No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 August 2015
Approximations have been removed from the derivation of the coefficients in the binomial expansion for astronomical refraction, 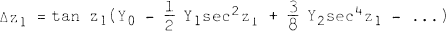 , allowing the calculation of any number of terms to any precision desired. The range of the refraction formula has been extended to greater zenith distances (<90°) by inserting a damping factor into the binomial formula, truncating the expansion at a proper point, and rearranging the terms. Another, computer-manipulated series has been developed for zenith distances at or near the horizon. Further applications include the calculation of photogrammetric and parallactic refractions, as well as range corrections in satellite geodesy.
, allowing the calculation of any number of terms to any precision desired. The range of the refraction formula has been extended to greater zenith distances (<90°) by inserting a damping factor into the binomial formula, truncating the expansion at a proper point, and rearranging the terms. Another, computer-manipulated series has been developed for zenith distances at or near the horizon. Further applications include the calculation of photogrammetric and parallactic refractions, as well as range corrections in satellite geodesy.