No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 07 February 2017
A general approach to overall system optimization is developed using the concepts of mechanical and electrical signal-to-noise ratios (MSNR and ESNR). These are proportional to  and to
and to  respectively, where Qsys=mechanical Q of the complete detector, μ = (transducer mass/metal mass), and n = resolving time in units of one-half of the detector fundamental period. The overall SNR becomes a maximum for n = n∗ = optimum resolving time; this procedure yields
respectively, where Qsys=mechanical Q of the complete detector, μ = (transducer mass/metal mass), and n = resolving time in units of one-half of the detector fundamental period. The overall SNR becomes a maximum for n = n∗ = optimum resolving time; this procedure yields 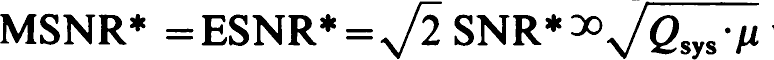 whereas
whereas 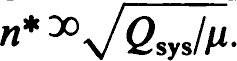
Application to ‘strong-coupling’ type antennae (such as divided-cylinder systems) gives a high SNR∗ which depends very little on μ if μ > 0.01. Q-factor and coupling efficiency relations were checked for 22 kg-prototypes using μ = 0.26%, 0.9%, and 1.8%. Two new detector configurations are suggested: the ‘bridged-tube’ allows strong-coupling for very long detectors; the ‘folded-tube’ operates at lower frequencies for a given length.