No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 May 2016
Long planetary and lunar ephemerides like the JPL DE102 and LE51 (Newhall et al., 1983) and the Bureau des Longitudes VSOP (Bretagnon, 1982) and ELP (Chapront-Touze and Chapront, 1983) have enabled more positive ancient eclipse, planetary and cometary identifications, which have in turn refined ephemerides, e.g., the reconstruction of the orbit of comets Halley and Swift-Tuttle (Yeomans and Kiang, 1981; and Yau et al., 1994). The data used to initialize DE102 are pre-1977. Much more observational data have been collected since. The lunar ephemeris has also been improved. The secular lunar acceleration, 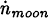 , from laser ranging, is −25.9±0.5″/cen2 (Williams et al., 1992). We can now uniquely solve for ΔT, the clock error, from ancient eclipse records. The lack of ΔT values before 700 B.C. has left the early timescale of the ephemerides unconstrained (Morrison, 1992). Our solution of this problem is outlined here.
, from laser ranging, is −25.9±0.5″/cen2 (Williams et al., 1992). We can now uniquely solve for ΔT, the clock error, from ancient eclipse records. The lack of ΔT values before 700 B.C. has left the early timescale of the ephemerides unconstrained (Morrison, 1992). Our solution of this problem is outlined here.