No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 19 July 2016
In the framework of the magnetohydrodynamic equations with dissipative terms in the form of turbulent viscosity (Vt) the linear stage of the instability of a subphotospheric field with respect to magnetic buoyancy is considered. For an exponential in z, isothermal plane-parallel atmosphere with a constant Alfvenic velocity
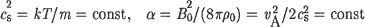 the perturbations of the form
the perturbations of the form
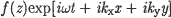 are described by differential equation with constant coefficients. The qualitative dependence of the growth rate of instability on transverse wave number is determined (see Figures 1 and 2) and characteristic scales of the magnetic tubes are evaluated at the linear stage of instability (Kuznetsov, 1987, 1988).
are described by differential equation with constant coefficients. The qualitative dependence of the growth rate of instability on transverse wave number is determined (see Figures 1 and 2) and characteristic scales of the magnetic tubes are evaluated at the linear stage of instability (Kuznetsov, 1987, 1988).