It has been suggested that earlier onset of psychosis reflects a greater deviation than later-onset psychosis from the normal sexually dimorphic course of brain development leading to cerebral lateralisation (Reference Crow, Colter and FrithCrow et al, 1989; Reference CrowCrow, 1990). Cerebral hemisphere volume, as a marker for structural change, has been reported to be reduced by 5–10% in patients with early disease onset relative to age-matched controls (Table 1), compared with average reductions of 2–3% in adult schizophrenia (Reference HarrisonHarrison, 1999; Reference Wright, Rabe-Hesketh and WoodruffWright et al, 2000). Correspondingly, full-scale IQ scores, as a marker for functional change, have been reported to be 70–95 in early-onset samples (Table 2) relative to 85–100 in adult patients (Reference Aylward, Walker and BettesAylward et al, 1984; Reference Gold, Arndt and NopoulosGold et al, 1999). Correlations between brain volume and cognitive ability in healthy individuals (Reference Reiss, Abrams and SingerReiss et al, 1996; Reference Wickett, Vernon and LeeWickett et al, 2000; Reference Thompson, Vidal and GieddThompson et al, 2001) are reported to depend on age and sex (Reference Willerman, Schultz and RutledgeWillerman et al, 1992; Reference Andreasen, Flaum and SwayzeAndreasen et al, 1993; Reference Coffey, Lucke and SaxtonCoffey et al, 1998; Reference Raz, Gunning-Dixon and HeadRaz et al, 1998; Reference Gur, Turetsky and MatsuiGur et al, 1999). Here we investigate sex-dependent alterations in brain volume, asymmetry and IQ in males and females with early onset of psychosis relative to controls.
Table 1 Demographic characteristics of study groups of patients with early-onset schizophrenia and percentage change in ventricular, temporal lobe and total cerebral volumes in early-onset cohorts relative to matched normal controls
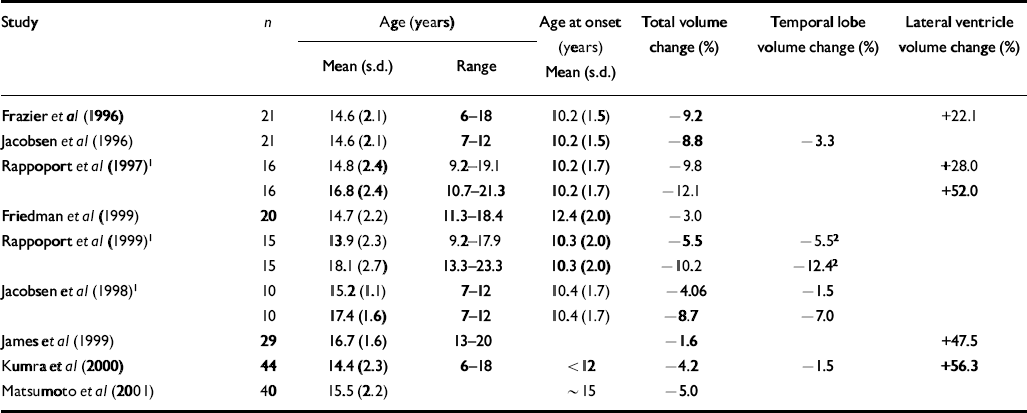
| Study | n | Age (years) | Age at onset (years) | Total volume change (%) | Temporal lobe volume change (%) | Lateral ventricle volume change (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (s.d.) | Range | Mean (s.d.) | |||||
| Frazier et al (Reference Frazier, Giedd and Hamburger1996) | 21 | 14.6 (2.1) | 6-18 | 10.2 (1.5) | −9.2 | +22.1 | |
| Jacobsen et al (Reference Jacobsen, Giedd and Vaituzis1996) | 21 | 14.6 (2.1) | 7-12 | 10.2 (1.5) | −8.8 | −3.3 | |
| Rappoport et al (Reference Rappoport, Giedd and Kumra1997)1 | 16 | 14.8 (2.4) | 9.2-19.1 | 10.2 (1.7) | −9.8 | +28.0 | |
| 16 | 16.8 (2.4) | 10.7-21.3 | 10.2 (1.7) | −12.1 | +52.0 | ||
| Friedman et al (Reference Friedman, Findling and Kenny1999) | 20 | 14.7 (2.2) | 11.3-18.4 | 12.4 (2.0) | −3.0 | ||
| Rappoport et al (Reference Rappoport, Giedd and Blumenthal1999)1 | 15 | 13.9 (2.3) | 9.2-17.9 | 10.3 (2.0) | −5.5 | −5.52 | |
| 15 | 18.1 (2.7) | 13.3-23.3 | 10.3 (2.0) | −10.2 | −12.42 | ||
| Jacobsen et al (Reference Jacobsen, Giedd and Castellanos1998)1 | 10 | 15.2 (1.1) | 7-12 | 10.4 (1.7) | −4.06 | −1.5 | |
| 10 | 17.4 (1.6) | 7-12 | 10.4 (1.7) | −8.7 | −7.0 | ||
| James et al (Reference James, Crow and Renowden1999) | 29 | 16.7 (1.6) | 13-20 | −1.6 | +47.5 | ||
| Kumra et al (Reference Kumra, Wiggs and Bedwell2000) | 44 | 14.4 (2.3) | 6-18 | < 12 | −4.2 | −1.5 | +56.3 |
| Matsumoto et al (Reference Matsumoto, Simmons and Williams2001) | 40 | 15.5 (2.2) | ∼ 15 | −5.0 | |||
Table 2 Mean verbal, performance and full-scale IQ scores in early-onset cohorts relative to matched normal controls
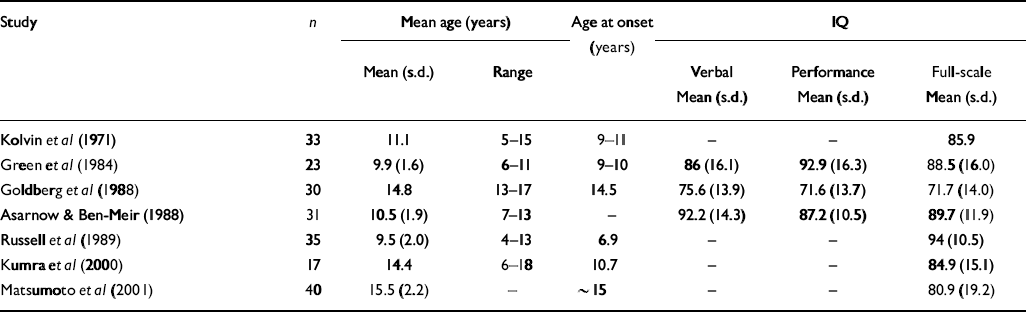
| Study | n | Mean age (years) | Age at onset (years) | IQ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (s.d.) | Range | Verbal Mean (s.d.) | Performance Mean (s.d.) | Full-scale Mean (s.d.) | |||
| Kolvin et al (Reference Kolvin, Humphrey and McNay1971) | 33 | 11.1 | 5-15 | 9-11 | - | - | 85.9 |
| Green et al (Reference Green, Campbell and Hardesty1984) | 23 | 9.9 (1.6) | 6-11 | 9-10 | 86 (16.1) | 92.9 (16.3) | 88.5 (16.0) |
| Goldberg et al (Reference Goldberg, Karson and Leleszi1988) | 30 | 14.8 | 13-17 | 14.5 | 75.6 (13.9) | 71.6 (13.7) | 71.7 (14.0) |
| Asarnow & Ben-Meir (Reference Asarnow and Ben Meir1988) | 31 | 10.5 (1.9) | 7-13 | - | 92.2 (14.3) | 87.2 (10.5) | 89.7 (11.9) |
| Russell et al (Reference Russell, Bott and Simmons1989) | 35 | 9.5 (2.0) | 4-13 | 6.9 | - | - | 94 (10.5) |
| Kumra et al (Reference Kumra, Wiggs and Bedwell2000) | 17 | 14.4 | 6-18 | 10.7 | - | - | 84.9 (15.1) |
| Matsumoto et al (Reference Matsumoto, Simmons and Williams2001) | 40 | 15.5 (2.2) | - | ∼ 15 | - | - | 80.9 (19.2) |
METHOD
Study group
Thirty-three (22 males, 11 females) with early-onset schizophrenia were selected from a larger sample of patients referred to the Oxford Early Psychosis Project. Patients were recruited from both in-patient and out-patient National Health Service (NHS) and private adolescent units across the south of England. All participants met DSM–IV criteria for schizophrenia (American Psychiatric Association, 1994) following a semi-structured interview using the Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia for School-aged Children: Present and Lifetime Version (KSADS–PL; Reference Kaufman, Birmaher and BrentKaufman et al, 1997); most of them had experienced only one psychotic episode. Exclusion criteria were history of significant substance misuse, brain injury, epilepsy, or other neurological or psychiatric disorder. The mean age, height, estimated age at onset, duration of illness, and medication are shown in Table 3. In addition 30 control participants (18 males, 12 females) were recruited from local general practitioners within the Oxford area. The same exclusion criteria were applied. Cases and controls were closely matched for age and had comparable levels of education. After a complete description of the study to the participants, written informed consent was obtained from both the young people and their parents.
Table 3 Demographic characteristics of 33 study participants with early-onset schizophrenia (‘cases’) and 30 participants in a matched normal control group (‘controls’)

| n | Age (years) Mean (s.d.) | Hand preference Right/left | Height (cm) Mean (s.d.) | Age at onset (years) Mean (s.d.) | Duration (months) Mean (s.d.) | CPZeq medication (mg) Mean (s.d.) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cases | |||||||
| Male | 22 | 16.8 (1.3) | 15/6 | 179.0 (8.0) | 15.9 (1.3) | 11.5 (11.4) | 438 (345) |
| Female | 11 | 16.8 (1.5) | 10/0 | 163.7 (7.6) | 15.3 (1.4) | 15.6 (14.7) | 692 (927) |
| Total | 33 | 16.8 (1.4) | 25/6 | 174.3 (10.5) | 15.7 (1.4) | 12.9 (12.6) | 528 (614) |
| Controls | |||||||
| Male | 18 | 16.3 (1.6) | 15/3 | 171.8 (10.0) | |||
| Female | 12 | 16.4 (1.9) | 12/0 | 168.7 (6.6) | |||
| Total | 30 | 16.4 (1.7) | 27/3 | 170.4 (8.7) |
Magnetic resonance image acquisition and analysis
Magnetic resonance images were acquired using a 1.5 T Magnetom Vision whole body system (Siemens Medical System Inc., Erlangen, Germany). One hundred and fifty-six coronal T 1-weighted images were obtained using a three-dimensional spoiled gradient echo pulse sequence (time to repetition=34 ms, time to echo=9 ms, flip angle 30°). The field of view of the images was 20 cm, with 1.5 mm slice thickness. The left and right temporal lobes were optimally visualised, and their volumes best measured, on image sections oriented perpendicularly to the long axis of the hippocampus (Reference Mackay, Roberts and MayesMackay et al, 1998). These sections were obtained by reformatting oblique sections through the acquired three-dimensional data using New Region of Interest Analysis (NRIA) software (Brain Behavior Laboratory, University of Pennsylvania, USA) running on an Ultra 10 Workstation (Sun Microsystems, California, USA), where the 256 × 256 × 156 acquired voxels of side 0.78 mm × 0.78 mm × 1.5 mm were linearly interpolated to 256 × 256 × 256 cubic voxels of side 0.78 mm. This was also a convenient sectioning direction for volume estimation of the left and right cerebral hemisphere and lateral ventricles.
Unbiased estimates of structure volume were obtained using the mathematically unbiased Cavalieri method of modern design stereology in combination with point counting (Reference Roberts, Garden and Cruz-OriveRoberts et al, 1994; Reference Mackay, Roberts and MayesMackay et al, 1998), using EasyMeasure software (http://www.easymeasure.co.uk); see Roberts et al (Reference Roberts, Puddephat and McNulty2000). The posterior limit of the temporal lobe was defined as the point where the lateral ventricles divide into frontal and temporal horns. The cerebral hemispheres were separated from the brain-stem at the superior limit of the pons. A more detailed description of these definitions and the methodology is given in Mackay et al (Reference Mackay, Roberts and Mayes1998). An inter/intrarater reliability study was carried out by three raters. Intraclass correlation coefficients were calculated (Reference BartkoBartko, 1966) and found to be greater than 0.9 for the lateral ventricles, and above 0.8 for temporal lobe and cerebral hemisphere. An index of asymmetry was computed by subtracting the volume of the structure in the left hemisphere (L) from the volume in the right hemisphere (R) and expressing the difference as a percentage of mean volume, i.e. (R-L)/[(R+L)/2] × 100. Temporal lobe volume, lateral ventricle volume and asymmetry measures were considered both as absolute values and as proportions of total cerebral hemisphere volume.
Intelligence assessment
Verbal, performance and full-scale IQ data were collected for 28 participants in the ‘cases’ group and 30 in the control group. Five of the original 33 participants did not complete IQ testing, and were not considered in the analysis of IQ. Participants were tested with either the full version of the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children – Revised (Reference WechslerWechsler, 1992) or, if they were more than 16 years old, the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale – Revised (Reference WechslerWechsler, 1981). Whenever possible, testing was performed in one uninterrupted session. Following testing, all sub-scale scores were transformed into age-scaled scores to render them equivalent. Standard IQ indices were calculated.
Statistical analysis
Data were analysed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences, version 10 for PC. First, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed in order to detect main effects and/or sex interactions in demographic variables. Between-groups comparisons of regional volumes and IQ were performed using the generalised linear model. Multiple analysis of variance (MANOVA) was used to examine structural volume, verbal, performance and full-scale IQ and sub-test differences in IQ performance.
Non-parametric chi-squared analysis was used to determine differences in the distribution of positive and negative asymmetries between groups. All correlations between demographic, treatment and illness-related variables were performed with non-parametric rho connected for multiple comparisons with the Bonferroni test. Given that the normal male brain is significantly larger than the normal female brain (e.g. Reference Gur, Turetsky and MatsuiGur et al, 1999), and previous studies that show differences in asymmetry between the sexes (e.g. Reference Bear, Schiff and SaverBear et al, 1986), males and females were examined separately in both volumetric and IQ analyses.
RESULTS
Volume measurements
Absolute mean volumes of the left and right cerebral hemisphere, temporal lobe and ventricle are shown in Table 4. When examined as a group, covarying for sex, participants with schizophrenia had significantly smaller total brain volumes than those in the control group (ANOVA, F=6.37, P=0.01); with an overall difference of 4.5%. In particular, the ‘cases’ group had significantly reduced left (F=7.18, P=0.009) and right (F=5.33, P=0.02) hemisphere volume compared with controls. There was no significant difference in temporal lobe volumes between case and control groups, but a trend to reduced right temporal lobe volume in cases was observed (P=0.08). Volumes of the lateral ventricles were, on average, 20% larger in the cases group, although this difference did not reach statistical significance. No significant difference was found in ventricle volume as a proportion of hemisphere volume between case and control groups.
Table 4 Mean volumes (ml) of the left and right hemisphere, lateral ventricle and temporal lobe and mean asymmetry indices for each structure in the group of participants with schizophrenia (‘cases’) and in the control group (‘controls’). Standard deviations are shown in parentheses

| Hemisphere | Temporal lobe | Lateral ventricle | Asymmetry index | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left | Right | Left | Right | Left | Right | H | TL | LV | |
| Cases | |||||||||
| Male | 547.8 (47.8) | 554.0 (52.8) | 80.54 (9.8) | 80.17 (8.9) | 7.32 (4.7) | 7.41 (7.3) | 6.18 (18.4) | −0.36 (5.3) | 9.0 (4.1) |
| Female | 501.0 (33.6) | 493.1 (31.8) | 72.6 (9.3) | 71.1 (8.8) | 5.29 (3.0) | 4.87 (2.0) | −7.87 (11.4) | −1.50 (2.9) | −0.42 (2.2) |
| Total | 532.2 (48.5) | 533.7 (54.7) | 77.9 (10.2) | 77.1 (9.7) | 6.64 (4.3) | 6.56 (6.1) | 1.50 (17.6) | −0.74 (4.6) | −8.12 (3.5) |
| Controls | |||||||||
| Male | 582.9 (39.6) | 579.3 (43.1) | 85.5 (7.5) | 84.02 (6.1) | 5.84 (3.2) | 5.72 (2.8) | −3.58 (14.4) | −1.47 (4.8) | −0.11 (2.3) |
| Female | 522.5 (53.3) | 523.8 (52.5) | 73.7 (8.6) | 74.7 (9.9) | 5.20 (1.7) | 4.24 (1.4) | 1.35 (8.2) | 0.91 (4.8) | −0.96 (1.3) |
| Total | 558.7 (53.8) | 557.1 (53.8) | 80.8 (9.8) | 80.3 (9.8) | 5.58 (2.7) | 5.13 (2.5) | −1.61 (12.4) | −0.45 (2.0) | −0.52 (4.8) |
A significant main effect of sex (F=22.15, P=0.0001) indicated that males as a group had significantly larger brains than females, regardless of diagnosis. Males in the cases group demonstrated a 5.1% reduction in overall brain volume (right plus left hemisphere) relative to males in the control group (MANOVA, F=4.28, P=0.45), whereas females in the case group demonstrated a smaller, 3.5% reduction (P=0.17, NS). MANOVA of individual hemisphere volumes in males and females revealed a significant reduction in left, but not right, hemisphere volume in cases relative to controls in males (F=6.17, P=0.01) but not in females. Males also showed a trend to left temporal lobe reduction compared with male controls (P=0.08).
Overall there was no statistically significant (P<0.05) asymmetry of the cerebral hemispheres, temporal lobes or lateral ventricles. However, when sex was entered as an independent variable, a significant diagnosis × sex interaction was detected in hemisphere asymmetry after correction for overall brain size (MANOVA, F=4.39, P=0.01). Post hoc analyses revealed that the female cases group showed significant leftward asymmetry of cerebral hemisphere volume (t=2.28, P=0.04), and this was significantly different from a tendency to rightward asymmetry in the female control group (F=4.97, P=0.03). No significant asymmetry was detected in males, where the cases group tended towards rightward asymmetry and the control group towards leftward asymmetry. In total, 9 out of 11 participants (82%) in the female cases group demonstrated left greater than right asymmetry, which was present in only 5 out of 12 (41%) of the females in the control group (χ2=4.5, P <0.04). There was no difference in the proportion of the male cases group relative to the male control group that showed rightward asymmetry.
IQ analysis
Mean performance IQ, verbal IQ and full-scale IQ scores are shown in Table 5. Both males and females in the case group showed significant impairments on all three tests relative to controls (Table 5). Seventy per cent of the early-onset group had IQs beneath the low average range of performance (full-scale IQ less than 90). There was large variability in the average verbal–performance IQ discrepancy. In the cases group the average discrepancy was 5.14 IQ points (s.d.=14.8) compared with -0.16 in controls (s.d.=17.5) but this was not statistically significant (P=0.22). When the sexes were compared between groups, no significant discrepancy was found between the male case and control groups (3.21, s.d.=14.5, and -0.88, s.d.=19.0, respectively; P=0.47). The female cases group demonstrated a large verbal–performance IQ discrepancy compared with the female control group (9.22, s.d.=15.4, and 0.83, s.d.=15.8, respectively), but this was not statistically significant (P=0.23). When individual Wechsler sub-test scores were examined by MANOVA, significant differences between case and control groups were found across all 11 sub-tests. The average sub-test score in the early-onset group was 7.6 (s.d.=2.0), whereas the control group average was 3 IQ points higher (10.6, s.d.=2.4). A 3-point discrepancy in IQ sub-scale performance is indicative of abnormality (Reference KaufmanKaufman, 1990).
Table 5 Mean verbal, performance and full-scale IQ scores in the group of participants with schizophrenia (‘cases’) and the control group (‘controls’). Standard deviations are shown in parentheses

| n | IQ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Verbal Mean (s.d.) | Performance Mean (s.d.) | Full-scale Mean (s.d.) | ||
| Cases | ||||
| Male | 19 | 85.9 (15.0) | 82.7 (15.2) | 83.0 (14.5) |
| Female | 9 | 85.9 (12.8) | 76.7 (10.0) | 79.8 (8.4) |
| Total | 28 | 85.8 (14.1) | 80.7 (13.8) | 81.9 (12.6) |
| Controls | ||||
| Male | 18 | 97.7 (18.6) | 98.5 (19.2) | 98.2 (17.8) |
| Female | 12 | 109.2 (16.9) | 108.4 (14.8) | 109.6 (15.2) |
Correlation analysis
Age, duration of illness and current medication did not correlate with any of the structural of IQ measures in the cases group. However, earlier age of onset was associated with increasing ventricle volume as a proportion of total brain volume (ρ= -0.35, P <0.05). There were no statistically significant correlations between IQ and brain structure measures in the control group as a whole, or for males and females separately. This was also the case for the combined patient group. However, when the males and females were examined separately, full-scale IQ was significantly correlated with left hemisphere volume (ρ=0.47, P <0.05) in male cases, and verbal IQ was positively correlated with increased rightward hemispheric asymmetry in female cases (ρ=0.81, P <0.01).
DISCUSSION
In this study we examined broad indices of cerebral structure and function in relation to sex in early-onset schizophrenia. In line with expectations, there was clear evidence of significant brain volume deficit; a large reduction in intellectual capacity; and a significant interaction, suggesting that alterations in cerebral asymmetry are sexually dimorphic. Hemisphere volume in males and asymmetry in females were significantly correlated with IQ in the cases group but not in the control group. The relationship between brain structure and intellect cannot be understood without considering the influence of sex.
Volume and IQ
In agreement with previous studies in early-onset schizophrenia (see Tables 1 and 2), this sample showed an average 4.5% deficit in total brain volume relative to controls, which was greater on the left than the right, and average full-scale IQ that was close to the cut-off (80) between low average (IQ=90–80) and borderline (IQ=79–66) ranges of performance. Previous studies have reported greater severity of intellectual disturbance in earlier-onset than in later-onset disease (Reference Yang, Liu and ChiangYang et al, 1995; Reference Basso, Nasrallah and OlsonBasso et al, 1997). Our findings corresponded particularly well with those of Matsumoto et al (Reference Matsumoto, Simmons and Williams2001), who found comparable reductions in brain volume and full-scale IQ in a cohort of similar age. Together, these findings suggest that alterations in gross cerebral structure and IQ in early-onset schizophrenia are less severe than those observed in childhood-onset disease, but greater than those observed in adult-onset schizophrenia.
Two unexpected findings require further elucidation. First, unlike some previous studies of normal adults, we did not find significant volume–IQ correlations in our normal control sample. Most, but not all, studies find modest but significant positive correlations between overall brain volume (Willerman et al, Reference Willerman, Schultz and Rutledge1991, Reference Willerman, Schultz and Rutledge1992; Reference Andreasen, Flaum and SwayzeAndreasen et al, 1993; Reference Wickett, Vernon and LeeWickett et al, 2000) or asymmetry (Reference Yeo, Turkmeimer and RazYeo et al, 1987; Reference Reiss, Abrams and SingerReiss et al, 1996) and IQ. It is possible that a larger normal control group would have revealed comparable volume–IQ correlations. Second, the increase (average 20%) in ventricular volume in cases relative to controls failed to reach significance, although ventricle-to-brain ratio was inversely related to age at onset. Ventricular enlargement is a robust finding in adult schizophrenia (Reference McCarley, Wible and FruminMcCarley et al, 1999) and most studies of early-onset cohorts report increased (Reference James, Crow and RenowdenJames et al, 1999; Reference Kumra, Wiggs and BedwellKumra et al, 2000; Reference Sowell, Levitt and ThompsonSowell et al, 2000) and/or progressive enlargement of lateral ventricular volume (Reference Rappoport, Giedd and KumraRappoport et al, 1997). Our findings indicate considerable variability in the present sample, a finding that is consistent with studies showing variability in ventricular enlargement in first-onset patients (Reference Lieberman, Chakos and WuLieberman et al, 2001; Reference Puri, Hutton and SaeedPuri et al, 2001), particularly in the early stages of the illness (Reference Gur, Cowell and TuretskyGur et al, 1998; Reference Puri, Hutton and SaeedPuri et al, 2001).
Sex differences
Our findings provide evidence that changes in brain volume and the relationship to IQ are, to some extent, sexually dimorphic in patients with early-onset schizophrenia. Male, but not female, participants in the cases group had reduced left hemisphere volume and a trend to reduced temporal lobe volume. A significant diagnosis × sex interaction in cerebral hemisphere asymmetry was found such that the tendency for rightward asymmetry in the female control group was reversed to a leftward asymmetry in females with schizophrenia. Males did not show a significant effect, although there was a trend to reversal of the normally observed leftward pattern (i.e. in the opposite direction to females). Sex differences in asymmetry in adults have been previously observed in frontal, temporal and whole brain measurements (Reference Bilder, Wu and BogertsBilder et al, 1994; Reference Highley, Esiri and Cortina-BorjaHighley et al, 1998) and have been shown to interact with age at onset (Reference Highley, Esiri and Cortina-BorjaHighley et al, 1998; Reference Maher, Manschreck and Yurgelun-ToddMaher et al, 1998; Reference McDonald, Highley and WalkerMcDonald et al, 2000). Our findings suggest that sex-specific alterations in asymmetry are present in patients with early-onset schizophrenia, consistent with the hypothesis (Crow, Reference Crow1993, Reference Crow2000) that a sex-linked determinant of asymmetry has a critical role in the aetiology of psychosis.
Correlations between hemisphere volume and IQ measures in this cohort were sex-specific. In the male cases group, reduced left hemisphere volume was correlated with lower full-scale IQ. The reduction in rightward asymmetry in female cases relative to controls was associated with a selective reduction in verbal IQ. In effect, these structure–function relationships were consistent with a body of evidence indicating that sex differences in IQ decline are associated with lateralised cerebral disturbance (see Reference KaufmanKaufman, 1990, for review). A simple interpretation of the significant differences and trends in our findings is that in males with schizophrenia the deficits are associated with loss that is relatively selective to the left hemisphere, whereas in females they are associated with a loss that is relatively greater in the right hemisphere. This differs somewhat from the findings of Flaum et al (Reference Flaum, Andreasen and Swayze1994) who also examined brain structure and IQ in adults with schizophrenia in relation to sex. They reported that the pattern of structure–function correlations in females with schizophrenia was similar to those of female controls, but males with schizophrenia demonstrated no significant structure–function relationships. Further studies are required, but it is noteworthy that Flaum et al did not examine indices of cerebral asymmetry, where sexual dimorphism in healthy individuals is established (Reference Bear, Schiff and SaverBear et al, 1986; Reference Barrick, Mackay and CrowBarrick et al, 2001).
Neurodevelopmental antecedents of volume and IQ reduction
Although the relationship between age, sex and onset of psychosis is complex, our findings are consistent with neurodevelopmental explanations of schizophrenia. Adolescence is a critical stage in cerebral maturation involving substantial volume increases in white matter relative to grey matter (Reference Reiss, Abrams and SingerReiss et al, 1996; Reference Giedd, Castellanos and JacobsenGiedd et al, 1997; Reference Courchesne, Chisum and TownsendCourchesne et al, 2000), accompanied by increase in the volume of the lateral ventricles (Giedd et al, Reference Giedd, Snell and Lange1996, Reference Giedd, Castellanos and Jacobsen1997). Furthermore, these changes are influenced by sex, as the extent of grey-matter volume reduction is greater in males than females (Reference Coffey, Lucke and SaxtonCoffey et al, 1998; Reference Raz, Gunning-Dixon and HeadRaz et al, 1998). Our findings indicate that, in adolescents with schizophrenia, the intellectual deficits depend on an interaction between sex and relative hemispheric development.
Clinical Implications and Limitations
CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS
-
▪ Early-onset schizophrenia is associated with an average 4.5% reduction in brain volume which is greater in males.
-
▪ People with early-onset schizophrenia demonstrate significant impairment of intellectual abilities, with the majority of full-scale intelligence quotient scores within the low average to borderline range.
-
▪ Significant reduction in intellectual abilities is associated with sexually dimorphic and asymmetrical structural change in early-onset disease consistent with the developmental hypothesis.
LIMITATIONS
-
▪ The young age range of the participants may limit the general applicability to adult-onset schizophrenia.
-
▪ The absence of significant ventricular enlargement is unexpected and may be related to small sample size and high variance in this study.
-
▪ Changes in structure are likely to reflect ongoing deviation from normal development. Longitudinal studies including samples in the general population are required.
Acknowledgements
This research project was supported by the Medical Research Council UK (grant G9900348), and SANE. The authors wish to thank Susan James, Gina Clark, Kristin Bohn and Jocasta Webb for their contributions to collecting the sample and assessing and analysing the data.








eLetters
No eLetters have been published for this article.