No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 August 2015
A knowledge of the flux of antiprotons is of value in examining the manner in which cosmic rays propagate, assuming, as is conventional, that the antiprotons arise from interactions in the I.S.M. Golden et al. (1979) have recently measured the 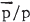 ratio in the region of 10 GeV and, although confirmatory measurements are needed, it is instructive to compare with expectation. In a recent paper (Szabelski et al., 1980) we presented results of a new calculation of the expected
ratio in the region of 10 GeV and, although confirmatory measurements are needed, it is instructive to compare with expectation. In a recent paper (Szabelski et al., 1980) we presented results of a new calculation of the expected 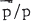 ratio using the standard (equilibrium) ‘leaky box model’.
ratio using the standard (equilibrium) ‘leaky box model’.