No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 May 2016
We have performed a 2.5D, nonsteady, general-relativistic MHD simulation. Initially, we assumed a uniform magnetic field, a geometrically thin accretion disk rotating at Keplerian velocity, and a hydrostatic corona around a Schwarzschild black hole. We have investigated the formation mechanism of gas-pressure driven jets expected by Koide et al. and found the strong dependence of jet velocities 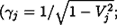 Lorentz factor of jets) on the ratio of the density of the accretion disk to that of the corona (ρd/ρc), where γ2j - γj ∝ (ρd/ρc)0.75.
Lorentz factor of jets) on the ratio of the density of the accretion disk to that of the corona (ρd/ρc), where γ2j - γj ∝ (ρd/ρc)0.75.