric assessment, diagnosis, treatment adherence and recovery. Reference Bhui and Bhugra7,Reference Kirmayer, Groleau, Guzder, Blake and Jarvis8 Dissatisfaction among immigrants and ethnic minorities can emerge if there are cultural differences in expectations and health beliefs (also called explanatory models) between the patient and professional. Reference Szczepura9,Reference Johnson, Clark, Owen and Szczepura10 For example, non-biological explanatory models for mental illness are associated with poorer therapeutic relationships and greater dissatisfaction. Reference McCabe and Priebe11 In such circumstances professionals struggle to empathise, assess the patient's emotions Reference Shioiri, Someya, Helmeste and Tang12–Reference Elfenbein, Mandal, Ambady, Harizuka and Kumar16 and understand symbolic and metaphorical idioms of distress and these can compromise clinical decisions and accurate diagnosis, and lead to disengagement. Reference Bhui and Bhugra7,Reference McCabe and Priebe11, Reference Tesone17–Reference Bhui, Bhugra and Goldberg19
These findings have led to calls for cultural competence in communications during clinical assessment, diagnosis and treatment. Reference Bennett and Keating20,Reference Bhui, Warfa, Edonya, McKenzie and Bhugra21 One approach to improve cultural competence is to explore patients' narratives about their illness during the assessment and use these to culturally adapt interventions. Reference Kleinman22–Reference Chowdhary, Jotheeswaran, Nadkarni, Hollon, King and Jordans24 For example, adaptation can involve practical changes to the venue or the sequence in which components of an intervention are provided in order to improve access and uptake; other changes include modifications of the content of written materials and interventions in terms of language or metaphors, the philosophical aims of the treatment (tolerance or cure or recovery) can be renegotiated; and the proposed theories, often shared with the patient, of how the intervention works may need to be discussed and modified as more research evidence emerges. Reference Chowdhary, Jotheeswaran, Nadkarni, Hollon, King and Jordans24,Reference Tseng25 So, interventions targeting therapeutic communications may reduce inequalities of experiences and outcomes from psychiatric care. Although many systematic reviews of devices or technologies seek out a single intervention and a single context, in this review we synthesise diverse types of evidence on the effectiveness of interventions designed to improve ‘therapeutic communication’ between Black and minority ethnic (BME) patients receiving specialist psychiatric care and the professionals who deliver that care (the THERACOM project). We identify and describe the elements of effective interventions and assess evidence from quantitative randomised and non-randomised trials as well as qualitative studies that help us understand what is an effective intervention.
Method
This paper is an accessible evidence summary of a National Institute for Health Research funded study; the full protocol and PROSPERO registration details are in the public domain (PROSPERO: CRD42011001661). Reference Bhui, McCabe, Weich, Singh, Johnson and Szczepura26
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Eligible studies included all age groups and all ethnic groups known to be prominent in healthcare settings in the UK: people from Indian, Pakistani, Bangladeshi, Sri Lankan, Black Caribbean, Black British, Black African, Irish and Chinese backgrounds (see online supplement DS1). We included all evaluative methodologies. We amended the original protocol to include studies on diaspora and interventions judged to be of relevance to the UK. We excluded studies on interventions that were considered to be generic therapeutic communications themselves, such as psychological therapies or music therapies, rather than interventions that adapted and improved practice. For example, we looked for evidence of the elements of cultural adaptation recommended by Tseng, including philosophical, technical, theoretical or practical adaptations. Reference Tseng25 We excluded studies of translation or interpretation as there is already a strong evidence base. Reference Cambridge, Singh and Johnson27,Reference Liu, Davidson, Bhopal, White, Johnson and Netto28
Search strategy
An information scientist and a researcher jointly developed, iteratively tested and refined the search strategy to capture known seminal papers. The final search strategy was agreed following further discussion with all investigators, user and carer representatives (online supplement DS2). Separate data sources and search strategies were developed for distinct sources: published papers, grey literature, websites, special collections and theses. Experts were invited to comment on omissions in the searches and to put forward candidate papers and to volunteer research work that was unpublished or in progress. Community groups and charities were also contacted to identify materials in community-based collections. The search terms from previous reviews were adapted to reflect specific ethnic groups, Reference Bhui, Warfa, Edonya, McKenzie and Bhugra21,Reference Anderson, Scrimshaw, Fullilove, Fielding and Normand29–Reference Bhui, Stansfeld, Hull, Priebe, Mole and Feder31 and for different aspects of therapeutic communication, types of mental disorder, professional groups and measures of clinical outcome.
Selecting appropriate sources
Citations were downloaded into an Endnote library. Their relevance was assessed against the predetermined inclusion and exclusion criteria (online supplement DS1) by two researchers who independently screened all titles and abstracts. Forward and backward citation tracking complemented the database searches. Full-text manuscripts were obtained for all studies entering the review. Any uncertainties about entering the review were resolved by consensus and, if necessary, by a third reviewer and examination of the full text.
The database searches yielded 7329 hits of which 3733 records were screened as potentially relevant after removing duplicates (Fig. 1). An extensive search for grey literature yielded 608 sources.

Fig. 1 PRISMA diagram showing selection of papers at each stage.
BME, Black and minority ethnic; ADHD, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder.
Quality assessment
To score methodological quality we used some core criteria for all papers, irrespective of study design, augmented by design-specific criteria (online supplement DS3). Reference Moncrieff and Drummond32–Reference Spencer, Ritchie, Lewis and Dillon36 The scores for each element were summed to produce a total score, and then presented as percentages of the maximum score (for each of the items and the total overall quality score) (Table 1). These were then categorised into low, medium or high quality on the basis of percentage of the maximum score: <33% low, 33–66% medium and >66% high.
TABLE 1 Quality scores, given as percentages of maximum score possible
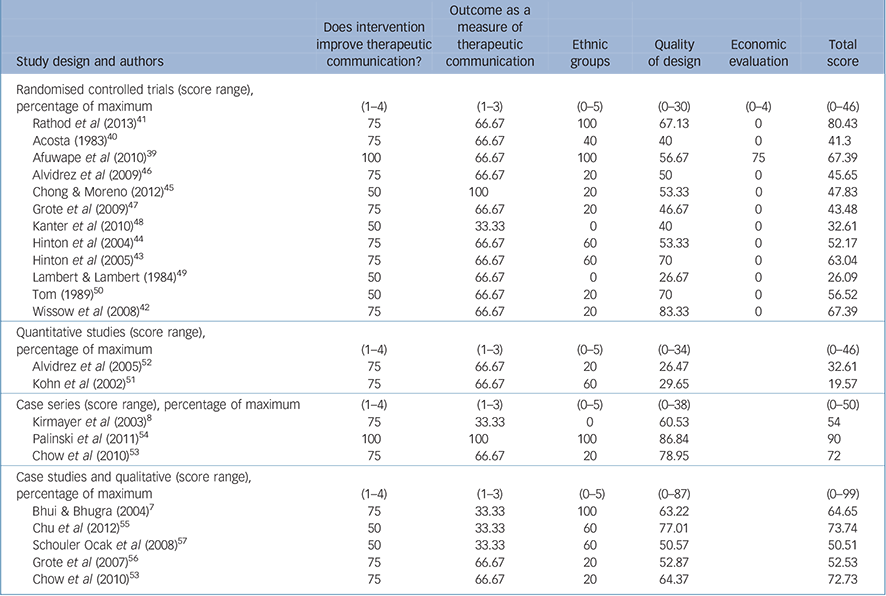
| Study design and authors | Does intervention improve therapeutic communication? |
Outcome as a measure of therapeutic communication |
Ethnic groups |
Quality of design |
Economic evaluation |
Total score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Randomised controlled trials (score range), percentage of maximum |
(1–4) | (1–3) | (0–5) | (0–30) | (0–4) | (0–46) |
| Rathod et al (2013) Reference Rathod, Phiri, Harris, Underwood, Thagadur and Padmanabi41 | 75 | 66.67 | 100 | 67.13 | 0 | 80.43 |
| Acosta (1983) Reference Acosta40 | 75 | 66.67 | 40 | 40 | 0 | 41.3 |
| Afuwape et al (2010) Reference Afuwape, Craig, Harris, Clarke, Flood and Olajide39 | 100 | 66.67 | 100 | 56.67 | 75 | 67.39 |
| Alvidrez et al (2009) Reference Alvidrez, Snowden, Rao and Boccellari46 | 75 | 66.67 | 20 | 50 | 0 | 45.65 |
| Chong & Moreno (2012) Reference Chong and Moreno45 | 50 | 100 | 20 | 53.33 | 0 | 47.83 |
| Grote et al (2009) Reference Grote, Swartz, Geibel, Zuckoff, Houck and Frank47 | 75 | 66.67 | 20 | 46.67 | 0 | 43.48 |
| Kanter et al (2010) Reference Kanter, Santiago-Rivera, Rusch, Busch and West48 | 50 | 33.33 | 0 | 40 | 0 | 32.61 |
| Hinton et al (2004) Reference Hinton, Pham, Tran, Safren, Otto and Pollack44 | 75 | 66.67 | 60 | 53.33 | 0 | 52.17 |
| Hinton et al (2005) Reference Hinton, Chhean, Pich, Safren, Hofmann and Pollack43 | 75 | 66.67 | 60 | 70 | 0 | 63.04 |
| Lambert & Lambert (1984) Reference Lambert and Lambert49 | 50 | 66.67 | 0 | 26.67 | 0 | 26.09 |
| Tom (1989) Reference Tom50 | 50 | 66.67 | 20 | 70 | 0 | 56.52 |
| Wissow et al (2008) Reference Wissow, Gadomski, Roter, Larson, Brown and Zachary42 | 75 | 66.67 | 20 | 83.33 | 0 | 67.39 |
| Quantitative studies (score range), percentage of maximum |
(1–4) | (1–3) | (0–5) | (0–34) | (0–46) | |
| Alvidrez et al (2005) Reference Alvidrez, Arean and Stewart52 | 75 | 66.67 | 20 | 26.47 | 32.61 | |
| Kohn et al (2002) Reference Kohn, Oden, Muñoz, Robinson and Leavitt51 | 75 | 66.67 | 60 | 29.65 | 19.57 | |
| Case series (score range), percentage of maximum | (1–4) | (1–3) | (0–5) | (0–38) | (0–50) | |
| Kirmayer et al (2003) Reference Kirmayer, Groleau, Guzder, Blake and Jarvis8 | 75 | 33.33 | 0 | 60.53 | 54 | |
| Palinski et al (2011) Reference Palinski, Owiti, Ascoli, De Jongh, Archer and Staples54 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 86.84 | 90 | |
| Chow et al (2010) Reference Chow, Law, Andermann, Yang, Leszcz and Wong53 | 75 | 66.67 | 20 | 78.95 | 72 | |
| Case studies and qualitative (score range), percentage of maximum |
(1–4) | (1–3) | (0–5) | (0–87) | (0–99) | |
| Bhui & Bhugra (2004) Reference Bhui and Bhugra7 | 75 | 33.33 | 100 | 63.22 | 64.65 | |
| Chu et al (2012) Reference Chu, Huynh and Arean55 | 50 | 33.33 | 60 | 77.01 | 73.74 | |
| Schouler Ocak et al (2008) Reference Schouler-Ocak, Reiske, Rapp and Heinz57 | 50 | 33.33 | 60 | 50.57 | 50.51 | |
| Grote et al (2007) Reference Grote, Zuckoff, Swartz, Blesdoe and Geibel56 | 75 | 66.67 | 20 | 52.87 | 52.53 | |
| Chow et al (2010) Reference Chow, Law, Andermann, Yang, Leszcz and Wong53 | 75 | 66.67 | 20 | 64.37 | 72.73 | |
Data extraction, analysis and synthesis
Two reviewers extracted data directly to an Excel spreadsheet. Randomised trials provide the most definitive evidence of effectiveness. Reference Concato, Shah and Horwitz37 Therefore, we separately report randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and non-randomised designs: comparative observational studies, case series, qualitative studies or qualitative elements of other studies and case studies. We contrasted narrative outcomes, effectiveness, and design strengths and weaknesses across the studies. Wherever possible for important quantitative findings, we give the measures of effect presented in the original publications (reported effects), and in the absence of such measures; wherever possible, we calculated the standardised mean difference ‘d’ and 95% confidence interval (calculated effects) from the published data. Calculations used the Campbell collaboration online calculator (http://www.campbellcollaboration.org/resources/effect_size_input.php).
Owing to the diversity of study settings, interventions and outcomes, the data were not suited to meta-analyses or meta-regressions. Instead, the results were subjected to a narrative synthesis that included four elements: Reference Popay, Roberts, Sowden, Petticrew, Arai and Rodgers38 textual description, tabulation, grouping and thematic analysis. The effective components of each intervention were identified during the thematic analysis. As part of this analysis, we classified how interventions were culturally adapted using the framework originally proposed by Tseng. Reference Tseng25
Patients' and carers' views
We worked with the Afiya Trust, who recruited a panel of mental health service users and carers with experience of similar research, and from both genders, and diverse ethnic and religious groups. In three workshops, panel members discussed their perspectives on therapeutic communication, and then they commented on and ranked the interventions identified in the review as high or low priority. These judgements informed the synthesis and recommendations.
Results
In total, 21 publications met the inclusion criteria and were included in the review (online Tables DS1–4 give details of samples, settings, methods and findings). These included 12 randomised trials, Reference Afuwape, Craig, Harris, Clarke, Flood and Olajide39–Reference Tom50 1 of which was from the grey literature; Reference Tom50 2 non-randomised and comparative observational studies; Reference Kohn, Oden, Muñoz, Robinson and Leavitt51,Reference Alvidrez, Arean and Stewart52 3 consecutive case series. Reference Kirmayer, Groleau, Guzder, Blake and Jarvis8,Reference Chow, Law, Andermann, Yang, Leszcz and Wong53,Reference Palinski, Owiti, Ascoli, De Jongh, Archer and Staples54 One of the case series was identified from the grey literature Reference Palinski, Owiti, Ascoli, De Jongh, Archer and Staples54 and the other was a qualitative substudy of a trial. Reference Chow, Law, Andermann, Yang, Leszcz and Wong53 There were two qualitative studies that each included a case study, Reference Chu, Huynh and Arean55,Reference Grote, Zuckoff, Swartz, Blesdoe and Geibel56 and two pure case studies. Reference Bhui and Bhugra7,Reference Schouler-Ocak, Reiske, Rapp and Heinz57 Two studies included preliminary economic evaluation. Reference Afuwape, Craig, Harris, Clarke, Flood and Olajide39,Reference Palinski, Owiti, Ascoli, De Jongh, Archer and Staples54 The summary findings are reported in Tables DS2 and DS4 and the effect sizes (calculated or reported) are given below.
RCTs
The RCTs examined interventions that fell into four broad types.
-
(a) Preparing patients or professionals for their expected role in a therapy before they received a therapeutic intervention. Reference Acosta40,Reference Wissow, Gadomski, Roter, Larson, Brown and Zachary42,Reference Alvidrez, Snowden, Rao and Boccellari46,Reference Lambert and Lambert49,Reference Tom50
-
(b) Enhancing and adapting existing therapies in terms of technical content and attention to cultural beliefs and idioms of distress. Reference Afuwape, Craig, Harris, Clarke, Flood and Olajide39,Reference Rathod, Phiri, Harris, Underwood, Thagadur and Padmanabi41,Reference Hinton, Chhean, Pich, Safren, Hofmann and Pollack43,Reference Hinton, Pham, Tran, Safren, Otto and Pollack44,Reference Kanter, Santiago-Rivera, Rusch, Busch and West48
-
(c) Influencing wider social systems (community agencies, family, social networks) before and during therapy. Reference Afuwape, Craig, Harris, Clarke, Flood and Olajide39,Reference Grote, Swartz, Geibel, Zuckoff, Houck and Frank47
-
(d) Ethnic matching of the professional and patient by the use of telepsychiatry. Reference Chong and Moreno45
Outcomes
Symptoms of anxiety, depression or psychosis were assessed in 8 of the 11 trials. Reference Afuwape, Craig, Harris, Clarke, Flood and Olajide39,Reference Rathod, Phiri, Harris, Underwood, Thagadur and Padmanabi41–Reference Chong and Moreno45,Reference Grote, Swartz, Geibel, Zuckoff, Houck and Frank47,Reference Kanter, Santiago-Rivera, Rusch, Busch and West48 Other outcomes were insight, Reference Rathod, Phiri, Harris, Underwood, Thagadur and Padmanabi41 impairment, Reference Wissow, Gadomski, Roter, Larson, Brown and Zachary42 functioning, Reference Afuwape, Craig, Harris, Clarke, Flood and Olajide39,Reference Grote, Swartz, Geibel, Zuckoff, Houck and Frank47 adherence, Reference Rathod, Phiri, Harris, Underwood, Thagadur and Padmanabi41,Reference Chong and Moreno45–Reference Lambert and Lambert49 patient experience, Reference Afuwape, Craig, Harris, Clarke, Flood and Olajide39 perceived helpfulness, Reference Alvidrez, Snowden, Rao and Boccellari46 patient satisfaction, Reference Chong and Moreno45,Reference Lambert and Lambert49 knowledge and attitude towards treatment Reference Acosta40 and perceived stigma. Reference Alvidrez, Snowden, Rao and Boccellari46 One study included working alliance as an outcome, Reference Chong and Moreno45 otherwise, the relationship between the intervention and improved therapeutic communications were inferred and not direct measures of therapeutic communication.
High-quality trials
A study of African and Black Caribbean patients with depression and anxiety, compared treatment as usual with flexible outreach from psychiatric services into community venues to encourage use of cognitive–behavioural therapy (CBT). The CBT was supplemented with ethnically matched therapists alongside advocacy, mentoring and rapid access. The intervention led to reductions in the General Health Questionnaire (GHQ-28) scores 3 months after the intervention (calculated effect size d = −0.69, 95% CI −1.31 to 0.11, in favour of treatment; mean difference of reduction from baseline, unadjusted 4.19, 95% CI −2.19 to 10.5, P = 0.49; adjusted for age, past psychiatric history and baseline score 7.76, 95% CI 0.86 to 14.65, P = 0.03). Reference Afuwape, Craig, Harris, Clarke, Flood and Olajide39 There were also gains for the Short form (SF-12) mental component measure (adjusted mean difference −11.93, 95% CI −21.99 to −1.88, P = 0.02).
Compared with usual treatment, Rathod et al showed that culturally adapted CBT reduced symptoms (on the Comprehensive Psychopathological Ratings Scale) for Black British, African Caribbean and South Asian Muslim patients with schizophrenia (post-treatment calculated effect size d = −0.18, 95% CI −0.94 to 0.58; 6 months follow-up, calculated effect size d = 0.15, 95% CI −0.57 to 0.86; unadjusted mean difference of reduction from baseline 11.31, 95% CI 0.14 to 22.49, P = 0.05; adjusted mean difference from baseline 9.53, 95% CI 1.85 to 20.91, P = 0.01). Reference Rathod, Phiri, Harris, Underwood, Thagadur and Padmanabi41 At 6 months follow-up, benefit was only seen for depressive symptoms (mean difference of reduction from baseline interval 5.26, 95% CI 2.92 to 7.60, P<0.001; adjusted mean difference of reduction from baseline 4.24, 95% CI −0.44 to 8.94, P = 0.07).
Wissow et al trained paediatric professionals during three 1 h discussions using video examples of family/provider communication, followed by practise and self-evaluation. Reference Wissow, Gadomski, Roter, Larson, Brown and Zachary42 They recruited Black, Latin–American and other ethnicities in the USA. Parental symptoms on the GHQ diminished in the intervention group (reported effect size d = (1.7/5.4) = 0.31, mean difference −1.7, 95% CI −0.32 to −0.11) and children from minority ethnic groups had less impairment at 6-month follow-up (score reduction of Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ) by 0.91, 95% CI −1.8 to −0.01, P = 0.05). In subgroup analysis this was sustained only for Black children (mean difference SDQ score −1.1, 95% CI −2.0 to −0.24; effect size d = (1.1/2.5) = 0.44).
Medium-quality trials
There were two RCTs of culturally adapted CBT compared with treatment as usual, for treatment-resistant post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and panic attacks in Vietnamese and Cambodian refugees in the USA. Reference Hinton, Chhean, Pich, Safren, Hofmann and Pollack43,Reference Hinton, Pham, Tran, Safren, Otto and Pollack44 Adapted CBT led to significantly fewer anxiety symptoms at the end of the treatment of Vietnamese and Cambodian refugees (Anxiety Sensitivity Index, d = −4.3, 95% CI −6.32 to −2.22, and −3.78, 95% CI −4.82 to 2.75, respectively). Improvement was also noted for post-traumatic symptoms measured on the Harvard Trauma Questionnaire (Vietnamese patients: calculated d = −2.4, 95% CI −3.88 to −0.92), the Clinician Administered PTSD severity scale (Cambodian patients: calculated d = −2.17, 95% CI −2.95 to−1.39), and on the Hopkins Symptoms Checklist anxiety subscale (Vietnamese patients: calculated d = −2.21, 95% CI −3.64 to −0.77) and depression subscale (Vietnamese patients: calculated d = −1.99, 95% CI −3.38 to −0.61). Anxiety and depression symptoms improved for Cambodians on the Symptom Checklist-90 scale (calculated d = −2.8, 95% CI −3.68 to −1.94). The original paper did not present confidence intervals, nor effect sizes for follow-up assessments that showed less difference and sometimes no differences. Culturally shaped symptoms of headache and panic also improved.
A randomised pilot study of a multicomponent intervention screened for depression in African American and White pregnant women in antenatal services. Reference Grote, Swartz, Geibel, Zuckoff, Houck and Frank47 The intervention elements were motivational and ethnographic interviewing to empower women to seek access to interpersonal therapy for depression. Reference Grote, Swartz, Geibel, Zuckoff, Houck and Frank47 These methods of clinical assessment allowed patients' cultures, identity and shared priorities to be the focus of engagement before offering therapy, choices and information. Those receiving the intervention had less severe depressive symptoms at 3 and 6 months after the baseline (Beck Depression Inventory (BDI): reported effect size of treatment and time interaction: Cohen's d = 0.33 and 0.47, respectively; Edinburgh Postnatal Depression screening tool: Cohen's h = 0.71 and 0.89, respectively; Beck Anxiety Inventory Cohen's d = 0.27 and 0.24, respectively; and on an outcome of ‘no longer met diagnostic criteria for depression’: Cohen's h = 0.96 and 1.22, respectively; social and leisure functions: 0.26 and 0.46, respectively; confidence intervals not reported, and Cohen's h calculated from χ2).
A pilot randomised trial of a psychoeducational leaflet for older African Americans who were referred to out-patient psychotherapy had no effect on symptoms, attendance or stigma. Reference Alvidrez, Snowden, Rao and Boccellari46 Those with high perceived need and those with the most uncertainty about treatment had lower levels of stigma following the intervention. In contrast, those with low perceived treatment need and low uncertainty about treatment had lower stigma scores after receiving the usual information sheet (data not reported to calculate interaction effects).
A study of psychoeducation for Chinese Americans with chronic mental disorders offered some lessons for UK Chinese populations. Reference Tom50 This randomised study showed improved knowledge (calculated d = 0.83, 95% CI −0.01 to 1.66) about ‘Western concepts’ of mental disorder, treatment and professional roles following a psychoeducation intervention, but there was no impact on stigma, satisfaction with services or motivation. Younger and more educated people were more likely to show improvements in knowledge.
A pre-therapy trial used audiovisual instructions to prepare low-income, Black, Hispanic and White psychiatric out-patients to enter therapy. Reference Acosta40 This provided information about generic services. The intervention led to greater knowledge and more positive attitudes about therapy (reported analysis of variance: patient orientation, ethnicity, gender: F(1,149) = 9.44, P<0.01; n values not available for calculation of effect sizes). Reference Acosta40
In a feasibility trial of telepsychiatry, low-income Hispanic patients in primary care were ethnically matched with psychiatrists. Reference Chong and Moreno45 Attendance and symptoms were unaffected, but there were improvements in working alliance (intervention calculated d = 0.99, 95% CI 0.63–1.36; follow-up d = 1.64, 95% CI 1.25–2.05; intervention and follow-up interaction not significant) and in satisfaction (calculated effect size for interaction between follow-up time and intervention: d = 0.58, 95% CI 0.23–0.93). There was greater adherence with antidepressants (d = 0.35, 95% CI 0–0.69) but no effect on the number of unproductive days because of depression. More patients using telepsychiatry were willing to pay for care.
Poorer-quality trials
Lambert & Lambert prepared immigrants for a future psychotherapy in treatment centres in Hawaii. Reference Lambert and Lambert49 The patients receiving the intervention were more satisfied on several dimensions (for example experiencing change, calculated d = 1.52, 95% CI 0.53–2.52), recognising therapists' integrity, warmth and respect (calculated d = 1.01, 95% CI 0.08–1.95), attended a greater proportion of the total number of sessions offered (calculated d = 1.07, 95% CI 0.26–1.88) and dropping out less often (calculated d = 0.75, 95% CI 0.01–1.49).
Kanter et al conducted a pilot trial of a culturally and linguistically adapted version of CBT, and instigated behaviour change as a driver of emotional change (called behavioural activation) for Latin–American patients attending a bilingual clinic in USA. The intervention was to be applied during the course of the therapy. Reference Kanter, Santiago-Rivera, Rusch, Busch and West48 There was a significant decrease of depression severity (BDI and Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression; reported d = 1.07, d= 1.43, respectively).
Non-randomised designs
The outcome measures used in the non-randomised designs included a mixture of standardised instruments, evaluation questionnaires, evaluative statements and narrative findings (online Tables DS3 and DS4 shows the samples and designs; Table DS5 shows the intervention components).
Of two non-randomised and comparative observational studies, Reference Kohn, Oden, Muñoz, Robinson and Leavitt51,Reference Alvidrez, Arean and Stewart52 one involved enhancing CBT by improving the terminology and the manual content to address religion, identity, relationships and family values of African American women who were on low incomes and with depression. Reference Kohn, Oden, Muñoz, Robinson and Leavitt51 This produced a mean reduction of 12.5 points on the BDI for the adapted CBT group compared with 5.9 points for the usual unadapted CBT comparison group (no standard deviations were presented, so effect sizes were not calculated). The second non-randomised and comparative observational study included an intervention for older African American medical patients that aimed to promote adherence to a psychotherapy treatment through the use of peer-based psychoeducation before therapy. Reference Alvidrez, Arean and Stewart52 When compared with a historical comparison group, no differences were seen in the total number or the proportion of total number of sessions that were attended following intervention. And if two historical controls were removed as they had attended therapy in a previous year, there was a significant effect on the mean number of sessions attended (d = 0.8, 95% CI 0.30–1.30).
Three studies of consecutive patients examined peer-based family psychoeducation in Chinese and Tamil patients recruited from an assertive outreach team, Reference Chow, Law, Andermann, Yang, Leszcz and Wong53 and referrals from in-patient and out-patient community psychiatric services to specialist cultural consultation services (one in Canada and one in the UK) in order to elicit illness narratives to aid decision-making. Reference Kirmayer, Groleau, Guzder, Blake and Jarvis8,Reference Palinski, Owiti, Ascoli, De Jongh, Archer and Staples54 The family intervention led to more accepting attitudes towards patients (mean after 76.3 (s.d. = 14.72); mean before 64.2 (s.d. = 13.9), P = 0.01), and trends towards less stress and perceived burden alongside better mental health. The two cultural consultation studies were exploratory and demonstrated gains in knowledge and changes in clinical management for patients but no change in patient-reported outcomes (Table DS4).
There were two case studies of successful cultural adaptation of treatment. One reported enhancements of existing therapies in terms of content and attention to beliefs for trauma symptoms among Turkish patients; Reference Schouler-Ocak, Reiske, Rapp and Heinz57 and the other assessed culturally determined health beliefs (explanatory models) in Bangladeshi patients. Reference Bhui and Bhugra7
There were two qualitative studies that also included evaluative single case studies. Grote et al assessed an evolving model of ethnographic and motivational interviewing using qualitative interviews with African American women with a low-income. This showed positive findings, but the main evaluation was in the form of a single case study, Reference Grote, Zuckoff, Swartz, Blesdoe and Geibel56 which was then used to inform a trial that is also reported in this review. Reference Grote, Swartz, Geibel, Zuckoff, Houck and Frank47 Chu et al included qualitative focus groups to iteratively adapt problem-solving therapy for older Chinese adults, and this was proposed to be of value using a single case study. Reference Chu, Huynh and Arean55
Thematic analysis of interventions
The components of effective interventions were identified and contrasted across the studies using thematic analysis (Table 2). These also help to understand the elements of cultural adaptations, which were similar across randomised and non-randomised studies. Effective interventions in general included efforts to outreach to the wider community and social systems beyond hospital settings; an important aim of effective interventions was to engage or empower by increasing professional understanding of patients' belief systems about illness, either through formal training or through adapting the content and/or structure of treatment to accommodate ethnic and cultural difference. Compared with non-randomised studies, randomised studies were more likely to target multiple ethnic groups (2/10 and 5/12 respectively) and to focus on accessibility of treatment for patients (1/10 v. 4/12).
TABLE 2 Components of interventions emerging from thematic analysis
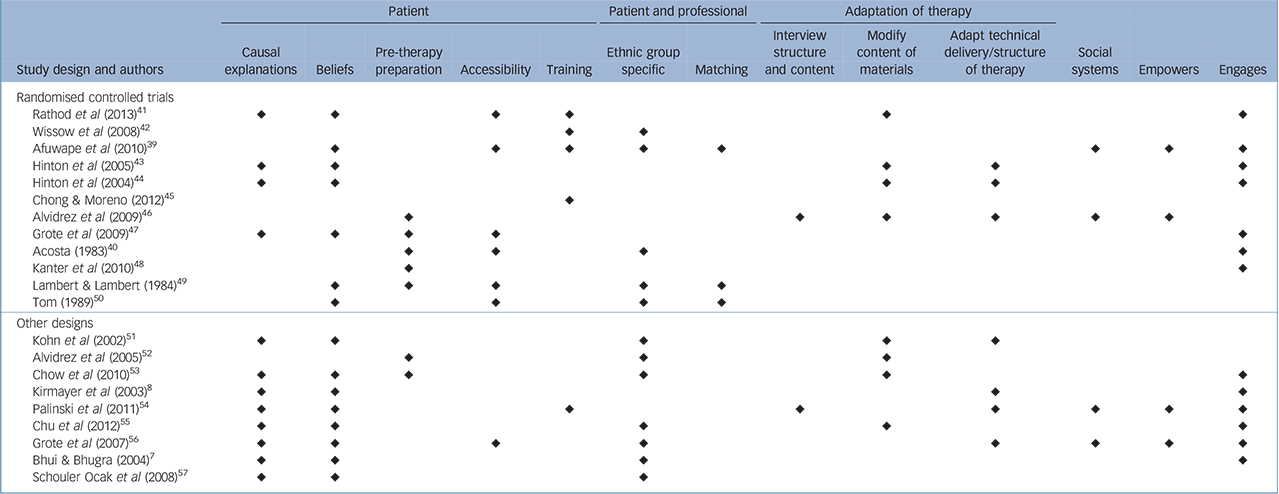
| Patient | Patient and professional | Adaptation of therapy | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study design and authors | Causal explanations |
Beliefs | Pre-therapy preparation |
Accessibility | Training | Ethnic group specific |
Matching | Interview structure and content |
Modify content of materials |
Adapt technical delivery/structure of therapy |
Social systems |
Empowers | Engages |
| Randomised controlled trials | |||||||||||||
| Rathod et al (2013) Reference Rathod, Phiri, Harris, Underwood, Thagadur and Padmanabi41 | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | |||||||
| Wissow et al (2008) Reference Wissow, Gadomski, Roter, Larson, Brown and Zachary42 | ♦ | ♦ | |||||||||||
| Afuwape et al (2010) Reference Afuwape, Craig, Harris, Clarke, Flood and Olajide39 | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | |||||
| Hinton et al (2005) Reference Hinton, Chhean, Pich, Safren, Hofmann and Pollack43 | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ||||||||
| Hinton et al (2004) Reference Hinton, Pham, Tran, Safren, Otto and Pollack44 | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ||||||||
| Chong & Moreno (2012) Reference Chong and Moreno45 | ♦ | ||||||||||||
| Alvidrez et al (2009) Reference Alvidrez, Snowden, Rao and Boccellari46 | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | |||||||
| Grote et al (2009) Reference Grote, Swartz, Geibel, Zuckoff, Houck and Frank47 | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ||||||||
| Acosta (1983) Reference Acosta40 | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | |||||||||
| Kanter et al (2010) Reference Kanter, Santiago-Rivera, Rusch, Busch and West48 | ♦ | ♦ | |||||||||||
| Lambert & Lambert (1984) Reference Lambert and Lambert49 | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ||||||||
| Tom (1989) Reference Tom50 | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | |||||||||
| Other designs | |||||||||||||
| Kohn et al (2002) Reference Kohn, Oden, Muñoz, Robinson and Leavitt51 | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ||||||||
| Alvidrez et al (2005) Reference Alvidrez, Arean and Stewart52 | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ||||||||||
| Chow et al (2010) Reference Chow, Law, Andermann, Yang, Leszcz and Wong53 | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | |||||||
| Kirmayer et al (2003) Reference Kirmayer, Groleau, Guzder, Blake and Jarvis8 | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | |||||||||
| Palinski et al (2011) Reference Palinski, Owiti, Ascoli, De Jongh, Archer and Staples54 | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | |||||
| Chu et al (2012) Reference Chu, Huynh and Arean55 | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ||||||||
| Grote et al (2007) Reference Grote, Zuckoff, Swartz, Blesdoe and Geibel56 | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | |||||
| Bhui & Bhugra (2004) Reference Bhui and Bhugra7 | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | |||||||||
| Schouler Ocak et al (2008) Reference Schouler-Ocak, Reiske, Rapp and Heinz57 | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ | ||||||||||
Patient and carer views
There was less support for approaches that provided ‘briefing’ or training in ‘how to be a patient’ (online Table DS5). Somewhat unexpectedly, the use of community workers providing advocacy and stepped-care (the second intervention in online Table DS5), despite attention to practical needs such as entitlement to benefits, was not well regarded. Members of the group felt stepped-care, gradually moving from community to more specialist hospital services, was overcomplicated and might lead to problems in communication between different professionals.
Discussion
This review identified several types of effective interventions evaluated in trials, including adapted cognitive–behavioural treatments, Reference Rathod, Phiri, Harris, Underwood, Thagadur and Padmanabi41,Reference Hinton, Chhean, Pich, Safren, Hofmann and Pollack43,Reference Hinton, Pham, Tran, Safren, Otto and Pollack44 adapted psychotherapies more generally, Reference Afuwape, Craig, Harris, Clarke, Flood and Olajide39,Reference Grote, Swartz, Geibel, Zuckoff, Houck and Frank47,Reference Kanter, Santiago-Rivera, Rusch, Busch and West48 complex interventions that engage with social systems (such as community groups) and stepped-care, Reference Afuwape, Craig, Harris, Clarke, Flood and Olajide39 interviewing techniques such as ethnographic and motivational interviewing, Reference Grote, Swartz, Geibel, Zuckoff, Houck and Frank47 behavioural activation within an adapted cognitive–behavioural paradigm, Reference Kanter, Santiago-Rivera, Rusch, Busch and West48 information and training for patients to make best use of their services and better use of encounters with professionals, Reference Acosta40,Reference Lambert and Lambert49 and a telepsychiatry intervention. Reference Chong and Moreno45
Adapted CBT
Adapted CBT for several ethnic groups Reference Rathod, Phiri, Harris, Underwood, Thagadur and Padmanabi41 worked as well as CBT adapted for a single ethnic group. Reference Hinton, Pham, Tran, Safren, Otto and Pollack44 Patients and carers reviewing the evidence were supportive of these interventions. Importantly, the methods of adaptation paid attention to technical, theoretical, philosophical and practical aspects. Reference Tseng25 These adapted interventions were promising as they showed benefit in terms of both symptoms and patient-reported outcomes, and were evolved by including culturally embedded styles of communications about distress within the CBT manual.
Complex interventions
Two trials evaluated complex interventions. Grote et al used ethnographic and motivational interviewing to empower pregnant African American single women with depression. Reference Grote, Swartz, Geibel, Zuckoff, Houck and Frank47 One of the key components of this intervention was the emphasis on empowerment through an understanding of personal stories before offering specialist interventions. This was similar to another complex intervention (Afuwape et al) Reference Afuwape, Craig, Harris, Clarke, Flood and Olajide39 offering a stepped-care model of engaging in social venues and then offering an adapted CBT intervention for Black African, Black Caribbean and Black British people living in South London. Both of these were effective at reducing symptoms, yet a consultative panel of patients and carers favoured the USA intervention, because of its emphasis on personal stories and empowering interviews, rather than a stepped-care to access CBT. The stepped-care approach was perceived to be too difficult to negotiate because several professionals at different stages of care risked a failure of communication between them. Reference Franx, Oud, de Lange, Wensing and Grol58
Training, education, communications skills
There was one study of a specialist psychiatric service that provided outreach into paediatric services. Reference Wissow, Gadomski, Roter, Larson, Brown and Zachary42 This led to less impairment in Black compared with White children and fewer parental symptoms overall. Of the two other trials that included an educational intervention, both included preparing patients for psychotherapy by education using written and audiovisual materials. Reference Acosta40,Reference Lambert and Lambert49 The first of these, a poor-quality study, was associated with higher premature drop-out, but more satisfaction in the intervention group and improvements in their expectations of what therapy might offer. The second, a medium-quality study, informed patients' about psychotherapy and improved attitudes so they expected more from therapy. Although less favoured by patients and carers, these preparatory interventions seem attractive to practitioners as a way of enhancing the benefit of existing interventions rather than developing new ones.
Despite the body of literature on cultural competence of professionals as a key way of improving health outcomes and communication between BME patients and professionals, Reference Bhui, Warfa, Edonya, McKenzie and Bhugra21 none of the trials that entered the review tested a specific model of cultural competence. Cultural competence is a concept with a broad framework, so there were examples of interventions that fell under this rubric but differed in their elements and proposed mechanism. Future research might select specific components of interventions from those listed in Table 2, and test them either individually or in combinations. The list might also be valuable to assess against new interventions, and understand potential mechanisms of effect.
One randomised study of telepsychiatry where both patients and psychiatrists were from Hispanic minority groups living in the USA, Reference Chong and Moreno45 showed greater adherence to antidepressants, and improved the working alliance and satisfaction compared with the treatment as usual group. Patients were willing to pay more for this intervention, which suggests its convenience was valued, but the relative benefits of ethnic matching and a telepsychiatry intervention were not disentangled. Telepsychiatry can facilitate provision of services to geographically remote or scattered populations in need of professionals with a similar ethnic background and language skills. In contrast to this study, many studies of ethnic matching are often observational and show an association between ethnic matching and outcomes in administrative data-sets rather than testing an intervention in a trial. Reference Cabral and Smith59,Reference Maramba and Hall60 The wider issue of using e-technology and social media in order to engage and deliver interventions was not investigated in the studies that entered the review. There is an emerging evidence base on e-interventions for mental health promotion and the treatment of mental illnesses, in remote and varied populations who may be hard to reach, and across age groups. Reference Lillevoll, Vangberg, Griffiths, Waterloo and Eisemann61–Reference Blankers, Nabitz, Smit, Koeter and Schippers65 More RCTs are needed among ethnic minorities and culturally diverse populations.
Other study designs
The non-randomised studies assessed psychoeducation, ways of adapting psychotherapies, including a family-oriented intervention, ethnographic interviewing and case studies concerning ethnographic principles. Given that these interventions were at an earlier stage of development, it is reasonable to suggest that their components, especially their ethnographic elements, may prove suitable for testing in trials. Reference Bhui and Bhugra7,Reference Kirmayer, Groleau, Guzder, Blake and Jarvis8,Reference Palinski, Owiti, Ascoli, De Jongh, Archer and Staples54,Reference Grote, Zuckoff, Swartz, Blesdoe and Geibel56,Reference Schouler-Ocak, Reiske, Rapp and Heinz57 Two of these studies showed how to involve the community as a resource to help adapt interventions. Reference Chow, Law, Andermann, Yang, Leszcz and Wong53,Reference Chu, Huynh and Arean55 Many excluded papers presented accounts of the cultural formulation (as described in the DSM-IV, 66 and now in modified form in DSM-5 67 ), and its use as part of the formal psychiatric assessment process, yet none evaluated the cultural formulation, or offered a sufficiently critical evaluative component for these studies to enter the review. Reference Baarnhielm68,Reference Fortuna, Porche and Alegria69
Intervention elements
Many elements of the interventions were not dissimilar when the trials and non-randomised designs were compared (see online Tables DS1 and DS3). The patient and carer rankings of interventions was instructive, in that these added an additional source of valuable information to the synthesis, alongside the evidence with respect to effectiveness, and methodological strengths and weaknesses of each study. Their opinions were by no means unanimous but still shed light on which interventions might not suit all patients and why. To some extent the patient and carer perspectives also combated the academically focused research questions and setting. Patients and carers emphasised the personal experience and journey, giving a clear indication that the way professionals communicate and interact are as important as the intervention itself. Therefore, the interventions that encouraged understanding of patient beliefs and causal explanations about illness may not always lead to a direct symptomatic benefit, but nonetheless seem to be important in a recovery-oriented approach. In particular, ethnography, motivational interviewing, engaging with social systems, before and during therapy, and professional-centred interventions seem to warrant further research of their impact on positive professional–patient communication.
Strengths and weaknesses
The remit of this systematic review was specific, namely communications between professionals in psychiatric services and BME-origin patients using these services. However, the findings included multiple interventions with diverse outcomes, and diverse study design.
The effect of improved therapeutic communication was evaluated by assessing various outcomes such as symptoms and adherence. The quality scores were a helpful summary of a complex set of strengths and weaknesses, each of which was taken into consideration alongside the views of the patients and carers in drawing our overall conclusions. The majority of studies assessed entry into psychotherapy interventions rather than routine psychiatric care.
Only four studies were from the UK. Reference Bhui and Bhugra7,Reference Afuwape, Craig, Harris, Clarke, Flood and Olajide39,Reference Rathod, Phiri, Harris, Underwood, Thagadur and Padmanabi41,Reference Palinski, Owiti, Ascoli, De Jongh, Archer and Staples54 The remaining 17 were from the USA, suggesting more research is needed in the UK and other countries within and outwith Europe. The review found only two studies offering weak economic evidence based on health and social care costs over a 3-month follow-up period. Reference Afuwape, Craig, Harris, Clarke, Flood and Olajide39,Reference Palinski, Owiti, Ascoli, De Jongh, Archer and Staples54 Palinksi et al published more detailed costs of accident and emergency attendance, and consultations with nurses and doctors. Reference Palinski, Owiti, Ascoli, De Jongh, Archer and Staples54 Both studies can be described as exploratory rather than definitive, partly because of their small sample sizes, short follow-up periods, and recruitment from a single locality, but both studies offer encouraging economic evidence. There is a need for more economic research.
In conclusion, culturally adapted psychotherapies and ethnographic and motivational assessment leading to psychotherapy were effective and preferred by patients and carers. Further trials are needed from outside of the UK and USA, including studies of routine psychiatric practices, economic evaluations and some testing of the effectiveness of specific elements of interventions that were identified.
Funding
The study was funded by the National Institute of Health Research – Health Technology Assessment: evidence synthesis (10/141/02).
Acknowledgements
The Afiya Trust for organising the patient and public involvement (PPI) group, Patrick Vernon, former Chief Executive Officer of Afiya; Rampaul Chamba, former trustee at Afiya and chair of the PPI group; Sola Afuape, Chair of Afiya, and the service users and members of the public who commented, returned survey responses and participated in discussions and critical feedback over the lifetime of the project. Diana Clay (information scientist at Warwick Medical School) for constructing, testing and running the searches of the peer-reviewed literature; Josh Elliott (research assistant, Institute of Digital Healthcare, University of Warwick) for undertaking the grey literature and web searches, and running the survey of experts






eLetters
No eLetters have been published for this article.