Published online by Cambridge University Press: 21 May 2020
Cognitive inhibition is part of executive functions. When it exercises control over memory processes, it has the function of regulating the accessibility of memories and allows interference to be resolved. The impairment of its functioning has been related to the presence of forgetfulness of relevant information. In this research, we study the functioning of cognitive memory inhibition processes in people with intellectual disabilities in tasks of delayed visual recognition and analyze the influence of age. For this purpose, 36 people with Down syndrome (mean age = 33.44, standard deviation = 7.54, 50% females) and 36 people with neurotypical development (mean age = 33.55, standard deviation = 7.52, 50% females) participated. The results reflected a lower effectiveness in the group of people with Down syndrome, F(1, 68) = 159.09, p < .001,  $ {\upeta}_{\mathrm{p}}^2 $ = .70. The people in the group with Down syndrome had difficulties in interference resolution, both in the subgroup of young people (p = .014,
$ {\upeta}_{\mathrm{p}}^2 $ = .70. The people in the group with Down syndrome had difficulties in interference resolution, both in the subgroup of young people (p = .014, 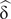 $ \hat{\updelta\ } $= 0.88) and in the subgroup of older people (p = .022,
$ \hat{\updelta\ } $= 0.88) and in the subgroup of older people (p = .022, 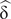 $ \hat{\updelta\ } $= 0.67). The impairment of cognitive inhibition in people with Down syndrome warrants the need to develop specific intervention programs for this process.
$ \hat{\updelta\ } $= 0.67). The impairment of cognitive inhibition in people with Down syndrome warrants the need to develop specific intervention programs for this process.
Part of this work has been supported by “Autour des Williams”. Project “Inhibitory processes and memory mechanisms in adults with Williams syndrome: A neuropsychological and functional connectivity approach using magnetoencephalography”. Code 10.06.01.0050. The funder had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.