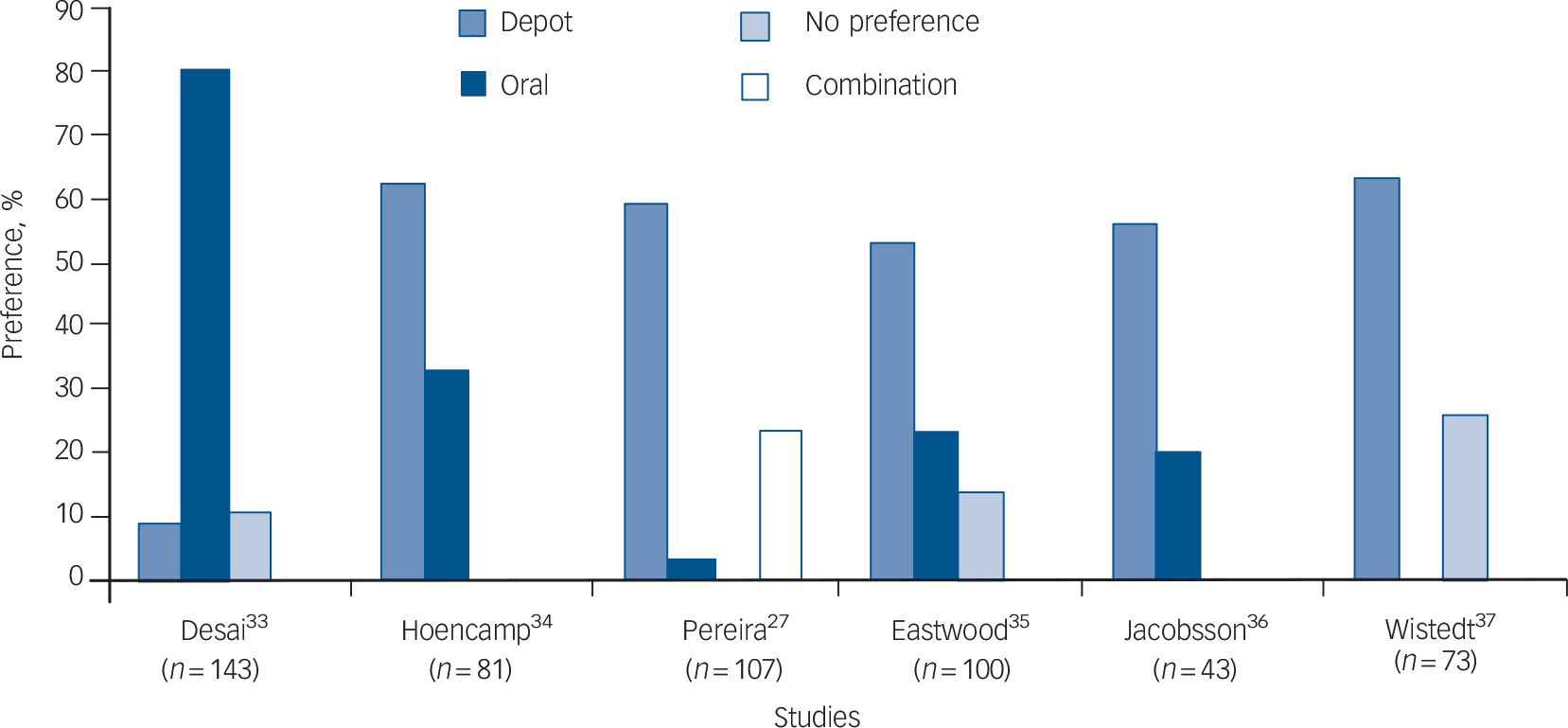
The attitudes of patients and staff towards antipsychotic long-acting (depot) injections (LAIs) have been assessed over the years, partly in an attempt to understand the relationship between attitudes, prescribing habits and patient acceptance of antipsychotic treatment. A comprehensive review of the literature between 1966 and 1999 was carried out by Walburn et al, looking specifically at patient and nurse attitudes towards antipsychotic depot medication. Reference Walburn, Gray, Gournay, Quraishi and David1 A quality analysis of the articles they found used a hierarchy of study design and a checklist, constructed by the authors, emphasising criteria commonly used in critical appraisal. Walburn et al found that five out of six studies showed a patient preference for LAIs over oral antipsychotic medication in those receiving LAIs (Fig. 1), but provided little information on the opinions of those taking oral medication. Reference Walburn, Gray, Gournay, Quraishi and David1 There was also little evidence of the attitudes of nursing staff and none for allied health or medical staff.

Fig. 1 Patient formulation preference (created using data derived from the six studies by Walburn et al, 2001). Reference Walburn, Gray, Gournay, Quraishi and David1
Non-adherence to antipsychotic medication regimens is recognised as increasing the risk of relapse of schizophrenia, Reference Robinson, Woerner, Alvir, Bilder, Goldman and Geisler2 and non-adherence among people receiving out-patient antipsychotic treatment is reported to reach 50% during the first year after discharge. Reference Zygmunt, Olfson, Boyer and Mechanic3 The therapeutic optimism accompanying the introduction of oral second-generation (atypical) antipsychotics arguably led to a lower usage of LAIs, and these injections tended to be prescribed to those with lower levels of insight, poor adherence, chronic illness and/or a history of aggression, Reference Davis and Chen4,Reference Mahadun and Marshall5 i.e. individuals likely to have a worse prognosis on oral medication. The impact of this prescribing stereotype on stigma and a perception of coercion associated with LAI use should not be underestimated. The impact of risperidone LAI, introduced in 2001, on the attitudes of patients and staff may counterbalance this stereotype and has led in some areas to the reconsideration of LAI use in first-episode psychosis. Reference Chue and Emsley6
We therefore set out to examine the attitudes of service users or patients and mental health staff to antipsychotic LAIs, and to examine factors that correlated with positive and negative attitudes towards LAIs.
Method
A systematic strategy was used to search the electronic databases MEDLINE, EMBASE, PsycINFO, the Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE), the Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL), Google Scholar and the Cochrane Library from June 1999 to the end of February 2008, with the intention of following on from a previous review. Reference Walburn, Gray, Gournay, Quraishi and David1 Searches were conducted using antipsychotic LAI OR depot, delayed action preparations, intramuscular injection, antipsychotic, neuroleptic and specific LAI drug names as subject and text words. These were combined with the words satisfaction, attitude and related terms. References of the included studies were also inspected for possible inclusion; this involved reviewing the abstract of the references with regard to the inclusion and exclusion criteria used in the original search. Authors of studies in the field were contacted to see whether there were any relevant studies in press and likely to be published before the end of 2008.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The abstracts of the studies found were reviewed and included if they reported original quantitative data describing patient or mental health staff attitudes to LAIs. As it was expected that most studies would be at the lower end of the hierarchy of study design, no quality threshold for inclusion of studies was set.
Assessment of studies
All included studies were assessed according to a hierarchy of evidence. 7 The studies were also assessed according to a 13-item checklist constructed by Walburn et al, Reference Walburn, Gray, Gournay, Quraishi and David1 and subjected to the same basic statistical analysis to identify the strengths and weaknesses of each study and to allow comparison with the quality of studies found in the previous review.
Results
In all, 1158 studies were identified using the search strategy. Of these, 12 satisfied the inclusion criteria. Five described the attitudes of patients, three those of psychiatrists, two those of psychiatric nurses and two those of a mixture of mental health staff. Of the studies that assessed patient attitudes the sample sizes ranged from 73 to 998 and the total number of participants was 2349. Studies assessing staff attitudes had sample sizes ranging from 50 to 246 with the total number of participants being 879.
Patient attitudes were assessed by interview and/or questionnaire in a variety of different settings, including in-patient wards, out-patient clinics, general practitioners' surgeries and the participant's own home. Staff surveys were conducted at conferences, meetings or by mail. Two of the patient attitude studies employed existing questionnaires or structured interviews; the other three patient attitude studies, and all seven studies addressing the attitudes of staff, used questionnaires or structured interviews specifically constructed for use in each study. The four studies conducted by Patel et al addressing staff attitudes used variations of the same questionnaire constructed by the authors (Table 1).
Table 1 Characteristics of included studies

| Study (first author, year and title) | Design | Participants | Sample size, n | Outcome measure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bradstreet (2004) Reference Bradstreet and Norris10 | Cross-sectional survey | No diagnosis specified. Individuals on new psychiatric medication in past 3 years recruited via the SAMH | 756 | Postal survey regarding attitude to psychiatric medication |
| All you need to know? Scottish survey of people's experience of psychiatric drugs | ||||
| Castle (2002) Reference Castle, Morgan and Jablensky11 | Cross-sectional survey | Patients diagnosed with a psychosis. Seen in GP surgeries, out-patient clinics, wards, shelters and hostels | 998 | Questions assessing the helpfulness of medications and positive and negative attributes related to treatment |
| Antipsychotic use in Australia: the patients' perspective | ||||
| Harris (2007) Reference Harris, Lovell and Day19 | Cross-sectional survey | Nurses, occupational therapists and social workers undertaking a degree-level course in psychosocial management of psychosis | 50 | Questionnaire comprising 25 items regarding attitude to antipsychotic treatment prescribed for individuals with schizophrenia, with one question pertaining to mode of delivery |
| Mental health practitioners' attitude towards maintenance neuroleptic treatment for people with schizophrenia | ||||
| Heres (2006) Reference Heres, Hamann, Kissling and Leucht18 | Cross-sectional survey | Psychiatrists attending the 8th World Congress of Biological Psychiatry 2006 | 246 | Sixteen-statement questionnaire regarding influences discouraging the prescribing of LAIs |
| Attitudes of psychiatrists toward antipsychotic depot medication | ||||
| Heres (2007) Reference Heres, Schmitz, Leucht and Pajonk12 | Cross-sectional survey | In-patients with schizophrenia | 300 | Questionnaire regarding preference in the mode of administration of antipsychotic treatment |
| The attitude of patients towards antipsychotic depot treatment | ||||
| Lambert (2003) Reference Lambert, Brennan, Castle, Kelly and Conley17 | Cross-sectional survey | Mental health professionals working with those with severe mental illness | 170 | Twelve-item questionnaire to evaluate opinion concerning depot antipsychotic use |
| Perception of depot antipsychotics by mental health professionals | ||||
| Patel (2003) Reference Patel, Nikolaou and David13 | Cross-sectional survey | Section 12 approved psychiatrists in South Thames Health Authority | 143 | Newly designed questionnaire, consisting of 44 statements, assessing attitudes and knowledge concerning depot antipsychotics |
| Psychiatrists' attitudes to maintenance medication for patients with schizophrenia | ||||
| Patel (2005) Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Baker and David14 | Cross-sectional survey | CPNs who attended one of two academic meetings in London | 70 | Questionnaire assessing attitude to and knowledge of depot medication, consisting of 34 statements |
| Antipsychotic depot medication and attitudes of community psychiatric nurses | ||||
| Patel (2008) Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Bernadt and David9 | Cross-sectional survey | Out-patients with schizophrenia/schizoaffective disorder | 73 | Structured clinical interview including Rating of Medication Influences and Beliefs about Medicines Questionnaire |
| A cross-sectional study of patients' perspectives on adherence to antipsychotic medication: depot versus oral | ||||
| Patel (2009) Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Bernadt and David8 | Cross-sectional survey | Out-patients with schizophrenia/schizoaffective disorder on maintenance antipsychotics | 222 | DAI–10 altered for formulation-specific questions and questions on formulation, preference, autonomy and stigma |
| Depot and oral antipsychotics: patient preferences and attitudes are not the same thing | ||||
| Patel (2008) Reference Patel, Yeung, Haddad and David15 | Cross-sectional survey | Psychiatric nurses working in Hong Kong who attended an academic meeting | 98 | Questionnaire regarding attitudes and knowledge about LAI antipsychotics (46 items). Compared with results from previous survey of British CPNs |
| Psychiatric nurses' attitudes to antipsychotic depots in Hong Kong and comparison with London | ||||
| Patel (2009) Reference Patel, Haddad, Chaudhry, McLoughlin, Husain and David16 | Cross-sectional survey | Consultant psychiatrists in north-west England | 102 | Postal survey consisting of 56 questions regarding attitudes to and knowledge of LAI antipsychotics. Compared with previous survey in 2001 |
| Psychiatrists use, knowledge and attitudes to first- and second-generation antipsychotic LAIs; comparisons over 5 years |
CPN, community psychiatric nurse; DAI–10, 10-item Drug Attitude Inventory; GP, general practitioner; LAI, long-acting injection; SAMH, Scottish Association for Mental Health
Quality of studies
All the studies were in the form of a cross-sectional survey, which is level IV evidence in the hierarchy of study design. 7 The assessment of the studies against the checklist designed by Walburn et al (Table 2) revealed a varied performance, with a range of scores from 4 to 11 (out of a maximum of 13). Reference Walburn, Gray, Gournay, Quraishi and David1 Eleven of the 12 studies had explicit aims and details of inclusion and exclusion criteria, but none carried out a sample size calculation. Other areas of poor performance were justification of response/drop-out rate and justification that the sample was representative of the population. Important demographic details were included in all studies – for example, years working in psychiatry and number of patients in their care currently receiving LAIs (in staff studies), and (in patient studies) diagnosis, age, gender, and current and past medication formulations.
Table 2 Quality analysis of all included studies

| Study | Explicit a priori aims | Definition/size of population under investigation | Sample size calculation | Justification that sample is representative of population | Inclusion/exclusion criteria stated | Demographic details | Research independent of routine care/practice | Justification of validity/reliability of measures | Original questionnaire available | Response/drop-out rate specified | Justification of response/drop-out rate | Discussion of generalisability | Statement of source of funding | Marks lost | Percentage of maximum quality score % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bradstreet (2004) Reference Bradstreet and Norris10 | – | – | – | – | – | + | + | – | + | N/A | N/A | – | + | 7 | 31 |
| Castle (2002) Reference Castle, Morgan and Jablensky11 | + | + | – | – | + | + | + | – | – | – | – | – | – | 8 | 39 |
| Harris (2007) Reference Harris, Lovell and Day19 | + | – | – | – | + | + | + | + | + | – | – | – | – | 7 | 46 |
| Heres (2006) Reference Heres, Hamann, Kissling and Leucht18 | + | – | – | – | + | + | + | – | + | + | – | + | + | 5 | 62 |
| Heres (2007) Reference Heres, Schmitz, Leucht and Pajonk12 | + | – | – | + | + | + | – | – | + | + | – | + | + | 5 | 62 |
| Lambert (2003) Reference Lambert, Brennan, Castle, Kelly and Conley17 | + | + | – | + | + | + | + | – | + | + | – | + | – | 4 | 69 |
| Patel (2003) Reference Patel, Nikolaou and David13 | + | + | – | – | + | + | + | + | + | + | – | + | + | 3 | 77 |
| Patel (2005) Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Baker and David14 | + | – | – | – | + | + | + | + | + | + | – | + | – | 5 | 62 |
| Patel (2008) Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Bernadt and David9 | + | – | – | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | – | – | + | 4 | 69 |
| Patel (2009) Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Bernadt and David8 | + | – | – | – | + | + | + | – | + | – | – | – | + | 7 | 46 |
| Patel (2008) Reference Patel, Yeung, Haddad and David15 | + | – | – | – | + | + | + | + | + | + | – | + | – | 5 | 62 |
| Patel (2009) Reference Patel, Haddad, Chaudhry, McLoughlin, Husain and David16 | + | + | – | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | – | 2 | 85 |
| Totals | 11/12 | 4/12 | 0/12 | 4/12 | 11/12 | 12/12 | 11/12 | 6/12 | 11/12 | 8/11 | 1/11 | 7/12 | 6/12 | Mean 5.2 | Mean 59.2 |
+, present; –, absent; NA, not applicable
The mean percentage of maximum-quality scores is higher for studies published since mid-1999 compared with the studies reviewed by Walburn et al (59% v. 44%). Reference Walburn, Gray, Gournay, Quraishi and David1
Patient attitudes
Of the five studies that contained quantitative data addressing patient attitudes to LAIs, one elicited a predominantly positive attitude, two were negative and two were neutral (Table 3). The two neutral studies revealed no difference in total scores on the 10-item Drug Attitude Inventory (DAI–10) and Beliefs about Medication Questionnaire (BMQ) between individuals on oral and LAI maintenance antipsychotics, leading the authors to suggest that the attitudes held by a group of voluntary out-patients regarding treatment were similar for those given LAIs and those taking tablets. Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Bernadt and David8,Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Bernadt and David9 In contrast, when asked detailed questions about their attitudes regarding medication adherence (using the Rating of Medication Influences questionnaire), those in the LAI group (v. oral) had higher non-adherence scores and more self-stated reasons for non-adherence. Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Bernadt and David9 A subsample analysis of DAI–10 scores by Patel et al found that those who had previously switched from LAIs to oral medication retained negative views regarding LAIs. Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Bernadt and David8 Embarrassment or shame associated with receiving an LAI concerned a significant proportion of those questioned, and just under half of participants who had current or previous experience of LAIs felt they were forced to start receiving LAIs. Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Bernadt and David8
Table 3 Patient preferences and attitudes to long-acting injections: data extraction
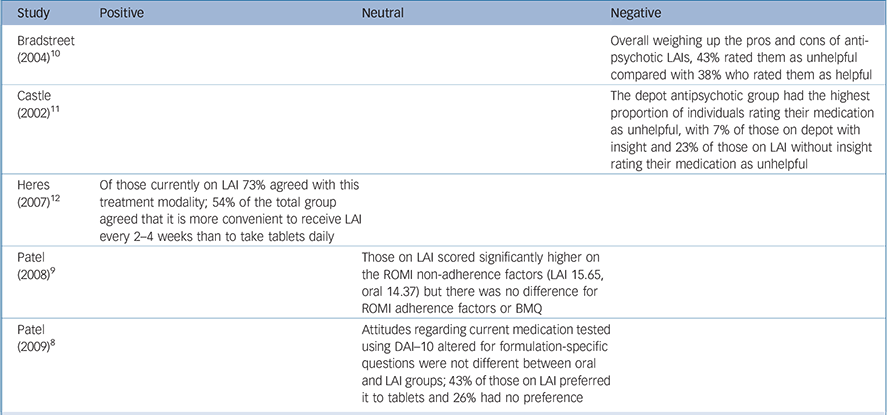
| Study | Positive | Neutral | Negative |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bradstreet (2004) Reference Bradstreet and Norris10 | Overall weighing up the pros and cons of antipsychotic LAIs, 43% rated them as unhelpful compared with 38% who rated them as helpful | ||
| Castle (2002) Reference Castle, Morgan and Jablensky11 | The depot antipsychotic group had the highest proportion of individuals rating their medication as unhelpful, with 7% of those on depot with insight and 23% of those on LAI without insight rating their medication as unhelpful | ||
| Heres (2007) Reference Heres, Schmitz, Leucht and Pajonk12 | Of those currently on LAI 73% agreed with this treatment modality; 54% of the total group agreed that it is more convenient to receive LAI every 2–4 weeks than to take tablets daily | ||
| Patel (2008) Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Bernadt and David9 | Those on LAI scored significantly higher on the ROMI non-adherence factors (LAI 15.65, oral 14.37) but there was no difference for ROMI adherence factors or BMQ | ||
| Patel (2009) Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Bernadt and David8 | Attitudes regarding current medication tested using DAI–10 altered for formulation-specific questions were not different between oral and LAI groups; 43% of those on LAI preferred it to tablets and 26% had no preference |
BMQ, Beliefs about Medicine Questionnaire; DAI–10, 10-item Drug Attitude Inventory; LAI, long-acting injection; ROMI, Rating of Medication Influences
Two studies reported a negative view of LAI medication. In both studies LAIs were unfavourably compared with other treatments. Bradstreet & Norris surveyed the opinions of individuals who had changed psychiatric medication within the preceding 3 years, and found that 43% of respondents who had used LAIs rated them as unhelpful compared with 38% who rated them as helpful. Reference Bradstreet and Norris10 When asked specifically about symptom relief, only just over half of respondents rated LAIs as helpful. All antipsychotic LAIs (first- and second-generation) were grouped together in these results and performed poorly in comparison with other grouped medications such as all first-generation antipsychotics and all second-generation antipsychotics.
Castle et al similarly found that the LAIs group (only conventional or first-generation depots at that time) had the highest proportion of individuals rating their medication as unhelpful. Reference Castle, Morgan and Jablensky11 Patients without insight were also noted to rate the usefulness of their medication lower than those with insight across all agents.
Patient preference
Data directly related to patient preference for mode of antipsychotic administration were found in two studies. Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Bernadt and David8,Reference Heres, Schmitz, Leucht and Pajonk12 Heres et al questioned 300 in-patients just before discharge about their preferences in the mode of administration of antipsychotic treatment, taking earlier LAI experience into account. Reference Heres, Schmitz, Leucht and Pajonk12 A predominantly positive attitude towards LAIs was conveyed with the main result found that the acceptance of LAI treatment increases with experience. Reference Heres, Schmitz, Leucht and Pajonk12 Only 23% of patients naive to LAIs considered them acceptable, compared with 45% of those previously given LAIs and 73% of those currently receiving LAIs. Looking at the entire group, 40% of patients fully or possibly agreed with LAI treatment. Oral maintenance treatment was still felt to be much more acceptable, with 88% fully or possibly agreeing with the use of tablets.
Patel et al found that patients tended to prefer the current formulation of their antipsychotic: 43% of those currently on LAIs preferred LAI medication to oral, whereas 26% had no preference and 30% preferred an oral formulation. Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Bernadt and David8 In contrast, 92% of those prescribed oral medication preferred tablets and only 6% preferred LAIs. Looking at the group as a whole, 18% preferred LAIs, 71% tablets and 11% had no preference.
Staff attitudes
Four of the seven studies addressing staff opinions found predominantly positive attitudes, with one study being neutral and two negative (Table 4). Using a questionnaire specifically designed for the study, Patel et al found that a large proportion of psychiatrists considered LAIs to have positive aspects, for example 71% of psychiatrists surveyed believed that LAIs are part of a patient-centred approach and 69% believed that the good aspects of LAI medication outweigh the bad. Reference Patel, Nikolaou and David13 Nevertheless, a substantial minority of psychiatrists surveyed felt that LAIs were old-fashioned and stigmatising. Patel et al noted that overall the route of administration did not appear to be the major determinant of psychiatrists' attitudes, as the majority agreed that they would be persuaded to prescribe LAIs or depots if they were associated with fewer side-effects, in patients for whom adherence was an issue.
Table 4 Staff attitudes to long-acting injections: data extraction

| Attitude | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Positive | Neutral | Negative | ||
| Harris (2007) Reference Harris, Lovell and Day19 | Of the mental health staff surveyed, 58% felt that oral medication is the option of choice if the service user agrees | ||||
| Heres (2006) Reference Heres, Hamann, Kissling and Leucht18 | Of the psychiatrists surveyed, 65% and 71% considered SGA–LAI and FGA–LAI respectively are inappropriate treatment for first-episode psychosis; 68% felt that neither FGA–LAIs nor SGA–LAIs are an appropriate option after relapse; 65% of respondents with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder had never been offered an LAI | ||||
| Lambert (2003) Reference Lambert, Brennan, Castle, Kelly and Conley17 | Fifty-nine per cent of all staff felt LAIs were used at the correct rate. Significant variation in attitudes to LAIs among different health professionals was evident | ||||
| Patel (2003) Reference Patel, Nikolaou and David13 | Of the psychiatrists surveyed, 71% believed LAIs are part of a patient-centred approach and 69% believed the good aspects of LAI medication outweighed the bad | ||||
| Patel (2005) Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Baker and David14 | Of CPNs surveyed, 79% believed LAIs are part of a patient-centred approach and 84% believed the good aspects of LAI medication outweighed the bad | ||||
| Patel (2008) Reference Patel, Yeung, Haddad and David15 | Of those surveyed, 72% felt LAIs are a patient-centred approach to treatment; 83% felt that the good aspects of LAI outweighed the bad | ||||
| Patel (2009) Reference Patel, Haddad, Chaudhry, McLoughlin, Husain and David16 | Of those surveyed, 89% and 75% regarded LAIs as associated with better adherence and lower relapse rates respectively; 72% felt that the good aspects of LAI outweighed the bad | ||||
CPN, community psychiatric nurse; FGA, first-generation antipsychotic; LAI, long-acting injection; SGA, second-generation antipsychotic
Similar results were found by Patel et al when the same questionnaire was applied to a group of community psychiatric nurses (CPNs) in the UK. Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Baker and David14 The majority of the CPNs surveyed reported favourably on carrying out the LAI administration role and had favourable attitudes towards antipsychotic LAIs. Similarly, a significant minority held negative attitudes, such as believing that prescribing LAIs is coercive, stigmatising and old-fashioned. The authors noted that this study revealed interprofessional differences, with CPNs having less favourable attitudes to LAIs regarding patient autonomy and coercion compared with psychiatrists.
The same questionnaire from the above two studies by Patel et al was used in two further comparative studies. In the first, Reference Patel, Yeung, Haddad and David15 a group of CPNs from Hong Kong were compared with the UK CPNs from the earlier study. Patel et al illustrated that although the Hong Kong CPNs were mostly positive about LAIs, overall they were much less positive than their UK CPN counterparts. The majority felt that most patients always prefer oral medication and 40% felt that force is sometimes required during LAI administration. A quarter of respondents admitted that they would feel ambivalent, negative or concerned if a patient requested an LAI.
In the second study a group of consultant psychiatrists' attitudes were assessed and compared with the previous psychiatrists' results 5 years earlier. Reference Patel, Haddad, Chaudhry, McLoughlin, Husain and David16 Consultants in north-west England had a range of views regarding LAIs – only 4% of psychiatrists rated LAIs as first choice for long-term maintenance treatment in schizophrenia, and most respondents reported that their use of LAIs had decreased or not changed over the past 5 years. Reference Patel, Haddad, Chaudhry, McLoughlin, Husain and David16 The majority of those surveyed regarded LAIs as associated with better adherence and lower relapse rates. The most commonly stated LAI prescribed over the past year was risperidone, and having more second-generation antipsychotics available in long-acting form was the most commonly cited factor that would persuade these psychiatrists to use more LAIs. The authors noted that concerns about stigma and autonomy were less than in the study of senior psychiatrists in the south London area conducted 5 years earlier, Reference Patel, Nikolaou and David13 but worries about patient acceptance persisted.
Lambert et al questioned simultaneously both psychiatrists and allied health professionals regarding their attitudes to LAIs. Reference Lambert, Brennan, Castle, Kelly and Conley17 Attitudes to the current rate of LAI use varied between different mental health professionals, with 53% of medical staff, 18% of nurses and 24% of allied health staff feeling that LAIs were being used too much; 59% of the total group felt they were being used at about the right rate. Medical staff tended not to consider patient preference as an indication for LAIs and gave lower ratings to limitation of patients' rights as a problem compared with nursing staff. Ninety-four per cent of medical staff and 81% of nursing staff reported feeling confident using oral antipsychotics, compared with 65% and 78% of medical and nursing staff respectively who reported feeling confident using LAIs.
Heres et al adopted a different approach by questioning psychiatrists as to their reasons for not prescribing a first- or second-generation antipsychotic LAI (FGA–LAI or SGA–LAI) to their patients diagnosed with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Reference Heres, Hamann, Kissling and Leucht18 The majority of psychiatrists surveyed considered LAIs to be inappropriate treatment for first-episode psychosis. The high cost of the one SGA available in LAI form was important in their decision not to prescribe it in 71% of respondents and 68% felt that both FGA–LAIs and SGA–LAIs were not an appropriate option after relapse. Presumed adequate adherence with oral medication and the perceived poorer control of antipsychotic effect with LAIs compared with the oral administration of the identical drug were commonly cited as reasons for not prescribing LAIs. Participants reported prescribing LAIs to only 20% of their patients diagnosed with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder but also admitted that 65% of their patients with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder had never been offered LAI treatment.
The aim of the study by Harris et al was to develop an inventory assessing the attitudes and beliefs of mental health practitioners towards maintenance neuroleptic treatment. Reference Harris, Lovell and Day19 Only one question pertained specifically to LAIs: 58% of the mental health staff surveyed felt oral medication was the option of choice if the service user agrees.
Correlation of attitude and knowledge
Heres et al found that psychiatrists aged 50 years and older offered LAI treatment to significantly more of their patients than did younger colleagues. Reference Heres, Hamann, Kissling and Leucht18 The 2003 study by Patel et al revealed the positive correlation between the attitudes of psychiatrists towards LAIs and the extent of their knowledge regarding LAIs. Reference Patel, Nikolaou and David13 A similar study in 2008 showed again that psychiatrists' attitudes were positively correlated with knowledge. Reference Patel, Haddad, Chaudhry, McLoughlin, Husain and David16 Psychiatrists who had decreased their overall use of LAIs over the preceding 5 years had significantly lower scores on the side-effects knowledge subscale than those whose use of LAIs had remained unchanged or increased.
Patel et al illustrated that CPNs who had more than 10 patients receiving LAIs had more favourable attitudes than those who had fewer than 10 patients on LAIs, and that the degree of knowledge concerning the side-effects of these injections was again positively correlated with current attitudes to LAIs. Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Baker and David14 Interestingly, a similar study of CPNs in Hong Kong showed that nurses who currently administered LAIs were more likely to have less favourable LAI-specific attitudes than those who did not, but their degree of knowledge concerning side-effects of LAIs still positively correlated with favourable attitudes to LAIs. Reference Patel, Yeung, Haddad and David15
Discussion
What have we learned since Walburn's study?
Some of the criticisms put forward by Walburn et al in 2001 have been addressed. Reference Walburn, Gray, Gournay, Quraishi and David1 Attempts have been made to recruit a more representative sample of people taking antipsychotic medication, with attempts at the recruitment of patients attending general practice surgeries, those staying at shelters and hostels, Reference Castle, Morgan and Jablensky11 through acute in-patient admission, Reference Heres, Schmitz, Leucht and Pajonk12 and through wide distribution of a questionnaire through voluntary organisations and online. Reference Bradstreet and Norris10 Although this still does not address the almost impossible task of gaining the opinion of those who refuse consent to take part, it does allow for a broader view than that of only those who regularly attend out-patient clinics. Also, individuals prescribed different treatment formulations were asked their opinion about formulation preference, Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Bernadt and David8,Reference Heres, Schmitz, Leucht and Pajonk12 including those previously given LAIs and now taking oral medication.
Heres et al found that patient acceptance of LAIs increased with duration of treatment. Reference Heres, Schmitz, Leucht and Pajonk12 Patel et al reported that patients generally preferred their current formulation, Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Bernadt and David8 but in both studies across all groups oral medication was still much more acceptable to patients, and those who had previous experience of LAIs but were currently taking an oral antipsychotic tended to find LAIs less appealing and retained negative views about them. Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Bernadt and David8,Reference Heres, Schmitz, Leucht and Pajonk12 The reason for this as well as the reasons for switching treatment are unclear and an important area of further investigation.
The attitudes of different disciplines within the mental health team have been assessed during more recent years, and attitudes to LAIs have been correlated with frequency of use and knowledge of LAIs. Studies carried out by Patel et al illustrate that those with more service users on LAIs, both nurses and psychiatrists, have more positive attitudes to LAIs, with the one exception being CPNs working in Hong Kong. Reference Patel, Nikolaou and David13–Reference Patel, Haddad, Chaudhry, McLoughlin, Husain and David16 However, all staff surveys by Patel et al revealed that those with greater knowledge regarding LAIs had more positive attitudes. This is perhaps hardly surprising. Heres et al also showed that psychiatrists over 50 years old offered LAIs to more patients than did younger psychiatrists, Reference Heres, Hamann, Kissling and Leucht18 which could be explained by the extra experience older psychiatrists may have with FGA–LAIs balancing the marketing of SGA-orals in the past decade. Heres et al also identified inconsistencies, with the majority of respondents stating that LAIs were frequently rejected by patients when offered, but then also admitting that 65% of their patients with a diagnosis of schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder had never been offered LAIs. Reference Heres, Hamann, Kissling and Leucht18 This raises questions regarding medical paternalism and the extent of patient choice – more education and shared decision-making was advocated by Heres et al. Reference Heres, Hamann, Kissling and Leucht18
Lambert et al found varied attitudes between different members of the mental health team, with all team members being more confident using oral atypicals than LAIs for chronic schizophrenia – these authors also concluded that more education was required. Reference Lambert, Brennan, Castle, Kelly and Conley17
No data regarding the opinion and attitudes of next of kin, general practitioners or those working in voluntary organisations toward LAIs have been identified in this review. It has been shown that relatives are well aware of the risks of discontinuing clozapine, Reference Angermeyer, Boitz, Loffler, Muller and Priebe20 and are aware of the positive and negative effects of antipsychotics taken by their family members, Reference Angermeyer and Matschinger21 which may influence treatment decisions. Further research into carers' opinions regarding mode of treatment of antipsychotic medication would be helpful.
Impact of SGA–LAIs
Patel et al noted a reported drop in the prescribing rate of LAIs over the past 5 years during the period risperidone LAI has been available. Reference Patel, Haddad, Chaudhry, McLoughlin, Husain and David16 Heres et al reported that the cost involved in the use of risperidone LAI and the fact that it was the only SGA available in LAI form had a role in the decision not to prescribe, Reference Heres, Hamann, Kissling and Leucht18 and Patel et al speculated that more psychiatrists would prefer to use SGA–LAIs currently but felt limited by local restrictions. Reference Patel, Haddad, Chaudhry, McLoughlin, Husain and David16 A study in Japan where only FGA–LAIs are available questioned why psychiatrists did not prescribe LAIs. Reference Kanazawa, Tsutsumi, Kawashige, Nishimoto and Yoneda22 Although the lack of availability of SGA–LAIs was cited by only 13.5% of respondents, over 80% wished to use SGA–LAIs in the future. The worldwide impact of the earlier introduction of SGA–orals should not be underestimated, as these have been heavily marketed, arguably to the detriment of the older antipsychotics, including FGA–LAIs, although this has not been systematically reviewed. Second-generation antipsychotic oral medication marketing campaigns initially focused on the lower incidence of extrapyramidal side-effects with these drugs, implying greater adherence and hence a reduced need for FGA–LAIs. Nevertheless, up to 30% of individuals on maintenance antipsychotic medication receive an LAI formulation, and despite evidence of a reduced relapse rate on LAIs as opposed to equivalent oral medications, Reference Haddad, Taylor and Niaz23 there does not appear to be a consensus that LAIs as a group are underutilised.
There is little evidence to support the idea that risperidone LAI has greatly changed patient or staff attitudes to all LAIs, although Heres et al found that reasons not to prescribe an FGA–LAI or depot were more common than reasons not to prescribe risperidone LAI. Reference Heres, Hamann, Kissling and Leucht18 Mental health staff seemed to hold similar views regarding coercion and stigmatism before and after the introduction of risperidone LAI, Reference Patel, Haddad, Chaudhry, McLoughlin, Husain and David16 and the main anxiety of staff is the presumption of patient non-acceptance. Reference Patel, Haddad, Chaudhry, McLoughlin, Husain and David16
Has the quality of the studies changed?
Following the earlier review by Walburn et al, Reference Walburn, Gray, Gournay, Quraishi and David1 a number of studies have investigated patient and staff attitudes to LAIs. Using Walburn's checklist, there appears to have been some improvement in the quality of studies since mid-1999, and in contrast with previous findings there appears to be a trend towards lower quality being associated with more negative results.
Patient choice
In the UK the ‘patient choice’ agenda and Creating a Patient-Led NHS encourage patient autonomy and involvement in treatment and care decisions, Reference Samele, Lawton-Smith, Warner and Mariathasan24,25 which is compatible with a recovery model for mental health, promoting a move away from medical paternalism and towards individuals making decisions about what services best meet their personal needs. Reference Samele, Lawton-Smith, Warner and Mariathasan24 However, it is clear from the new research on staff attitudes that mental health staff often simply assume that patients will not want an LAI and so a large proportion do not even consider discussing this treatment formulation with them.
Ethical concerns regarding coercion associated with using LAIs persist among psychiatrists and nurses alike. Reference Patel, Nikolaou and David13–Reference Patel, Haddad, Chaudhry, McLoughlin, Husain and David16 It has been suggested that possible underutilisation of LAIs in the USA (as suggested by lower LAI prescribing rates than in many other countries) may reflect concerns over ‘choice’, 25 medicolegal anxieties of the prescriber, or even a lower level of community-based services for individuals with schizophrenia compared with elsewhere. However, others view LAIs as promoting voluntarism or choice in individuals who prefer LAIs owing to their awareness of reduced relapse rates and non-adherence, Reference Pereira and Pinto27 and LAIs can be viewed as an ethical option by allowing the patient's mental illness to be adequately treated and therefore promoting chances of full recovery. Reference Pereira and Pinto27
Challenges associated with LAI prescribing
Clinicians
Having an appropriately set-up clinical space for LAI administration is essential. However, the LAI or depot clinic could also become a place where patients also receive support, education, physical check-ups and health promotion. A 2001 study showed that the average time spent with each patient while administering LAIs was 1–4 min, Reference Muir-Cochrane29 although many community nurses in the UK now have a personal case-load of only 20–30 patients. Training continues to be an issue: a UK national survey has shown that 70% of CPNs had not received any mental health training in the previous 5 years, Reference Gray, Parr and Plummer30 although 77% of London CPNs and 84% of Hong Kong CPNs felt their training was sufficiently up-to-date for all aspects of LAI administration. Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Baker and David14,Reference Patel, Yeung, Haddad and David15,Reference Basu and McIvor31 Medical staff may also have training needs, as those who had reduced their prescribing of LAIs had less knowledge regarding side-effects. Reference Patel, Haddad, Chaudhry, McLoughlin, Husain and David16
Patients
A substantial proportion of patients feel that LAIs cause more shame and lead to more stigma than oral antipsychotics. Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Bernadt and David8 Feelings of loss of control, as well as concerns over side-effects, have been postulated as the reason for wanting a switch from LAIs or depot to oral medication, and concerns about injection site pain and needle phobia continue. Discussing potentially embarrassing side-effects can be a challenge for both doctors and patients, emphasising the need for a simple, valid self-completed side-effect scale such as the Glasgow Antipsychotic Side-effect Scale. Reference Waddell and Taylor32
An image problem?
A pattern of stereotyped prescribing of LAIs to chaotic or even aggressive non-adherent individuals or to those with refractory illness will add to a negative perception of LAIs. Reference Davis and Chen4,Reference Mahadun and Marshall5 Furthermore, if an individual's first experience of injectable medication occurs during rapid tranquillisation and restraint, this can understandably lead to negative views on injectable medication. Addressing negative perceptions can take time and knowledge – creating a modern environment for treatment administration, where general health screening, support and information are available is a good start. Reference Gray, Parr and Plummer30 Educating staff, patients and family members about the positive and negative aspects of LAI medication can also help address prejudice or stigma.
Summary
Since the review by Walburn et al, Reference Walburn, Gray, Gournay, Quraishi and David1 new research has illustrated the attitudes and preferences of patients regarding different antipsychotic formulations, as well as of those previously given LAIs who have switched to tablets. For patients, the overall preference for LAIs ranges from 18% to 40%. Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Bernadt and David8,Reference Heres, Schmitz, Leucht and Pajonk12 Preference for LAIs increased with familiarity or duration of exposure, Reference Heres, Schmitz, Leucht and Pajonk12 and some but not all patients were aware of the potential benefits of LAIs. Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Bernadt and David9 Voluntary patients on maintenance antipsychotics respond similarly when questioned about their attitudes to antipsychotic medication whether they are on LAI/depot or oral formulations, suggesting no intrinsic problem with LAI. Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Bernadt and David8,Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Bernadt and David9 However those who have switched from LAIs to oral medications retain negative views about LAIs. Reference Patel, De Zoysa, Bernadt and David8 Also, when all different types of psychiatric medication are compared, patients suggest LAIs are least preferred. Reference Bradstreet and Norris10,Reference Castle, Morgan and Jablensky11
Results from recent staff surveys in the UK revealed generally positive views about LAIs, with staff being aware of the positive aspects associated with their use, Reference Patel, Nikolaou and David13–Reference Patel, Haddad, Chaudhry, McLoughlin, Husain and David16 although there is evidence that staff often assume that patients will not accept LAIs and large proportions of patients are never offered this treatment. Reference Heres, Hamann, Kissling and Leucht18 There appears to be a close correlation between attitudes and knowledge regarding LAIs in both community nurses and psychiatrists, highlighting a need for continuing education and updating of skills. Finally, there are not enough data since the introduction of risperidone LAI to determine whether this first SGA–LAI has had an impact on attitudes generally.
The articles reviewed add further weight to previous studies but still are at a low level of evidence in the hierarchy of study design. Future work could focus on the attitudes of family members towards LAIs v. orals; whether offering a full, informed choice improves either adherence or outcomes; and whether negative views regarding LAIs correlate with being detained or restrained at the time of injection.







eLetters
No eLetters have been published for this article.