No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 07 August 2017
Quasars with similar core-compact radio properties can be classified by their differences at optical and infrared frequencies. Their X-ray properties might be expected to be similar if the synchrotron self-Compton mechanism relates their radio and X-ray emission. We have compared the 0.2–3.5 keV mean power-law energy spectral indices, 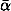 , for 4 quasar classes: 12 Highly Polarized QSOs (HPQs), 19 Flat Radio Spectrum, core-compact, low-polarization, QSOs (FRS QSOs), 24 radio-selected BL Lac objects, and 7 X-ray-selected BL Lac objects.
, for 4 quasar classes: 12 Highly Polarized QSOs (HPQs), 19 Flat Radio Spectrum, core-compact, low-polarization, QSOs (FRS QSOs), 24 radio-selected BL Lac objects, and 7 X-ray-selected BL Lac objects.