Diagnosis is essential in clinical practice, research, training and public health. Definitions for psychiatric diagnoses are derived from expert opinion rather than the biological basis of the disorder. The modest knowledge base regarding the causation of disease has hindered the use of aetiological factors in psychiatric classification systems. The current classifications (World Health Organization, 1992; American Psychiatric Association, 2000) were designed to achieve high interrater reliability of diagnostic assessment. It is widely believed that if future editions of the DSM and the ICD are to be a significant improvement on their predecessors, the validity of the diagnostic concepts they include will have to be enhanced (Reference Kendell and JablenskyKendell & Jablensky, 2003). Follow-up studies including evidence of diagnostic stability and diagnostic consistency over time have traditionally been proposed to test the validity of psychiatric diagnoses (Reference Robins and GuzeRobins & Guze, 1970; Reference KendlerKendler, 1980; Reference AndreasenAndreasen, 1995). However, several authors have noted that as longitudinal data become available, significant fluctuations in diagnostic stability and changes in clinical presentation are seen (Reference KrishnanKrishnan, 2005).
The aim of our study was to evaluate the long-term stability of the most prevalent chronic psychiatric diagnoses according to ICD–10 in a range of clinical settings.
METHODS
Participants
In total 34 368 patients received psychiatric care in the catchment area of Fundacion Jimenez Diaz General Hospital, Madrid, between 1 January 1992 and 31 December 2004. This hospital is part of the Spanish national health services and provides free medical coverage to a catchment area of 280 000 people. There were 449 317 psychiatric consultations in a variety of clinical settings, including visits to out-patient psychiatric facilities (438 622), emergency visits (9101) and admissions to the psychiatric brief hospitalisation unit (1594). The current study is based on 10 025 patients aged 18 years and over who were assessed on at least ten occasions during the period studied. These patients had 360 899 psychiatric consultations, including visits to out-patient psychiatric facilities (355 166), psychiatric emergency visits (4628) and admissions to the psychiatric brief hospitalisation unit (1105).
Individual service users are reliably identified in the database used for our analyses because each patient is given an identifying number (a numeric code is used to ensure patient anonymity), which remains the same throughout all contacts with psychiatric services within the study area. To ensure that no patient had been assigned more than one identifier, we reviewed all the cases in the database and removed any duplicates we found. We defined duplicates as ‘patients with identical first name, family name, gender and year of birth’; ‘patients with identical first name, family name, gender and street address’, or ‘patients with identical first name, family name, gender and hospital/ambulatory record number’. We deleted any cases with significant suspicion of duplication.
Settings
Participants (n=10 025) were assessed in three different clinical settings: in-patient unit (psychiatric brief hospitalisation unit), 2000–2004 (n=546); psychiatric emergency room, 2000–2004 (n=1408); and out-patient psychiatric facilities (mental health care centres) within the catchment area of the Fundacion Jimenez Diaz General Hospital, 1992–2004 (n=10 016).
Diagnostic procedures
Procedure during ambulatory visits
Since 1986 public mental health centres within the province of Madrid have had to record all ambulatory visits in a regional registry, the Registro Acumulativo de Casos de la Comunidad de Madrid. All diagnoses in this registry must be coded according to the ICD–9 (World Health Organization, 1978). Since 1992 diagnoses have been assigned according to ICD–10 (World Health Organization, 1992) criteria and recorded with the appropriate ICD–9 coding numbers; ICD–10 codes were converted to ICD–9 codes using the guidelines published by the World Health Organization (Organizacion Mundial de la Salud, 1993). The psychiatrists at each mental health centre recorded one or two diagnoses per patient during each ambulatory visit. Diagnoses were assigned after reviewing all available information, including data from medical records and clinical interviews with the patient and relatives.
Procedure during emergency visits
The emergency diagnoses were taken from the emergency medical records. Emergency diagnoses were assigned by clinical psychiatrists after reviewing all available information, including data from clinical interviews with the patient and relatives.
Procedure during admissions to the in-patient unit
Clinical diagnoses during admissions are the result of an intensive diagnostic and treatment process by physicians with specialty training in psychiatry, including data from medical records, other research assessments and clinical interviews. The psychiatrists who assigned the clinical diagnoses were not aware of the study in process.
Diagnostic groups included in analysis
Among all chronic psychiatric diagnoses, we selected those disorders assigned to more than 500 patients in our sample (prevalence higher than 5%). According to data from naturalistic studies like ours, the frequency and use of the ICD–10 two-digit, three-digit and four-digit diagnostic categories show significant variations. Some categories are not used at all, and others represent less than 0.1% of the samples studied (Reference Mussigbrodt, Michels and MalchowMussigbrodt et al, 2000). In the latter study of a sample of 33 857 treated cases from 19 departments of psychiatry in ten different countries, ‘on a four-character level (Fxx.x), the ten most often used diagnostic categories represented 40% of all main diagnoses, and 70% on a three-character level (Fxx.-)’ (Reference Mussigbrodt, Michels and MalchowMussigbrodt et al, 2000). The diagnoses analysed here (with ICD–10 codes) are:
-
(a) schizophrenia, schizotypal and delusional disorders (F20–29), including individual diagnoses of schizophrenia (F20), paranoid schizophrenia (F20.0), residual schizophrenia (F20.5) and persistent delusional disorders (F22);
-
(b) mood (affective) disorders (F30–39), including individual diagnoses of bipolar affective disorder (F31), bipolar affective disorder, current episode mild or moderate depression (F31.3), recurrent depressive disorder (F33), persistent mood (affective) disorders (F34), and dysthymia (F34.1);
-
(c) obsessive–compulsive disorder (F42);
-
(d) eating disorders (F50);
-
(e) disorders of adult personality and behaviour (F60–69), including the individual diagnoses of specific personality disorders (F60) and other specific personality disorders (F60.8).
Data extraction and analysis
Diagnostic stability through all the evaluations is calculated according to Schwartz et al (Reference Schwartz, Fennig and Tanenberg-Karant2000). Three measures of stability are presented for each diagnosis. The first, ‘prospective consistency’, is the proportion of individuals in a category at the first evaluation who retain the same diagnosis at their last evaluation. This would correspond to positive predictive value if the last diagnosis were the gold standard. The second measure, retrospective consistency, is the proportion of individuals with a diagnosis assigned at the last evaluation who had received the same diagnosis at the first evaluation; this is conceptually similar to sensitivity. The third measure is the proportion of patients who received the same diagnosis in at least 75% of the evaluations. The agreement between diagnoses at the first and the last evaluations was calculated by the kappa coefficient, which measures the agreement correcting the effect of chance.
Using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences, version 13.0 for Windows, we performed four different analyses: three separate analyses for each clinical setting (psychiatric emergencies, out-patient visits and hospitalisations) to control for influences of the setting on the stability of diagnoses; and a fourth analysis of the combined data from the three clinical settings to reflect the evolution of diagnoses through the clinical process.
RESULTS
The socio-demographic characteristics of the sample are presented in Table 1.
Table 1 Socio-demographic characteristics of the sample (n=10 025)

| Variable | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| Male | 3752 (37.4) |
| Female | 6186 (61.7) |
| Transsexual | 6 (0.1) |
| Missing data | 81 (0.8) |
| Marital status | |
| Single | 5281 (52.7) |
| Married | 2923 (29.2) |
| Divorced | 320 (3.2) |
| Widow | 620 (6.2) |
| Missing data | 881 (8.8) |
| Education | |
| Illiterate | 88 (0.9) |
| Never gone to school | 533 (5.3) |
| Primary school | 2401 (24.0) |
| High school | 3617 (36.1) |
| University | 2491 (24.8) |
| Other education | 49 (0.5) |
| Missing data | 846 (8.4) |
| Accommodation | |
| Alone | 1907 (19.0) |
| With partner | 3352 (33.4) |
| With parents | 2755 (27.4) |
| With children | 675 (6.7) |
| With other family members | 530 (5.3) |
| In an institution | 86 (0.9) |
| Adopted | 280 (2.8) |
| Missing data | 440 (4.4) |
| Current working status | |
| Military service | 14 (0.1) |
| Employed | 3617 (36.1) |
| Looking for first job | 92 (0.9) |
| Unemployed | 1221 (12.2) |
| Retired | 1133 (11.3) |
| Student | 1243 (12.4) |
| Homemaker | 1058 (10.6) |
| Transient disability | 425 (4.2) |
| Permanent disability | 186 (1.9) |
| Missing data | 1036 (10.3) |
Stability of diagnoses
Data about the prospective and retrospective consistency of the diagnoses across settings, in the out-patient setting, in the emergency setting and in the in-patient setting are presented in Tables 2, 3, 4, 5 and graphically in a data supplement to the online version of this paper. The percentages of patients who received the same diagnosis in at least 75% of their evaluations, across settings, in the out-patient setting, in the emergency setting and in the in-patient setting are presented in Table 6.
Table 2 Prospective and retrospective consistency of ICD–10 diagnoses across settings (n=10 025)
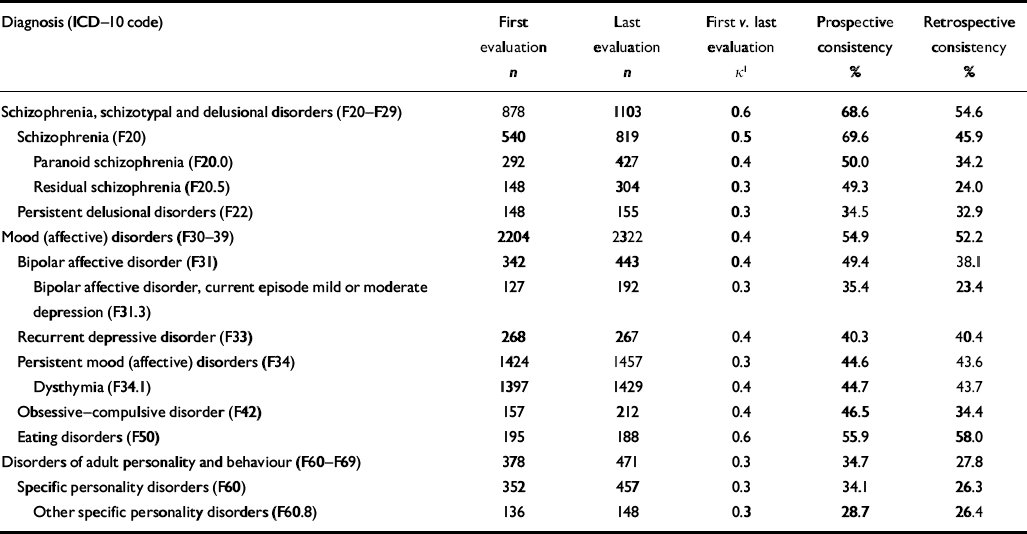
| Diagnosis (ICD–10 code) | First evaluation n | Last evaluation n | First v. last evaluation κ 1 | Prospective consistency % | Retrospective consistency % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schizophrenia, schizotypal and delusional disorders (F20–F29) | 878 | 1103 | 0.6 | 68.6 | 54.6 |
| Schizophrenia (F20) | 540 | 819 | 0.5 | 69.6 | 45.9 |
| Paranoid schizophrenia (F20.0) | 292 | 427 | 0.4 | 50.0 | 34.2 |
| Residual schizophrenia (F20.5) | 148 | 304 | 0.3 | 49.3 | 24.0 |
| Persistent delusional disorders (F22) | 148 | 155 | 0.3 | 34.5 | 32.9 |
| Mood (affective) disorders (F30–39) | 2204 | 2322 | 0.4 | 54.9 | 52.2 |
| Bipolar affective disorder (F31) | 342 | 443 | 0.4 | 49.4 | 38.1 |
| Bipolar affective disorder, current episode mild or moderate depression (F31.3) | 127 | 192 | 0.3 | 35.4 | 23.4 |
| Recurrent depressive disorder (F33) | 268 | 267 | 0.4 | 40.3 | 40.4 |
| Persistent mood (affective) disorders (F34) | 1424 | 1457 | 0.3 | 44.6 | 43.6 |
| Dysthymia (F34.1) | 1397 | 1429 | 0.4 | 44.7 | 43.7 |
| Obsessive–compulsive disorder (F42) | 157 | 212 | 0.4 | 46.5 | 34.4 |
| Eating disorders (F50) | 195 | 188 | 0.6 | 55.9 | 58.0 |
| Disorders of adult personality and behaviour (F60–F69) | 378 | 471 | 0.3 | 34.7 | 27.8 |
| Specific personality disorders (F60) | 352 | 457 | 0.3 | 34.1 | 26.3 |
| Other specific personality disorders (F60.8) | 136 | 148 | 0.3 | 28.7 | 26.4 |
1. All kappa statistics are significant (P<0.001)
Table 3 Prospective and retrospective consistency of ICD–10 diagnoses in the out-patient setting (n=10 016)

| Diagnosis (ICD–10 code) | First evaluation n | Last evaluation n | First v. last evaluation κ 1 | Prospective consistency % | Retrospective consistency % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schizophrenia, schizotypal and delusional disorders (F20–F29) | 875 | 1088 | 0.6 | 68.3 | 55.0 |
| Schizophrenia (F20) | 538 | 809 | 0.5 | 69.1 | 46.0 |
| Paranoid schizophrenia (F20.0) | 290 | 427 | 0.4 | 49.3 | 33.5 |
| Residual schizophrenia (F20.5) | 148 | 304 | 0.3 | 50.7 | 24.7 |
| Persistent delusional disorders (F22) | 148 | 158 | 0.3 | 35.1 | 32.9 |
| Mood (affective) disorders (F30–F39) | 2203 | 2343 | 0.4 | 55.6 | 52.2 |
| Bipolar affective disorder (F31) | 342 | 440 | 0.4 | 50.6 | 39.3 |
| Bipolar affective disorder, current episode mild or moderate depression (F31.3) | 127 | 194 | 0.3 | 35.4 | 23.2 |
| Recurrent depressive disorder (F33) | 268 | 270 | 0.4 | 40.3 | 40.0 |
| Persistent mood (affective) disorders (F34) | 1424 | 1496 | 0.4 | 45.8 | 43.6 |
| Dysthymia (F34.1) | 1397 | 1464 | 0.4 | 45.7 | 43.6 |
| Obsessive–compulsive disorder (F42) | 157 | 213 | 0.4 | 47.1 | 34.7 |
| Eating disorders (F50) | 194 | 189 | 0.6 | 56.2 | 57.7 |
| Disorders of adult personality and behaviour (F60–F69) | 375 | 456 | 0.3 | 35.7 | 29.4 |
| Specific personality disorders (F60) | 351 | 442 | 0.3 | 35.6 | 28.3 |
| Other specific personality disorders (F60.8) | 136 | 156 | 0.3 | 29.4 | 25.6 |
1. All kappa statistics are significant (P<0.001)
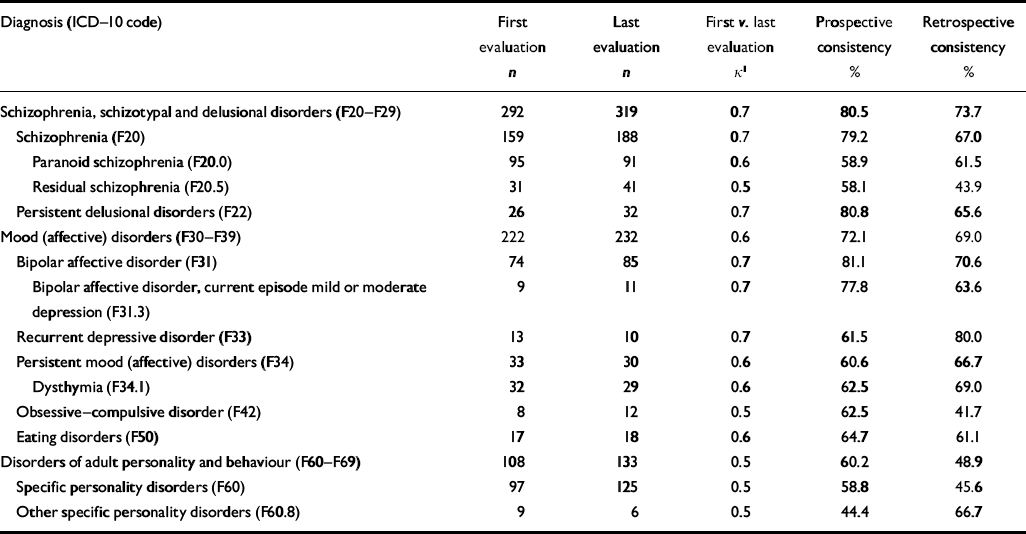
Table 4 Prospective and retrospective consistency of ICD–10 diagnoses in the emergency setting (n=1408)

| Diagnosis (ICD–10 code) | First evaluation n | Last evaluation n | First v. last evaluation κ 1 | Prospective consistency % | Retrospective consistency % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schizophrenia, schizotypal and delusional disorders (F20–F29) | 292 | 319 | 0.7 | 80.5 | 73.7 |
| Schizophrenia (F20) | 159 | 188 | 0.7 | 79.2 | 67.0 |
| Paranoid schizophrenia (F20.0) | 95 | 91 | 0.6 | 58.9 | 61.5 |
| Residual schizophrenia (F20.5) | 31 | 41 | 0.5 | 58.1 | 43.9 |
| Persistent delusional disorders (F22) | 26 | 32 | 0.7 | 80.8 | 65.6 |
| Mood (affective) disorders (F30–F39) | 222 | 232 | 0.6 | 72.1 | 69.0 |
| Bipolar affective disorder (F31) | 74 | 85 | 0.7 | 81.1 | 70.6 |
| Bipolar affective disorder, current episode mild or moderate depression (F31.3) | 9 | 11 | 0.7 | 77.8 | 63.6 |
| Recurrent depressive disorder (F33) | 13 | 10 | 0.7 | 61.5 | 80.0 |
| Persistent mood (affective) disorders (F34) | 33 | 30 | 0.6 | 60.6 | 66.7 |
| Dysthymia (F34.1) | 32 | 29 | 0.6 | 62.5 | 69.0 |
| Obsessive–compulsive disorder (F42) | 8 | 12 | 0.5 | 62.5 | 41.7 |
| Eating disorders (F50) | 17 | 18 | 0.6 | 64.7 | 61.1 |
| Disorders of adult personality and behaviour (F60–F69) | 108 | 133 | 0.5 | 60.2 | 48.9 |
| Specific personality disorders (F60) | 97 | 125 | 0.5 | 58.8 | 45.6 |
| Other specific personality disorders (F60.8) | 9 | 6 | 0.5 | 44.4 | 66.7 |
1. All kappa statistics are significant (P < 0.001)
Table 5 Prospective and retrospective consistency of ICD–10 diagnoses in the in-patient setting (n=546)

| Diagnosis (ICD–10 code) | First evaluation n | Last evaluation n | First v. last evaluation κ 1 | Prospective consistency % | Retrospective consistency % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schizophrenia, schizotypal and delusional disorders (F20–F29) | 206 | 206 | 0.9 | 92.2 | 92.2 |
| Schizophrenia (F20) | 143 | 142 | 0.9 | 90.9 | 91.5 |
| Paranoid schizophrenia (F20.0) | 99 | 91 | 0.9 | 83.8 | 91.2 |
| Residual schizophrenia (F20.5) | 29 | 34 | 0.8 | 89.7 | 76.5 |
| Persistent delusional disorders (F22) | 12 | 10 | 0.8 | 75.0 | 90.0 |
| Mood (affective) disorders (F30–F39) | 143 | 148 | 0.9 | 92.3 | 89.2 |
| Bipolar affective disorder (F31) | 82 | 84 | 0.9 | 91.5 | 89.3 |
| Bipolar affective disorder, current episode mild or moderate depression (F31.3) | 9 | 9 | 0.8 | 77.8 | 77.8 |
| Recurrent depressive disorder (F33) | 3 | 2 | 0.8 | 66.7 | 100.0 |
| Persistent mood (affective) disorders (F34) | 34 | 37 | 0.8 | 82.4 | 75.7 |
| Dysthymia (F34.1) | 33 | 36 | 0.8 | 81.8 | 75.0 |
| Obsessive–compulsive disorder (F42) | 4 | 4 | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Eating disorders (F50) | 10 | 12 | 0.9 | 100.0 | 83.3 |
| Disorders of adult personality and behaviour (F60–F69) | 86 | 113 | 0.8 | 95.3 | 72.6 |
| Specific personality disorders (F60) | 57 | 84 | 0.7 | 93.0 | 63.1 |
| Other specific personality disorders (F60.8) | 0 | 2 | – | – | – |
1. All kappa statistics are significant (P < 0.001)
Table 6 Percentage of patients who received a diagnosis in at least 75% of the evaluations across settings, in the out-patient setting, in the in-patient setting and in the emergency setting
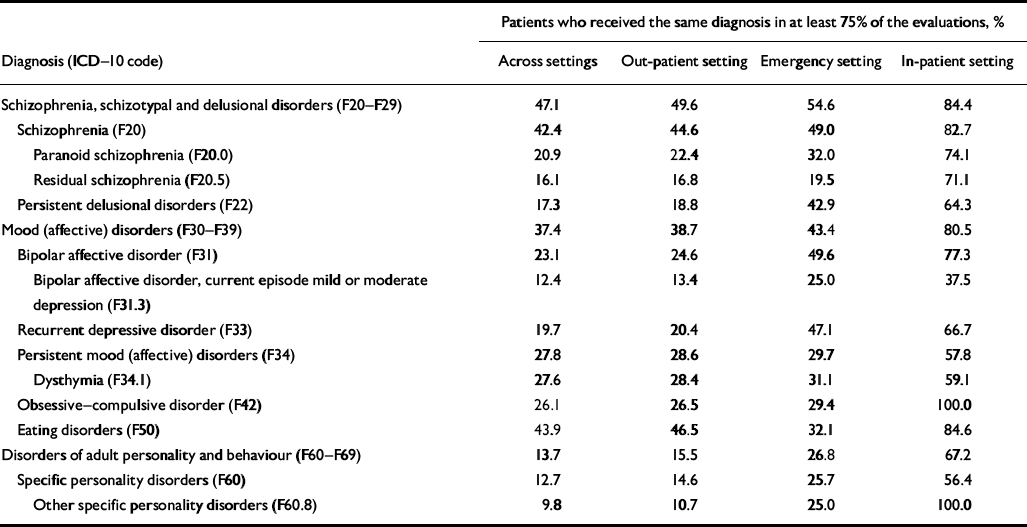
| Patients who received the same diagnosis in at least 75% of the evaluations, % | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnosis (ICD–10 code) | Across settings | Out-patient setting | Emergency setting | In-patient setting | |||
| Schizophrenia, schizotypal and delusional disorders (F20–F29) | 47.1 | 49.6 | 54.6 | 84.4 | |||
| Schizophrenia (F20) | 42.4 | 44.6 | 49.0 | 82.7 | |||
| Paranoid schizophrenia (F20.0) | 20.9 | 22.4 | 32.0 | 74.1 | |||
| Residual schizophrenia (F20.5) | 16.1 | 16.8 | 19.5 | 71.1 | |||
| Persistent delusional disorders (F22) | 17.3 | 18.8 | 42.9 | 64.3 | |||
| Mood (affective) disorders (F30–F39) | 37.4 | 38.7 | 43.4 | 80.5 | |||
| Bipolar affective disorder (F31) | 23.1 | 24.6 | 49.6 | 77.3 | |||
| Bipolar affective disorder, current episode mild or moderate depression (F31.3) | 12.4 | 13.4 | 25.0 | 37.5 | |||
| Recurrent depressive disorder (F33) | 19.7 | 20.4 | 47.1 | 66.7 | |||
| Persistent mood (affective) disorders (F34) | 27.8 | 28.6 | 29.7 | 57.8 | |||
| Dysthymia (F34.1) | 27.6 | 28.4 | 31.1 | 59.1 | |||
| Obsessive–compulsive disorder (F42) | 26.1 | 26.5 | 29.4 | 100.0 | |||
| Eating disorders (F50) | 43.9 | 46.5 | 32.1 | 84.6 | |||
| Disorders of adult personality and behaviour (F60–F69) | 13.7 | 15.5 | 26.8 | 67.2 | |||
| Specific personality disorders (F60) | 12.7 | 14.6 | 25.7 | 56.4 | |||
| Other specific personality disorders (F60.8) | 9.8 | 10.7 | 25.0 | 100.0 | |||
Across clinical settings
Prospective consistency ranged from 28.7% for other specific personality disorders to 69.6% for schizophrenia, (Table 2). The prospective consistency of the three most prevalent diagnoses at first evaluation was 44.7% for dysthymia, 69.6% for schizophrenia and 49.4% for bipolar affective disorder (see Table 2). Retrospective consistency at the last evaluation ranged from 23.4% for bipolar affective disorder, current episode mild or moderate depression, to 58.0% for eating disorders; it was 43.7% for dysthymia, 45.9% for schizophrenia and 38.1% for bipolar affective disorder (see Table 2). The proportion of patients who received the same diagnosis during at least 75% of their evaluations ranged from 9.8% for other specific personality disorders to 47.1% for schizophrenia, schizotypal and delusional disorders see Table 6).
Out-patient setting
Prospective consistency ranged from 29.4% for other specific personality disorders to 69.1% for schizophrenia. The prospective consistency of the three most prevalent specific diagnoses at the first evaluation was 45.7% for dysthymia, 69.1% for schizophrenia and 50.6% for bipolar affective disorder (see Table 3). Retrospective consistency at the last evaluation ranged from 23.2% for bipolar affective disorder, current episode mild or moderate depression, to 57.7% for eating disorders; it was 43.6% for dysthymia, 46.0% for schizophrenia and 39.3% for bipolar affective disorder (see Table 3). The proportion of patients who received the same diagnosis during at least 75% of the evaluations ranged from 10.7% for other specific personality disorders to 49.6% for schizophrenia, schizotypal and delusional disorders (see Table 6).
Emergency department setting
Prospective consistency ranged from 44.4% for other specific personality disorders to 81.1% for bipolar affective disorder. The prospective consistency of the three most prevalent specific diagnoses at the first evaluation was 79.2% for schizophrenia, 81.1% for bipolar affective disorder and 62.5% for dysthymia (see Table 4). Retrospective consistency at the last evaluation ranged from 41.7% for obsessive–compulsive disorder to 80.0% for recurrent depressive disorder; it was 67.0% for schizophrenia, 70.6% for bipolar affective disorder and 69.0% for dysthymia (see Table 4).
The proportion of patients who received the same diagnosis during at least 75% of the evaluations ranged from 19.5% for residual schizophrenia to 54.6% for schizophrenia, schizotypal and delusional disorders (see Table 6).
In-patient setting
Prospective consistency ranged from 66.7% for recurrent depressive disorder to 100.0% for obsessive–compulsive disorder and eating disorders. The prospective consistency of the three most prevalent specific diagnoses at the first evaluation was 90.9% for schizophrenia, 91.5% for bipolar affective disorder and 81.8% for dysthymia (see Table 5). Retrospective consistency at the last evaluation was between 63.1% for specific personality disorders and 100.0% for recurrent depressive disorder and obsessive–compulsive disorder; it was 91.5% for schizophrenia, 89.3% for bipolar affective disorder and 75.0% for dysthymia (see Table 5).
The proportion of patients who received the same diagnosis during at least 75% of the evaluations ranged from 37.5% for bipolar affective disorder, current episode mild or moderate depression, to 100.0% for obsessive–compulsive disorder and other specific personality disorders (see Table 6).
DISCUSSION
The main variable influencing diagnostic stability for the most prevalent chronic psychiatric diagnoses was the clinical setting in which the patients were assessed. The in patient setting showed the highest diagnostic stability, followed by the emergency and out-patient settings. The temporal consistency of psychiatric disorders was lower than that found in other studies.
Strengths and weaknesses of the study
The main strengths of this study are the large, representative sample, the length of follow-up (up to 12 years) and the large number of evaluations. Moreover, although most previous studies focused on one psychiatric diagnosis assessed in a single clinical setting, we assessed the stability of all psychiatric diagnoses naturally presenting in clinical practice. Psychiatric diagnoses were evaluated in three different clinical settings, using the same diagnostic procedure that is used during regular clinical practice. Clinicians who assigned the diagnoses were masked to the study process. Other work has used semi-structured interviews and other diagnostic instruments not used ordinarily in clinical practice. The results of our study may more accurately reflect the real use of diagnostic classifications in psychiatric practice and may be more useful in estimating the clinical utility of current psychiatric classification systems.
Diagnostic changes over time may reflect the evolution of an illness, the emergence of new information or unreliability of measurement (Reference Schwartz, Fennig and Tanenberg-KarantSchwartz et al, 2000). Spitzer et al (Reference Spitzer, Endicott and Robins1978) divided the sources of unreliability that lead to diagnostic disagreement among clinicians into categories (sources of variance): subject variance, occasions variance (e.g. different episodes of bipolar disorder), information variance (e.g. the differences across settings and informants), observation variance (e.g. differences among clinicians) and criterion variance. Our study has limitations that may reflect the influence of these sources of unreliability. The stability of bipolar disorder may be affected by the occasions variance, particularly the diagnostic category of bipolar affective disorder, current episode mild or moderate depression (ICD–10 F31.3). Information and observation variances can be significantly reduced by training clinicians in interviewing techniques and observational skills, and by the use of structured or semi-structured clinical interviews. Because of the naturalistic nature of our research, structured or semi-structured clinical interviews were not used in the study. This might have increased the criterion variance. The clinicians who assigned the diagnoses were not specifically trained to improve interrater reliability, which might have influenced the consistency of the analysed diagnoses. Psychiatrists used different diagnostic classifications to code the diagnoses through-out the study period.
Other research
The stability of chronic psychiatric diagnoses has been evaluated in a number of studies (Reference Tsuang, Woolson and WinokurTsuang et al, 1981; Reference Schwartz, Fennig and Tanenberg-KarantSchwartz et al, 2000; Reference Lieb, Zimmermann and FriisLieb et al, 2002; Reference Shea, Stout and GundersonShea et al, 2002; Reference Mojtabai, Susser and BrometMojtabai et al, 2003; Reference Barkow, Heun and WittchenBarkow et al, 2004; Reference Grilo, Sanislow and GundersonGrilo et al, 2004; Reference Veen, Selten and ScholsVeen et al, 2004; Reference Culverhouse, Bucholz and CroweCulverhouse et al, 2005; Kessing, Reference Kessing2005a ,Reference Kessing b ; Reference McGlashan, Grilo and SanislowMcGlashan et al, 2005; Reference Rufino, Uchida and VilelaRufino et al, 2005; Reference Schimmelmann, Conus and EdwardsSchimmelmann et al, 2005). Most of these studies have focused on one diagnostic cluster, mainly psychoses (schizophrenia spectrum and mood psychoses; Reference Schwartz, Fennig and Tanenberg-KarantSchwartz et al, 2000; Reference Mojtabai, Susser and BrometMojtabai et al, 2003; Reference Veen, Selten and ScholsVeen et al, 2004; Reference KessingKessing, 2005b ; Reference Rufino, Uchida and VilelaRufino et al, 2005; Reference Schimmelmann, Conus and EdwardsSchimmelmann et al, 2005) and personality disorders (Reference Shea, Stout and GundersonShea et al, 2002; Reference Grilo, Sanislow and GundersonGrilo et al, 2004; Reference McGlashan, Grilo and SanislowMcGlashan et al, 2005). These studies usually have a small number of evaluations – two or three in most of them (Reference Schwartz, Fennig and Tanenberg-KarantSchwartz et al, 2000; Reference Lieb, Zimmermann and FriisLieb et al, 2002; Reference Barkow, Heun and WittchenBarkow et al, 2004; Reference Grilo, Sanislow and GundersonGrilo et al, 2004; Reference Schimmelmann, Conus and EdwardsSchimmelmann et al, 2005) – and the follow-up period is usually under 3 years (Reference Schwartz, Fennig and Tanenberg-KarantSchwartz et al, 2000; Reference Shea, Stout and GundersonShea et al, 2002; Reference Barkow, Heun and WittchenBarkow et al, 2004; Reference Grilo, Sanislow and GundersonGrilo et al, 2004; Reference Veen, Selten and ScholsVeen et al, 2004; Reference McGlashan, Grilo and SanislowMcGlashan et al, 2005; Reference Rufino, Uchida and VilelaRufino et al, 2005; Reference Schimmelmann, Conus and EdwardsSchimmelmann et al, 2005) with a few exceptions (Reference Tsuang, Woolson and WinokurTsuang et al, 1981; Reference Lieb, Zimmermann and FriisLieb et al, 2002; Reference Mojtabai, Susser and BrometMojtabai et al, 2003; Reference Culverhouse, Bucholz and CroweCulverhouse et al, 2005; Kessing, Reference Kessing2005a ,Reference Kessing b ). Kessing (Reference Kessing2005b ) recently pointed out that no study has investigated the diagnostic stability of the most common ICD–10 psychiatric diagnoses given under ecological clinical conditions.
Other authors have reported rates of consistency that are much higher than the ones found in our study (Reference Tsuang, Woolson and WinokurTsuang et al, 1981; Reference Schwartz, Fennig and Tanenberg-KarantSchwartz et al, 2000; Reference Veen, Selten and ScholsVeen et al, 2004; Reference KessingKessing, 2005b ; Reference Schimmelmann, Conus and EdwardsSchimmelmann et al, 2005). However, most studies that have evaluated the stability of chronic psychiatric diagnoses have shorter follow-up periods than in our study and have focused on a single clinical setting (mainly the in-patient setting). Schwartz et al (Reference Schwartz, Fennig and Tanenberg-Karant2000) reported that rates of consistency of some diagnoses decreased as the follow-up period increased. For example, the retrospective consistency of schizophrenia was 73.1% in a comparison of 6-month and 24-month diagnoses, but fell to 55% (similar to the figure of 45.9% obtained in our study across clinical settings) when baseline and 24-month diagnoses were compared. However, the retrospective consistency of bipolar disorder remained high: 84.8% (6-month and 24-month diagnoses) and 73% (baseline and 24-month diagnoses). Compared with the data from the study by Schwartz et al (Reference Schwartz, Fennig and Tanenberg-Karant2000), the retrospective consistency of bipolar disorder across clinical settings in our study (38.1%) is strikingly low. The third measure of stability that we calculated (the percentage of patients who received the same diagnosis in at least 75% of the evaluations) may more accurately reflect the diagnostic process through different evaluations, and was also strikingly low in our study. Some examples of low values are bipolar affective disorder (23.1%) and specific personality disorders (12.7%), whereas schizophrenia (42.4%) and eating disorders (43.9%) showed the highest rates of stability.
The very low consistency for the category ‘bipolar affective disorder, current episode mild or moderate depression’ may be explained by the fact that this diagnosis is inherently expected to change, since it represents an episode rather than a disorder. Perhaps the use of semi-structured interviews would have enhanced reliability and therefore stability. A structured interview, the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM–III–R was used to provide DSM–III–R psychiatric diagnoses in the study by Schwartz et al (Reference Schwartz, Fennig and Tanenberg-Karant2000).
Explanations and implications for clinicians and policy makers
There may be several explanations for the differences in diagnostic stability across clinical settings. First, it may be easier to diagnose a disorder correctly when symptom severity is at its highest, as in hospital admissions and emergency visits. We did not have data regarding illness severity; however, it would be interesting to conduct a similar study controlling for symptom severity. Second, during hospitalisations, round-the-clock surveillance and symptom observation may increase the accuracy of the diagnoses. In addition, during hospitalisations, clinicians can more easily interview the patient's family, and there is more time for thorough diagnostic assessment and questioning about areas of functioning and symptoms. According to Spitzer et al (Reference Spitzer, Endicott and Robins1978), this may contribute to information variance, and may partially explain the differences in diagnostic stability across clinical settings. Third, the duration of the follow-up period was much longer in the out-patient setting (1992–2004) than in the emergency and hospitalisation settings (2000–2004). Finally, the number of psychiatric contacts was different in each setting (data not shown). Some authors have suggested that the causal relationship between diagnostic stability and the number of psychiatric contacts is unknown: It is surprising that diagnostic stability was higher in the emergency department setting than in the out-patient setting. Other authors (Reference Segal, Egley and WatsonSegal et al, 1995; Reference Rufino, Uchida and VilelaRufino et al, 2005) have noted that psychiatric diagnoses assigned in an emergency department may be less accurate than diagnoses assigned in other settings. In emergency department settings, time is usually limited, frequently there is no additional information from relatives, and in most cases, there is a need for immediate intervention (Reference Segal, Egley and WatsonSegal et al, 1995; Reference Rufino, Uchida and VilelaRufino et al, 2005).
‘Patients who have many psychiatric contacts may present with more unstable psychiatric illness leading to more diagnostic variation. On the other hand, it may be that clinicians have problems with diagnosing some patients accurately and that this may lead to less effective treatment and more psychiatric contacts for these patients.' (Reference KessingKessing, 2005b ).
The temporal consistency of mental disorders in our study is lower than that found in other longitudinal studies. The relative lack of diagnostic stability over time is striking given that there is likely to be a bias towards maintaining the same diagnosis over time. Psychiatrists treating the patients in this study often had access to past records and diagnoses, and may have been inclined to keep the previous diagnosis rather than assign a different one. It should be noted that the view that disorders may not be discrete ‘disease entities’ but rather dimensions of continuous variations has gained currency (Reference Kendell and JablenskyKendell & Jablensky, 2003). The categorical approach to psychiatric diagnostic classification has been criticised in favour of other classification systems, such as symptom-cluster dimensions (Reference Kendell and JablenskyKendell & Jablensky, 2003). The possibility of alternative approaches to diagnoses also raises questions about the value of diagnostic stability as an indicator of the validity of the diagnoses. Krishnan (Reference Krishnan2005) has recently stated that ‘the limits of the nominalist tradition have been reached’ and has suggested four criteria for defining disease: clinical symptoms; course and outcome; familial pattern; and treatment response.
The results of our investigation raise worrisome concerns regarding the validity of results of epidemiological, clinical and pharmacological psychiatric research, particularly in studies of chronic disorders with short follow-up periods that may not allow enough time to reach the right diagnosis or in studies that do not take setting into account. This underscores the inherent weaknesses in our diagnostic system, leading to instability of diagnoses which could reflect limitations of the nosology and result in inappropriate treatment recommendations or interventions.
Future research
It is likely that psychiatric diagnostic categories require revision. This can only be determined definitively with a large-scale study using structured or semi-structured interviews. Such a project may be feasible, but we believe that it might not accurately reflect the conditions of psychiatric practice in the real world.








eLetters
No eLetters have been published for this article.