No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 31 March 2025
Among various deep learning-based SLAM systems, many exhibit low accuracy and inadequate generalization on non-training datasets. The deficiency in generalization ability can result in significant errors within SLAM systems during real-world applications, particularly in environments that diverge markedly from those represented in the training set. This paper presents a methodology to enhance the generalization capabilities of deep learning SLAM systems. It leverages their superior performance in feature extraction and introduces Exponential Moving Average (EMA) and Bayes online learning to improve generalization and localization accuracy in varied scenarios. Experimental validation, utilizing Absolute Trajectory Error (ATE) metrics on the dataset, has been conducted. The results demonstrate that this method effectively reduces errors by 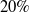 $20\%$ on the EuRoC dataset and by
$20\%$ on the EuRoC dataset and by 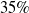 $35\%$ on the TUM dataset, respectively.
$35\%$ on the TUM dataset, respectively.